| Author |
doc. Ing. arch. Radek Lampa, Ing. Libor Hrdoušek, Ing. arch. Kateřina Havlová, Ing. arch. Hana Púčeková, Ing. arch. Oksana Džabarjan, Ing. arch. Oleg Kovalyuk, Ing. arch. Jana Věnečková, Ing. arch. David Skalický |
| Studio |
ra15 |
| Location |
Nad Kajetánkou 134/9, 169 00 Praha 6 |
| Investor |
Duhovka Group a.s. |
| Supplier |
Nábytek na míru: klrink, https://www.klrink.cz/
Dodavatel osvětlení: ZG Lighting Czech Republic s.r.o. https://www.zumtobel.com/cz-cs/index.html
Podhled: Knauf https://knauf.com/cs-CZ |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
May 2024 |
| Fotograf |
Radek Úlehla |
The environment we live in has a significant impact on our quality of life and this is even more true for the spaces where we are educated. Students of the Czech-English Montessori Elementary School Duhovka have now benefited from an improved quality of both life and learning as the school expanded its capacity to include the upper primary level and enhanced its service standards and comfort for students and staff. Throughout the entire project increasing functionality and improving the quality of the environment were key priorities.
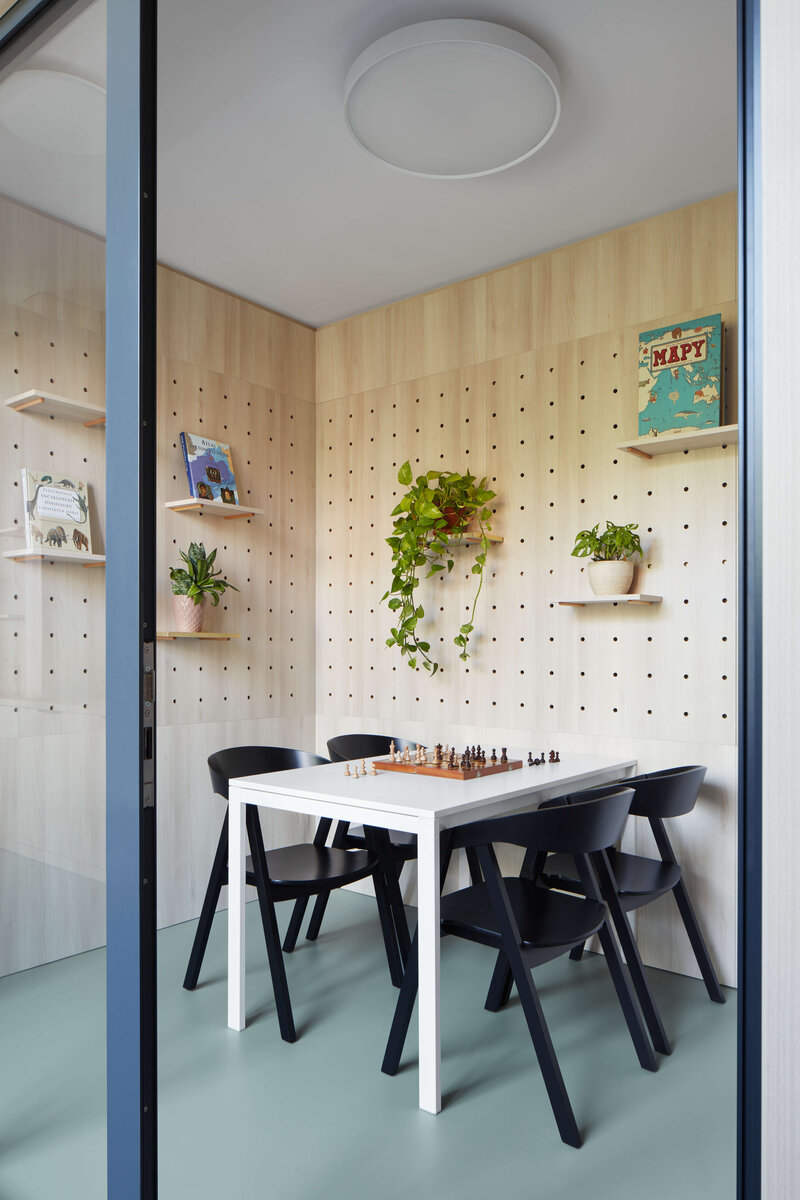
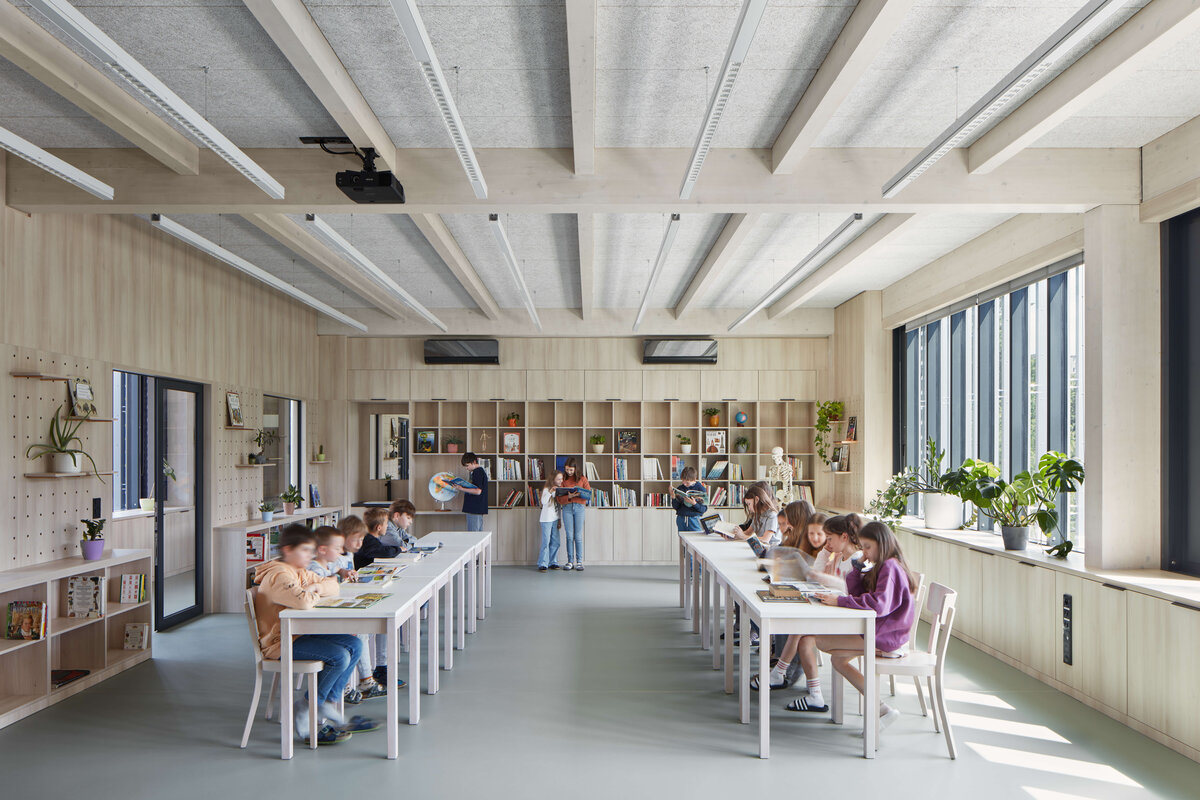
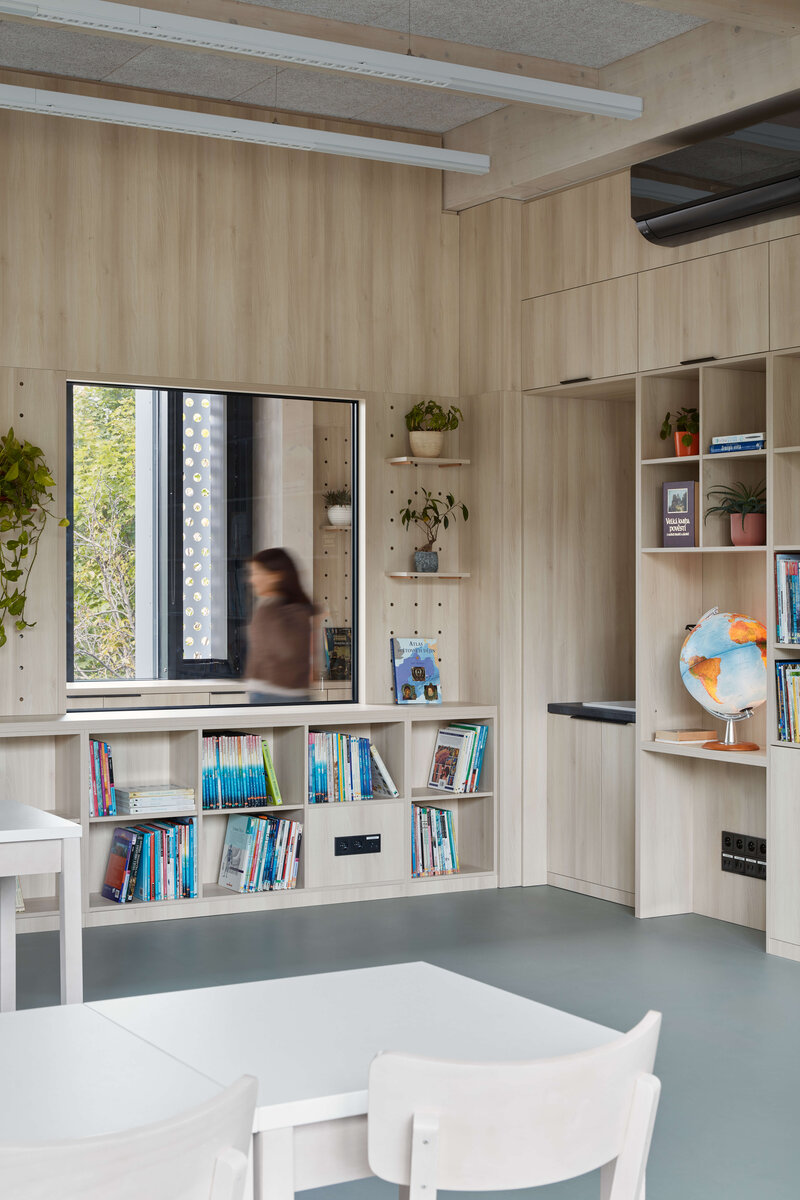
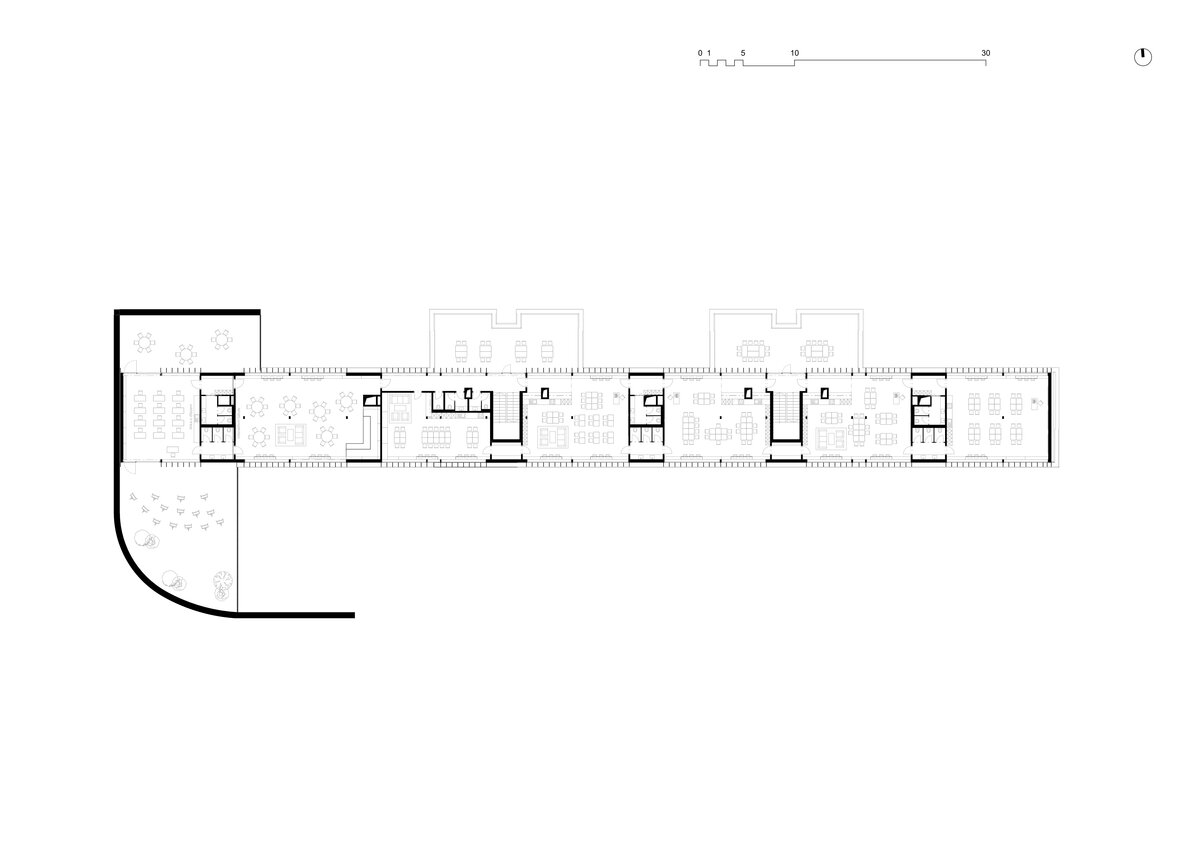
The Montessori education concept is built on the idea „Help me do it myself“ which fosters a child’s autonomy in the learning process. To fulfill this vision a stimulating environment is essential one that aligns with the child’s mental developmental needs during their sensitive periods. However this also brings increased demands on space and its utilization.
Wood, Metal, and Glass
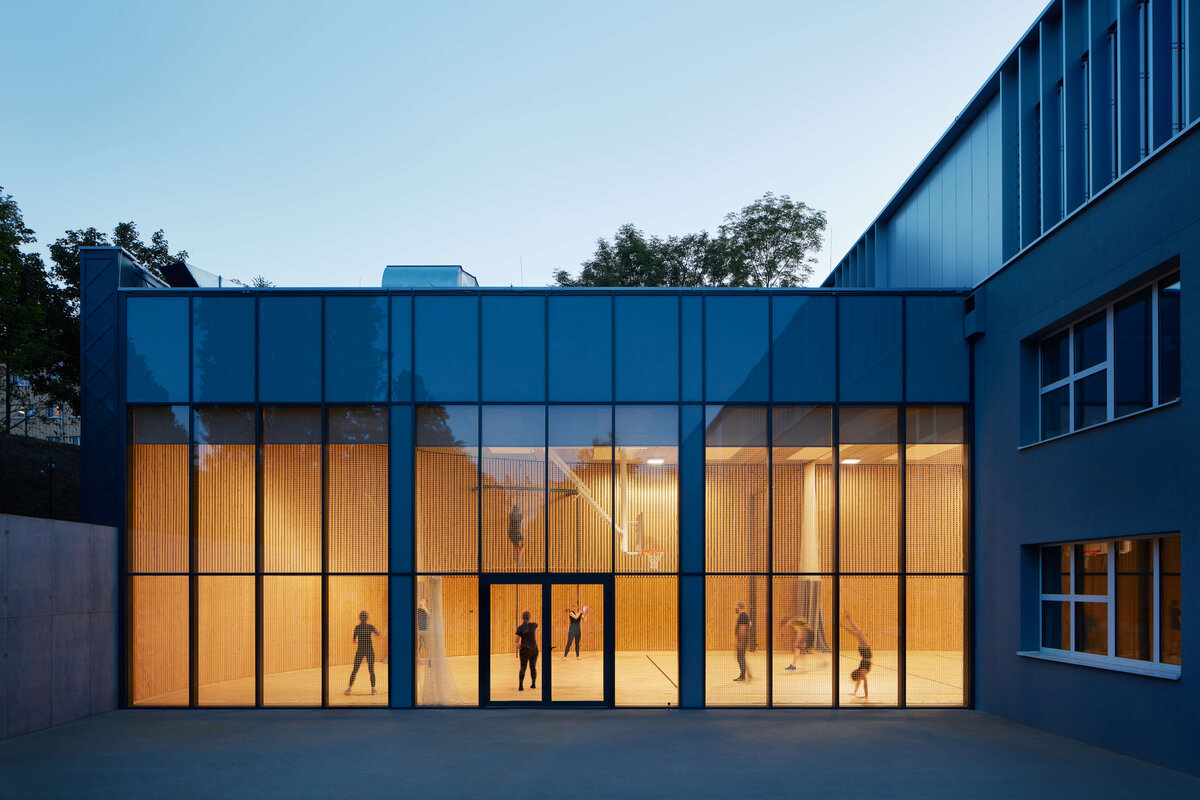
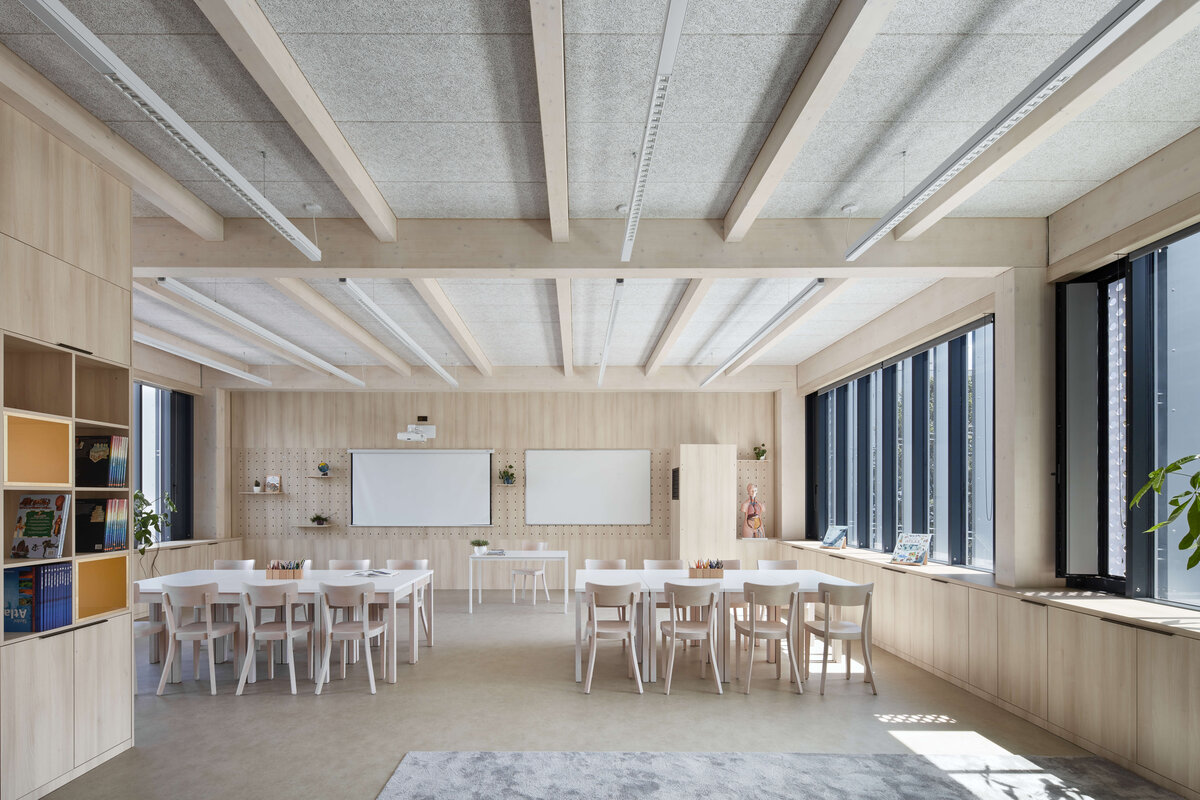
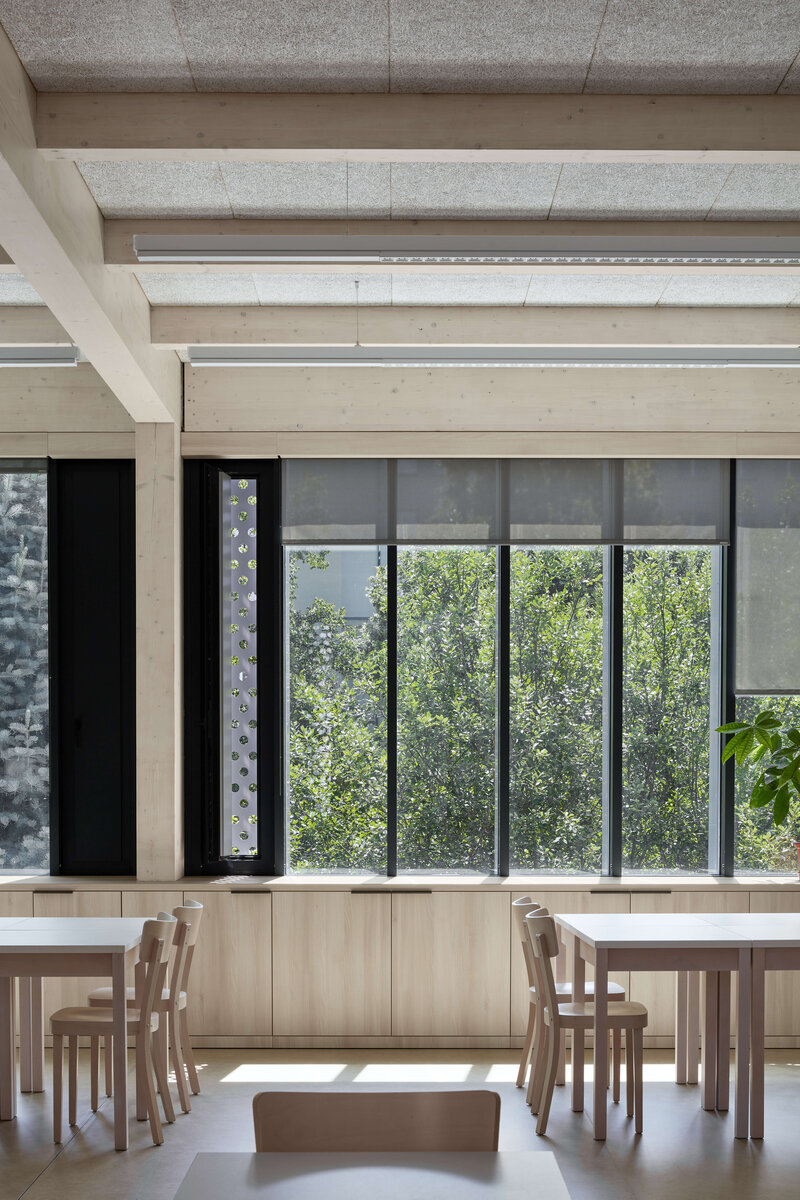
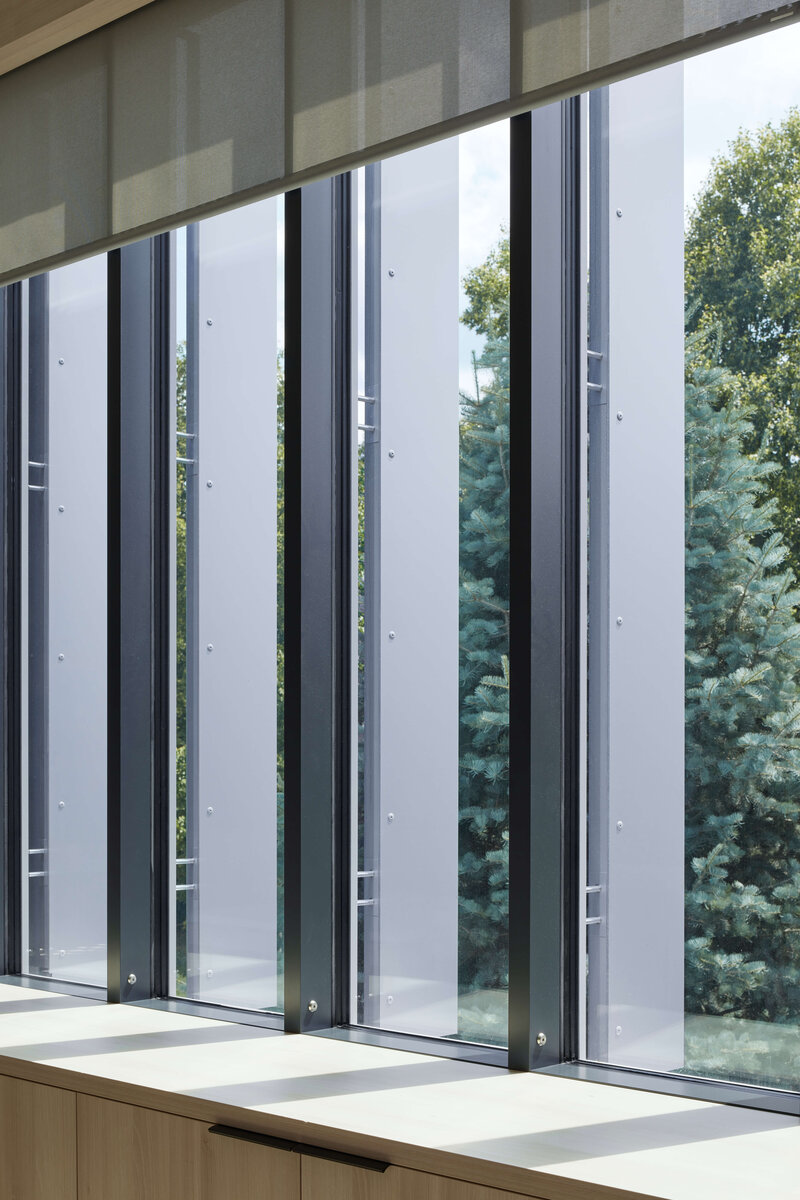
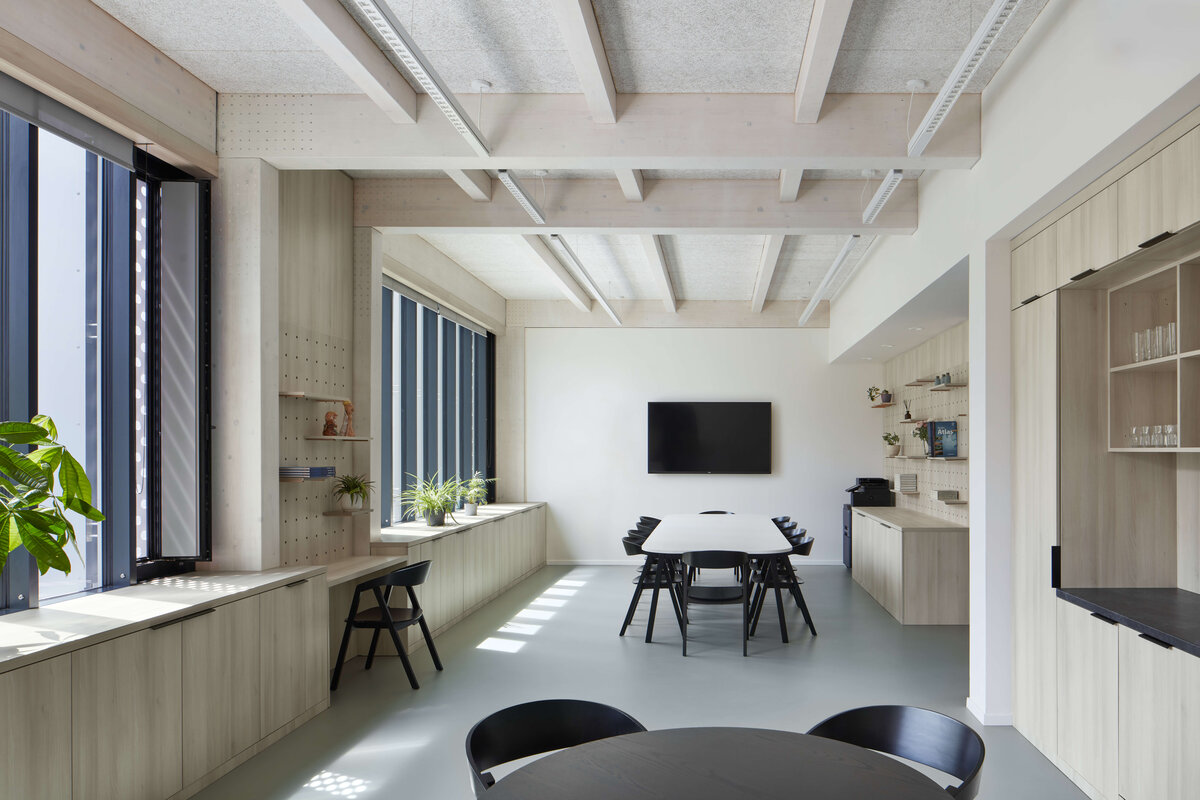
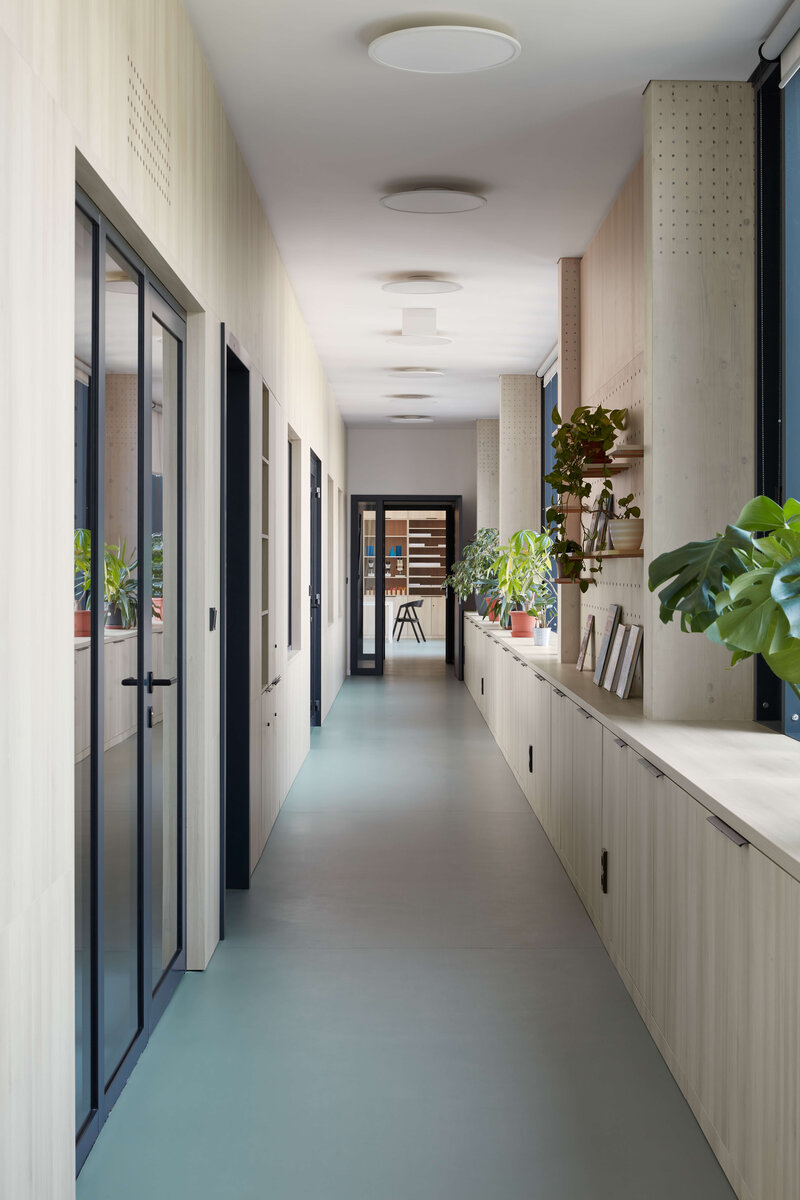
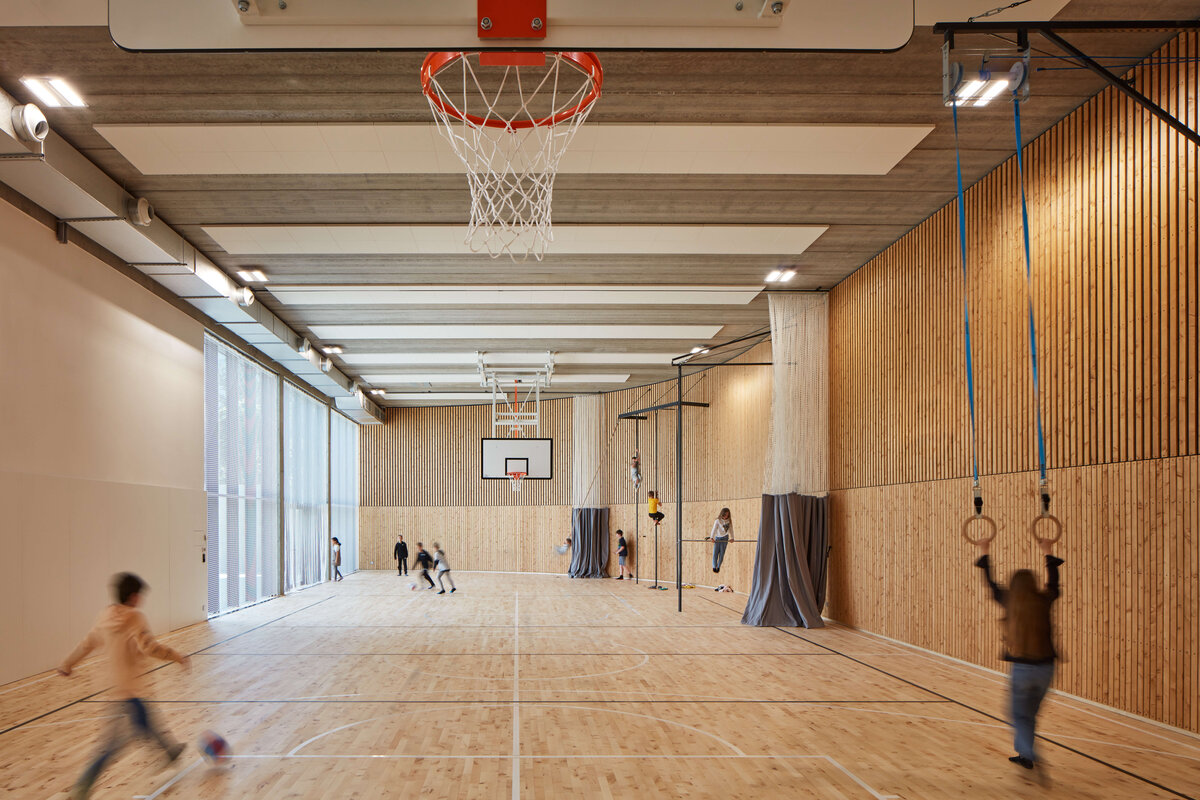
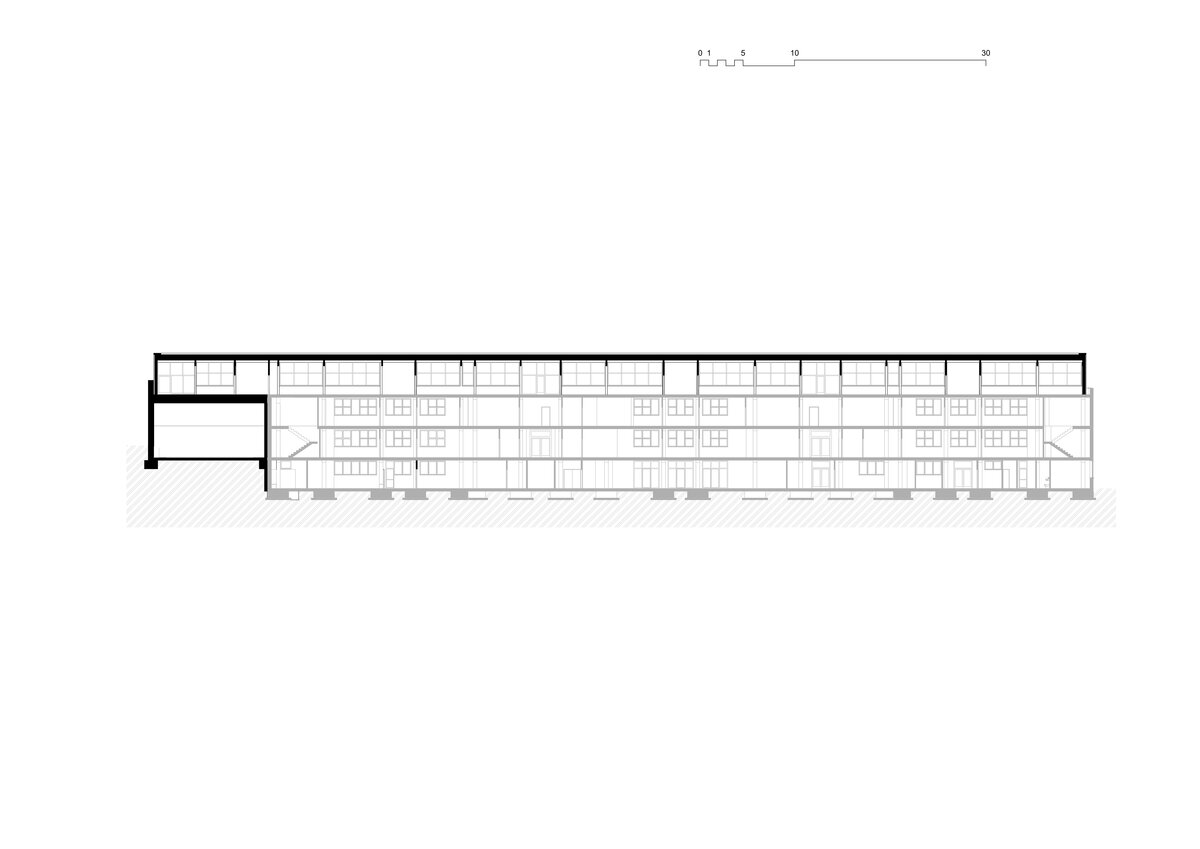
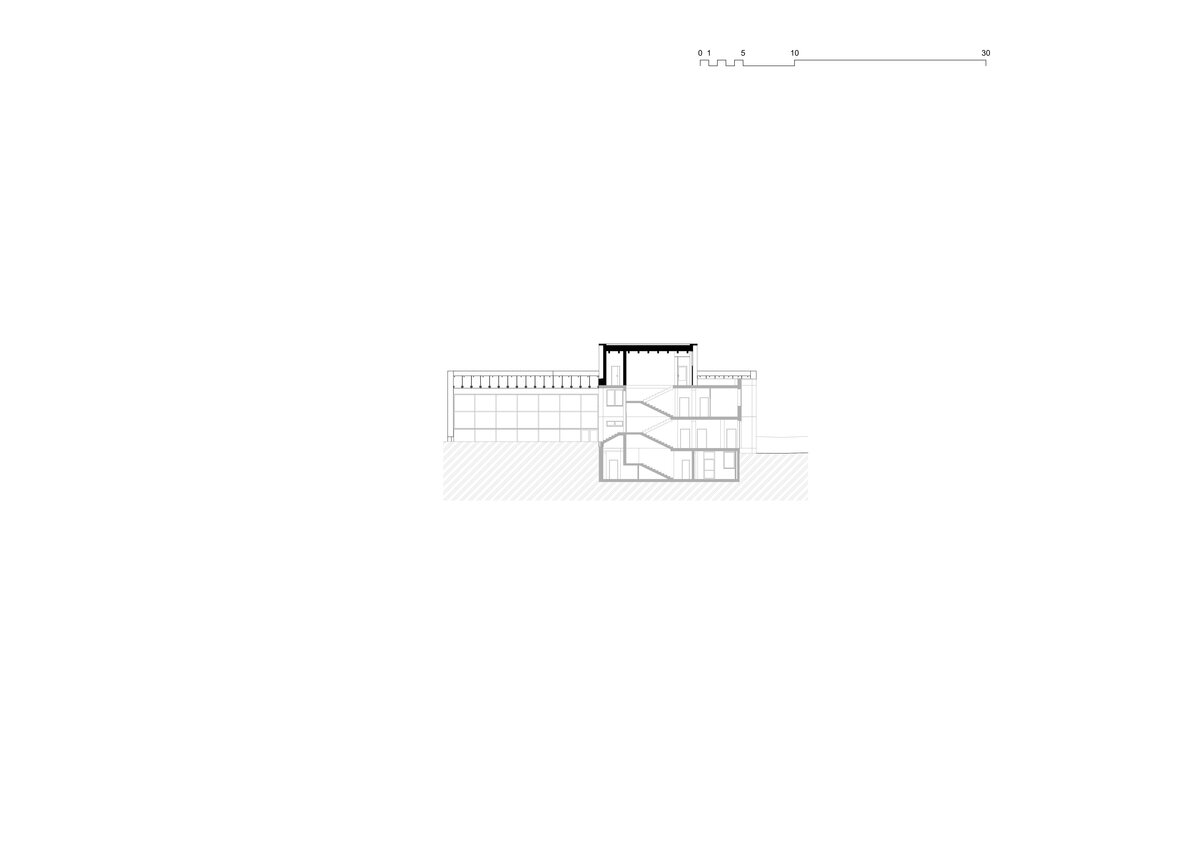
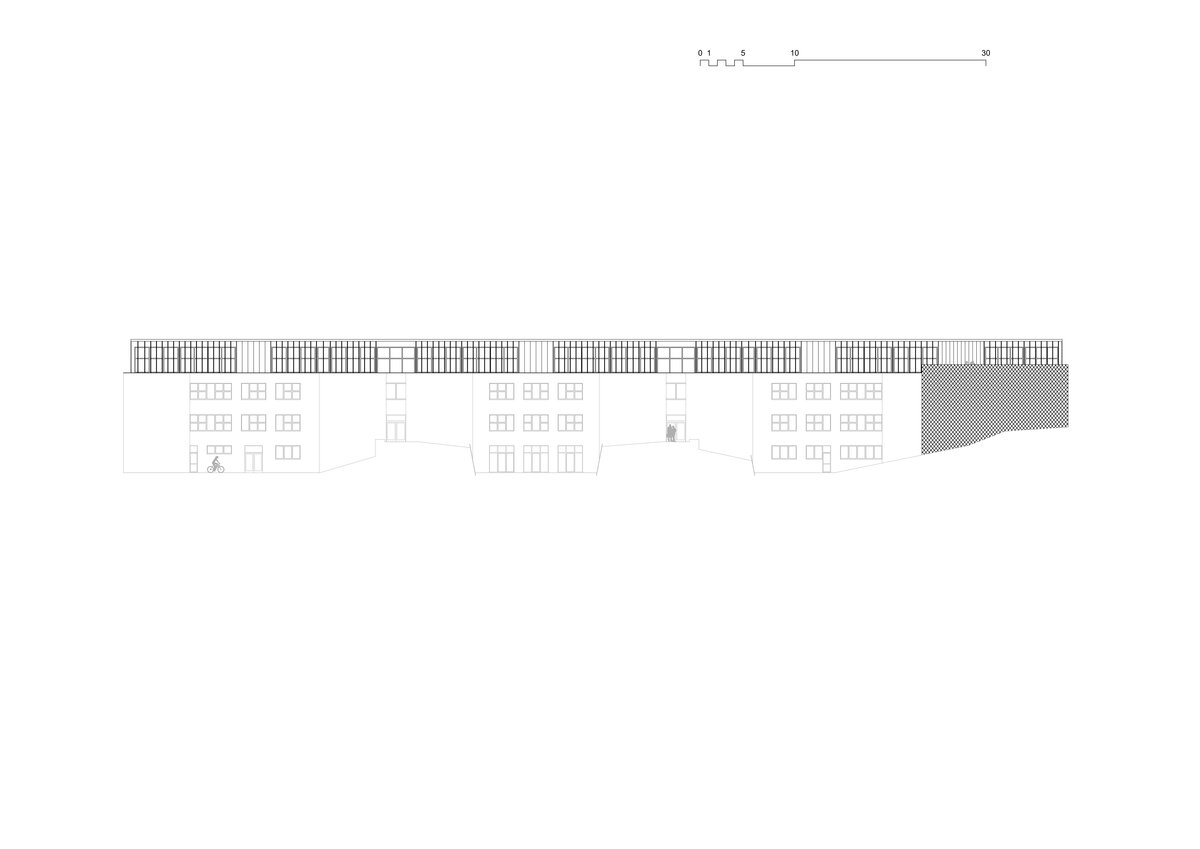
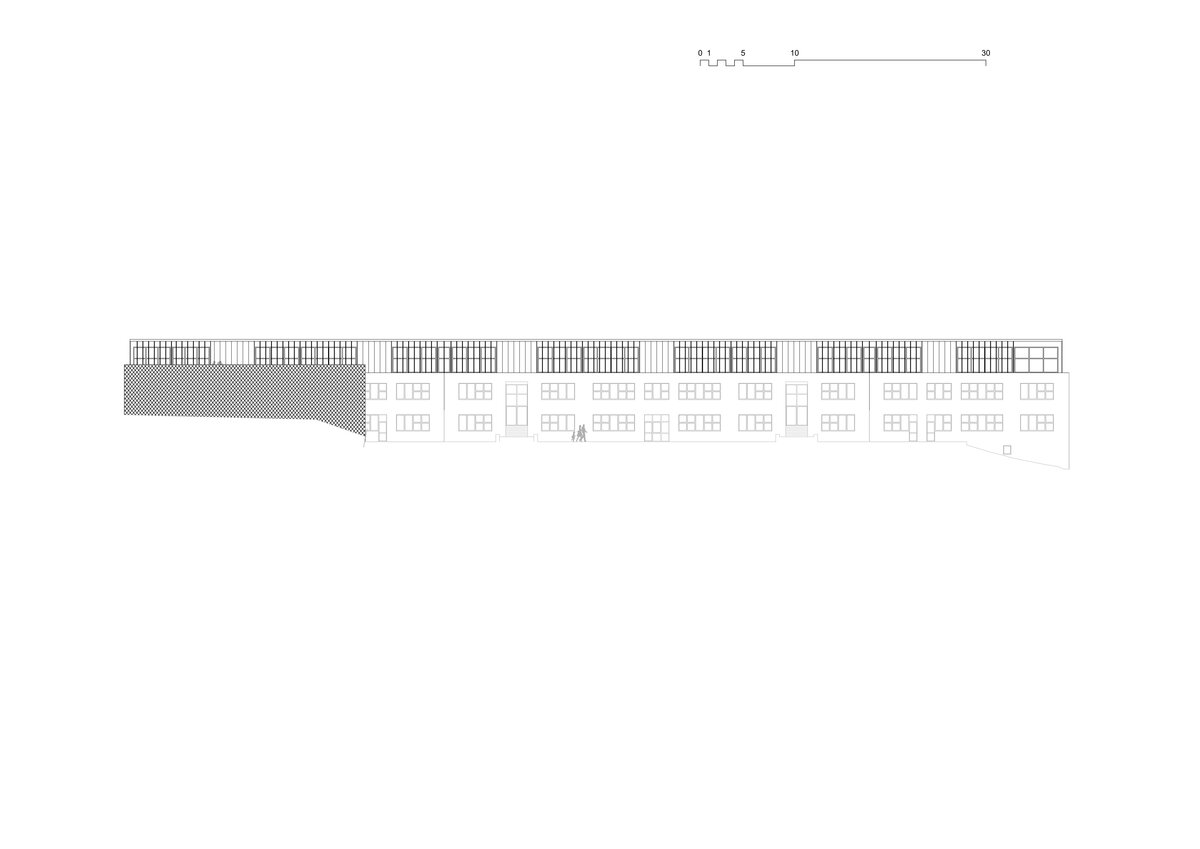
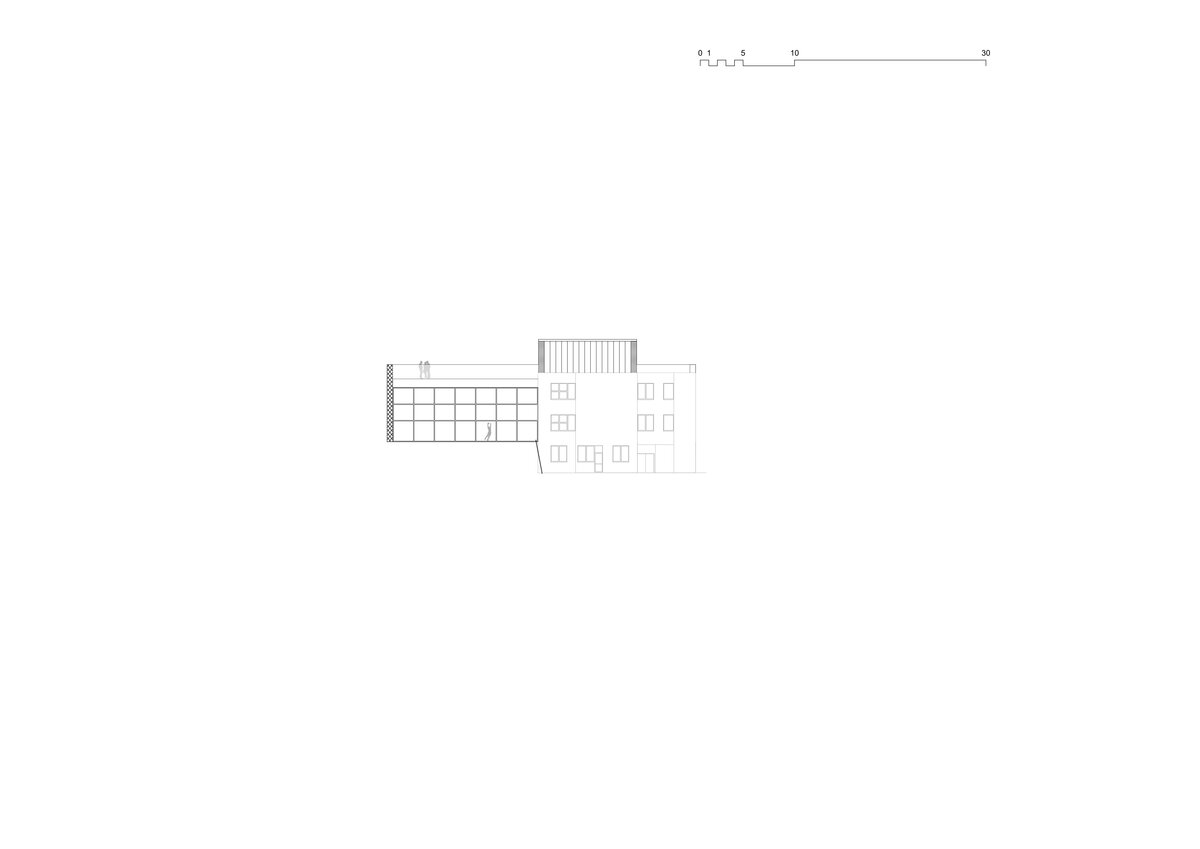
Considering the load-bearing capacity of the original structure, the vertical extension was built using a wooden framework, which remains exposed in the interior. Wood is also featured in the built-in furniture and gymnasium cladding. In combination with glass, it plays a dominant role in the classrooms, contributing to ample daylight and excellent acoustics—creating optimal conditions for concentration and effective learning.
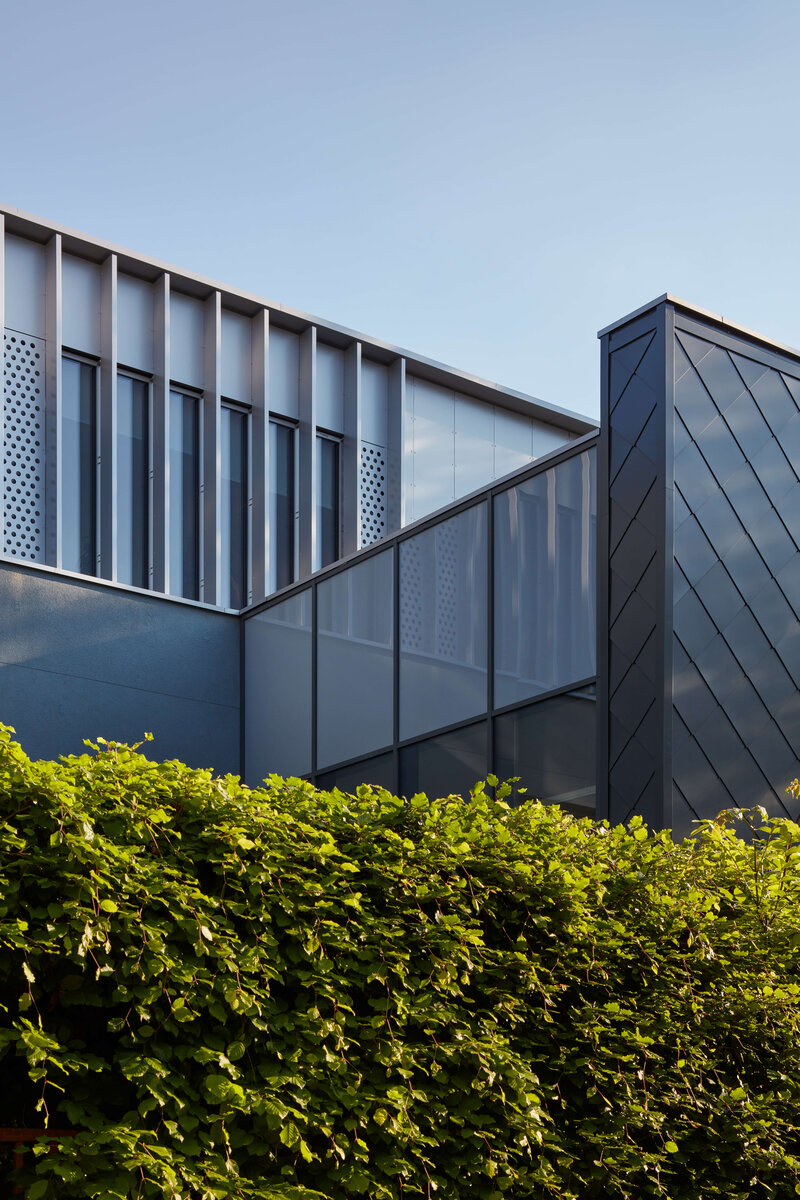
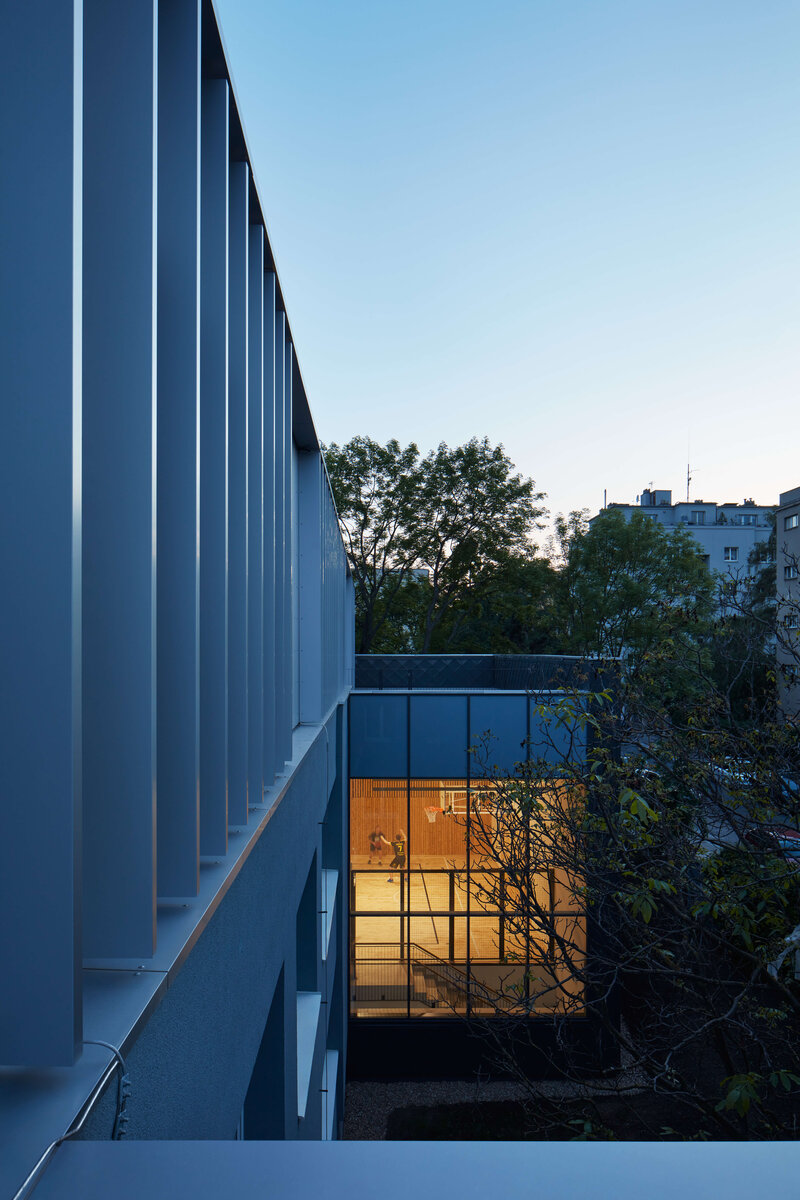
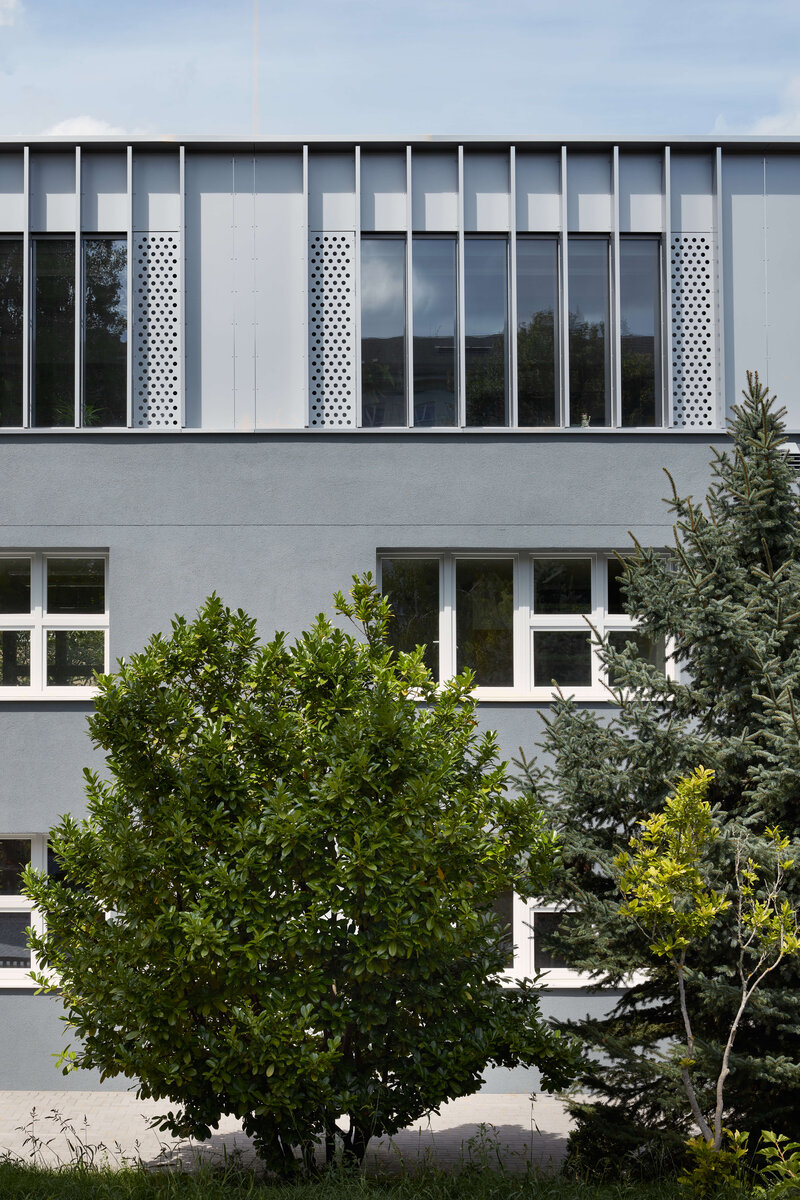
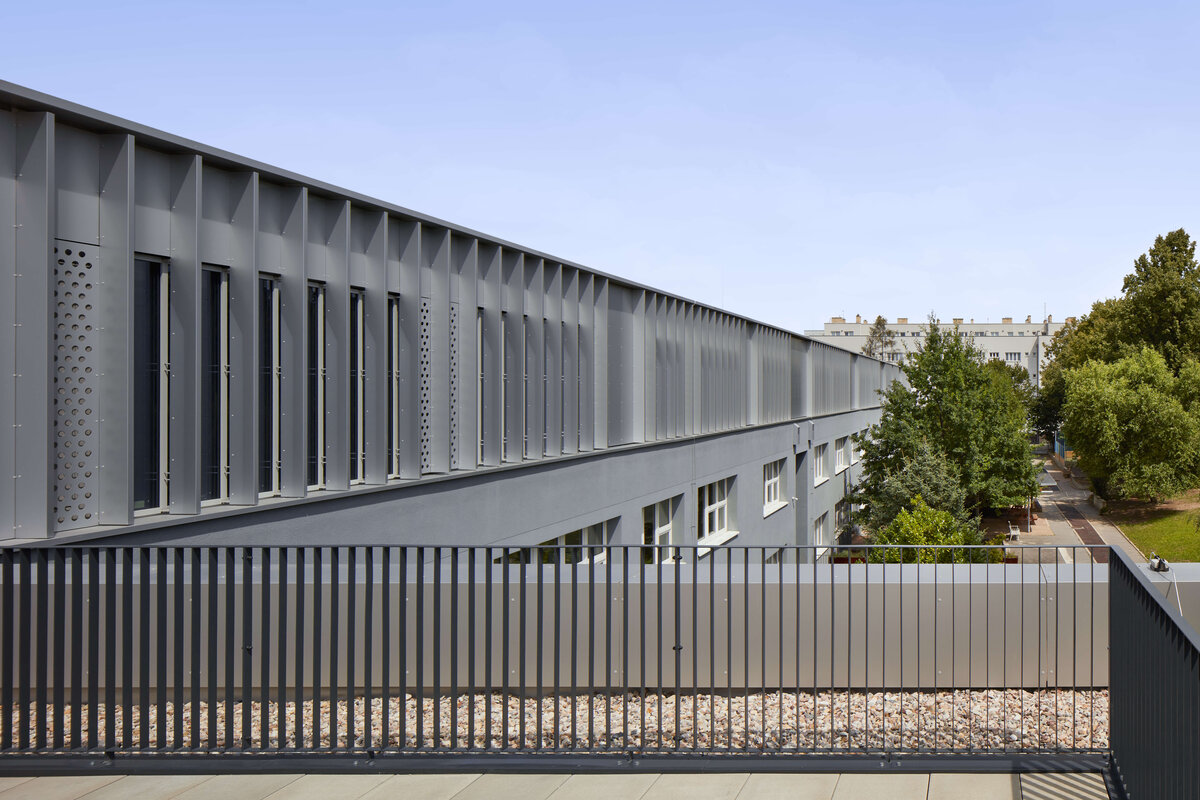
Both extensions’ facades are clad in durable metal sheeting. On the gymnasium, the metal panels resemble traditional wooden shingles, while on the classroom extension, they form vertical strips that transform into shading louvers around the windows, adding lightness and dynamic contrast to the robust contours of the original two-story building.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
C
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|