| Author |
Jiří Knesl, Jakub Kynčl, Jan Weiss |
| Studio |
knesl kynčl architekti s.r.o. |
| Location |
Štěpnice, Praha-Lysolaje, 165 00, 50°7'48.548"N; 14°21'51.036"E |
| Investor |
Landia - Zátiší s.r.o., MČ Prahy-Lysolaje |
| Supplier |
UNISTAV CONSTRUCTION a.s., ALSTAP s.r.o., RS CONSTRUCT s.r.o., JASPTEN s.r.o., DEREZA s.r.o., REVIS - Praha s.r.o., ENVIRONMENTAL BUILDING a.s. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
January 2024 |
| Fotograf |
Radek Brunecký / ATELIÉR BRUNECKÝ |
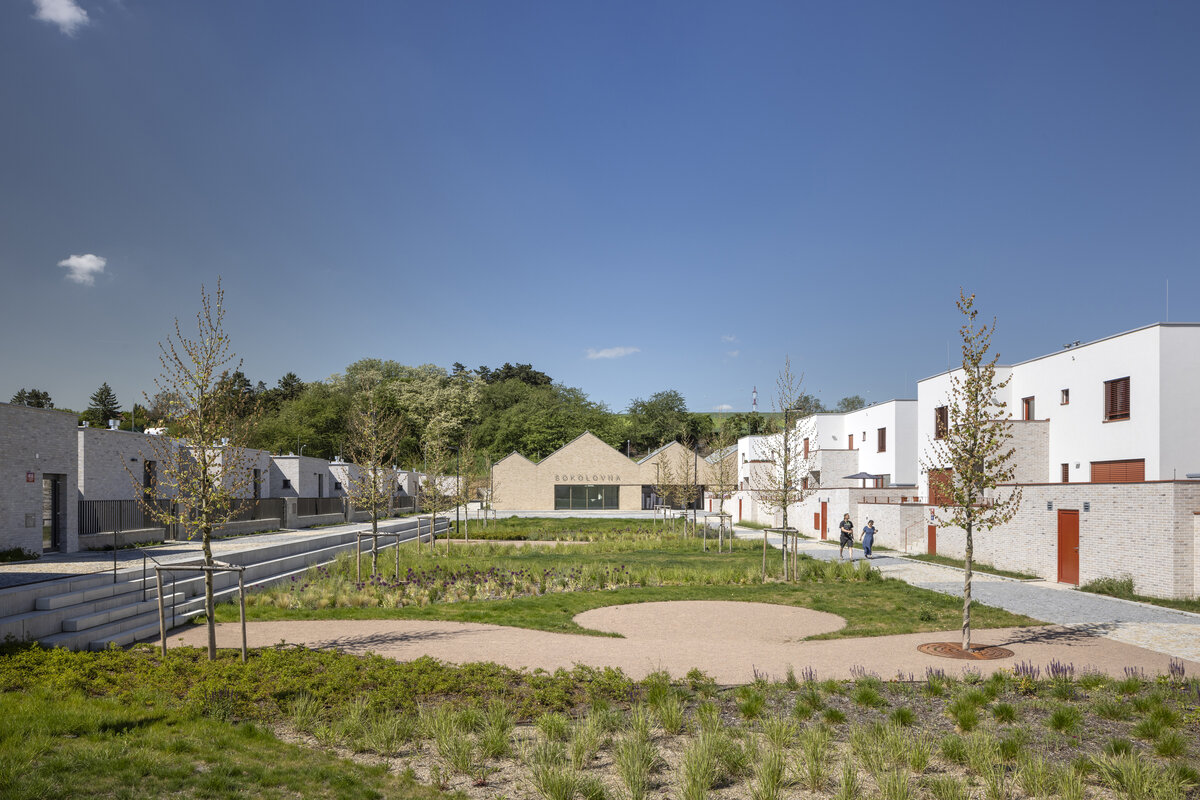
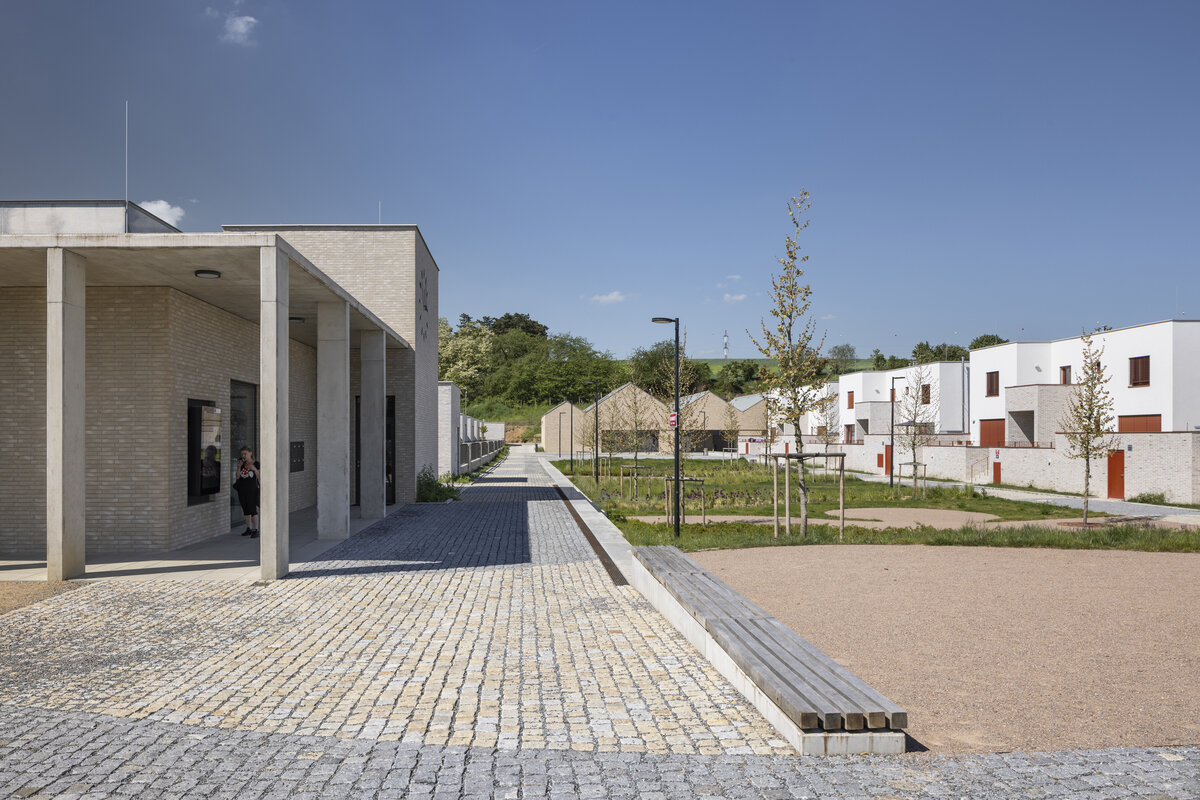
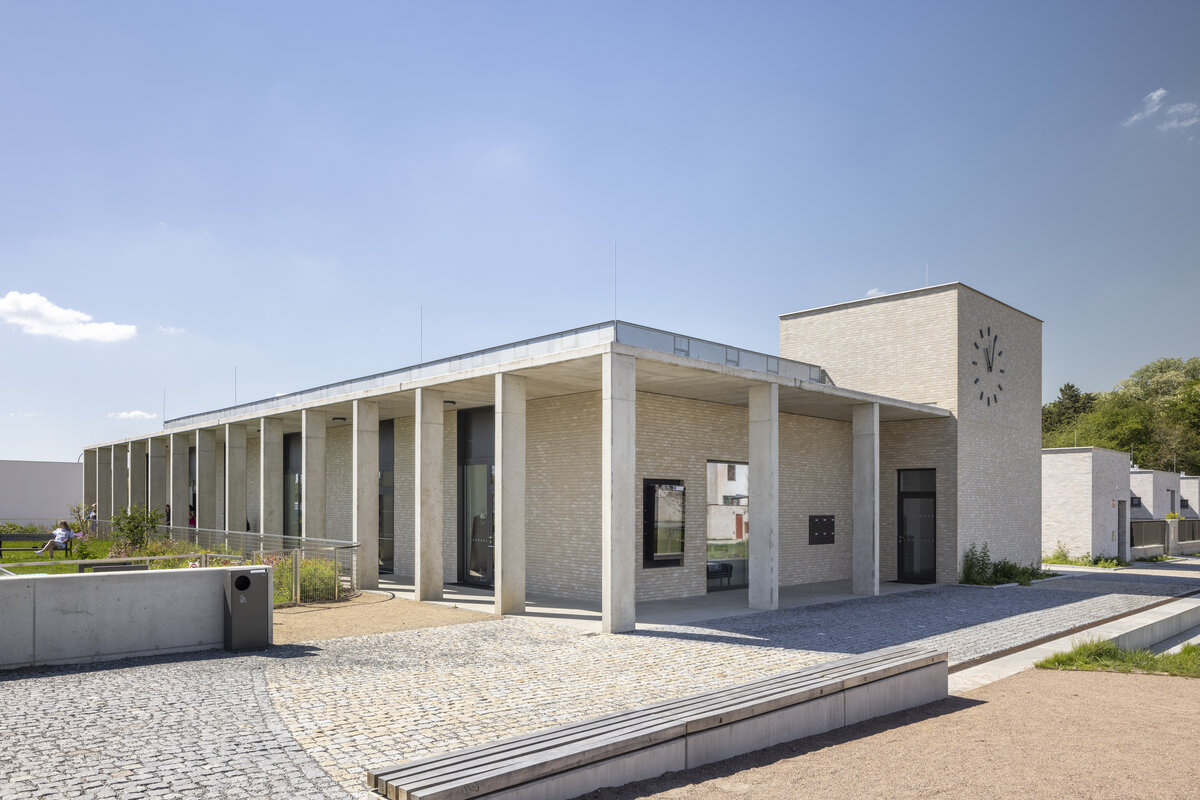
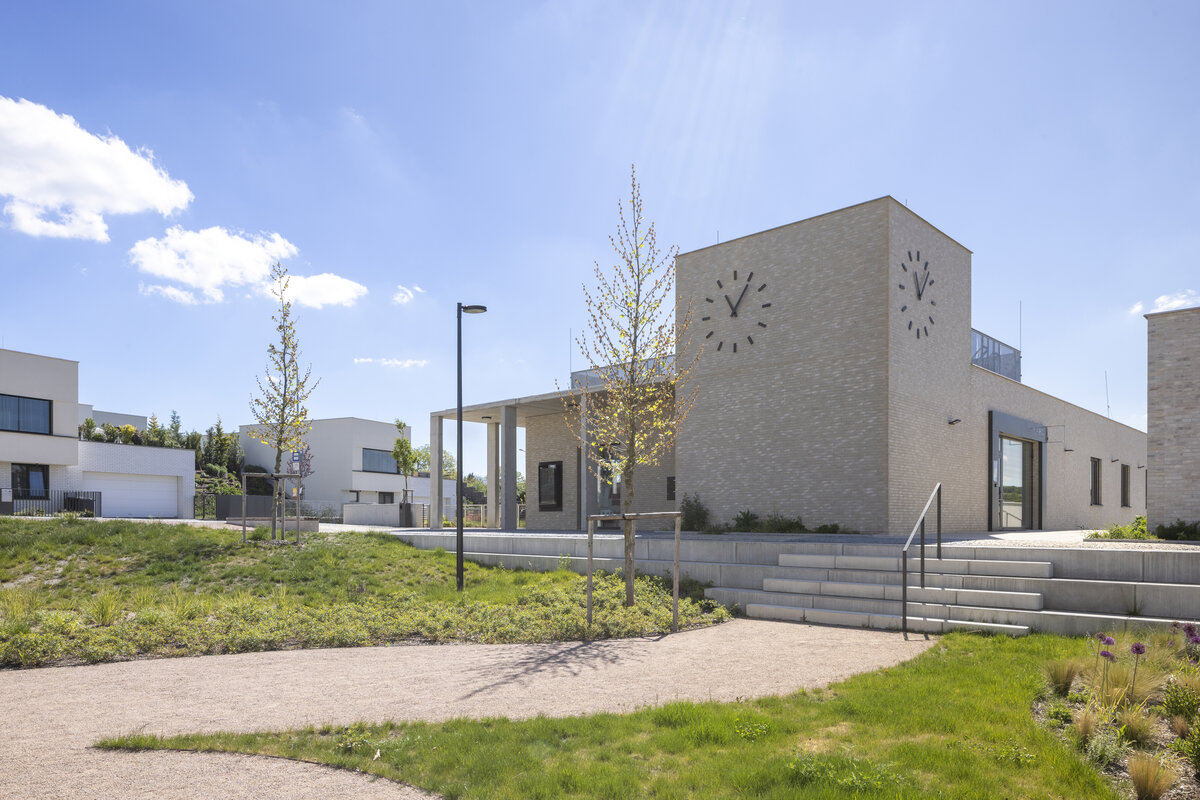
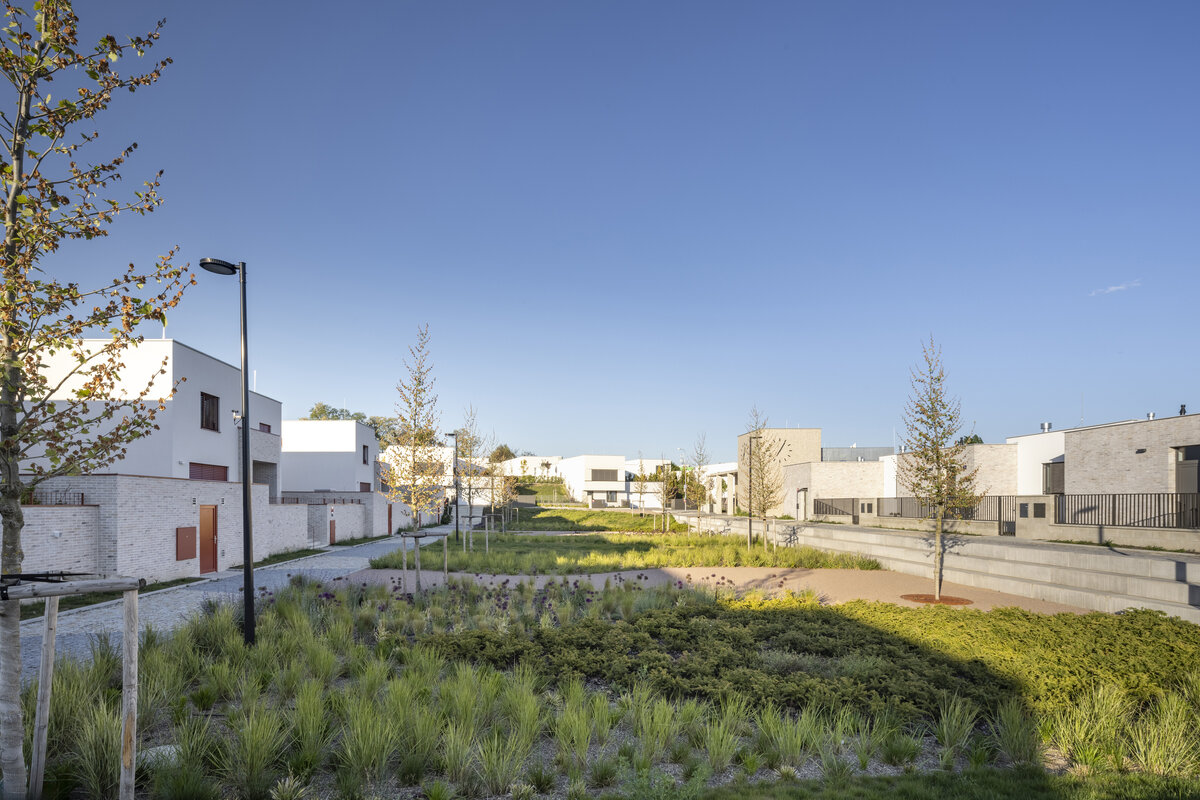
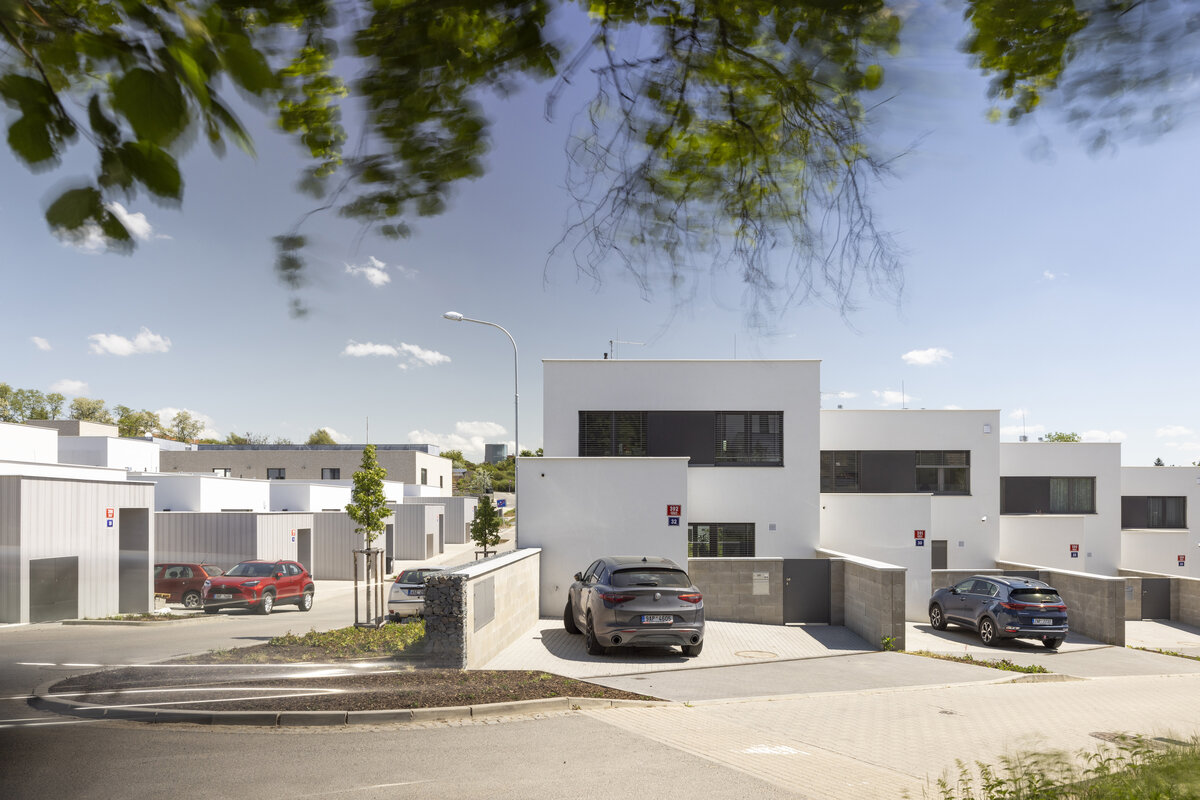
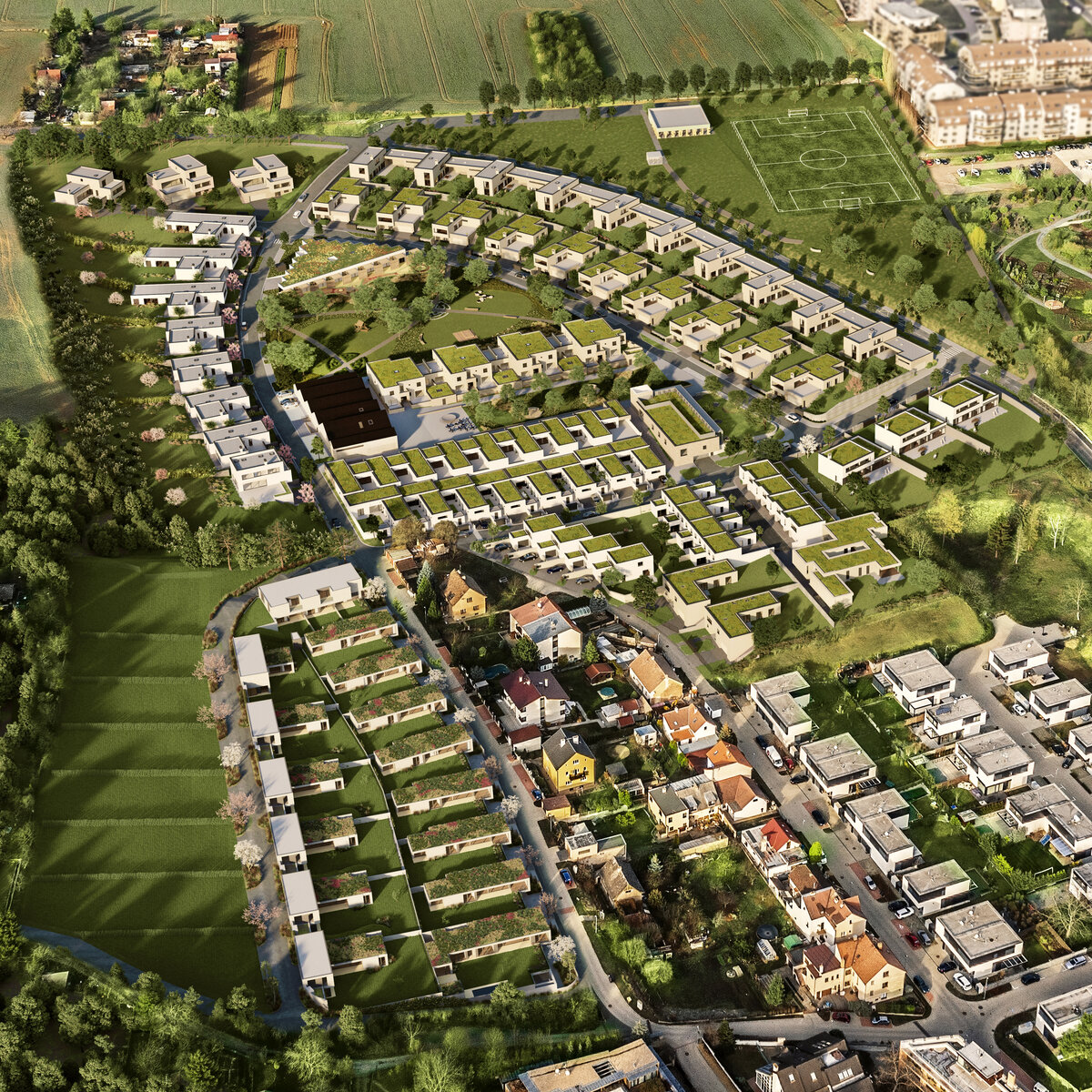
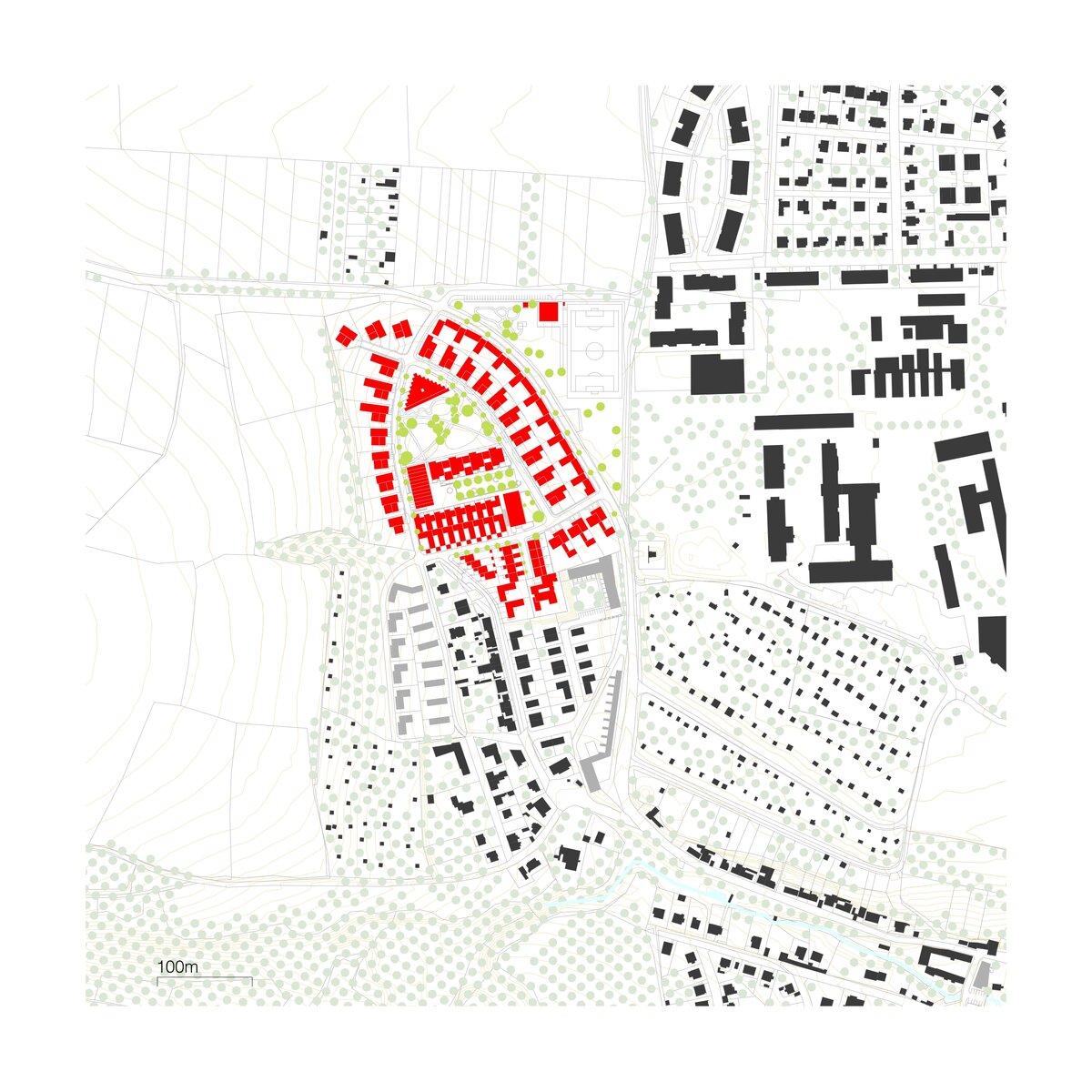
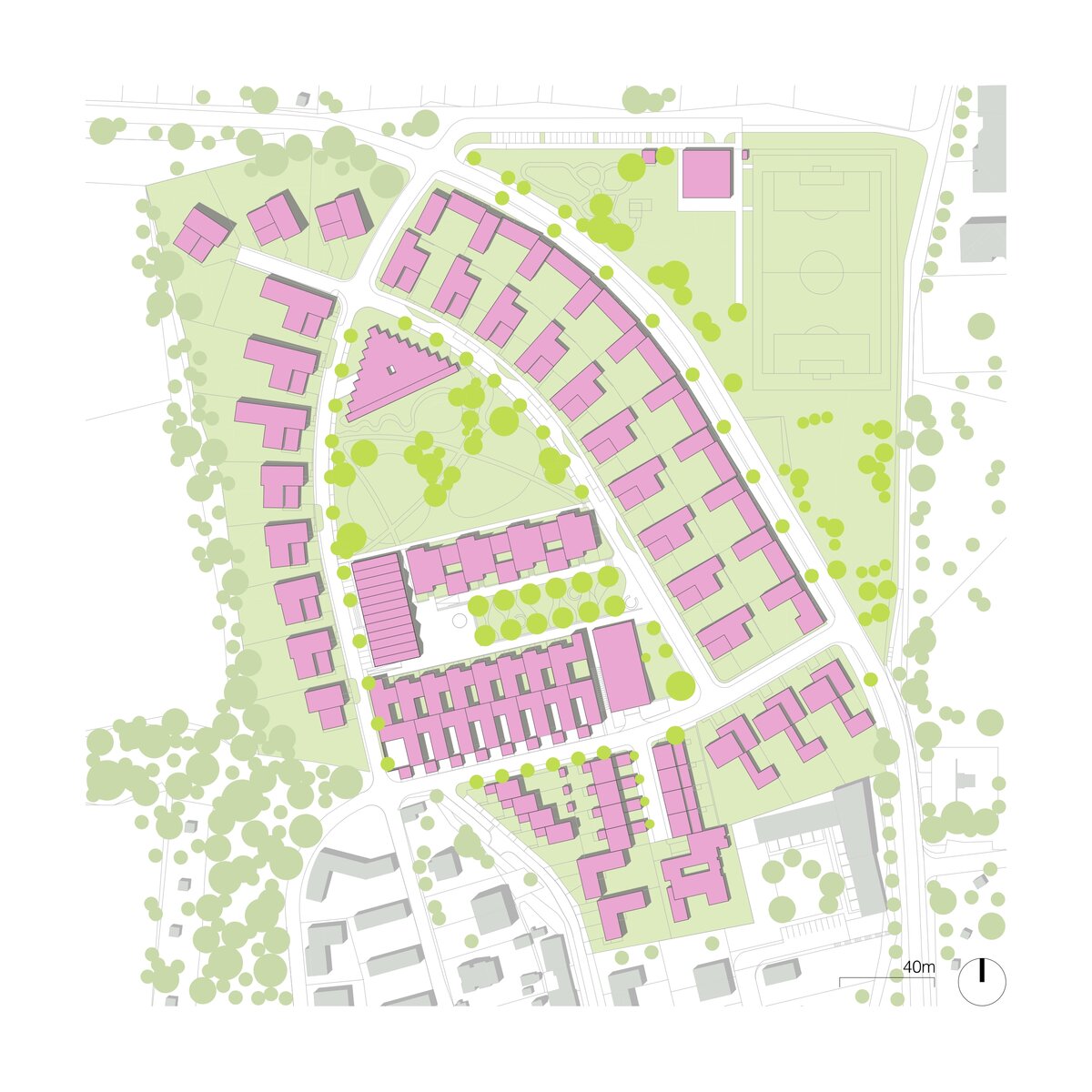
The new development on the north-western outskirts of the Prague - Lysolaje municipality was created in a mutual symbiosis of the public and private sectors (municipality and developer). The aim of the project was to create a new centre of the village and to supplement the missing public amenities for which there was no room in the existing development. The site is shaped like a natural amphitheatre and is connected to the existing street network in four places. The core of the area is two public spaces - a square and a park.
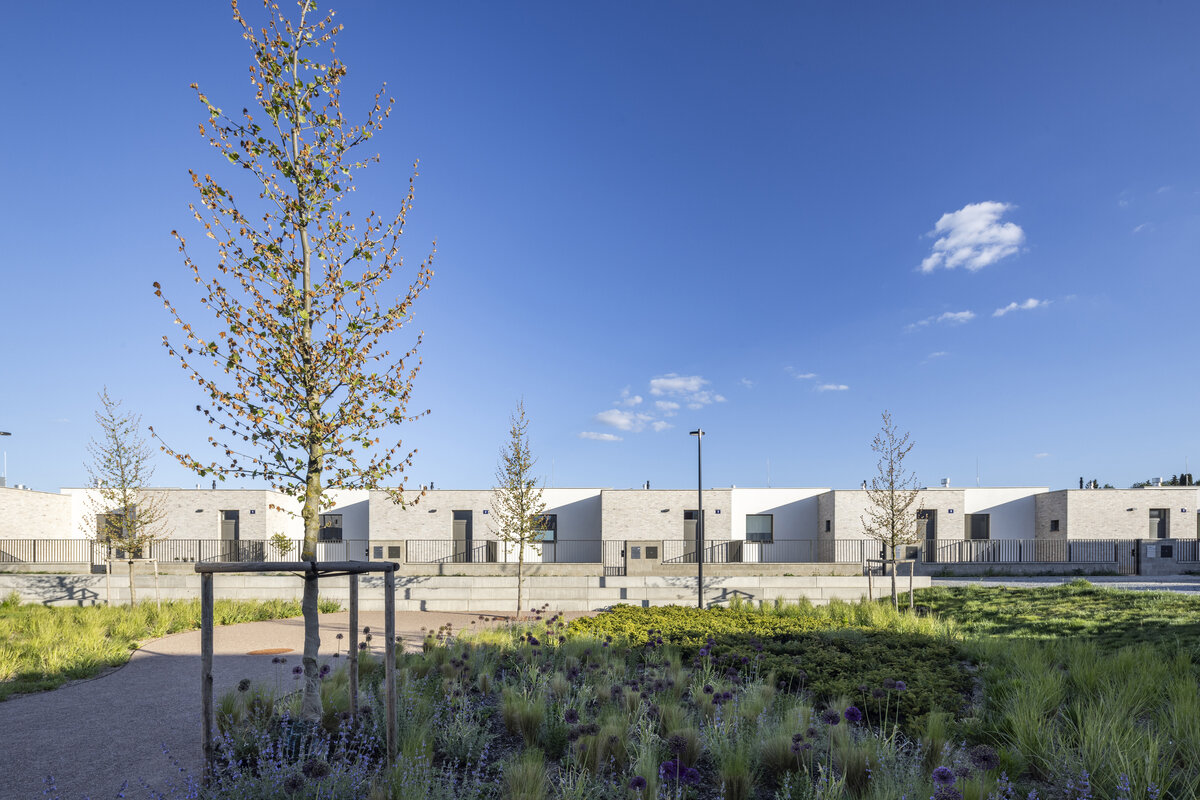
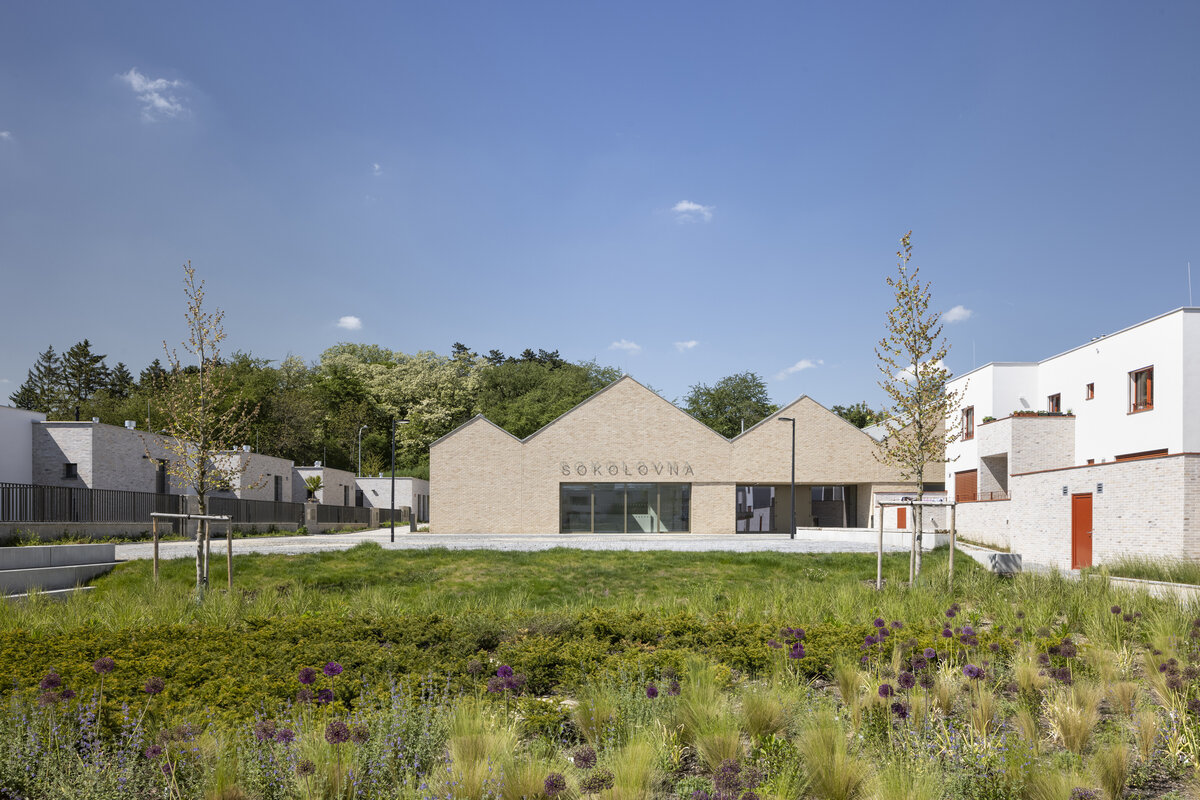
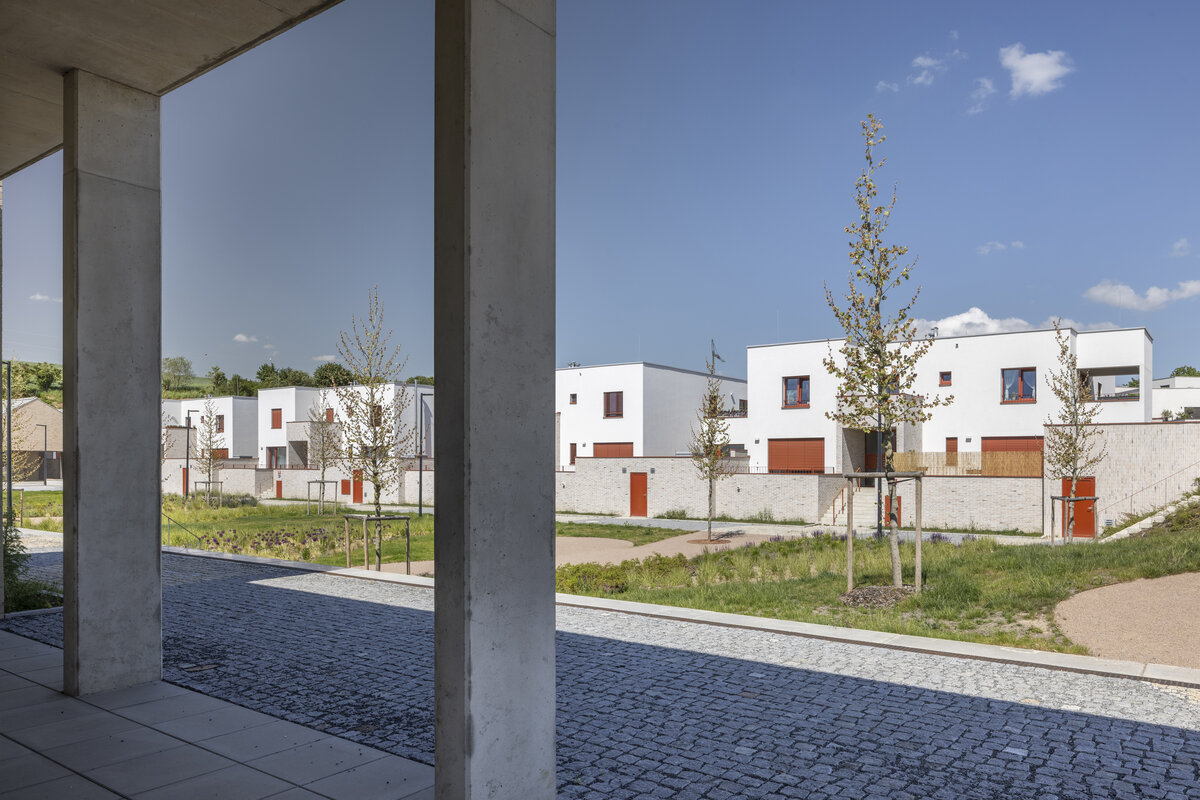
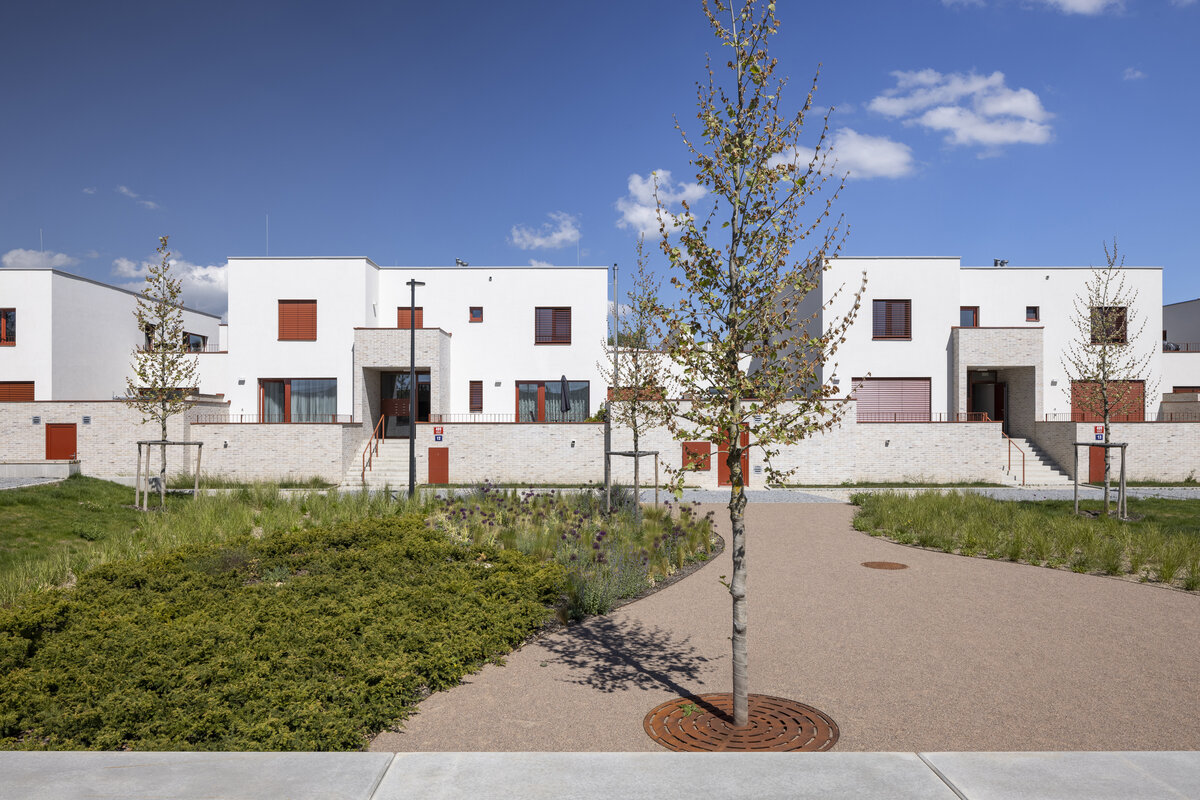
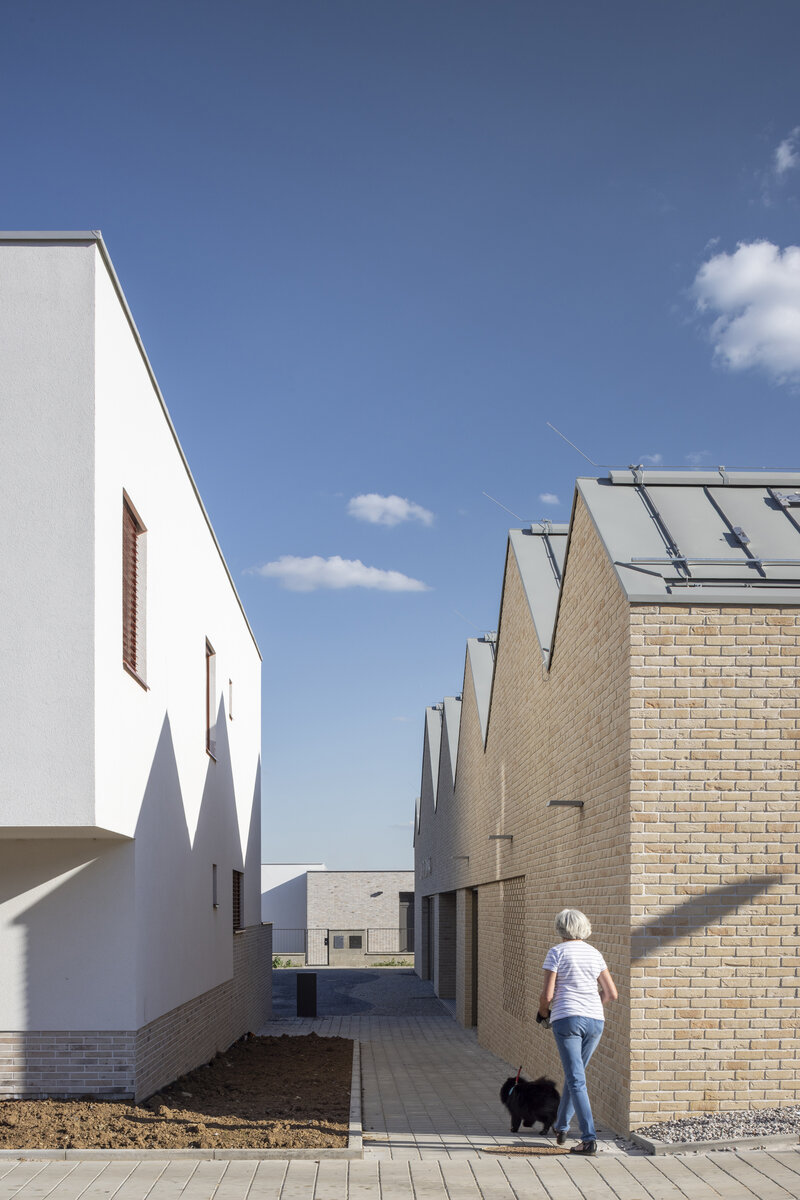
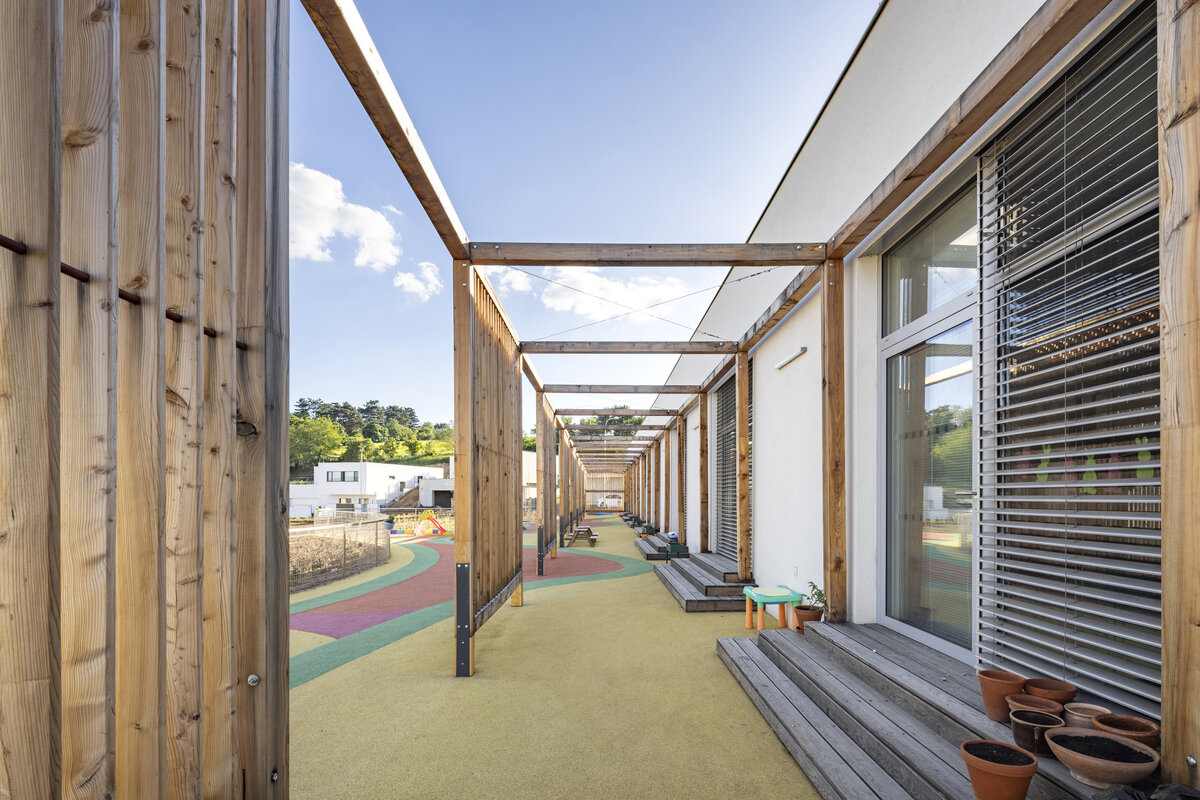
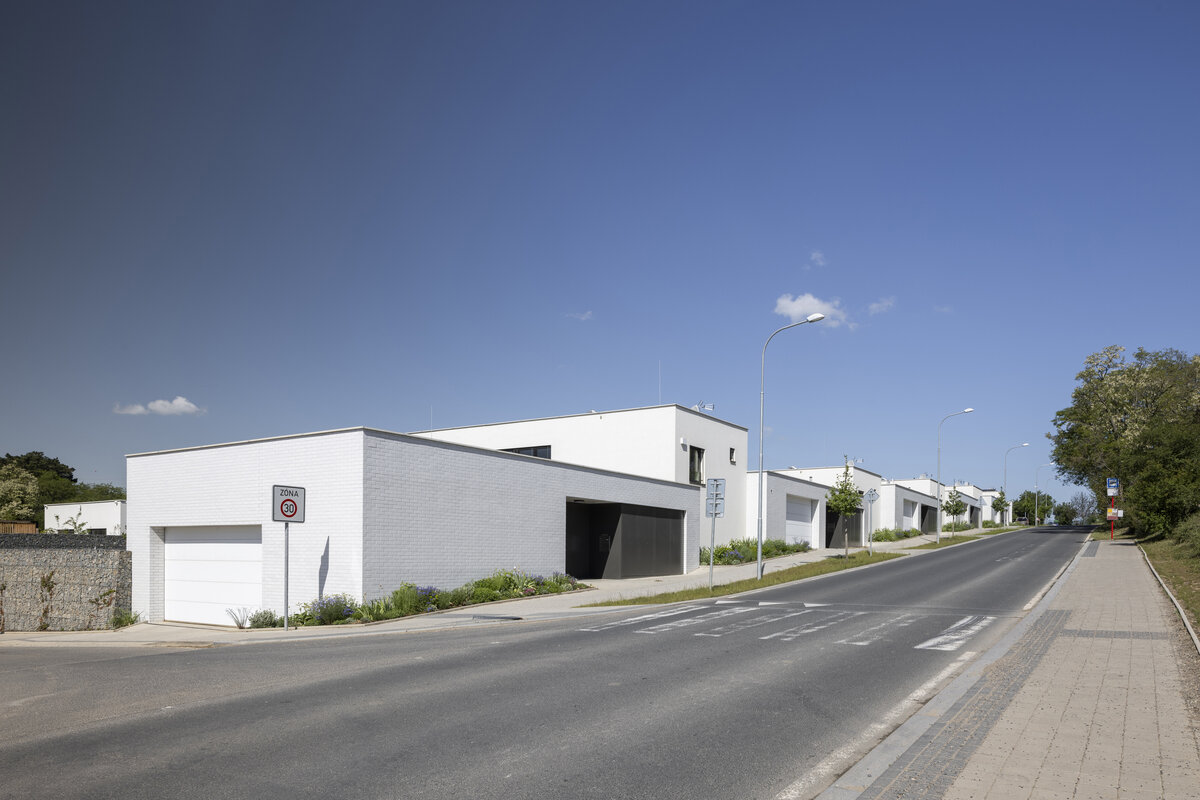
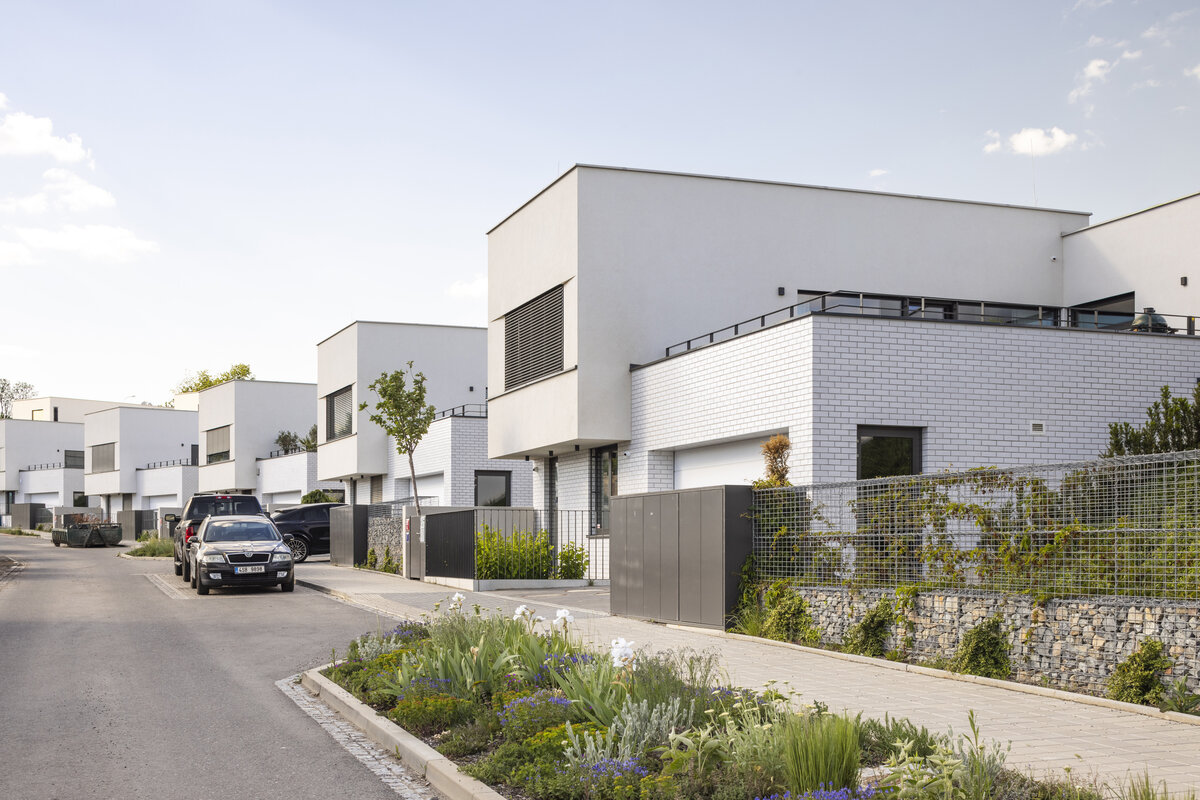
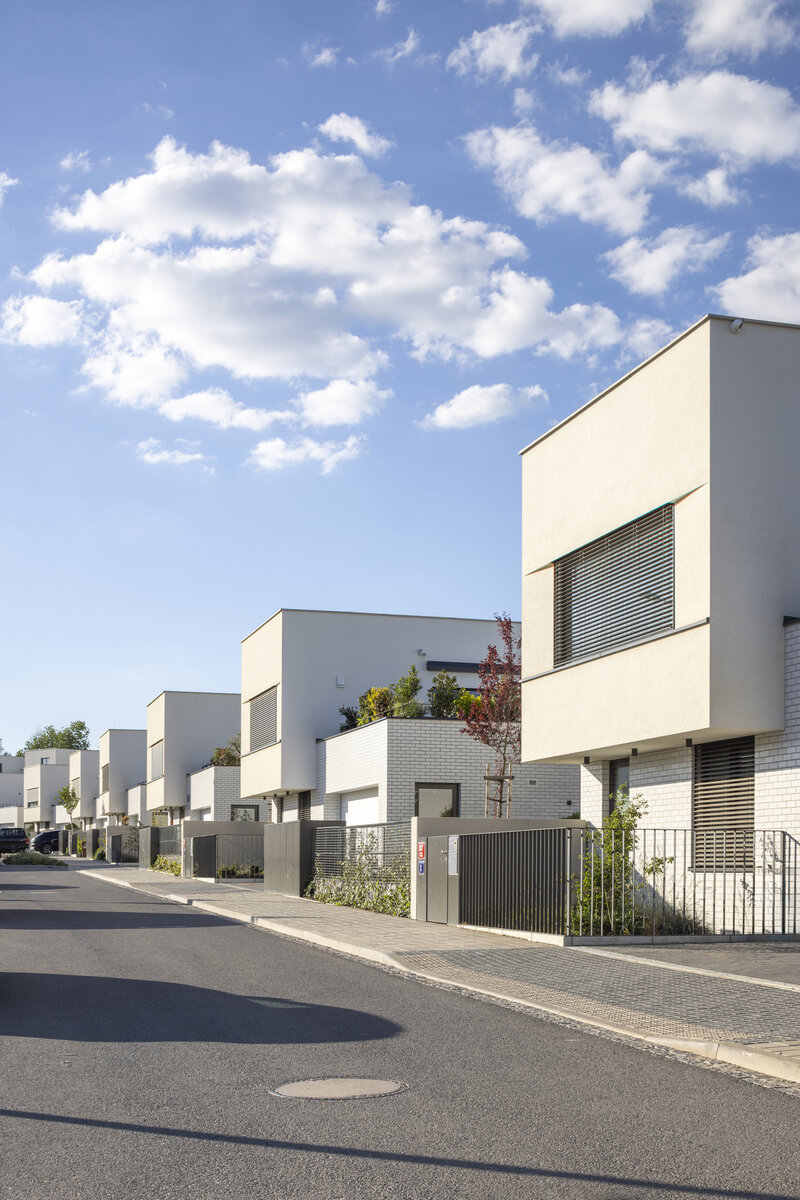
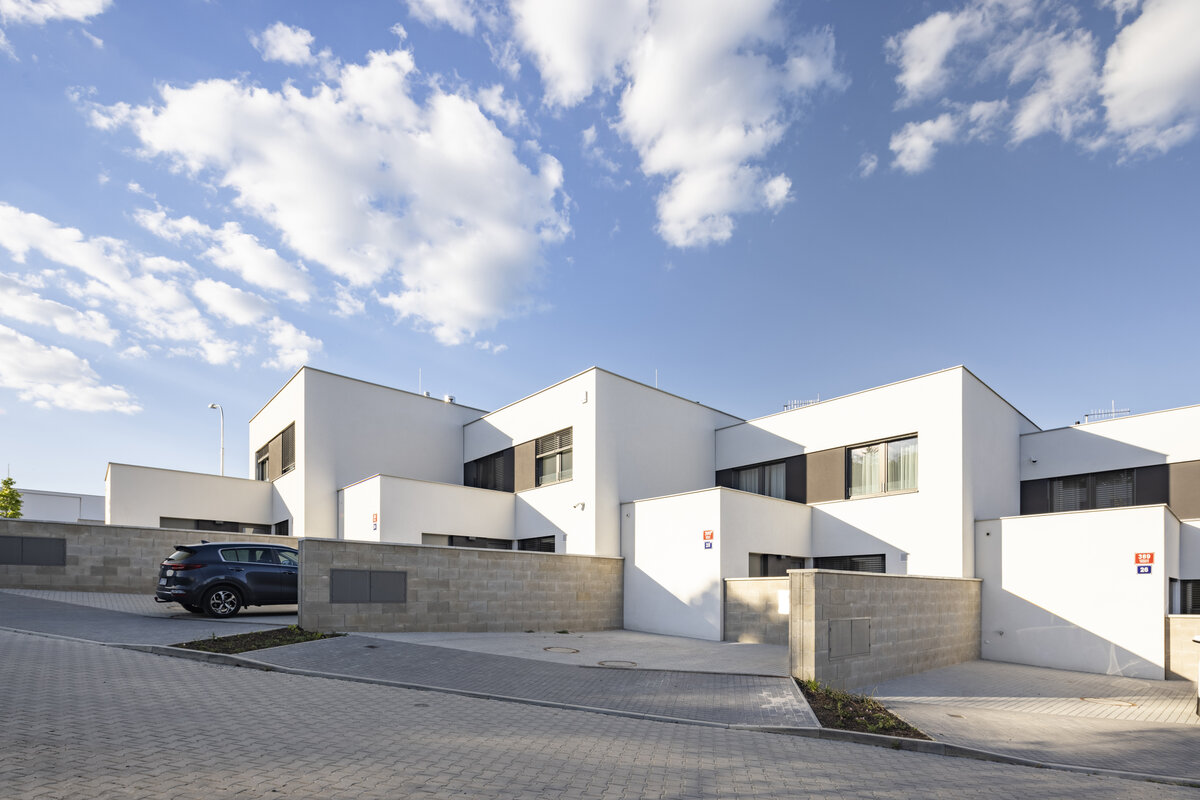
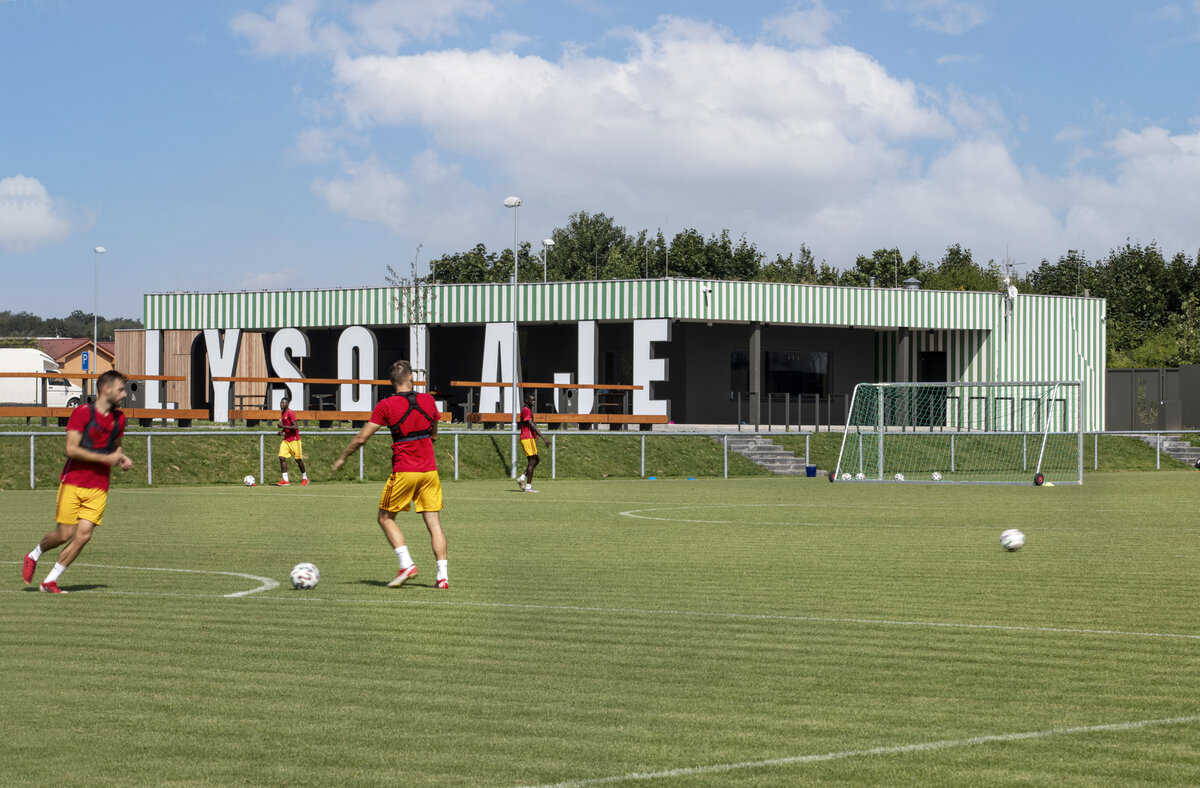
The square is defined by a community centre (multifunctional hall, restaurant, gym), an apartment building with communal flats, a service centre (doctor's office, maternity centre, grocery store, etc.) and a single-storey apartment building with atrium flats. The park is terminated to the north by a kindergarten partially recessed into the rising terrain. There are 57 houses of several types, arranged in a funnel-shaped pattern in accordance with the morphology of the terrain. The whole site is complemented by a new sports complex to the north-east.
The duality of the design is also reflected in the material design, with the public buildings around the square clad in ceramic banding and the other houses in a combination of light-coloured plaster and stone walls.
Vertical load-bearing structures are made of ceramic masonry fittings, underground concrete formwork fittings; or reinforced concrete monolithic. Horizontal load-bearing structures are made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
The public buildings around the square are clad in ceramic banding and the other houses are made in a combination of light-coloured plaster and stone walls.
The site is connected to all available technical infrastructure networks, rainwater is disposed of by deep septic tanks.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|