| Author |
Ján Antal, Martin Stára, Eva Schilhart Faberová, Anna Dománková, Petra Malovaná, Silvia Snopková, Branislav Kožej |
| Studio |
Studio Perspektiv |
| Location |
Planá 67, Planá, 370 01 |
| Collaborating professions |
VZT, UTCH: Petlach TZB, s. r. o.; Elektro: ExPlan s.r.o.; PBŘ: Jiří Ledinský, |
| Investor |
BUDEX HUB, s. r. o. |
| Supplier |
OHLA ŽS, a.s. (generální dodavatel stavby)
TAROS NOVA, a. s. (statika a realizace dřevostavby) |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
November 2024 |
| Fotograf |
Studio Flusser |
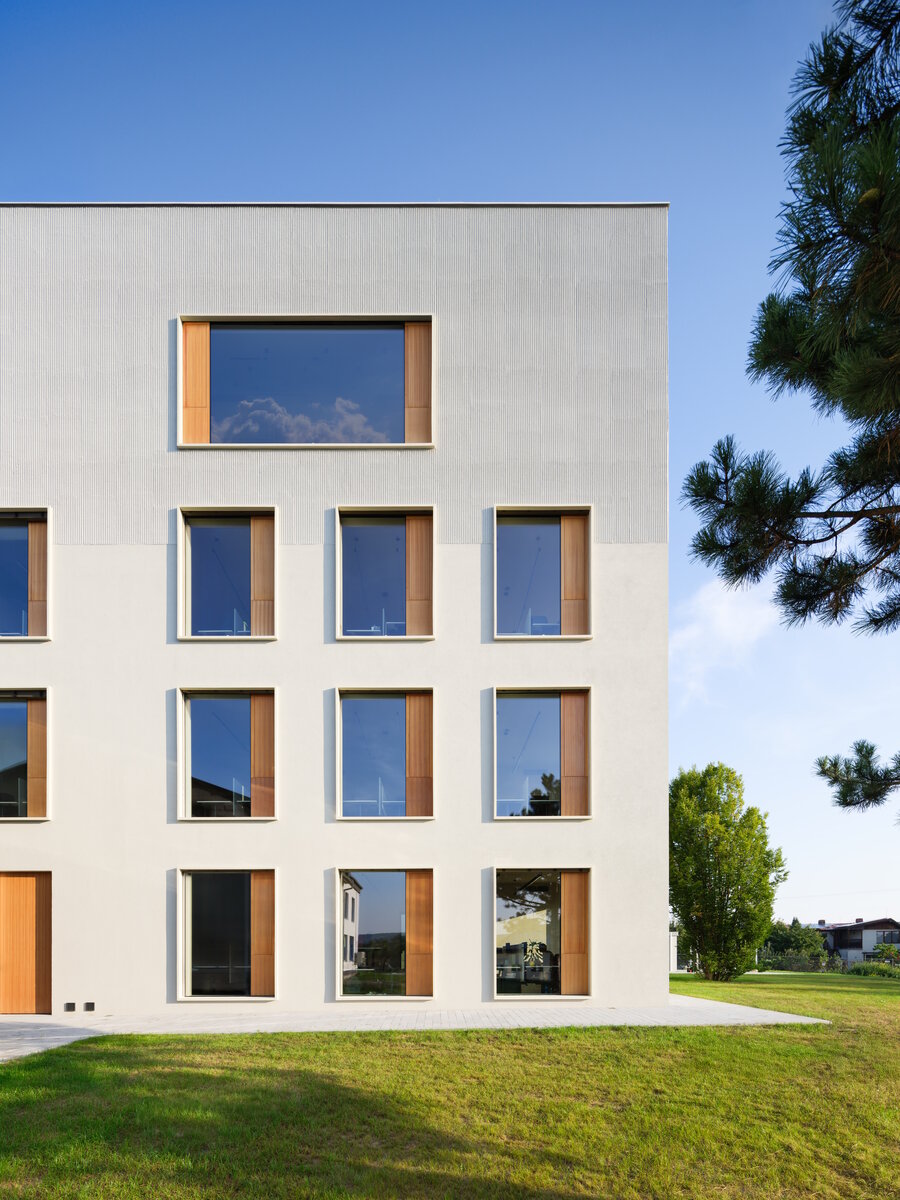
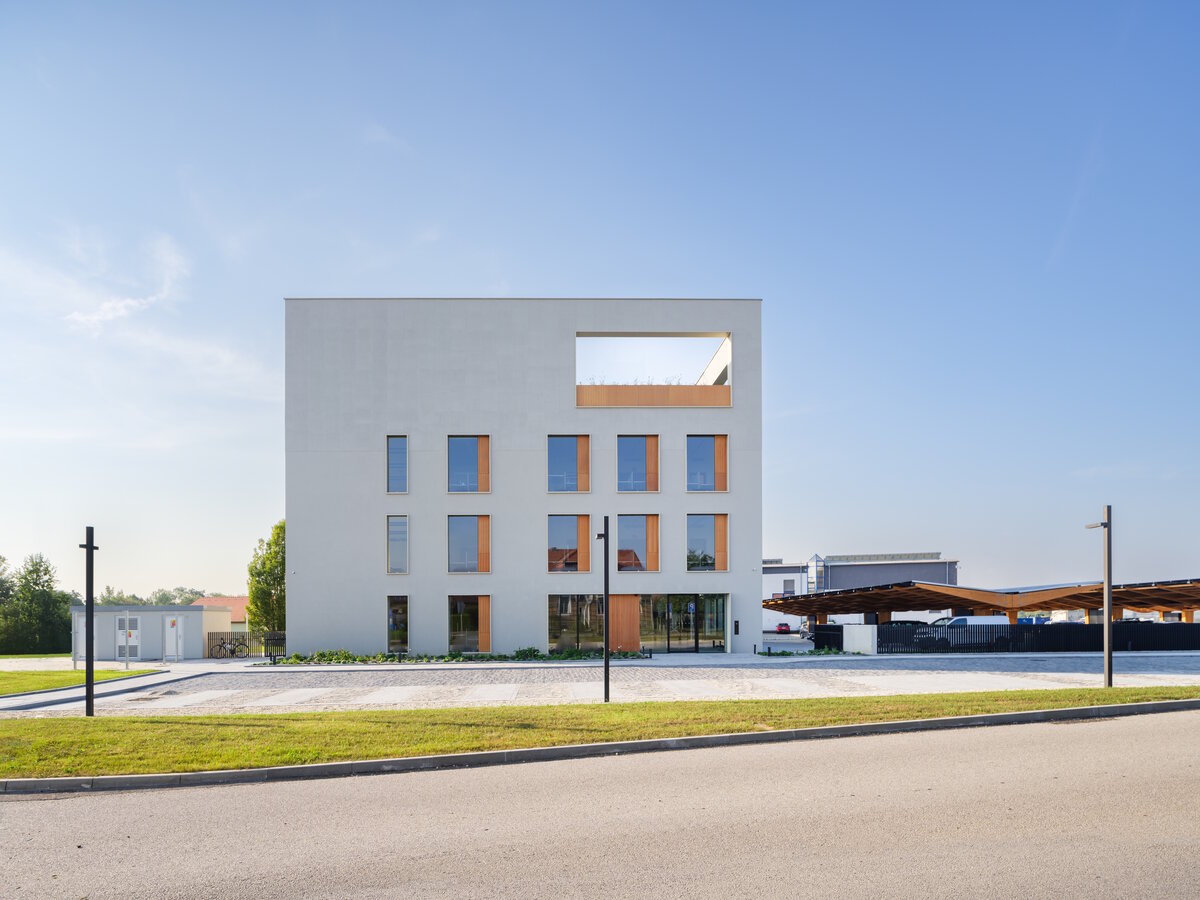
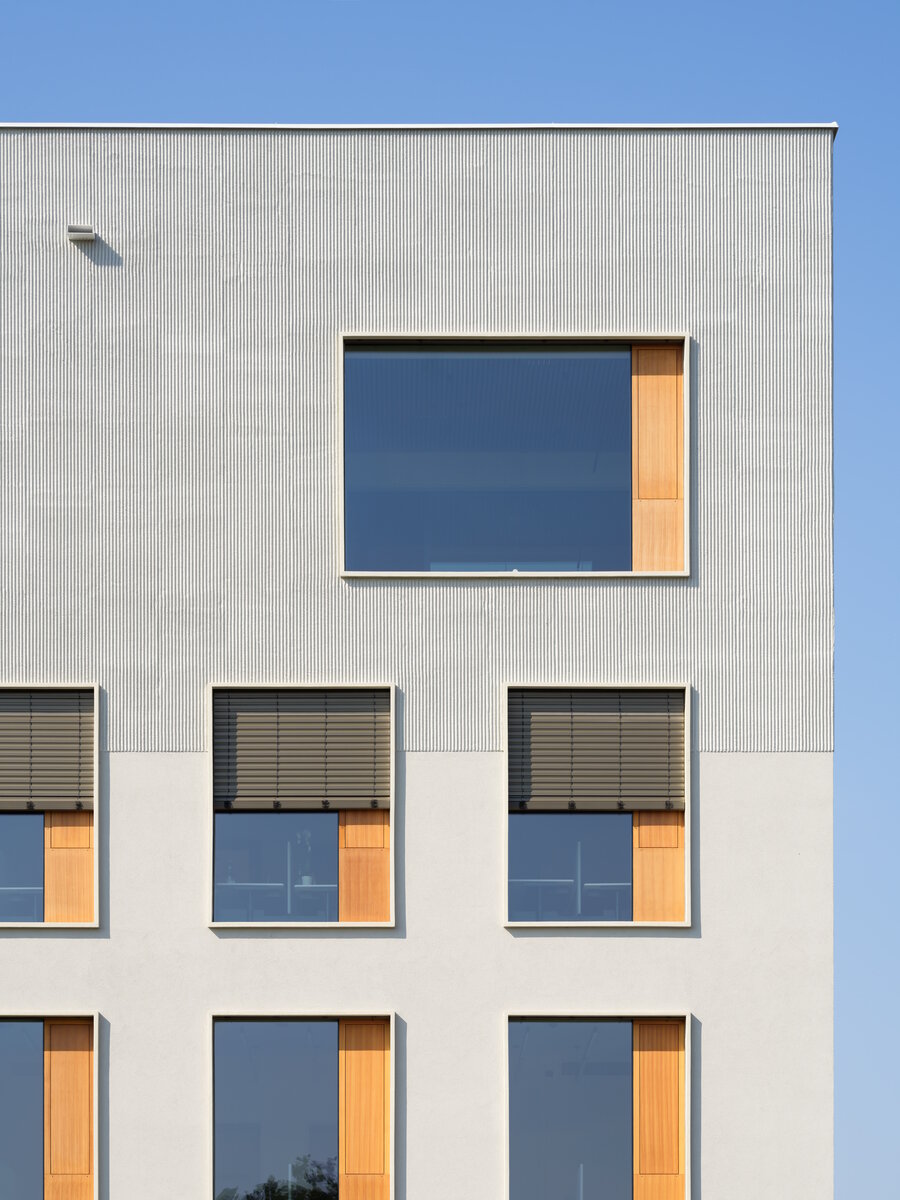
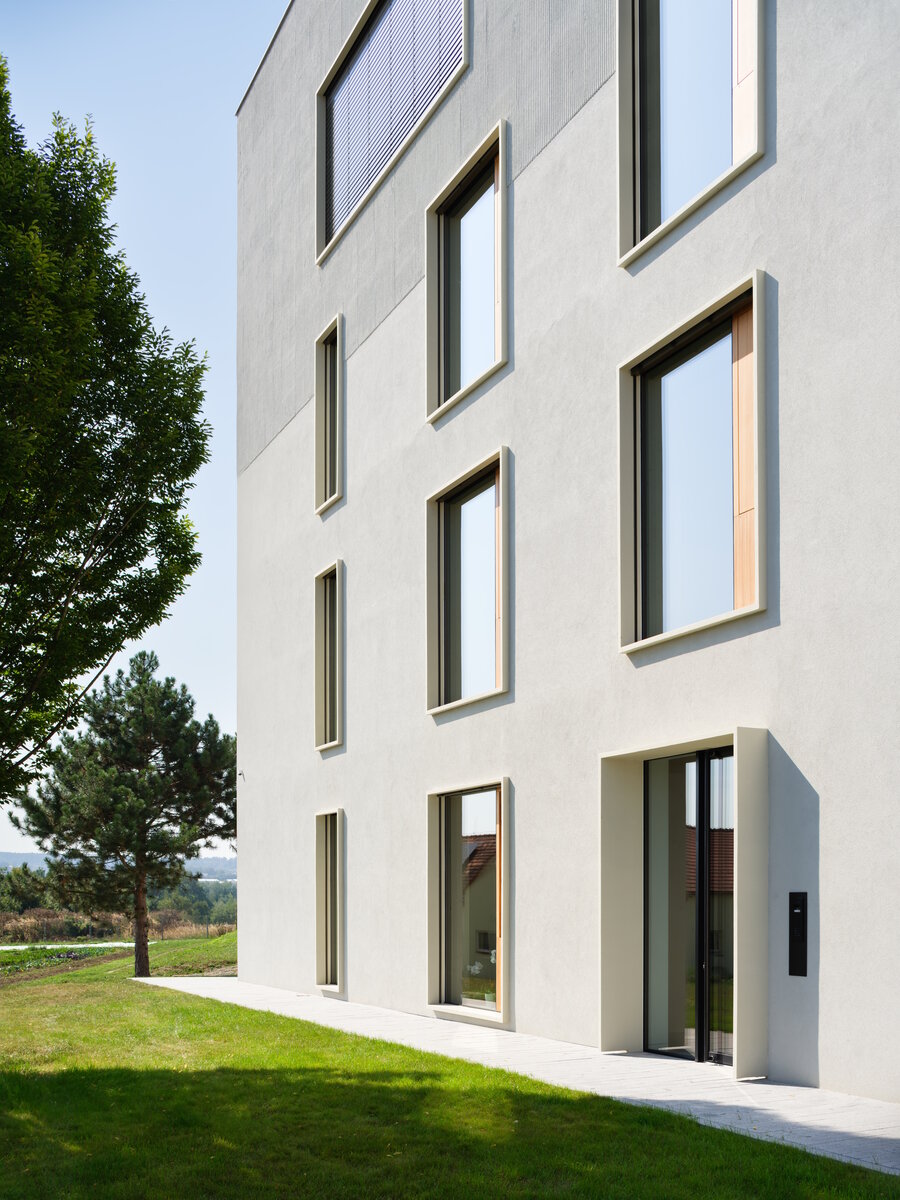
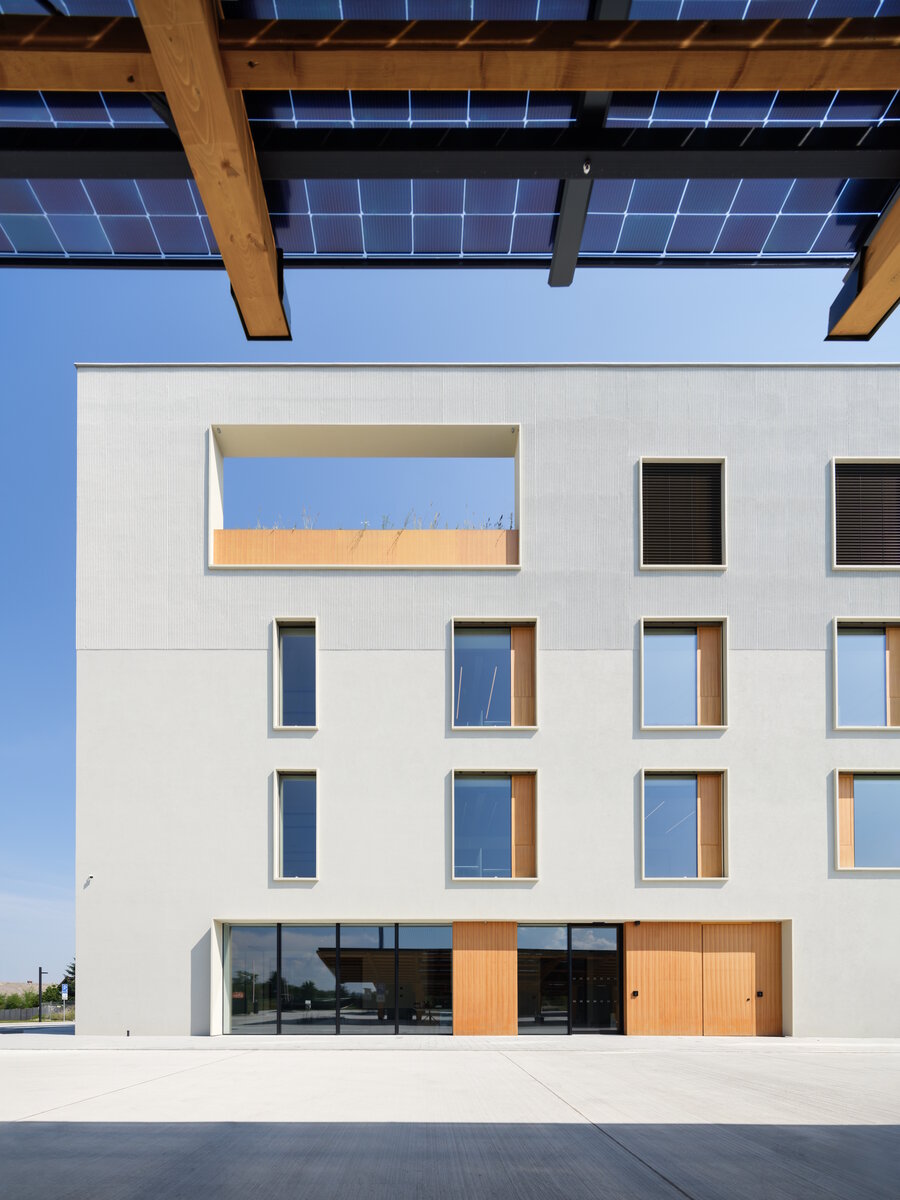
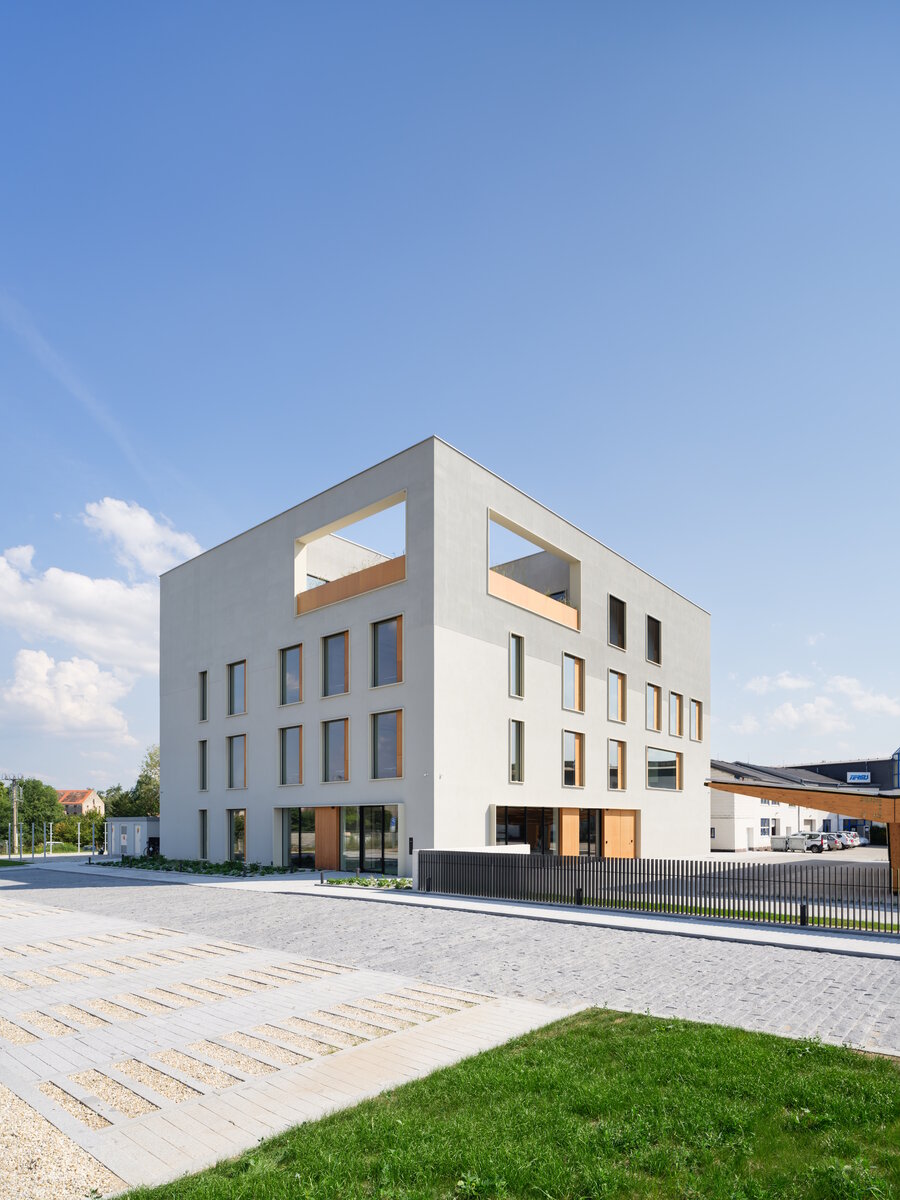
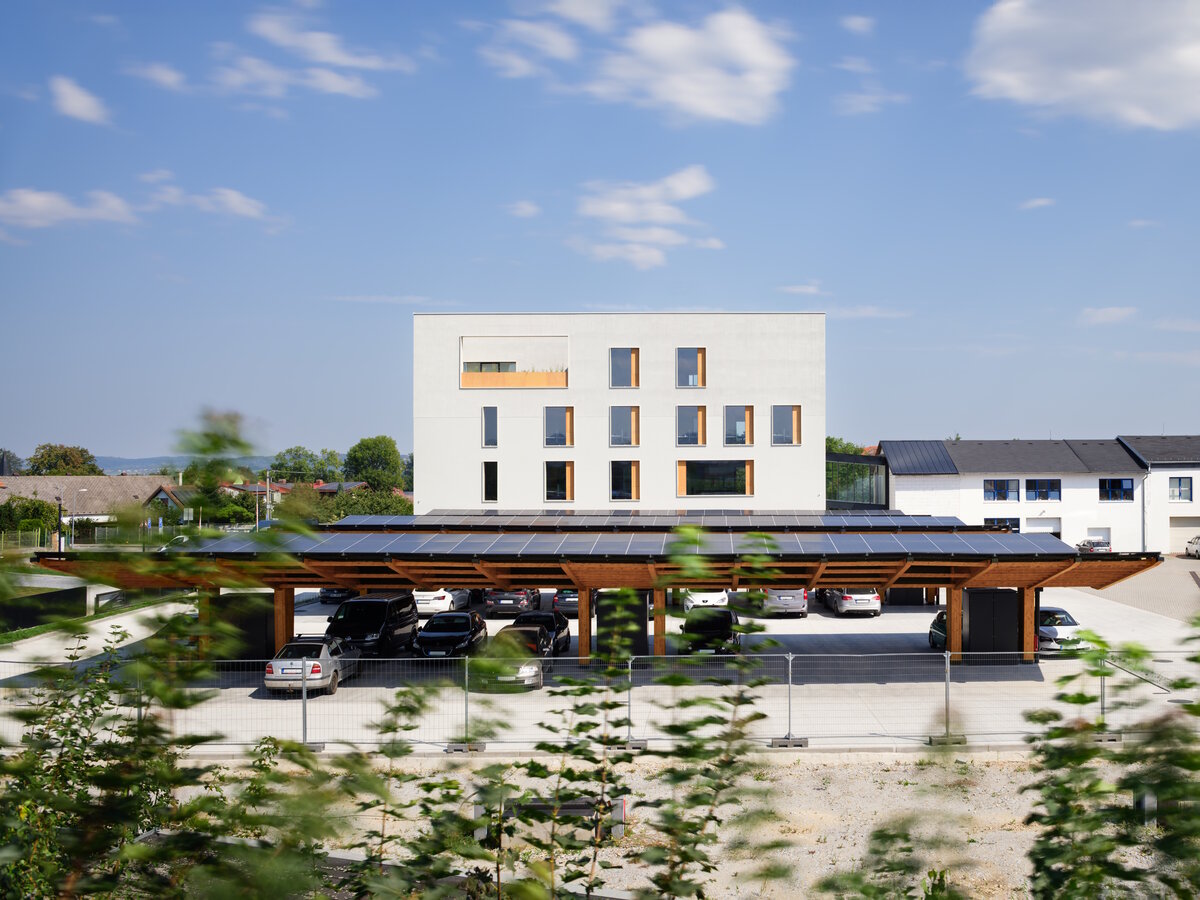
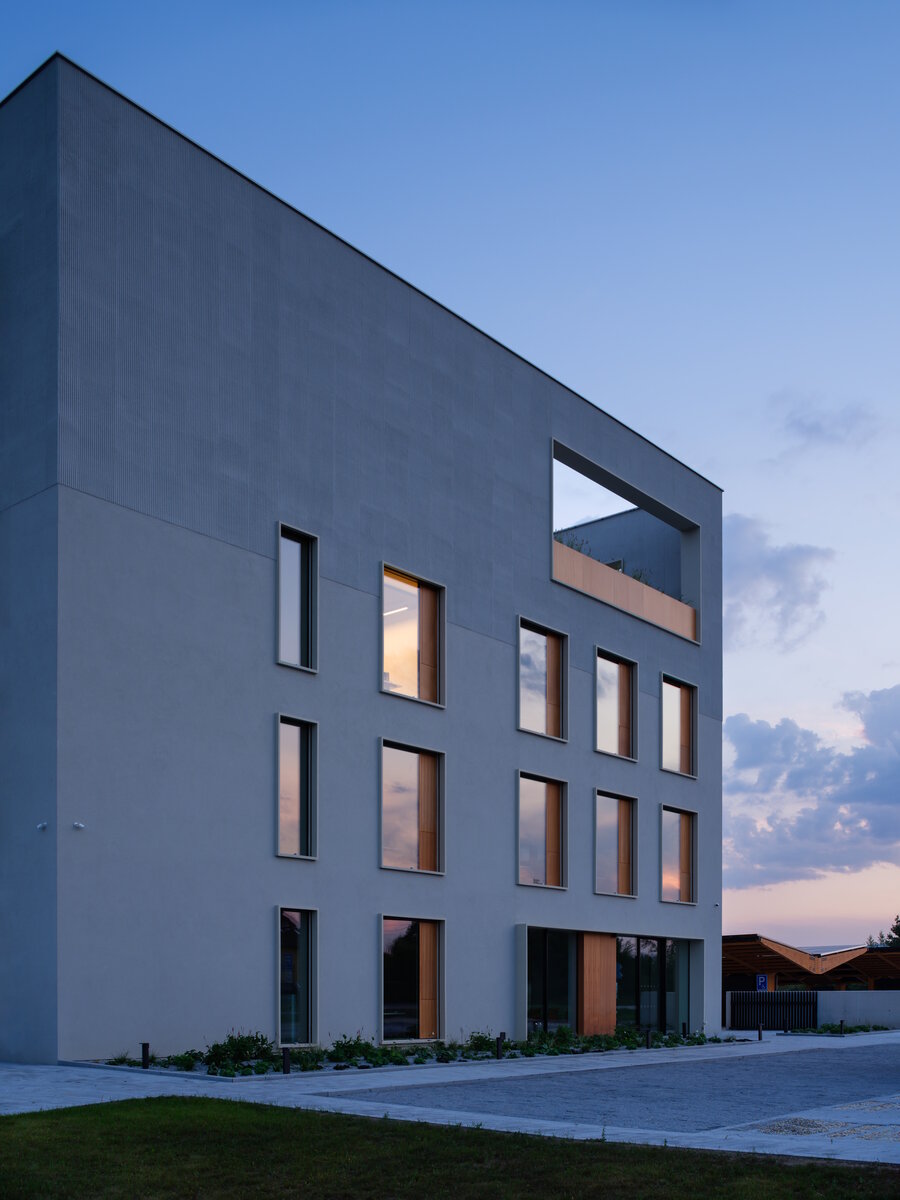
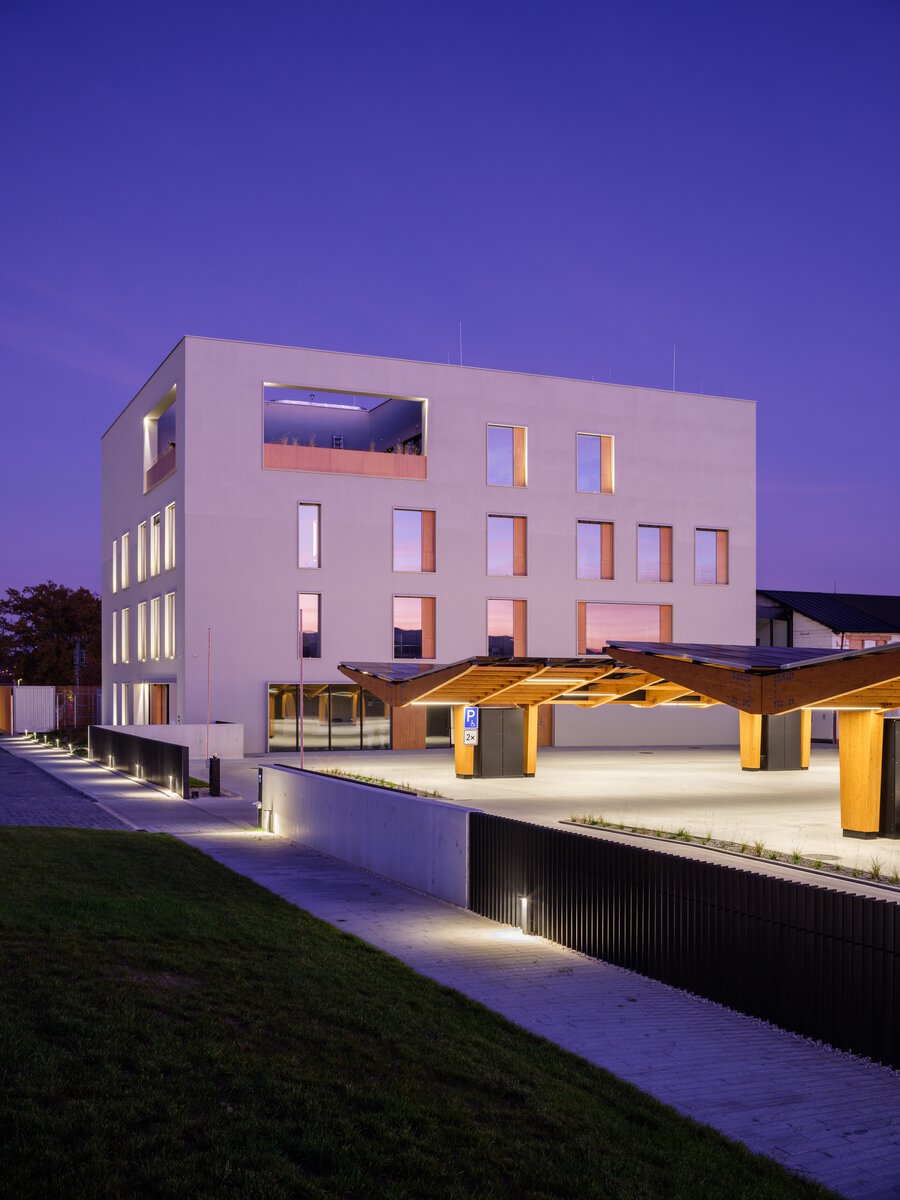
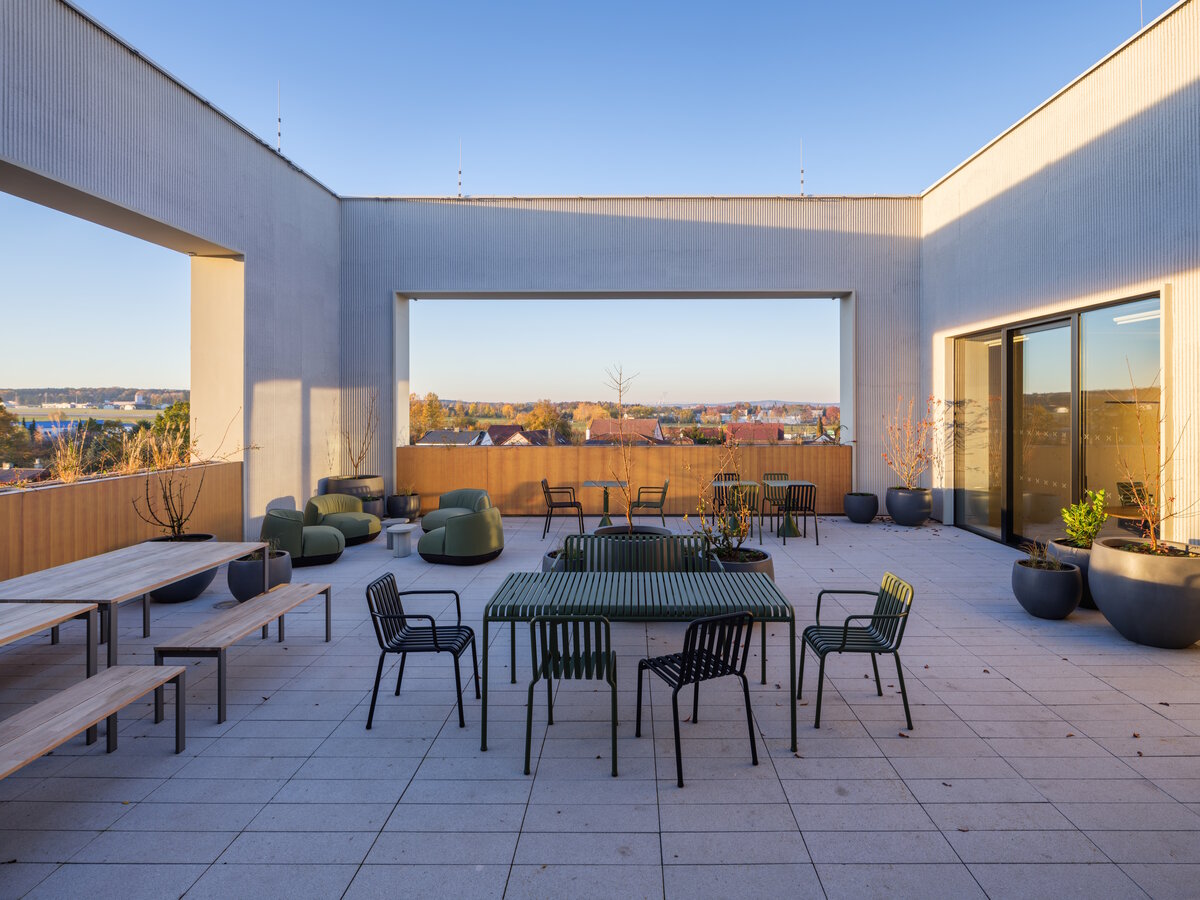
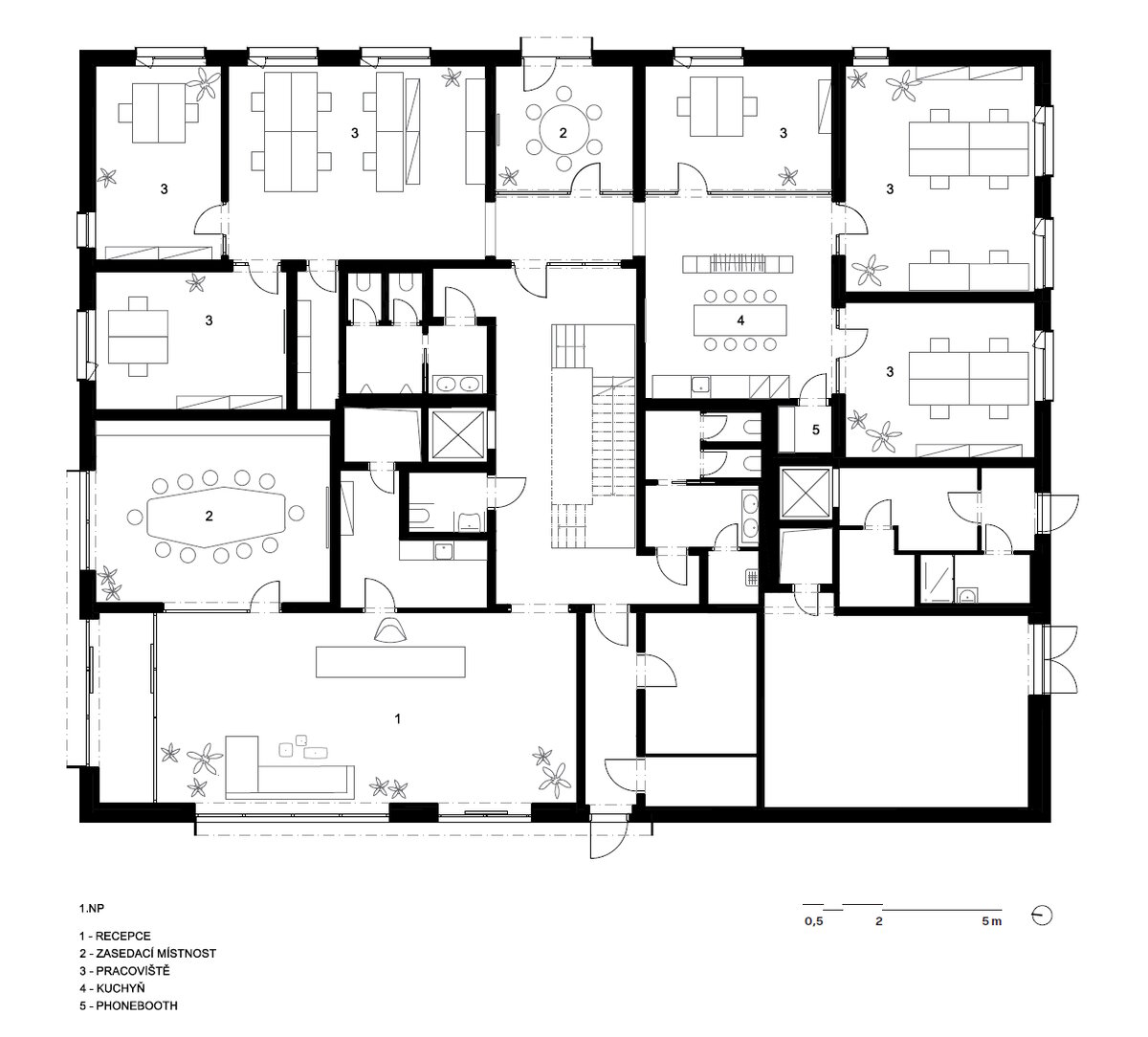
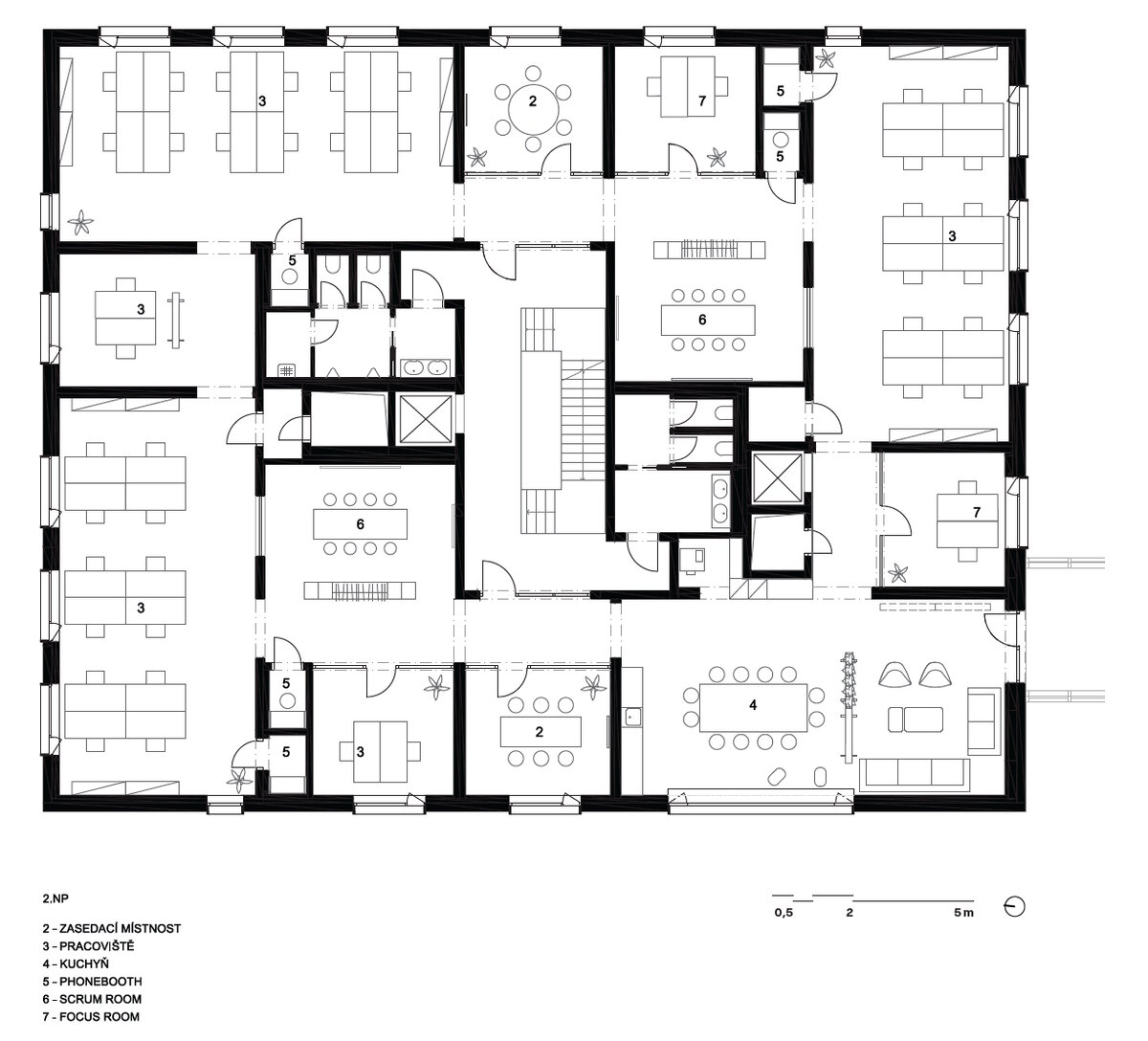
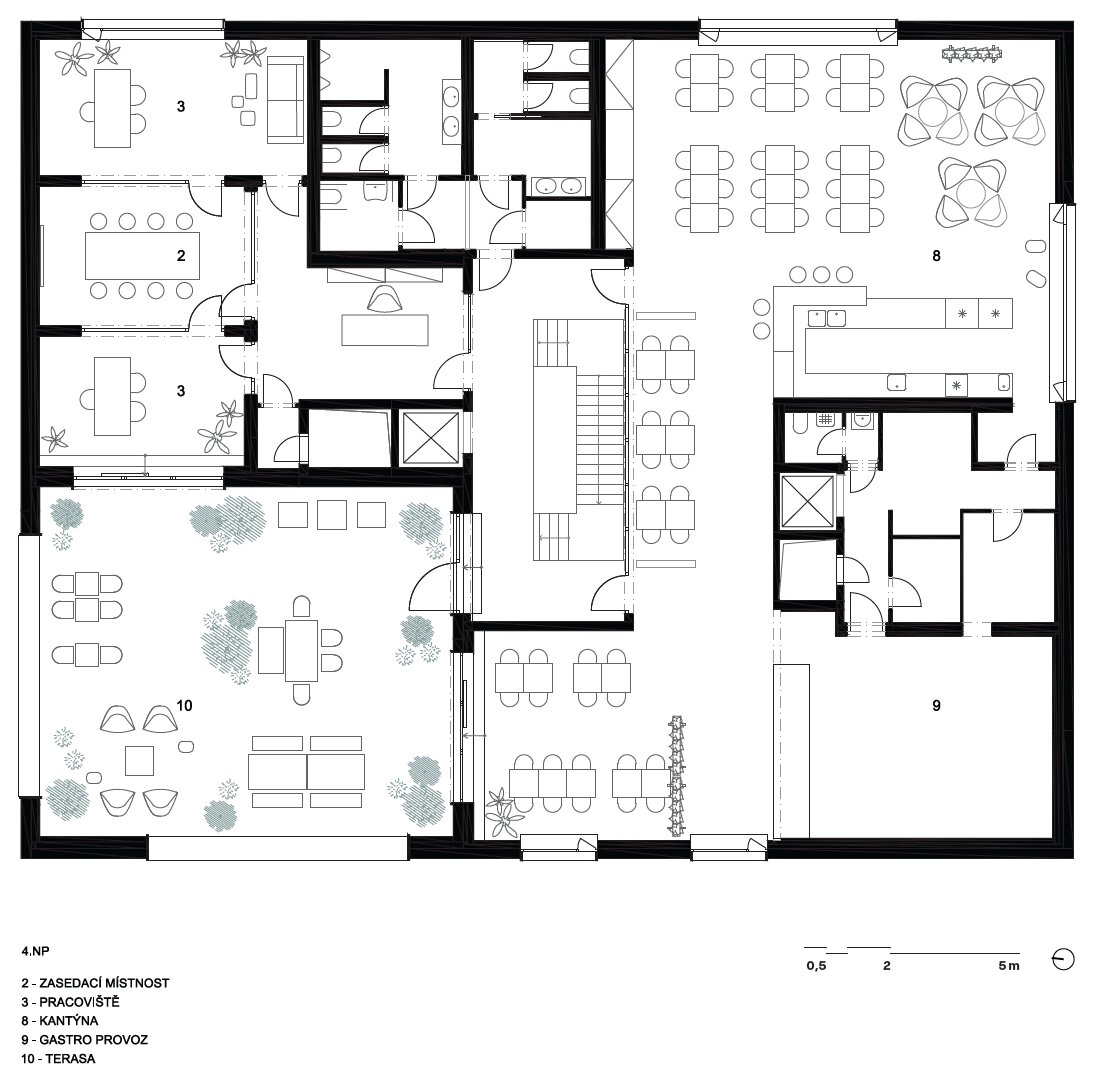
The BudexHUB administrative wooden building reaches the maximum permitted height limit in the Czech Republic at the time and was completed in the second half of 2024. The entire design of the building is carried out in the spirit of sustainability and modern technologies, as this is the area in which the investor does business.
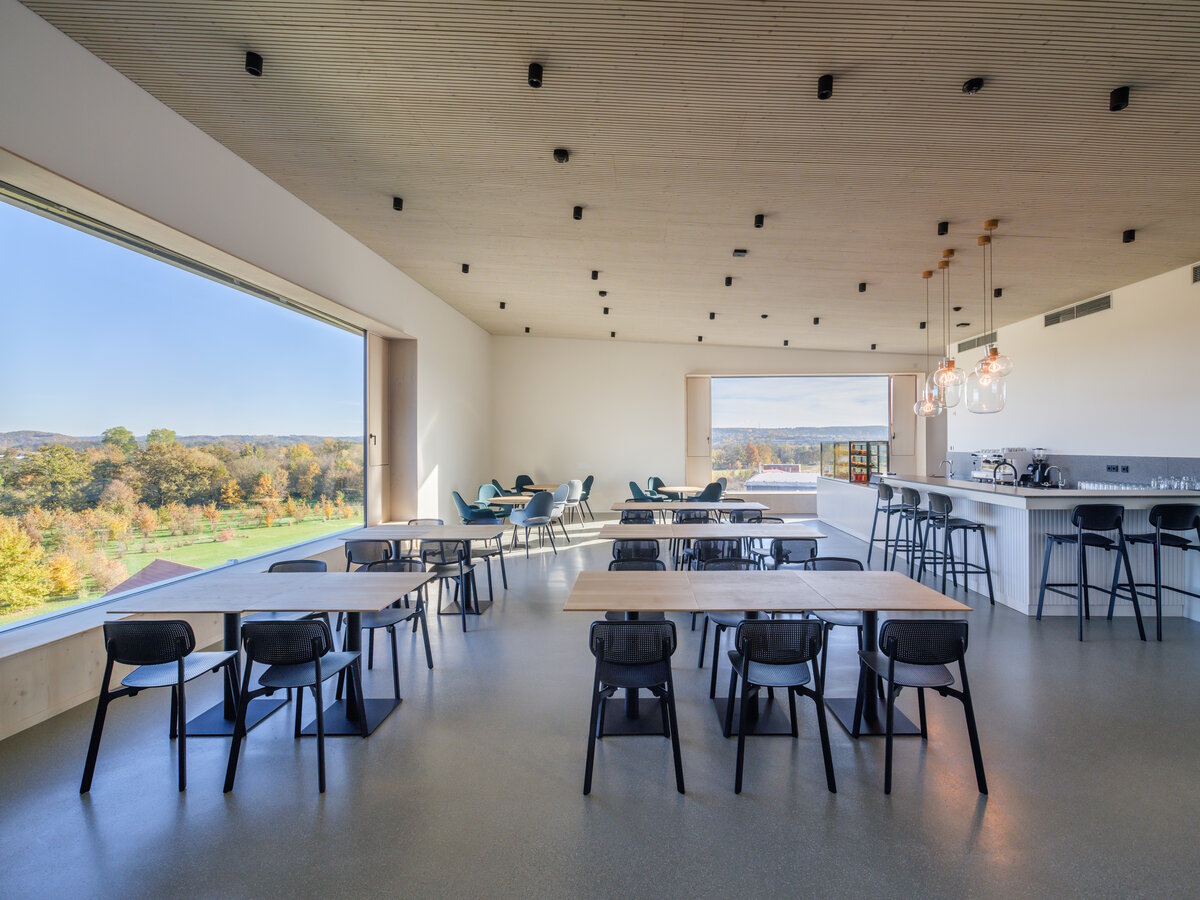
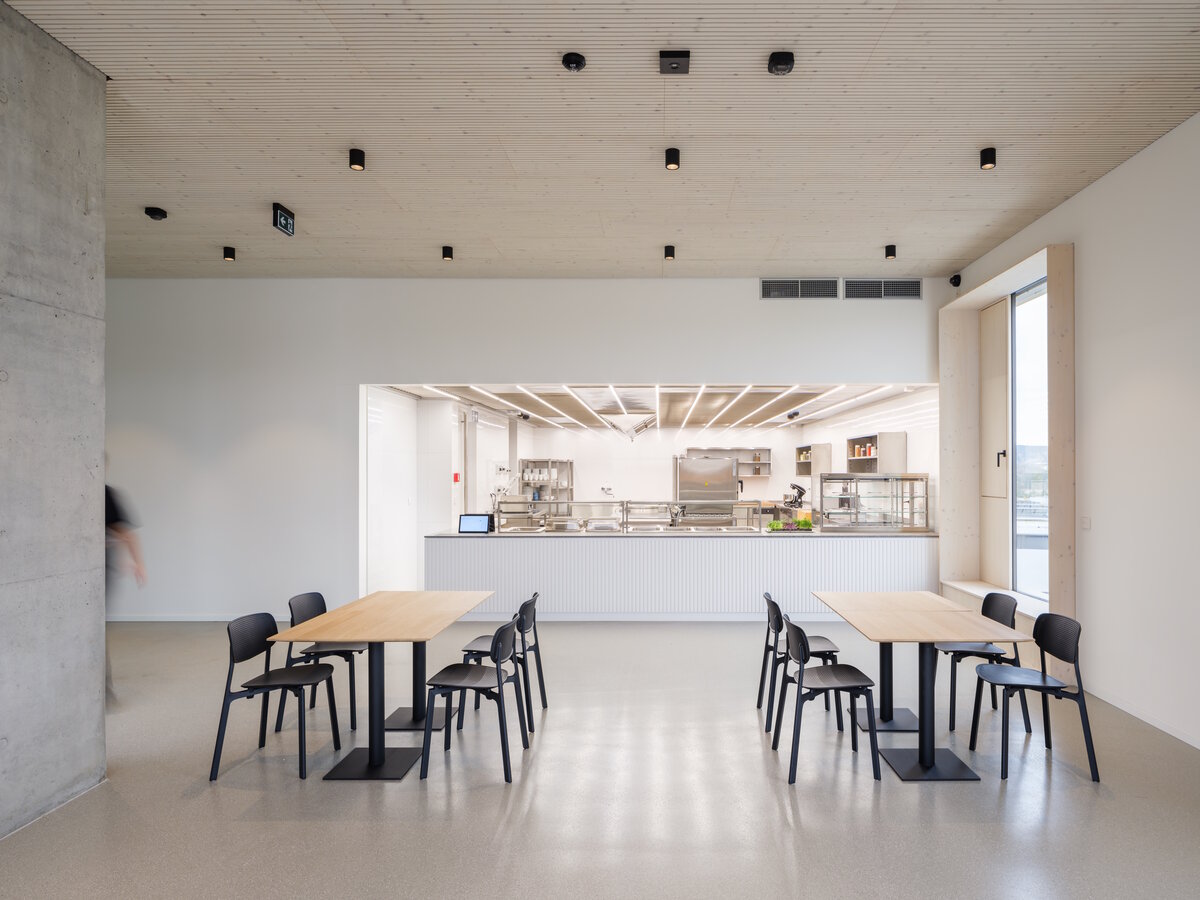
We conceived the design of the house as a passive four-story wooden building, the height of which reaches the permitted limit for this type of building in our country. The administrative wooden building is thus among the tallest in the Czech Republic. We designed the complex so that the client could apply his interest in the development of technologies and the acquisition and storage of clean energy. Accordingly, the operation of the building draws on renewable sources.
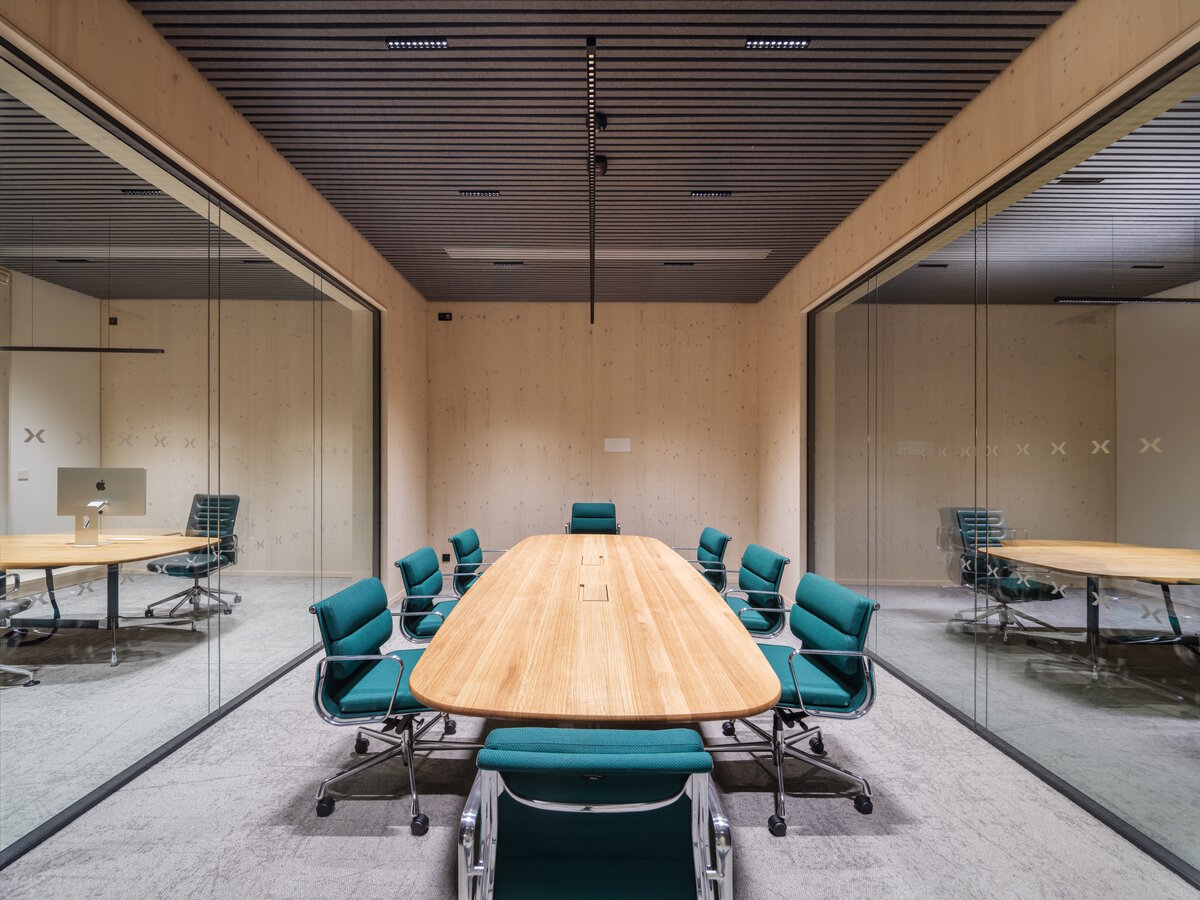
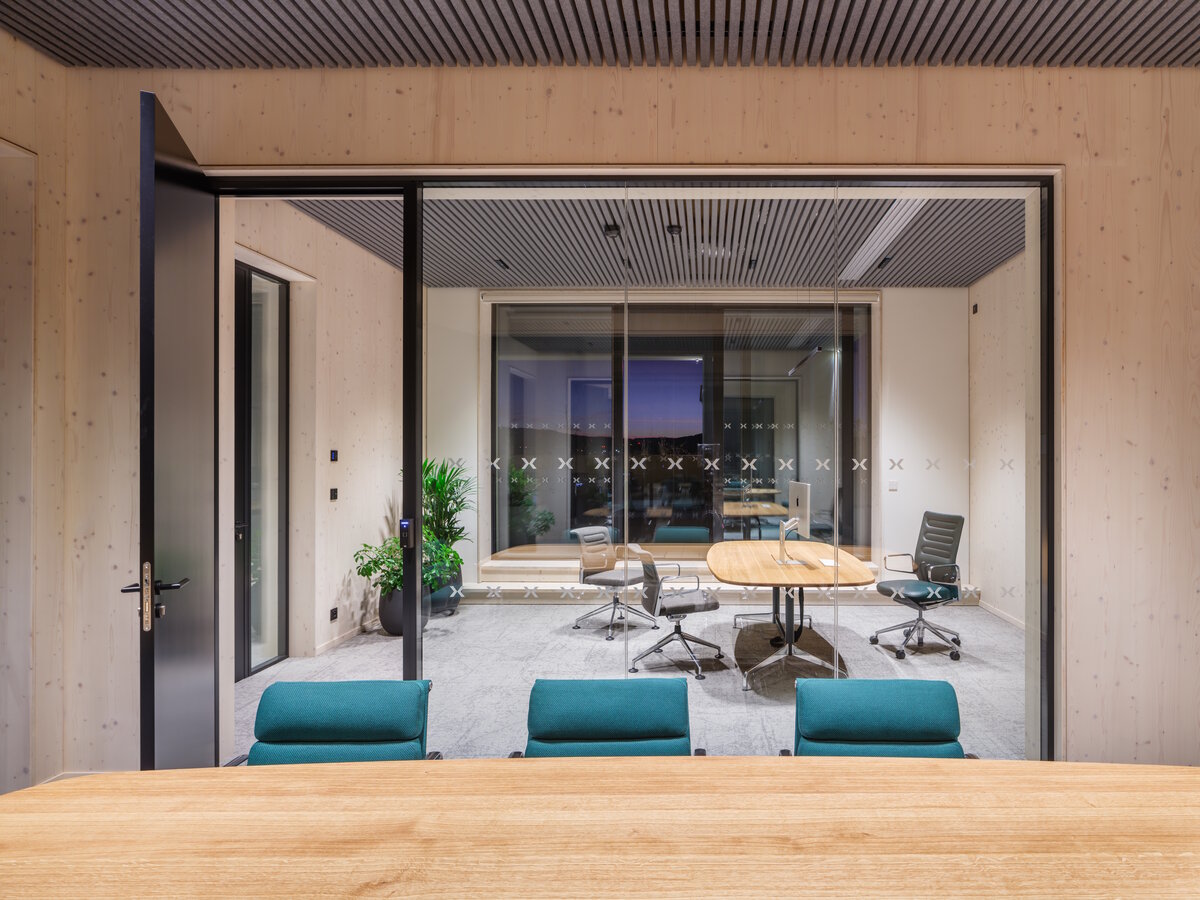
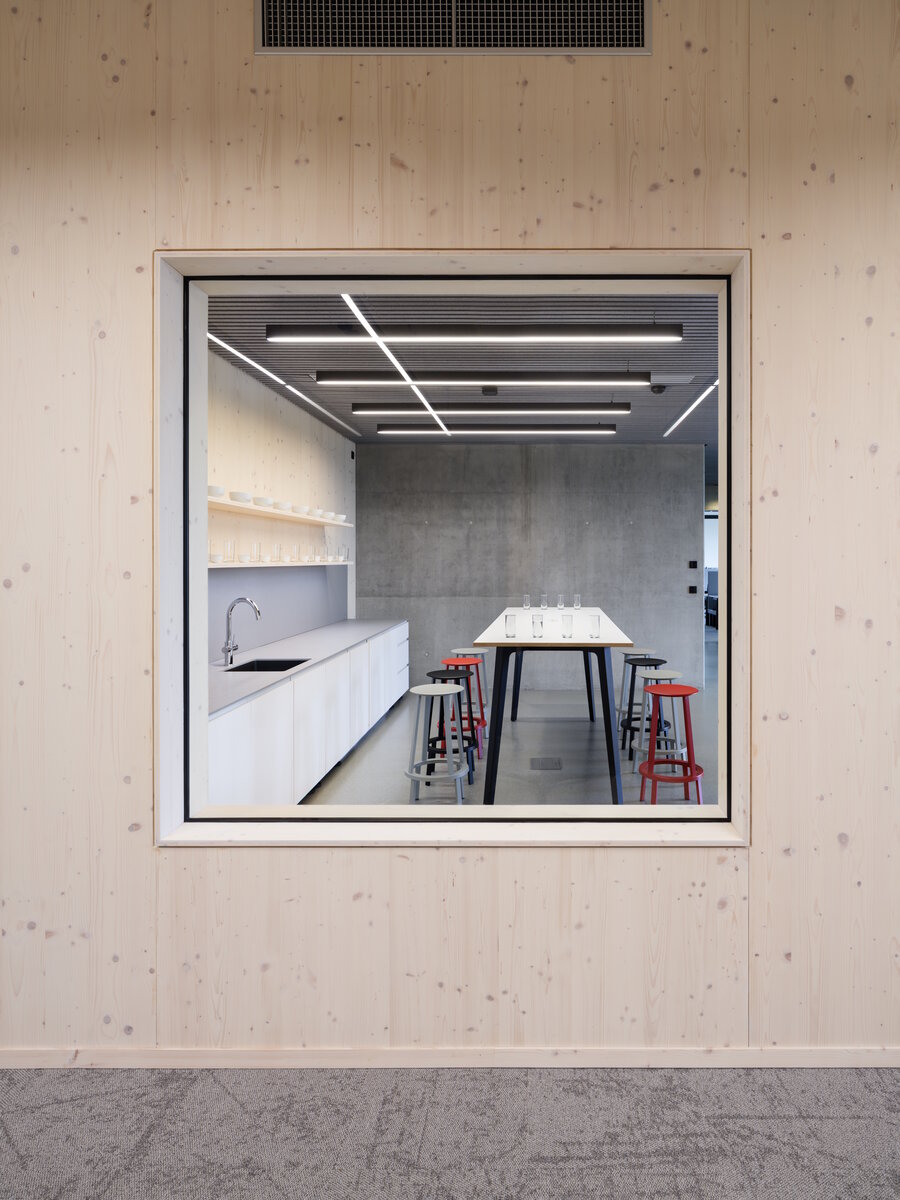
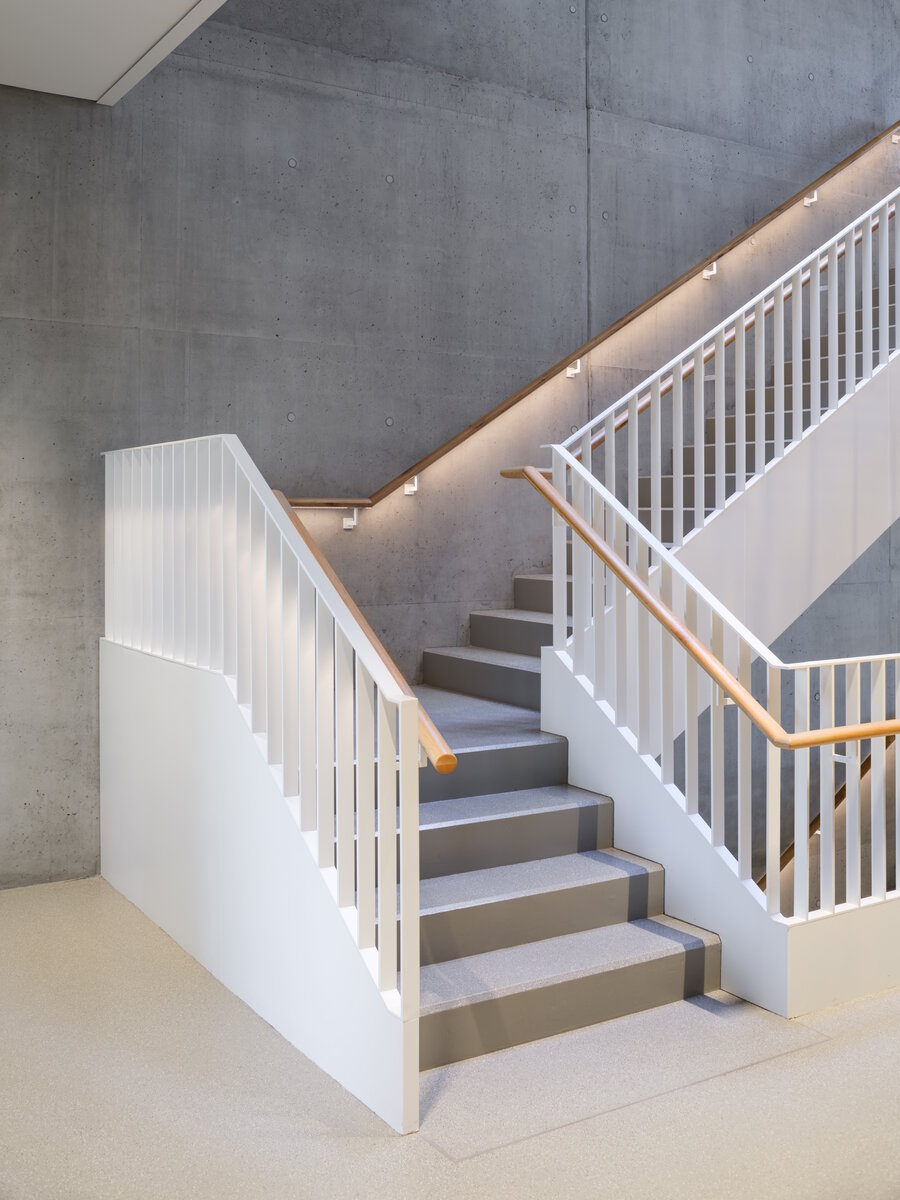
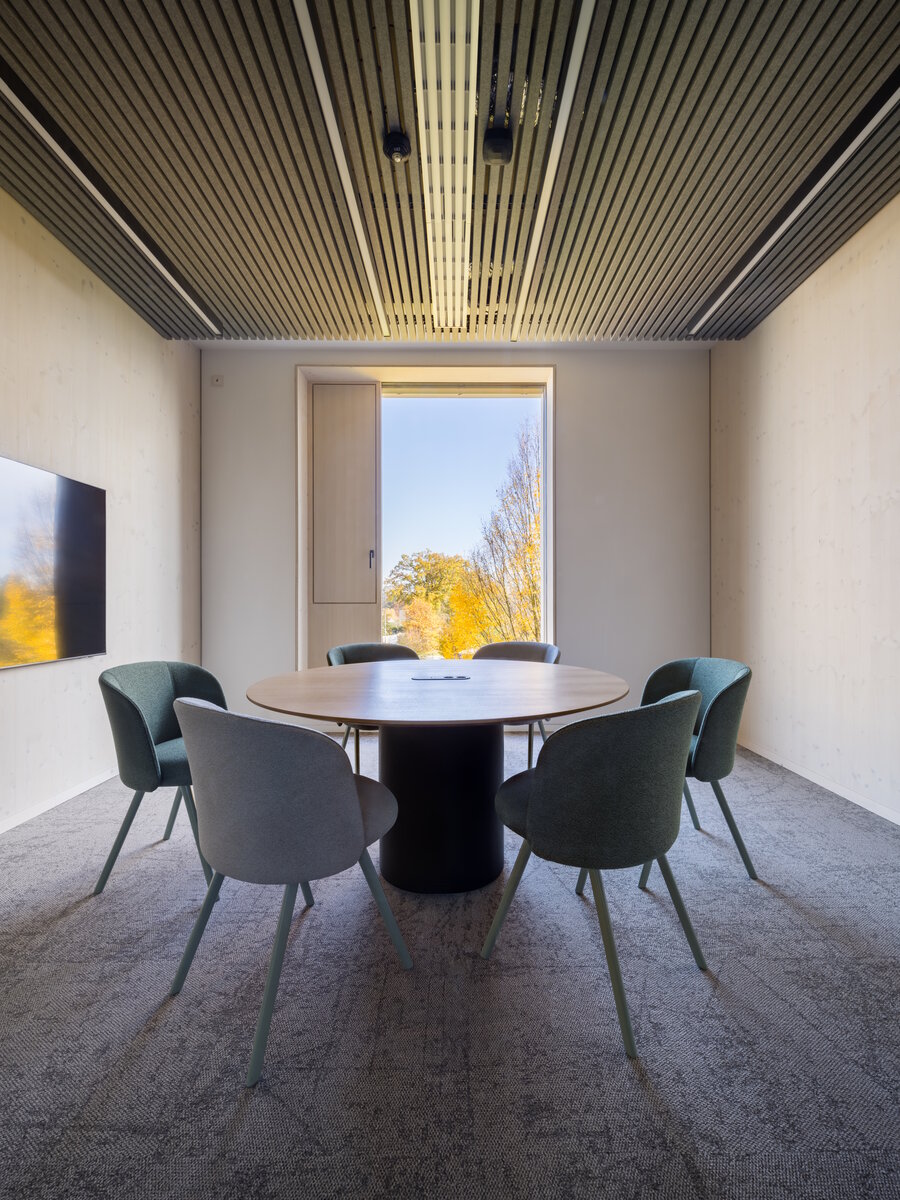
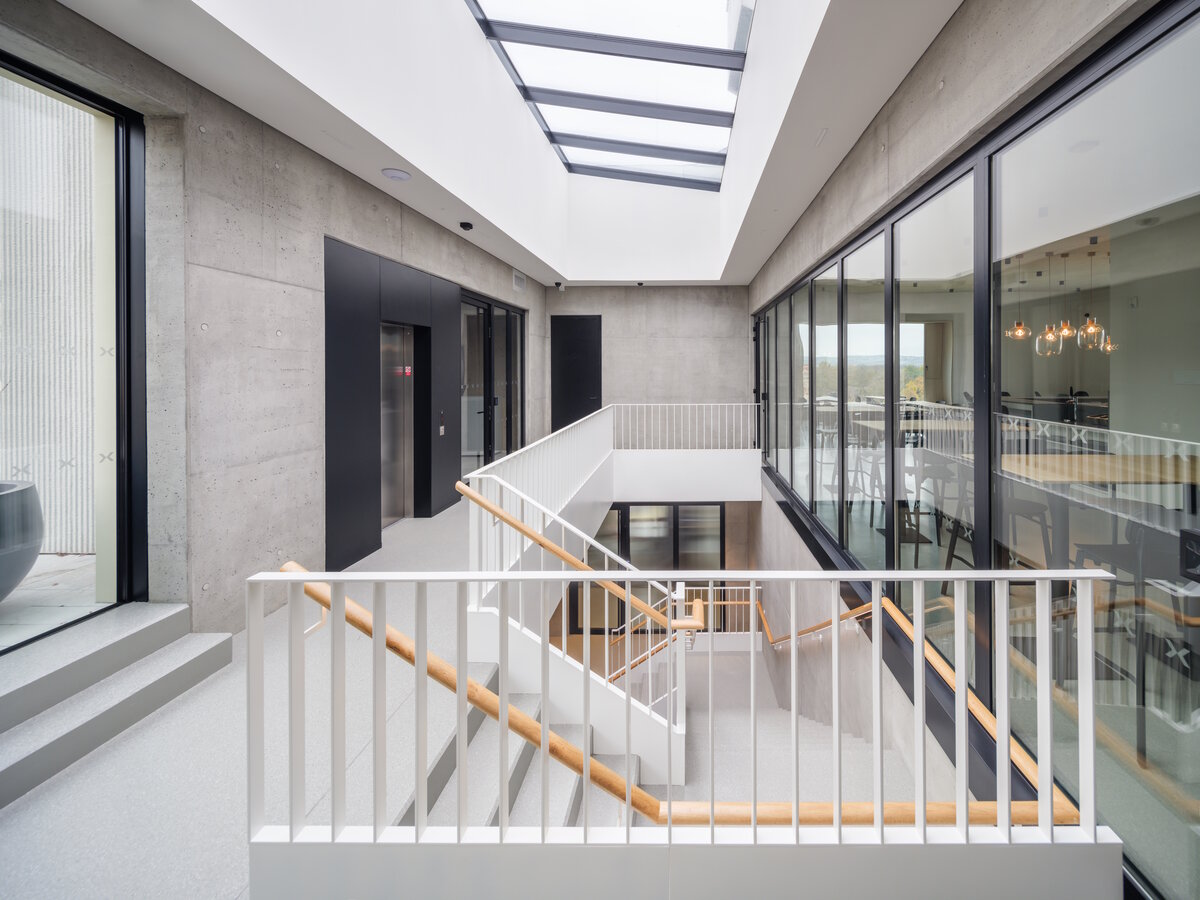
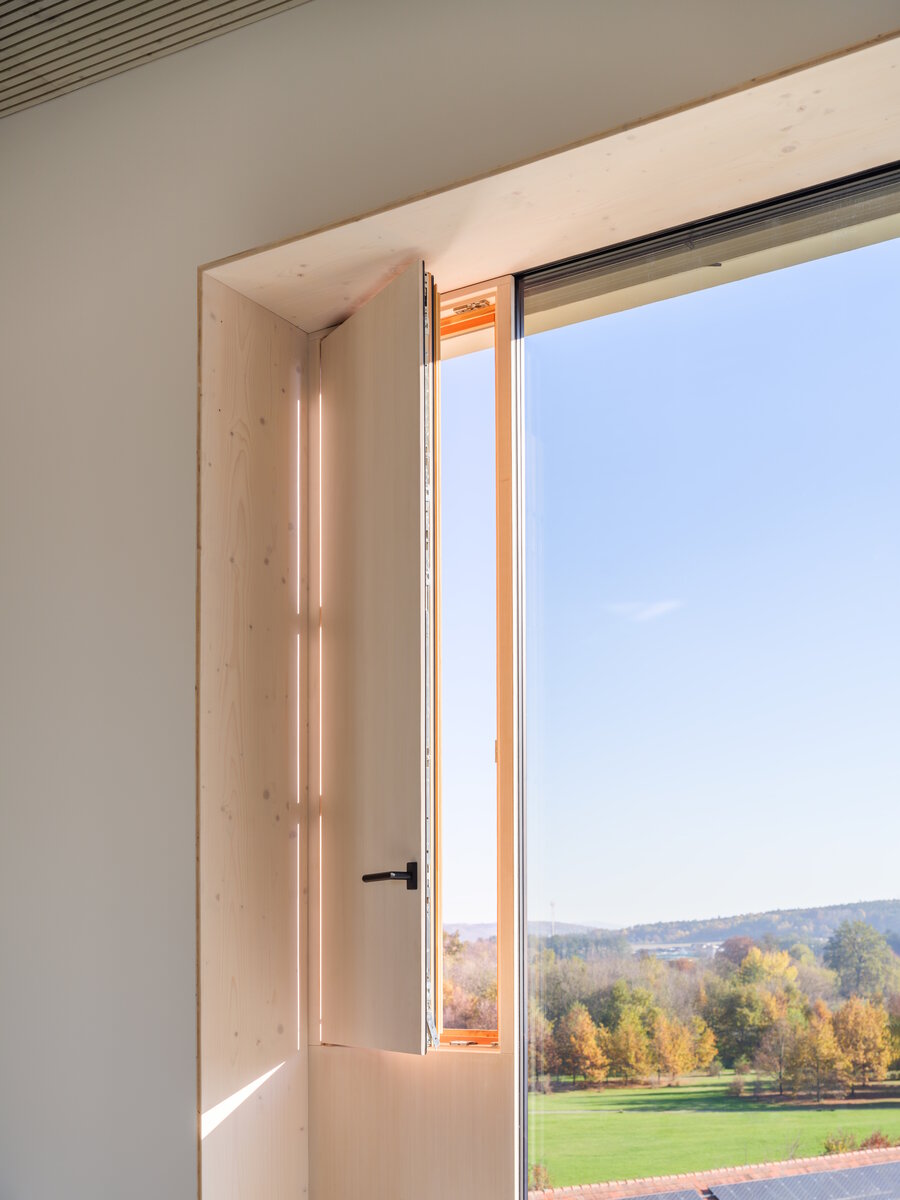
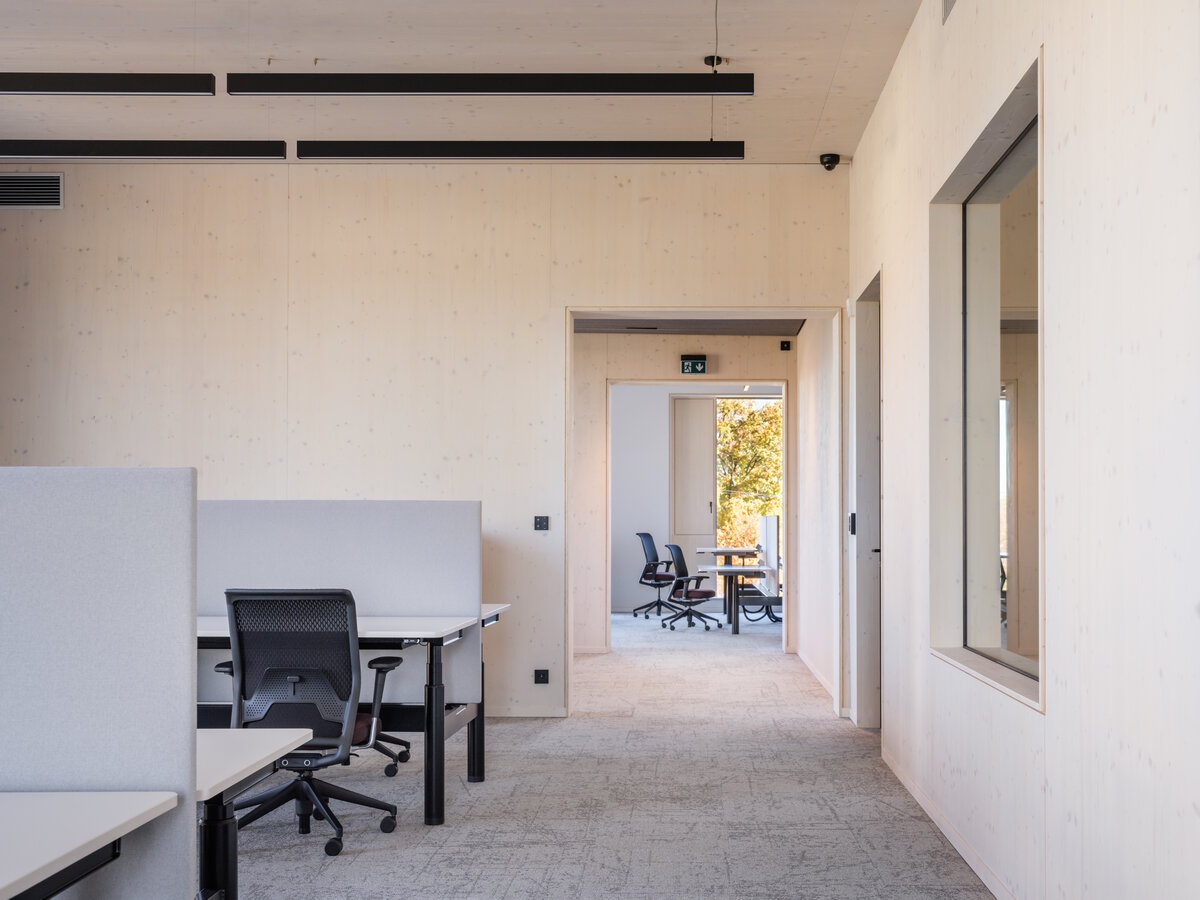
The structure made of wooden cellular ceilings and wall systems NOVATOP and CLT panels winds around the inner reinforced concrete core on four above-ground floors. Both materials of these structures are designed as visible in the dominant areas and both welcome the users of the building immediately upon entering the building. The panel supporting materials were chosen with regard to the preferred layout, size of the building and the intended visual appearance of the space.
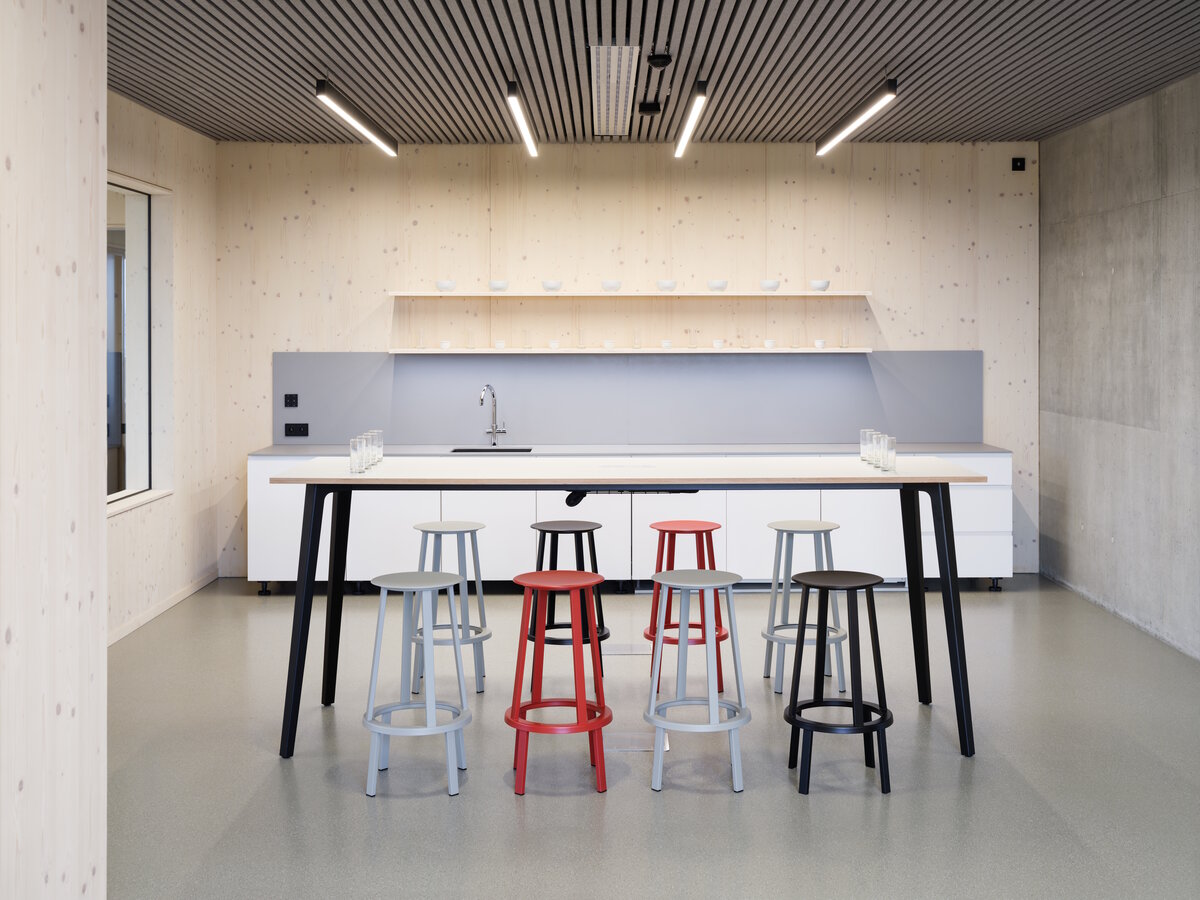
The client originally approached us only with a request for an interior solution for their administrative premises in a building that was to be built from prefabricated parts. In our opinion, this proposal did not reflect the requirement for a representative headquarters of a family business. We discussed the concept together and agreed on the project. Our task, among other things, was to ensure that the BudexHUB wooden building, including the entire area, lived up to the company's ideas about the significance of the company.
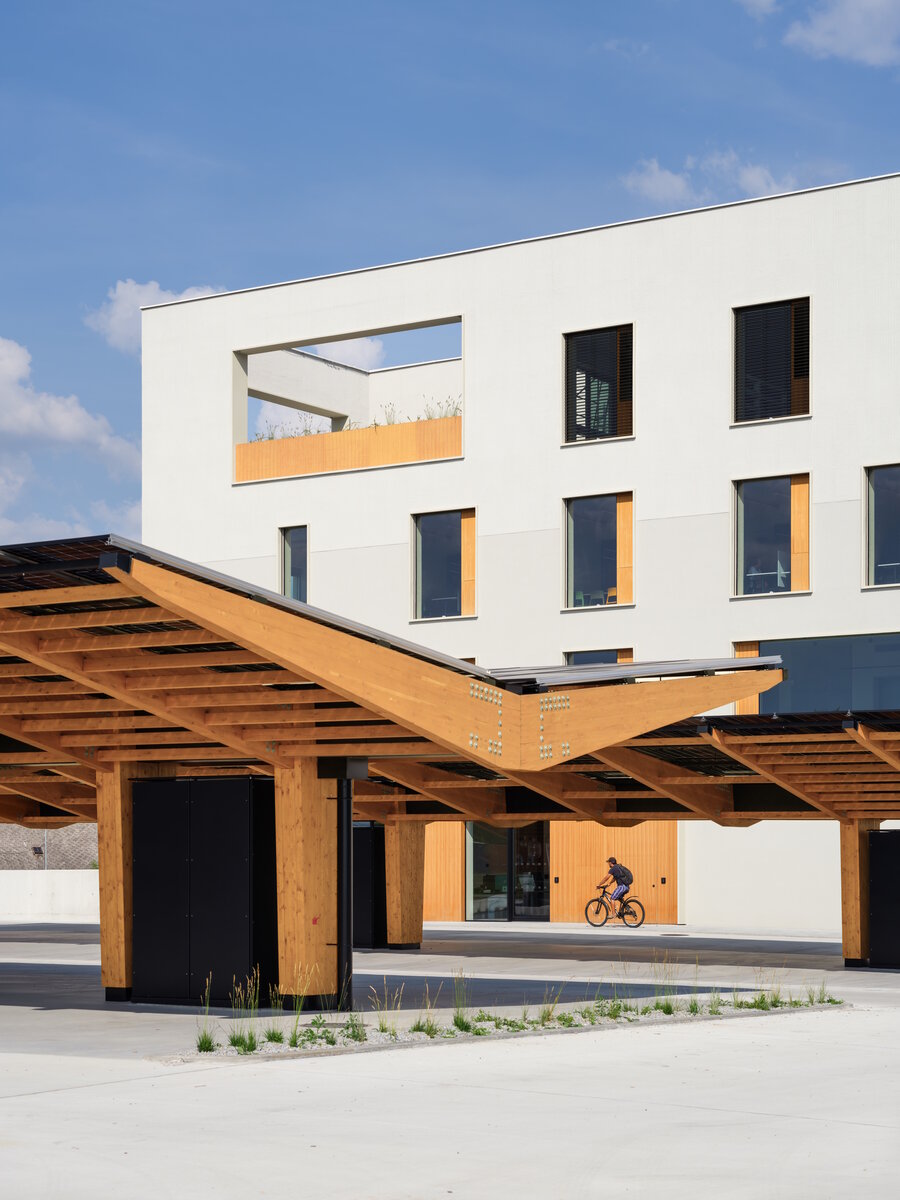
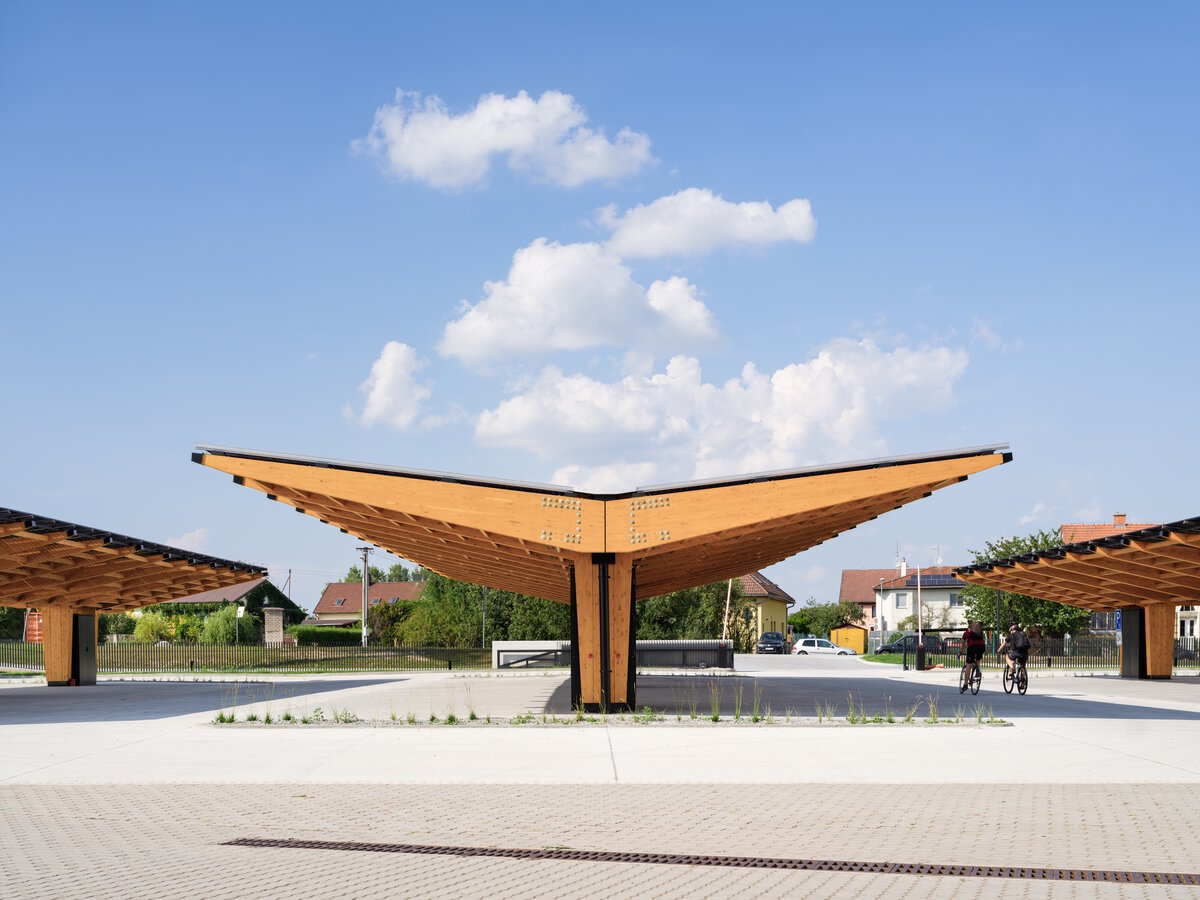
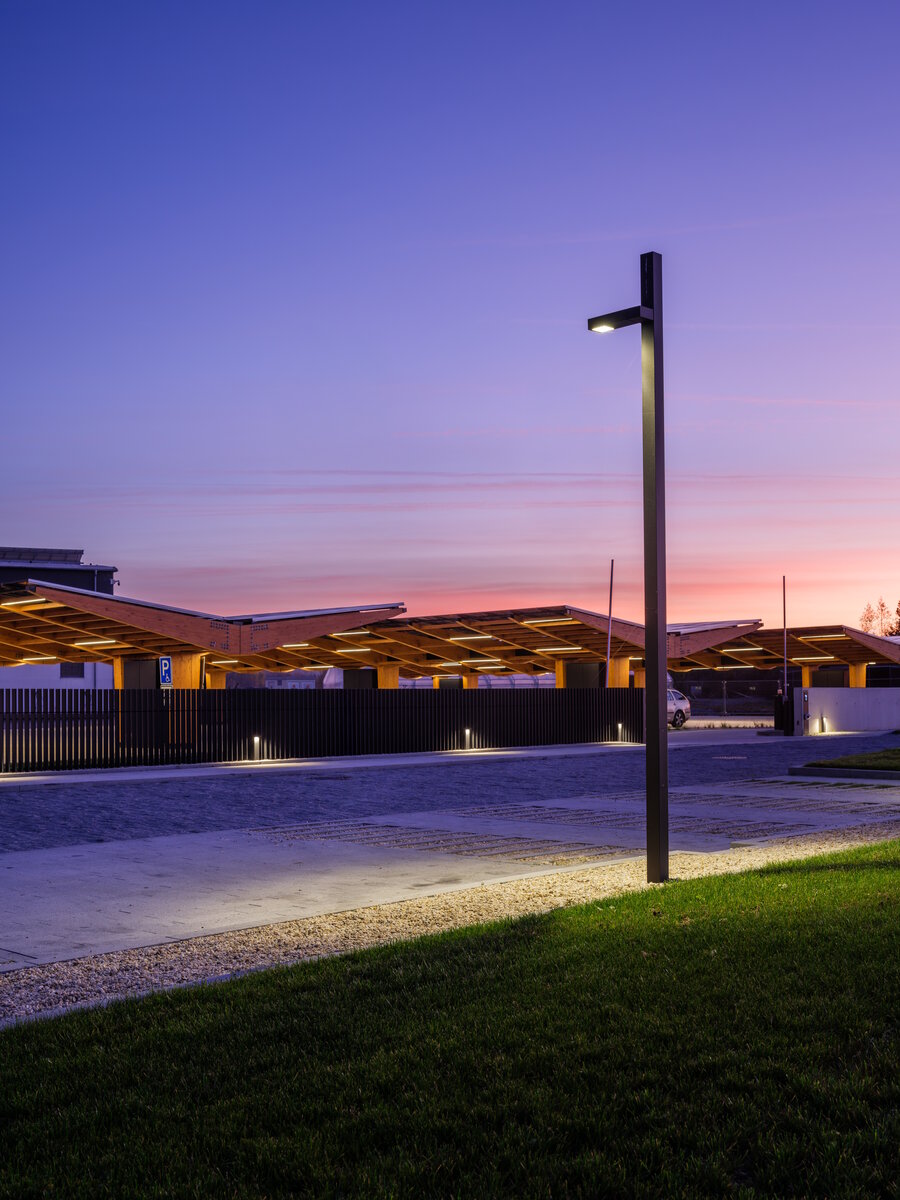
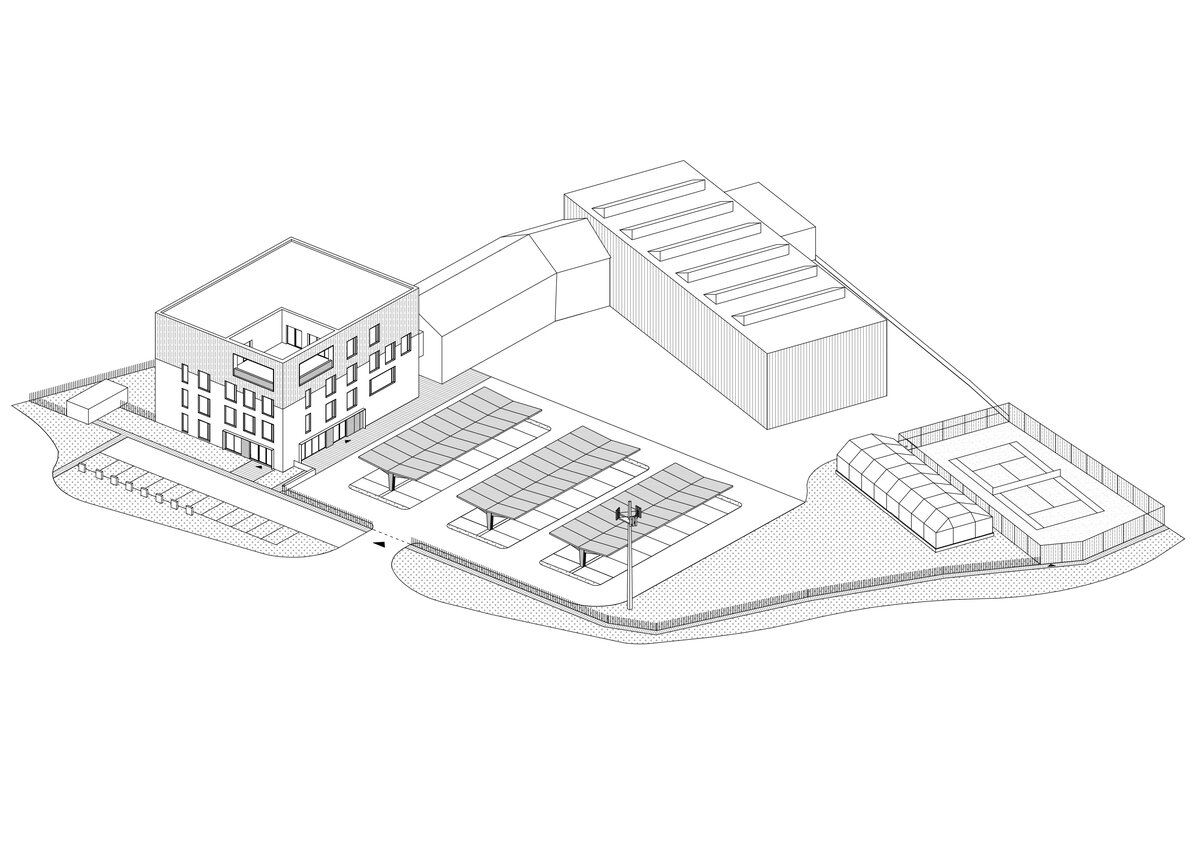
In order to obtain solar energy as efficiently as possible, we chose the latest technology of bifacial solar panels forming the roof of the shelters above the parking lot. The supply of thermal energy for cooling or underfloor heating of the building is primarily provided by geothermal wells and a heat pump.
We covered the project in all its phases. As the general designer, we had oversight of all planning and design processes. We allowed the client to step into the project on a real scale using a model created in virtual reality (VR). VR makes it easier to navigate spatial relationships, perceive dimensions and depth. This saved time during design process.
Roof structure
The load-bearing structure of the flat roof is made of prefabricated wooden Novatop SWP panels (thickness 240 mm), conventional CLT panels and BSH beams. SWP panels are made of three-layer SWP boards (thickness 27 mm), which form the upper and lower cover with internal ribs, dimensioned according to the load. The panels function as simple beams with spans of 6.2 and 6.8 m.
In places with limited thickness, CLT panels (thickness 160 and 220 mm) are used. For the hipped roof (span 12.1 m), BSH prisms 160/520 (GL24h) are used, covered with OSB boards.
The panels are placed on internal and peripheral load-bearing walls or on steel beams (closed profiles) anchored to the reinforced concrete core via steel shoes. In connection with the concrete structures, steel angles are used, anchored chemically from the side to the reinforced concrete core.
Ceiling structures
The ceilings are made of SWP panels 280 mm thick with a double bottom plate (27 + 33 mm) for fire resistance of 60 minutes. The panels function as simple beams with a span of max. 6.2 m and are hinged.
The support is solved by:
a) wooden load-bearing walls (screwing),
b) LVL beams 2×63/350 (laying over steel stirrups),
c) steel beams for greater loads,
d) steel angles anchored to the reinforced concrete cores.
The ceilings are laid on an acoustic pad with a fireproof seal, the steel elements are protected by fireproof cladding.
Attic structures
The attic structures are made of CLT panels 280 mm thick. 90 mm with vertical and horizontal ribs. Vertical ribs 80/180 mm (KVH, C24) ensure rigidity and anchorage to the walls and ceiling of the 4th floor. In the part near the terrace, the attic is made of a CLT panel 120 mm thick, reinforced with 120/480 mm outer BSH ribs, which function as horizontal beams in the corner of the building.
Vertical structures - walls
The load-bearing and perimeter walls are made of CLT and Novatop panels, they transmit both vertical and horizontal loads. The reinforcement is provided by a reinforced concrete core.
The perimeter walls are made of CLT 120 mm thick, invisible (covered with SDK). The internal load-bearing walls are made of CLT or Novatop panels depending on the load and the requirement for visibility.
The main load-bearing CLT panels are 160 and 180 mm thick, Novatop panels (168 mm thick) are used for the visible parts.
Anchoring is done with steel angles to the reinforced ceilings and substructure. Additional tension anchors are on the exterio
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
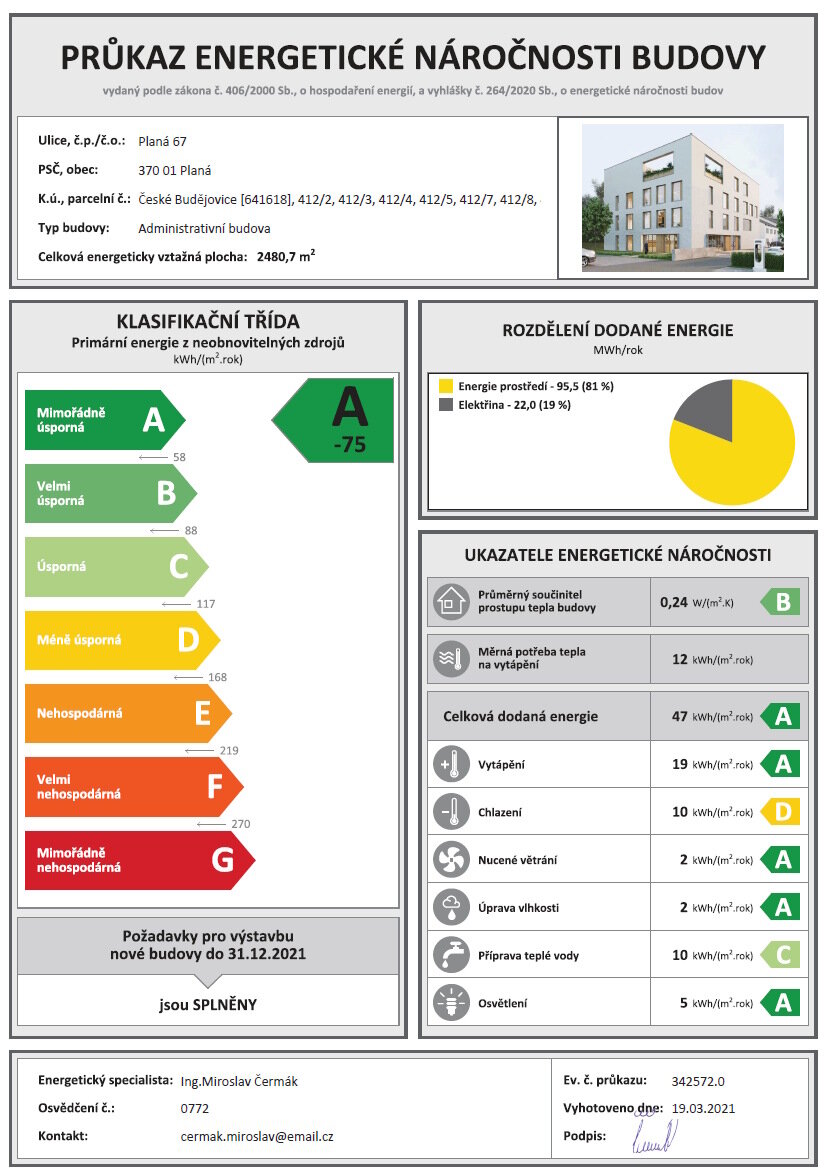
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
A
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|