Farní stodola Hostivař
Project category ‐ Reconstruction


























| Author | Ing. arch. Radek Vaňáč, Ing. arch. Pavel Nalezený, Ing. arch. Kristýna Sojka Rejsková, Ing. arch. Ján Šefčík |
|---|---|
| Studio | Studio Raketoplán |
| Location | Domkářská 21/1 Praha 15 - Hostivař |
| Investor | Arcibiskupství pražské Hradčanské nám. 56/16 Praha 1 – Hradčany |
| Supplier | JAPS TEN s.r.o., Suchdolská 1187 Praha - západ |
| Date of completion / approval of the project | January 2024 |
| Fotograf | Petr Polák |
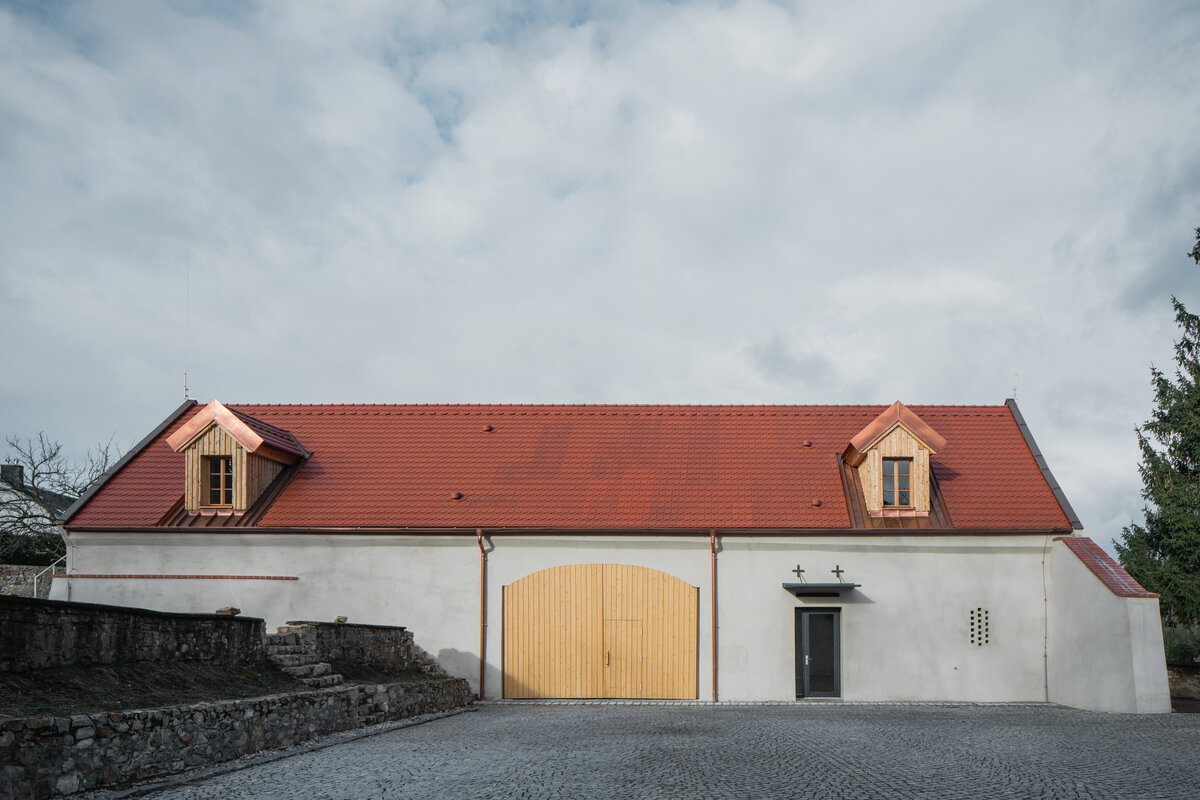
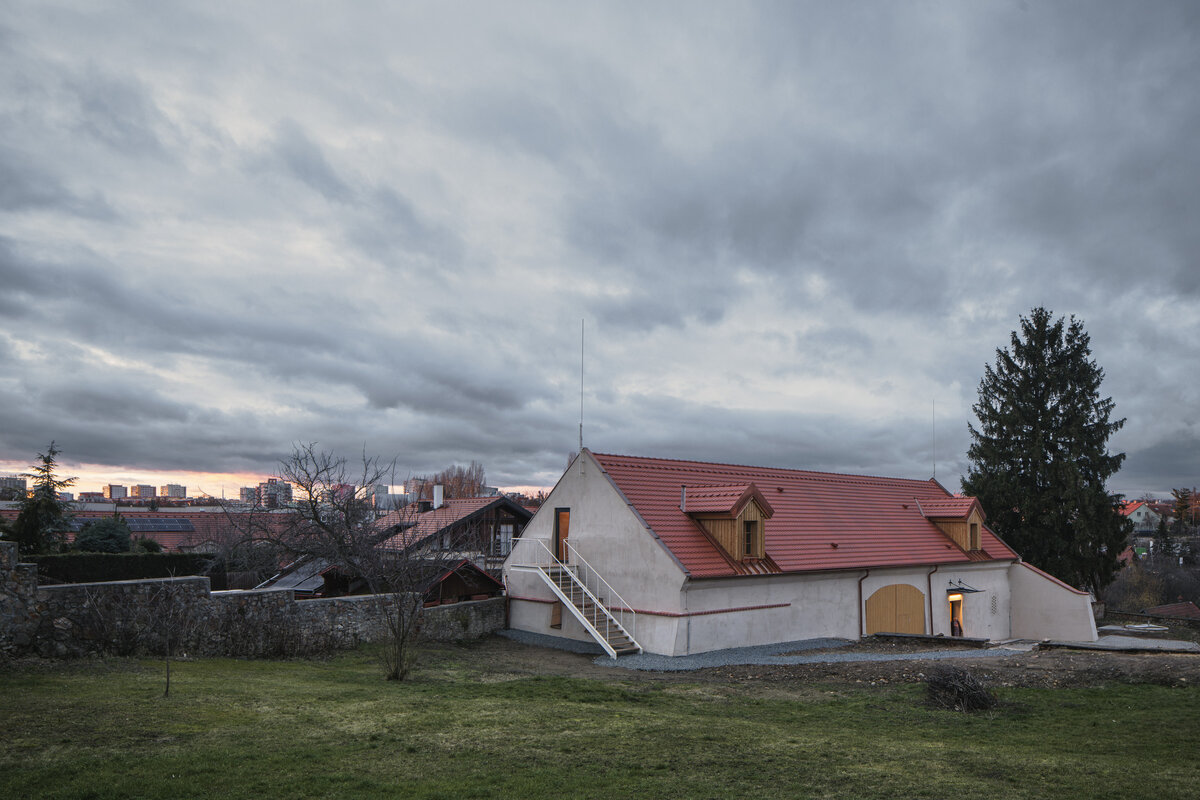
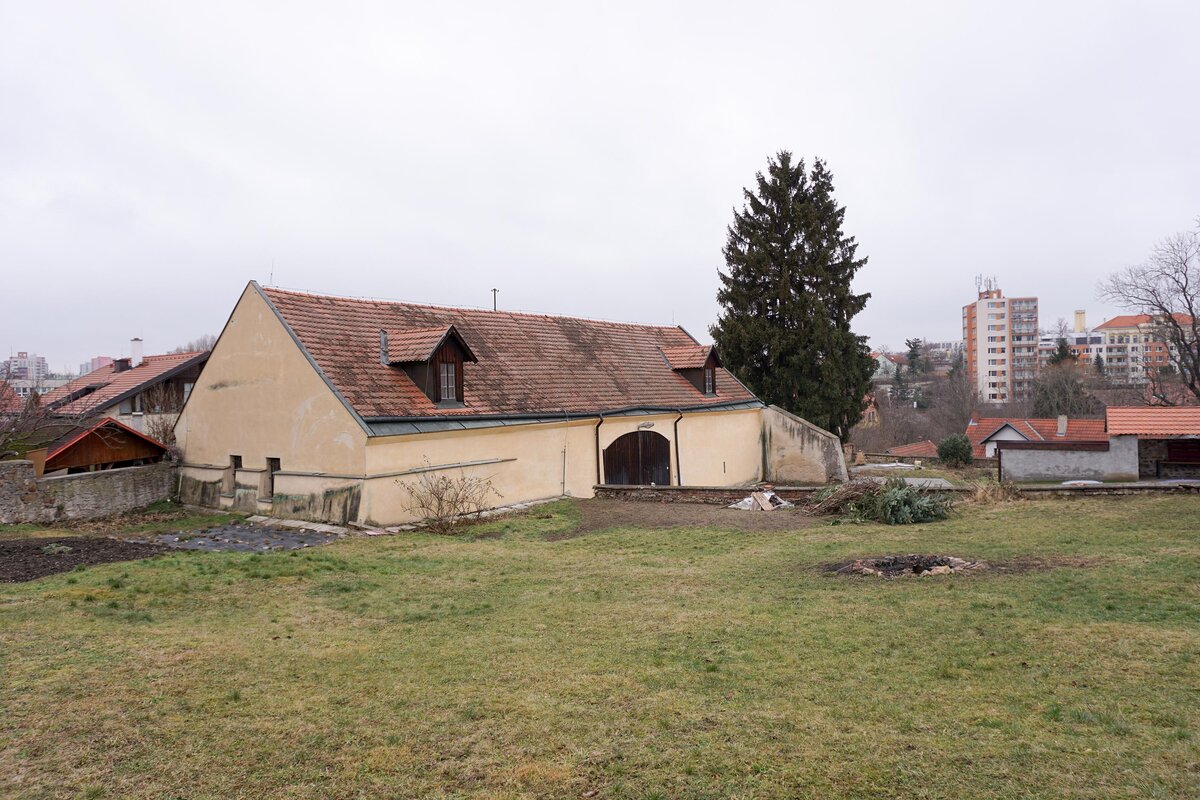
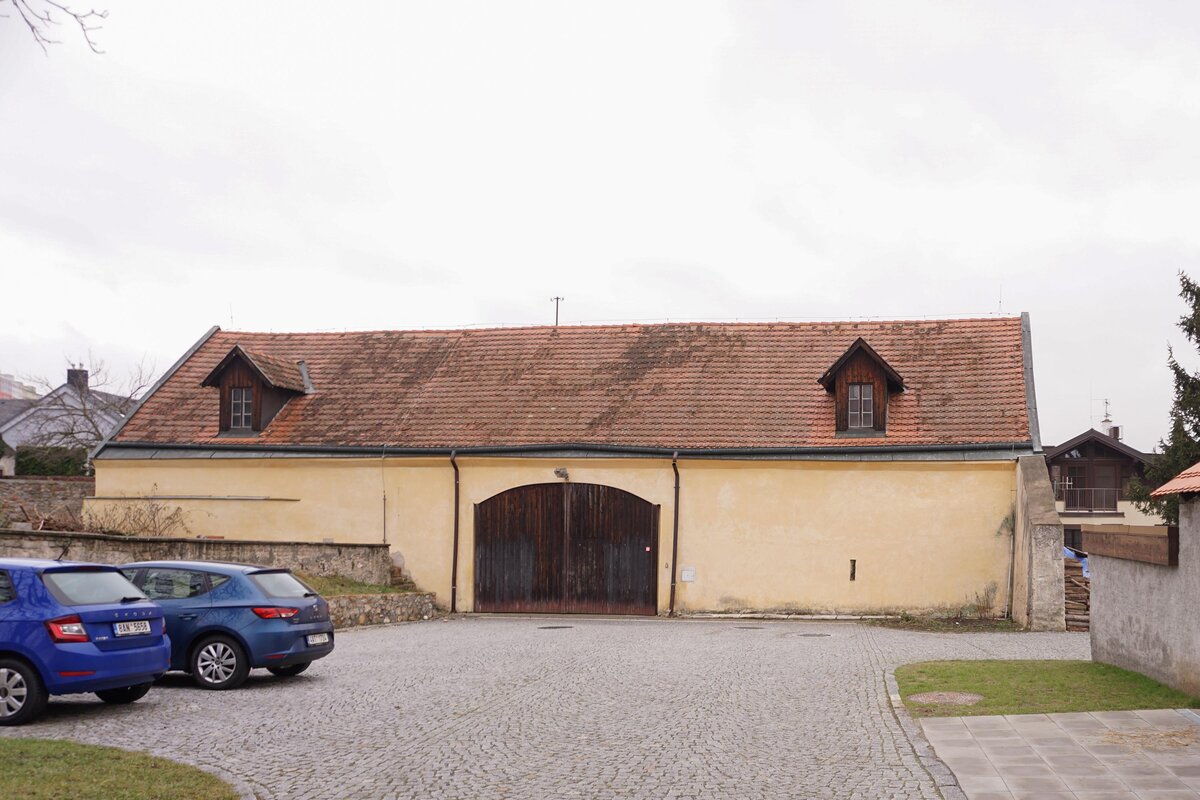
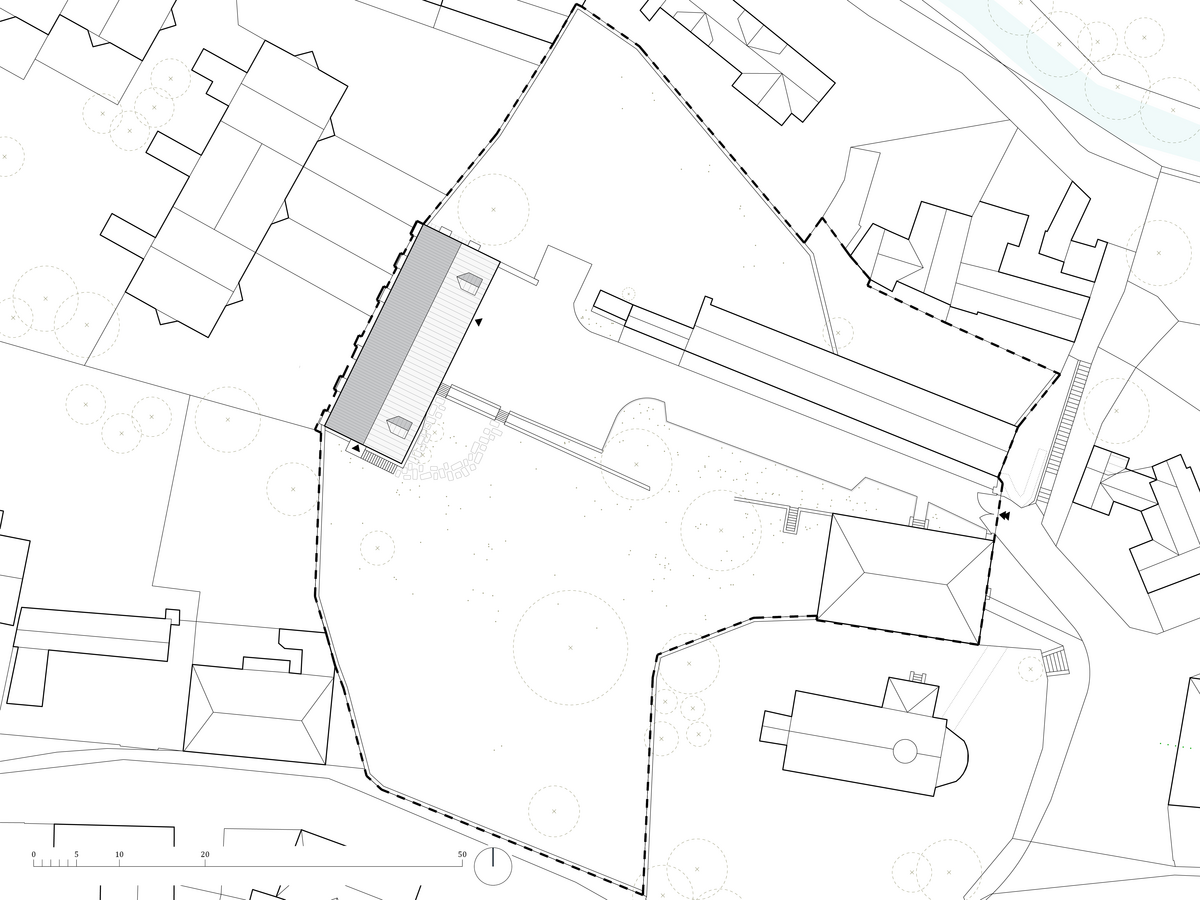
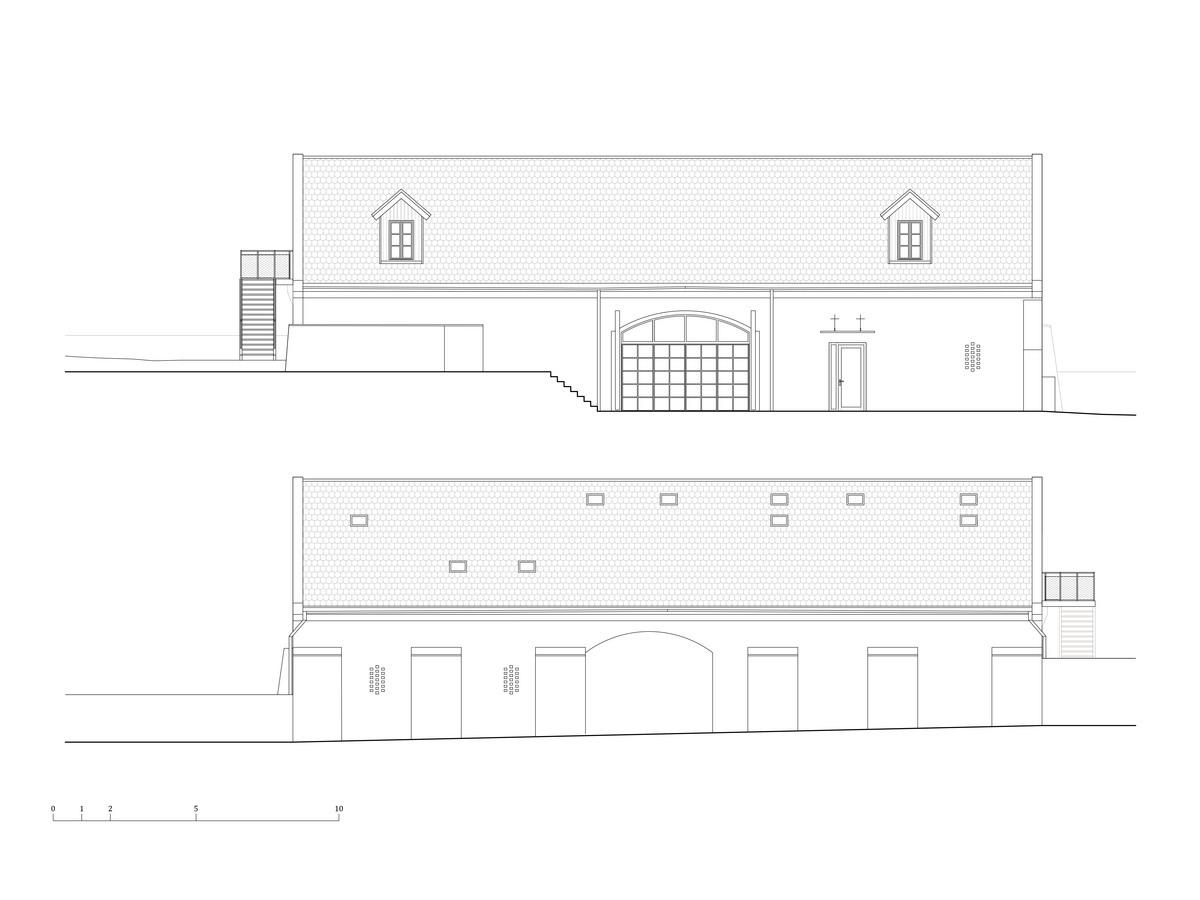
The barn is part of the parish complex of Church of the Decollation of St. John the Baptist in Hostivař, Prague. The valuable area (part of which is a cultural heritage) is located at the centre of the historical village. The urban structure and scale of urban fabric have been preserved in their authentic form.
The original farm building dates to the beginning of the 19th century. It was damaged by fire in 1876 and rebuilt as a workshop in the 1970s.
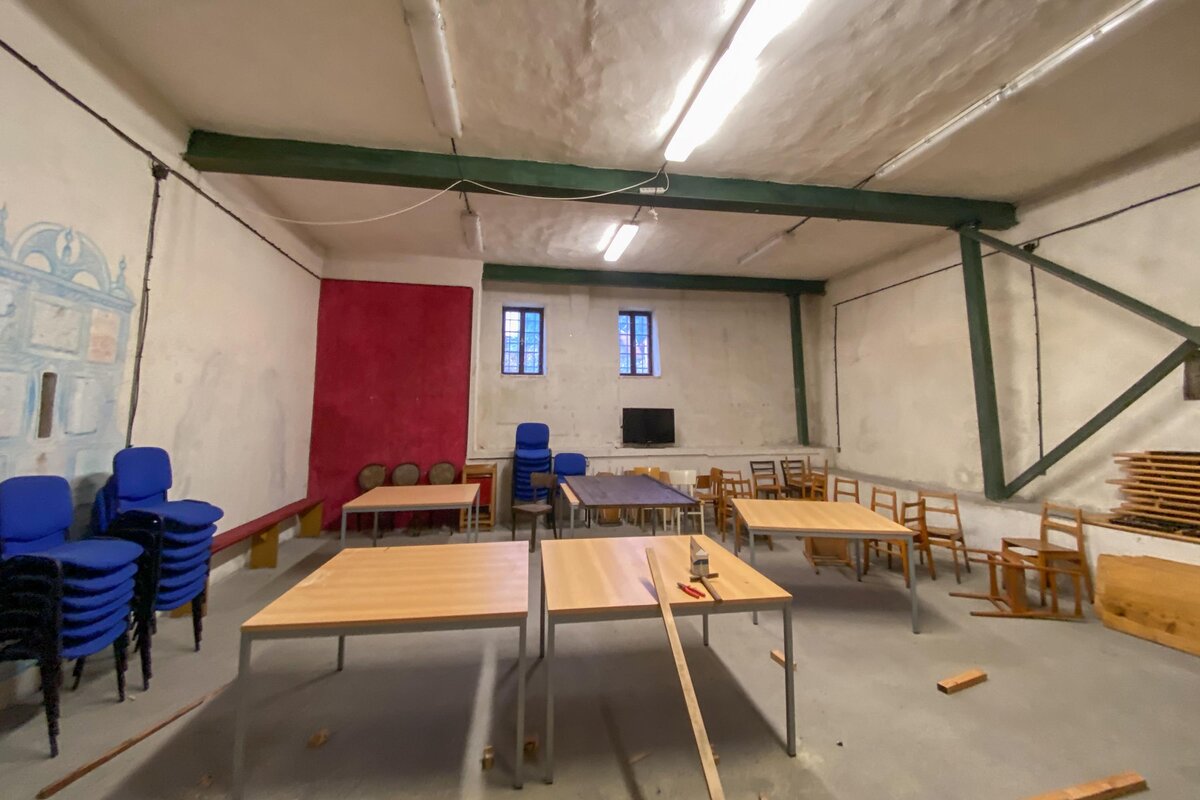
The design responds to the developer’s main request to provide a community and public gathering space.
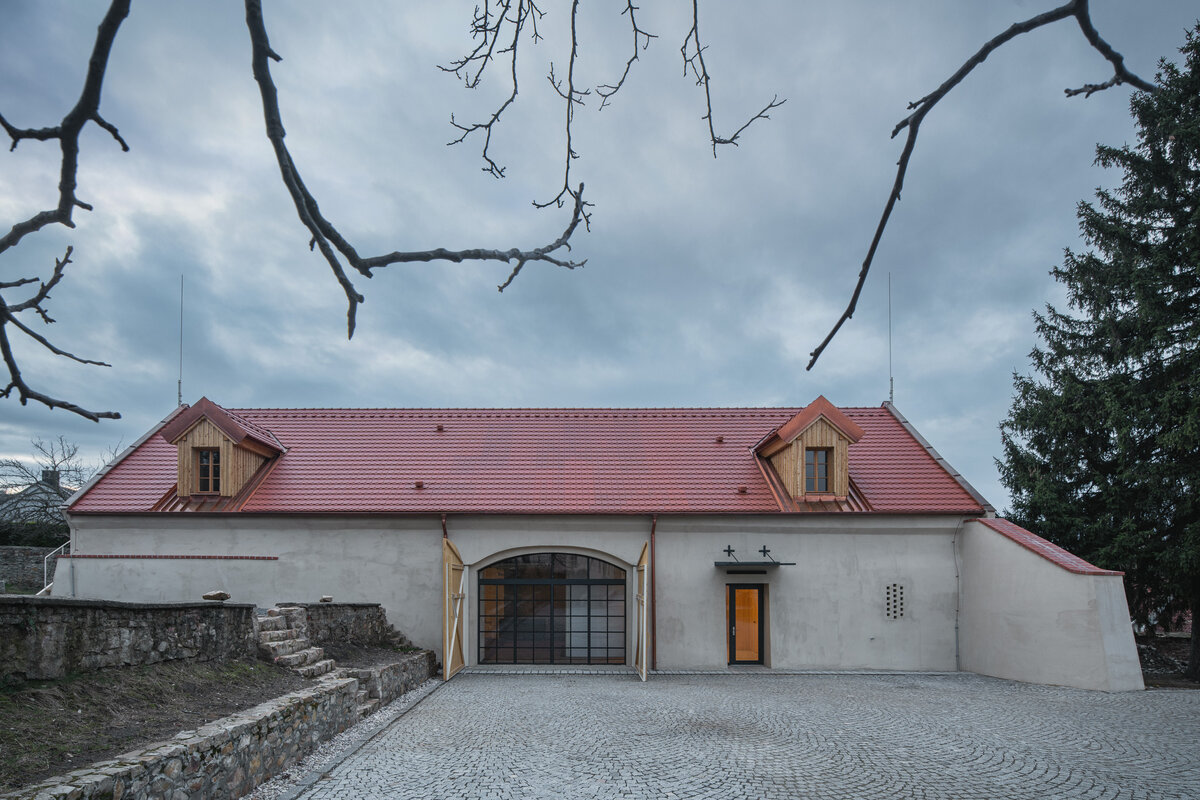
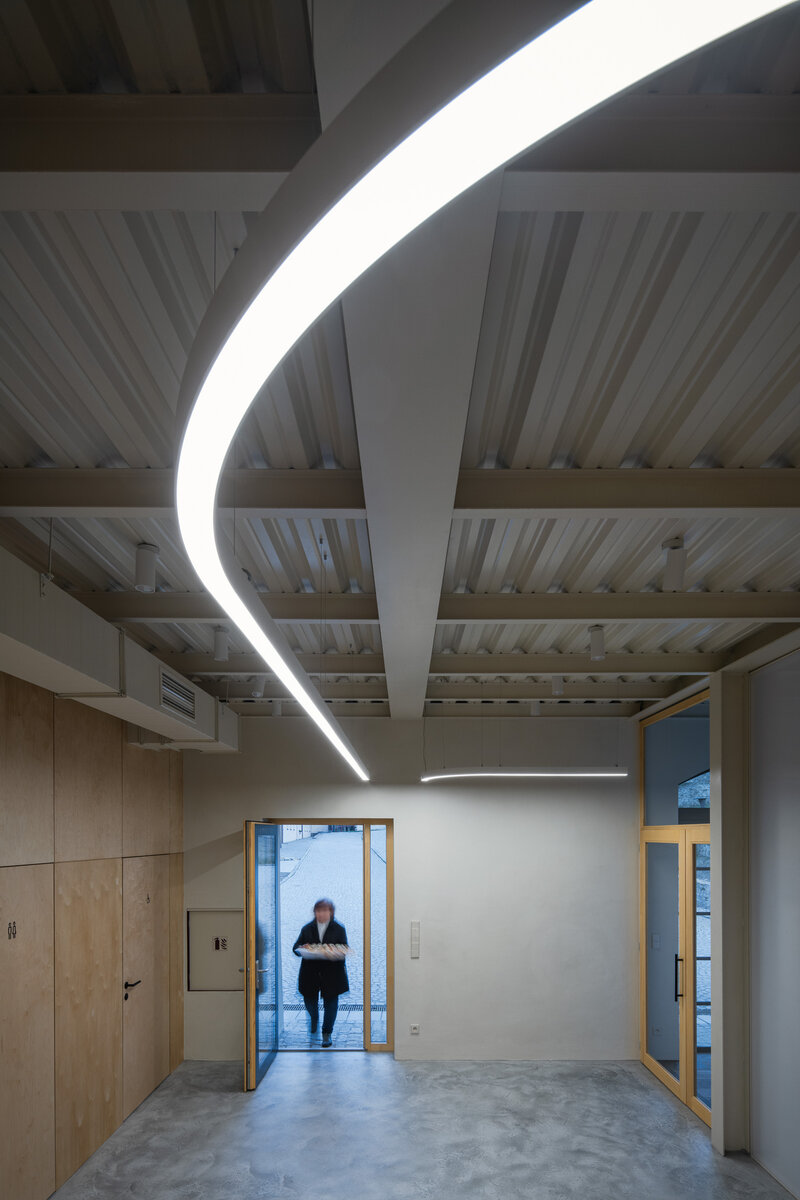
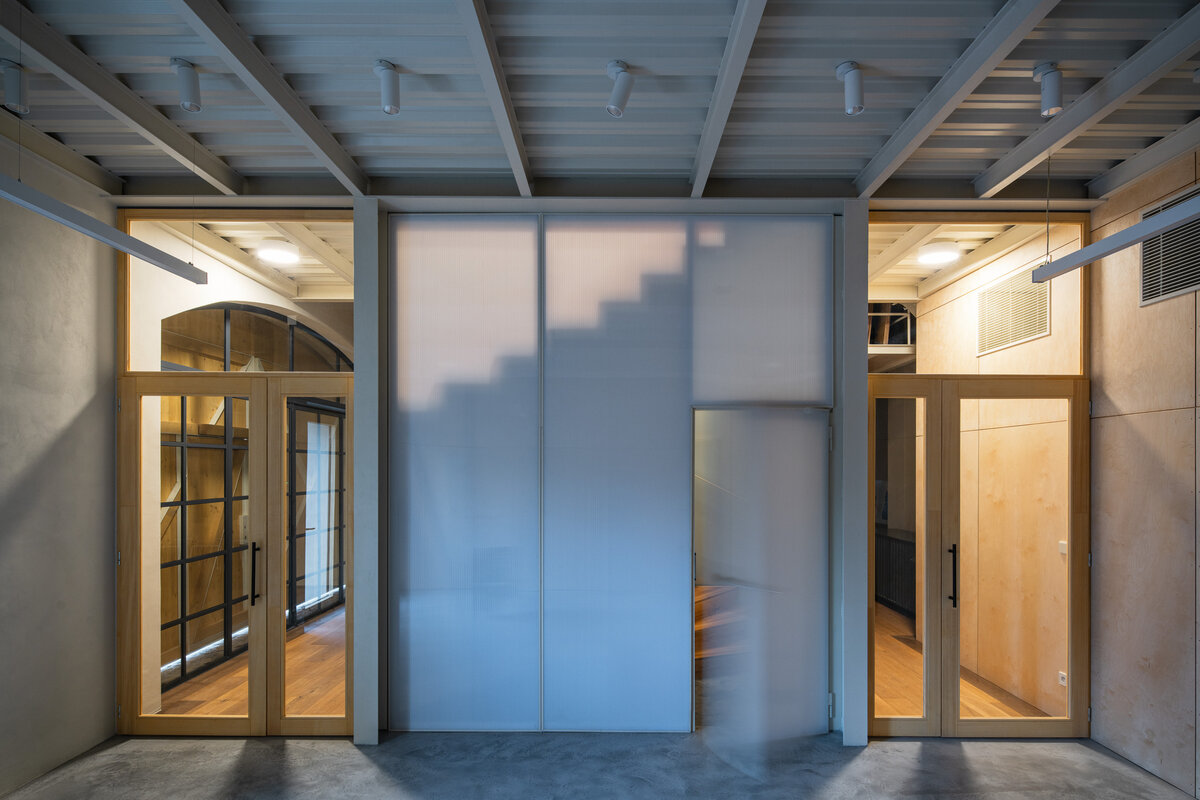
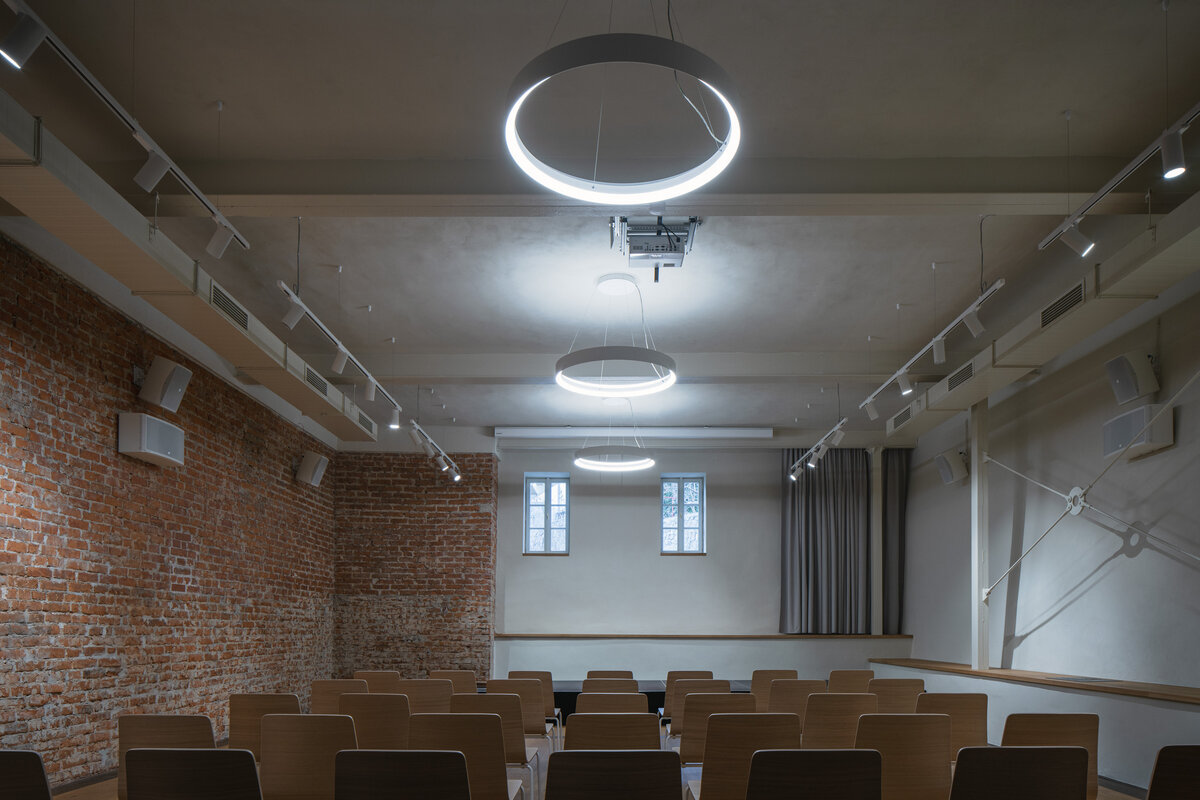
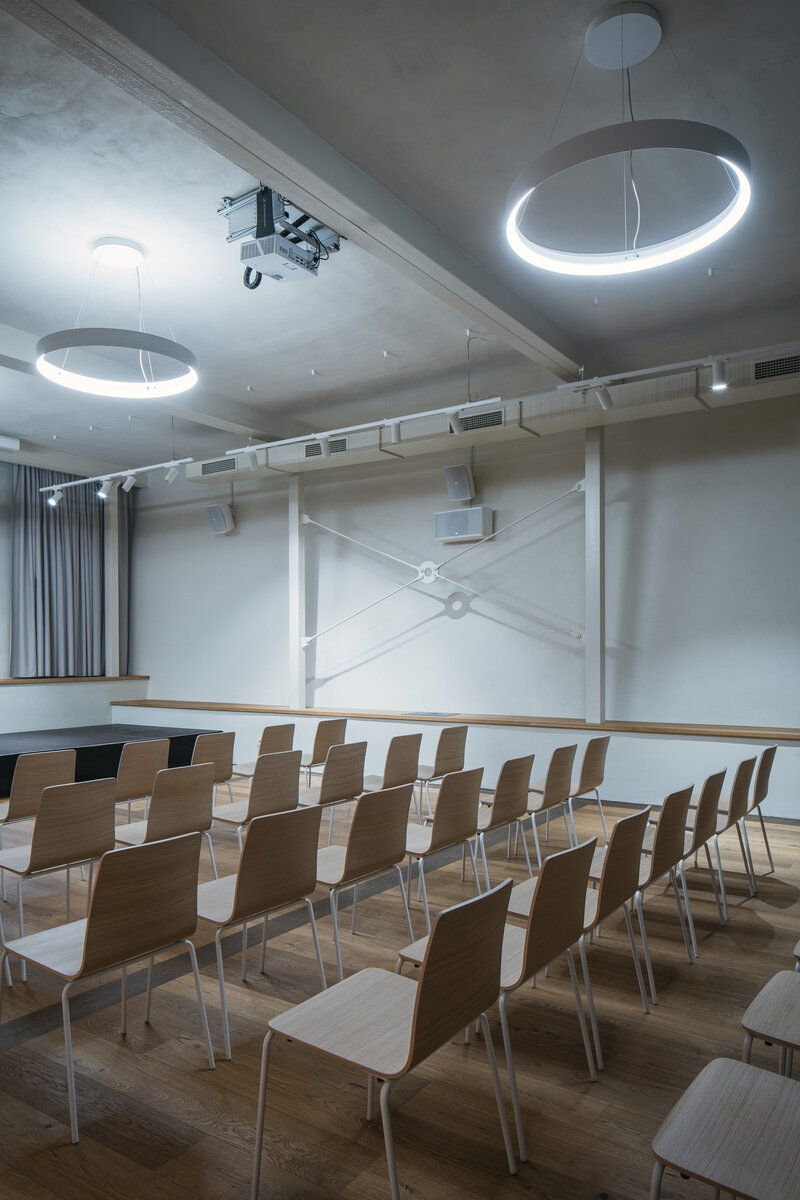
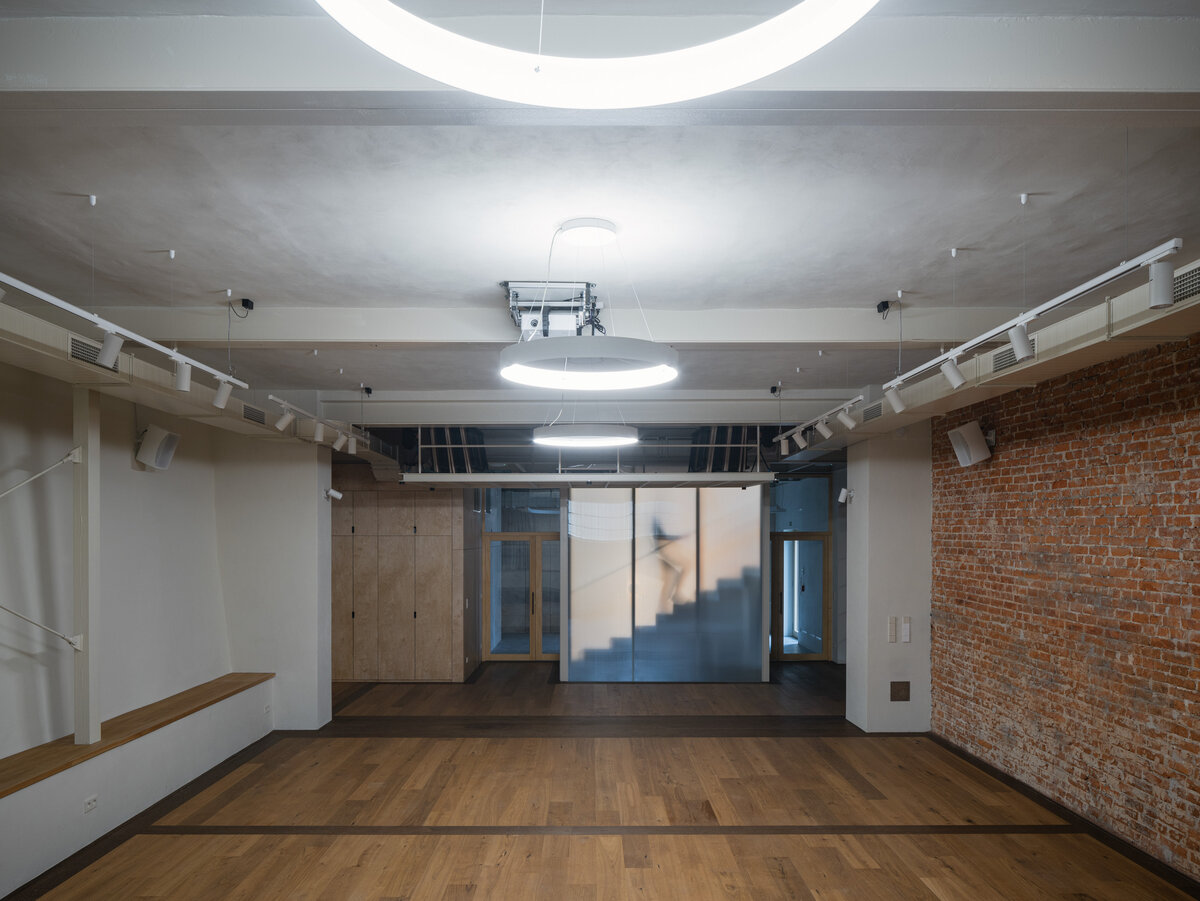
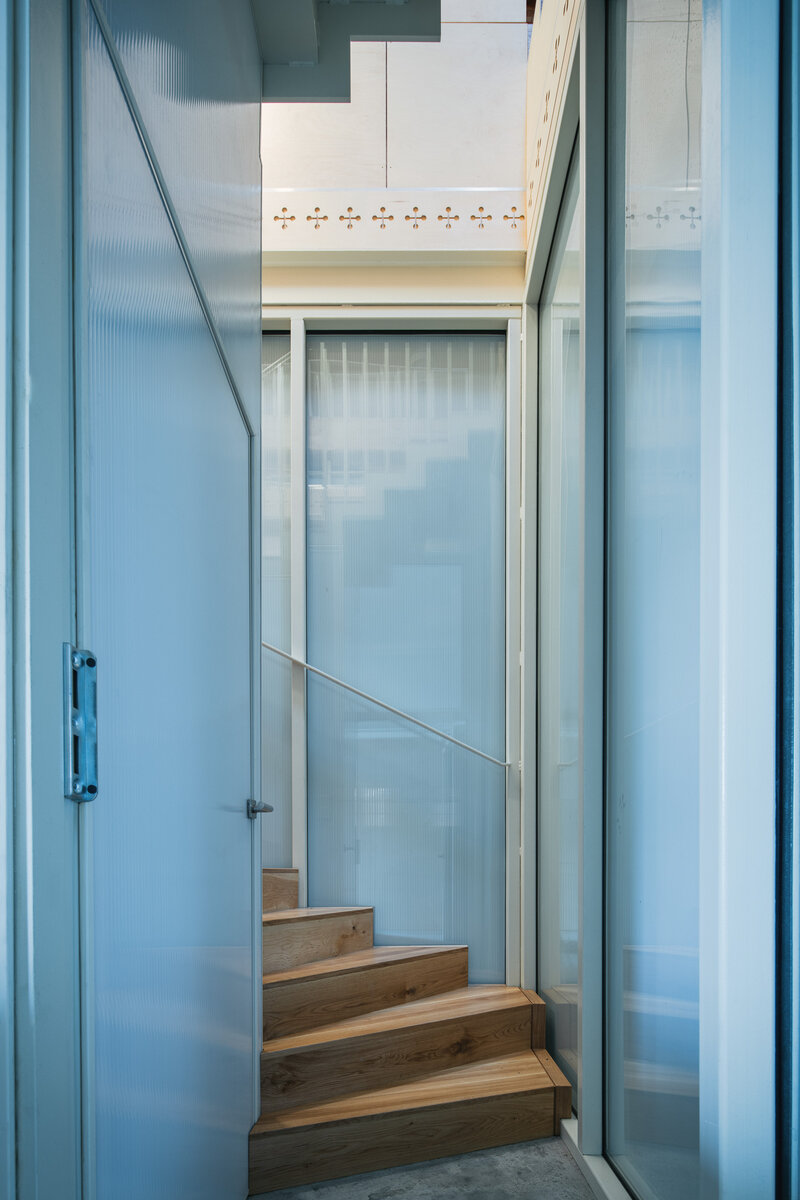
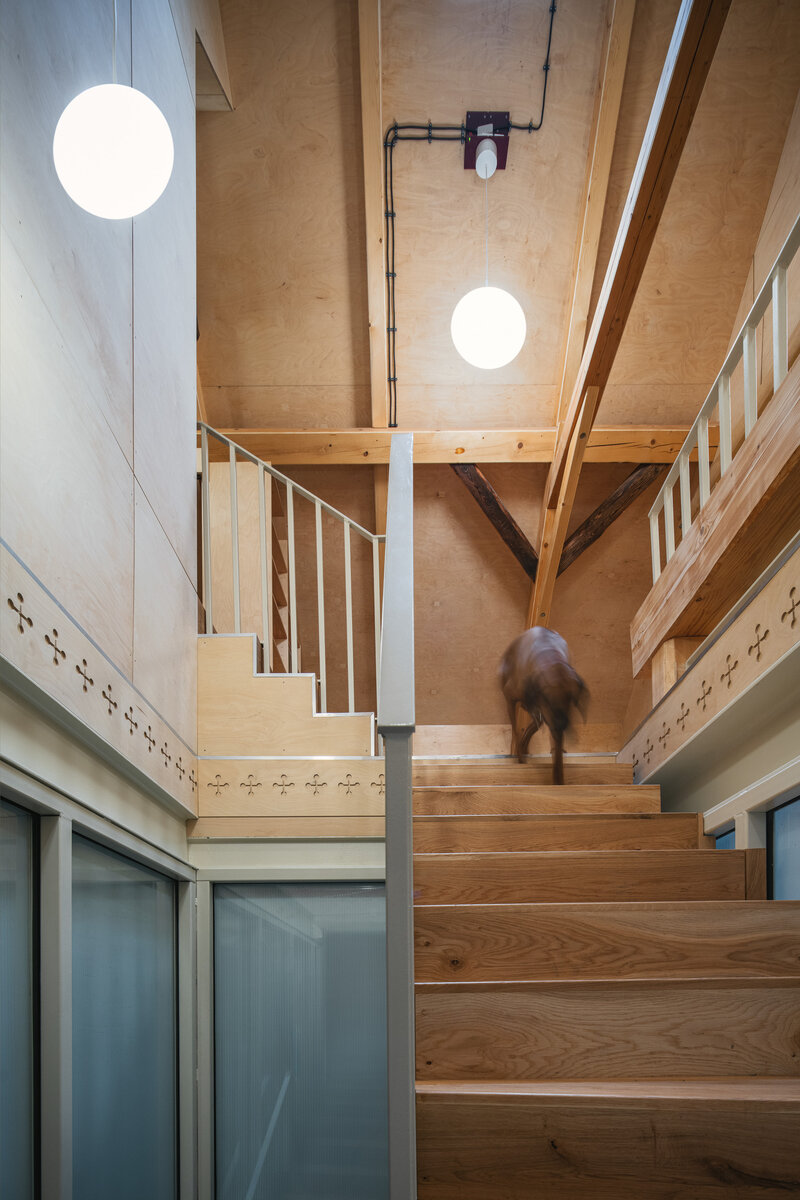
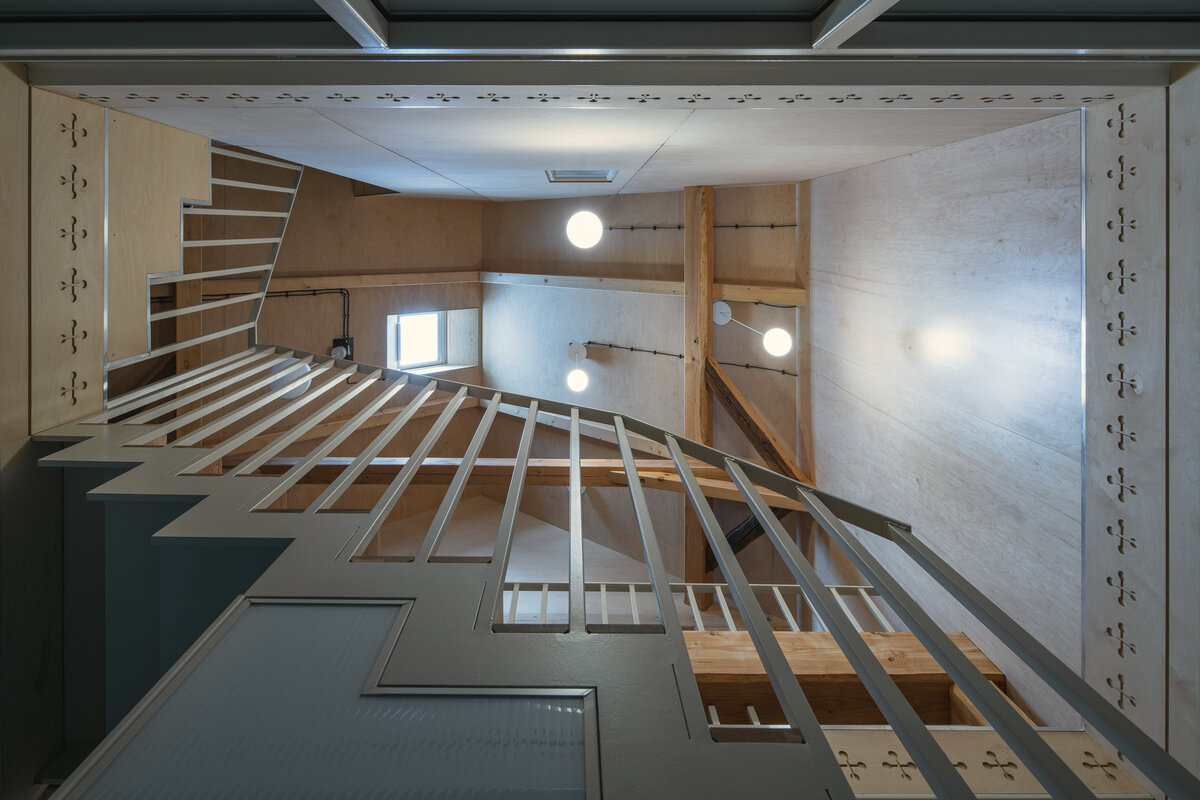
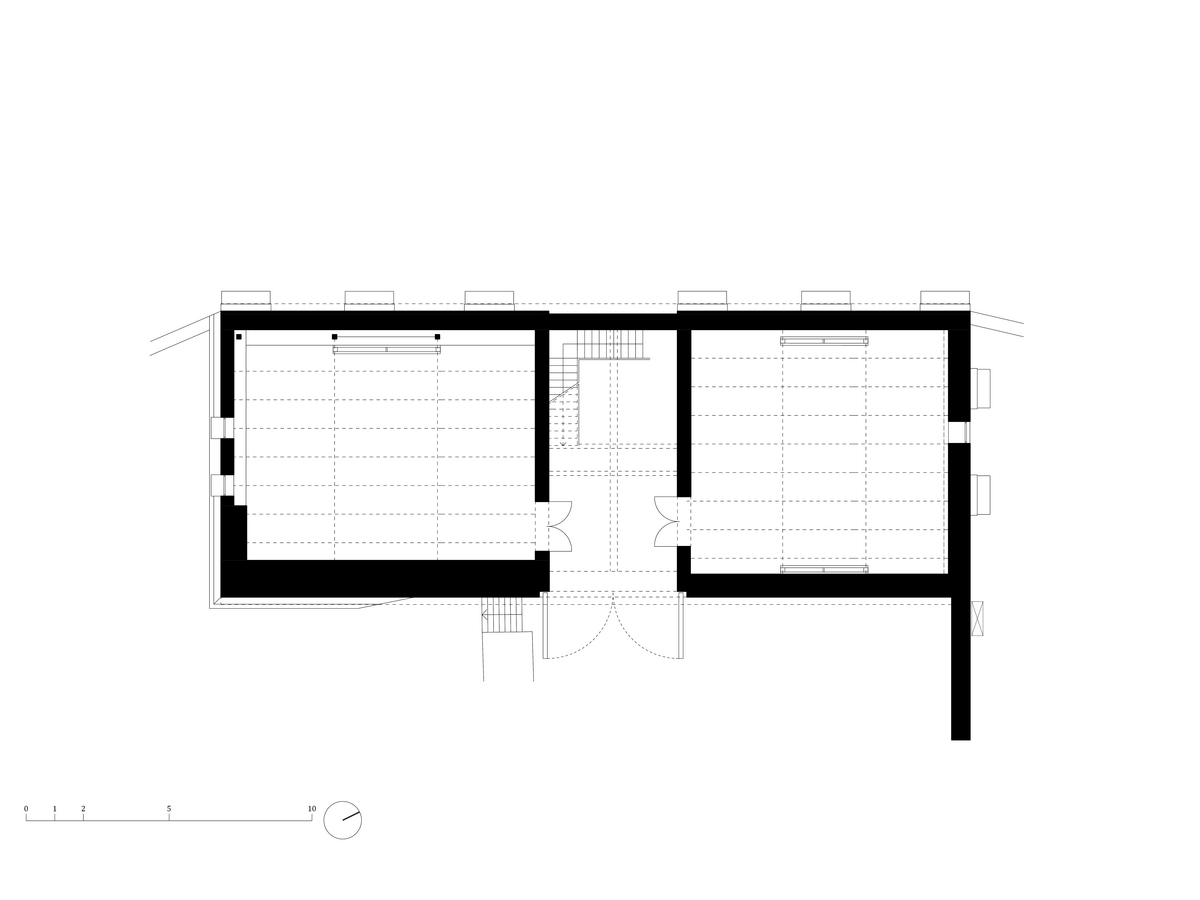
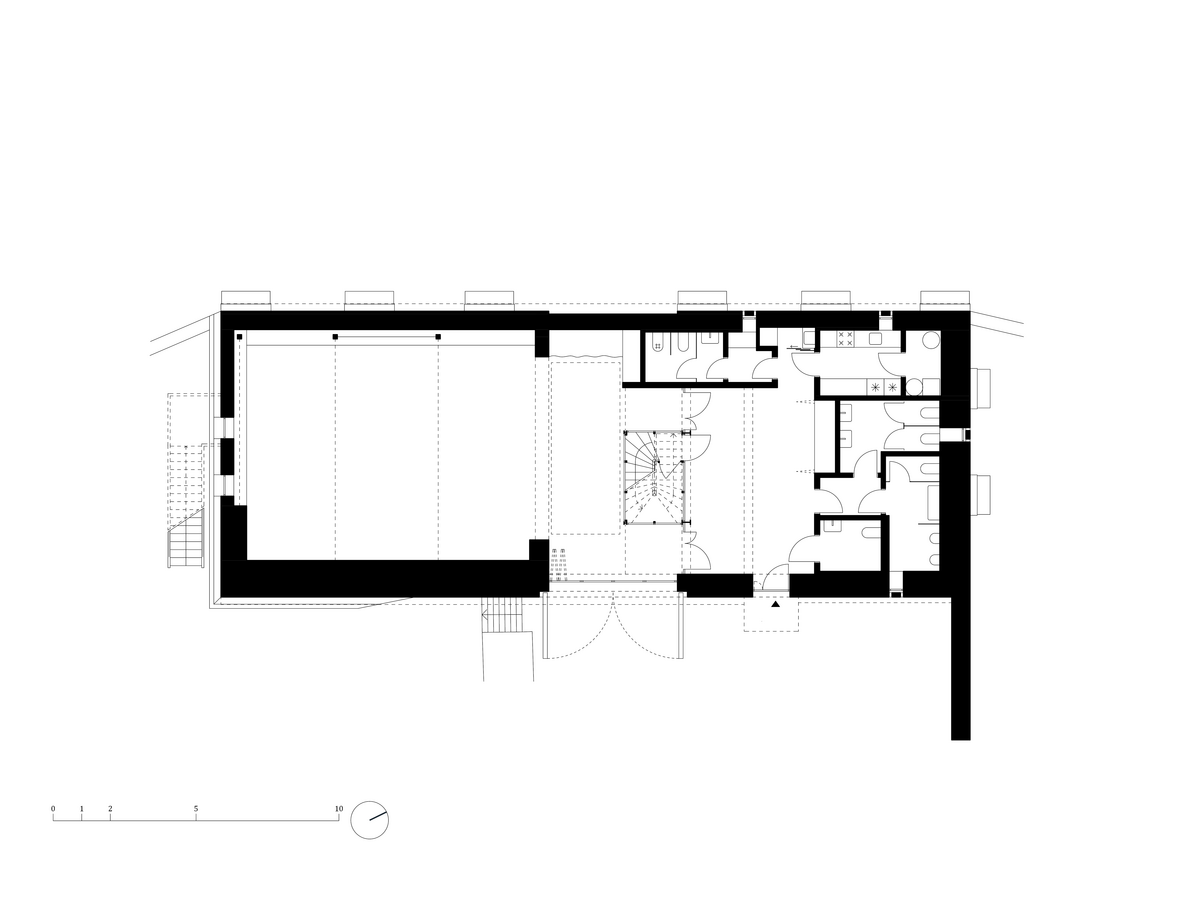
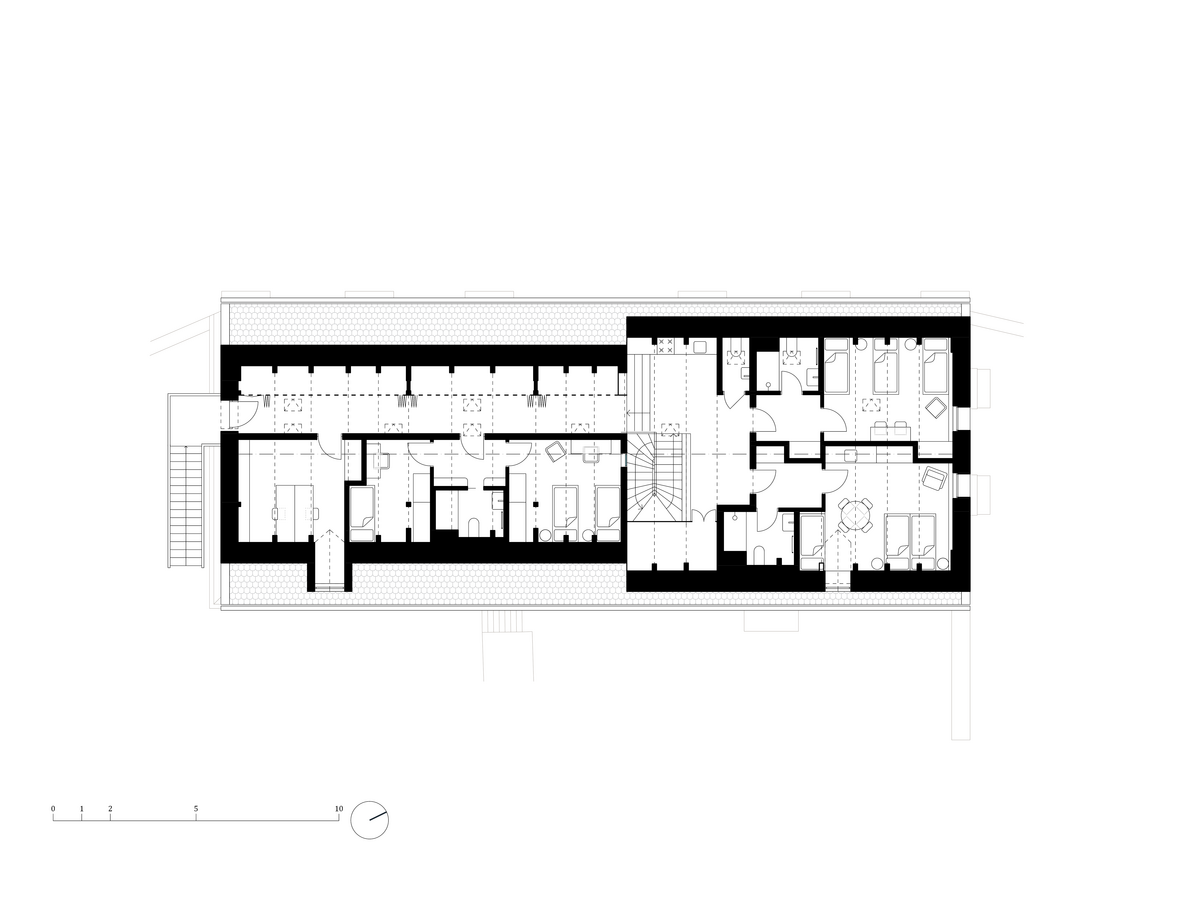
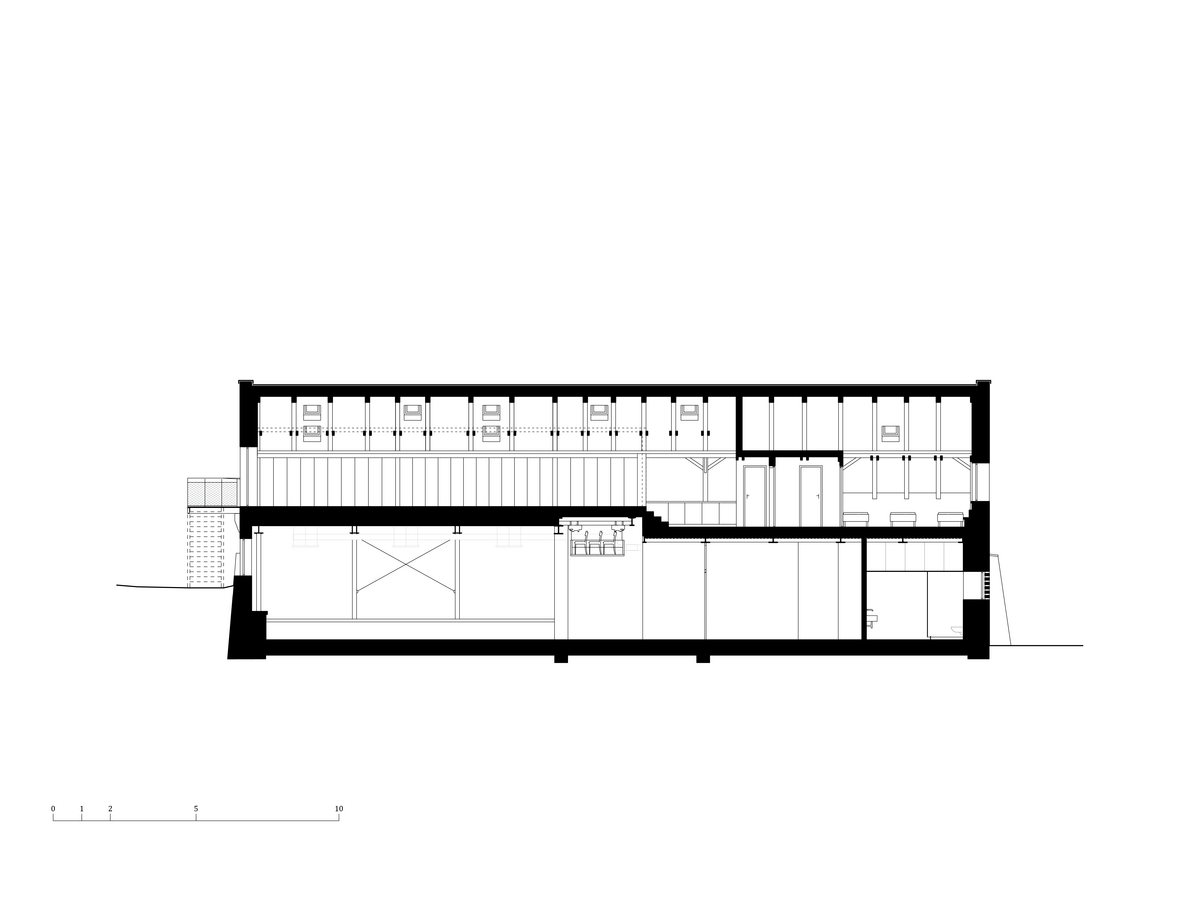
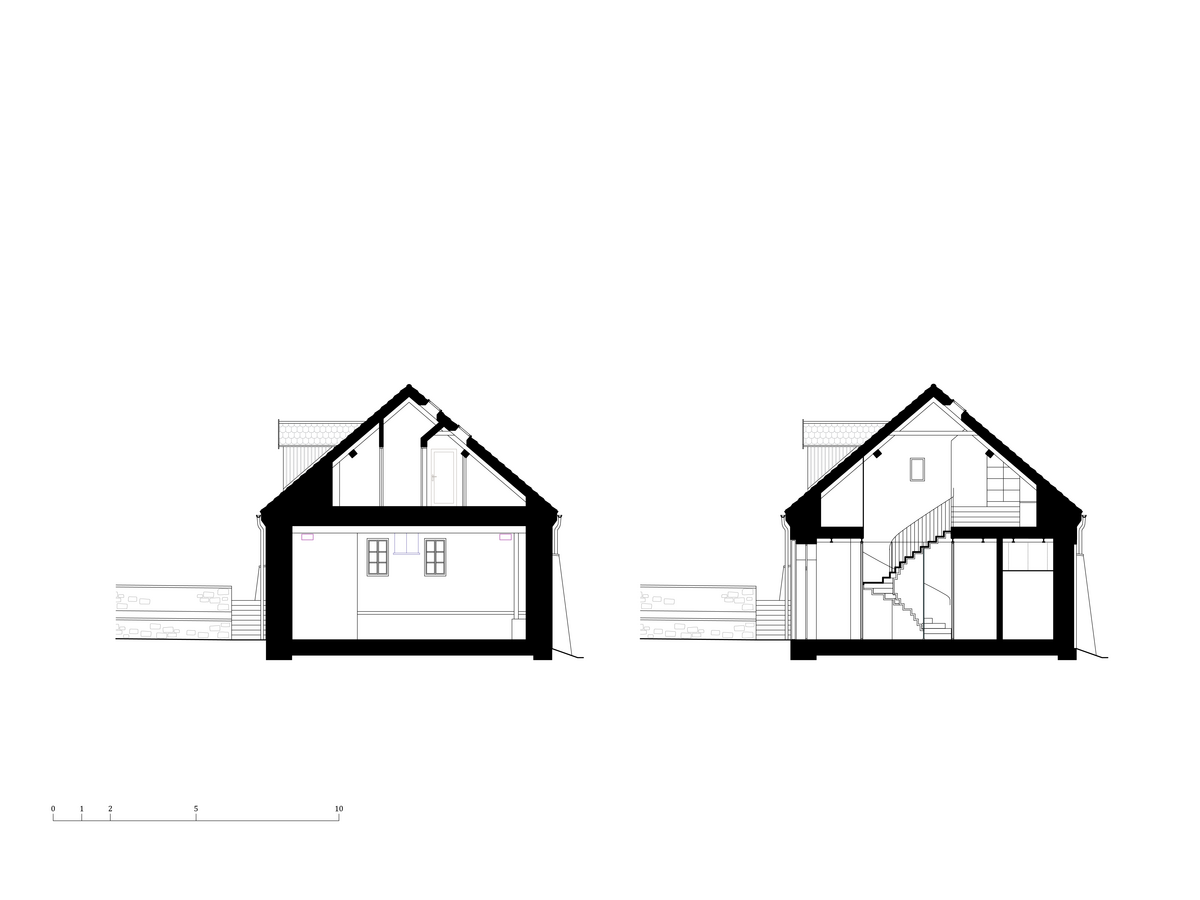
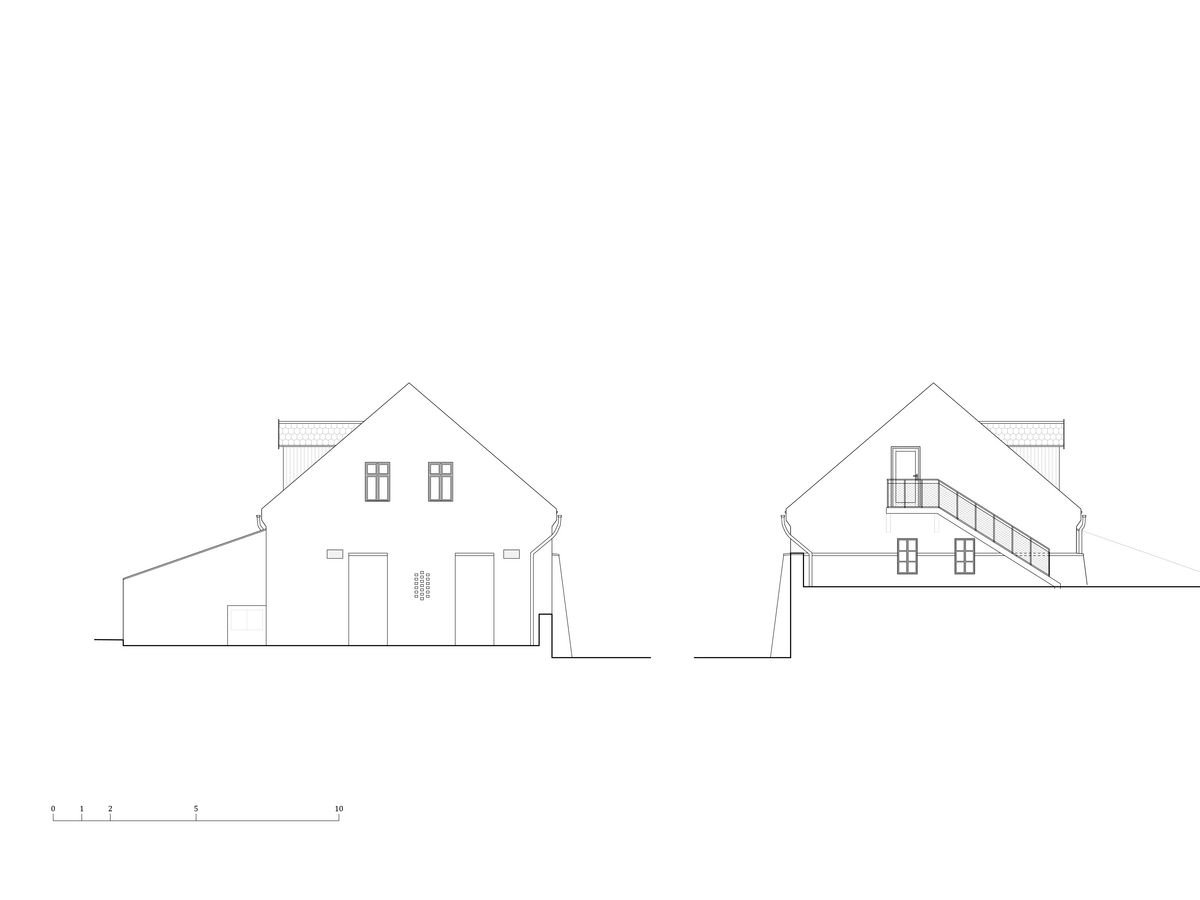
The primary axis of the site culminates at the main entrance and large glazed portal. The original layout has been cleared for new uses. The ground floor houses the multipurpose hall and lobby, around which the back-of-house spaces are tied. Dividing walls has been replaced by a staircase mass with translucent cladding. The vertical volume serves to connect the floors and separates the hall from the lobby.
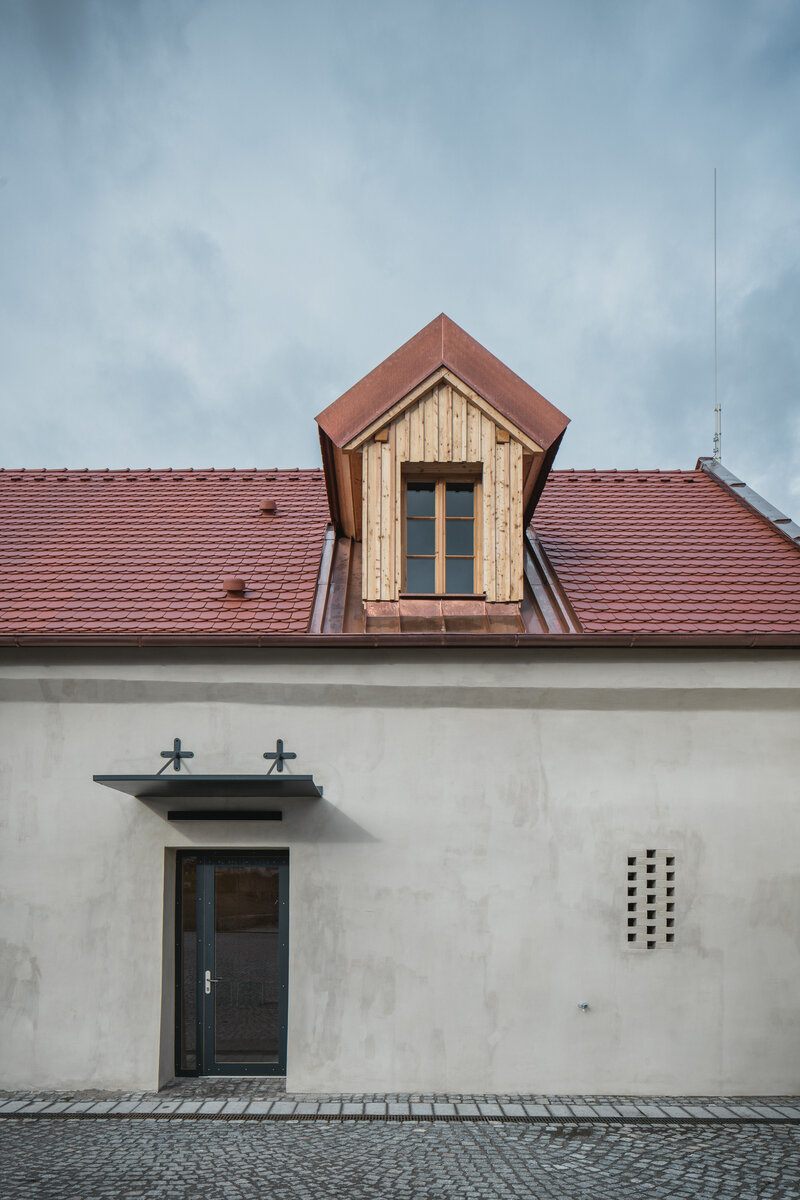
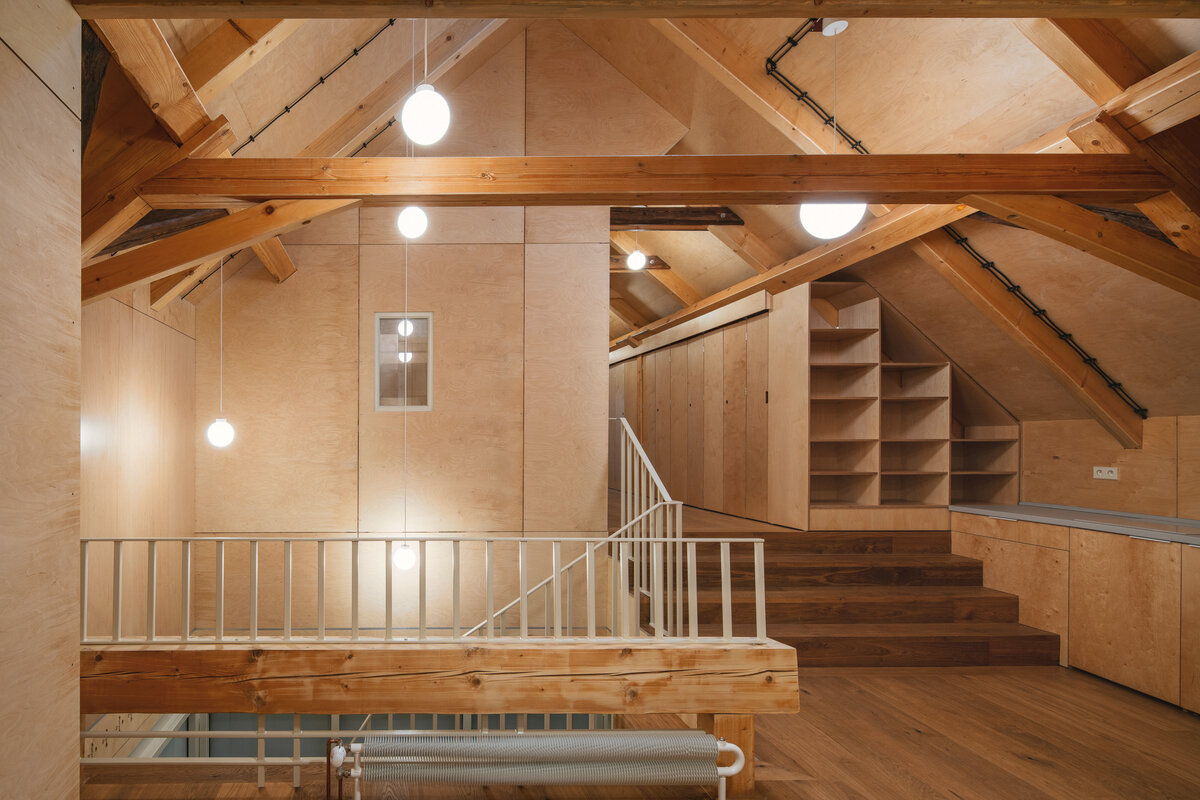
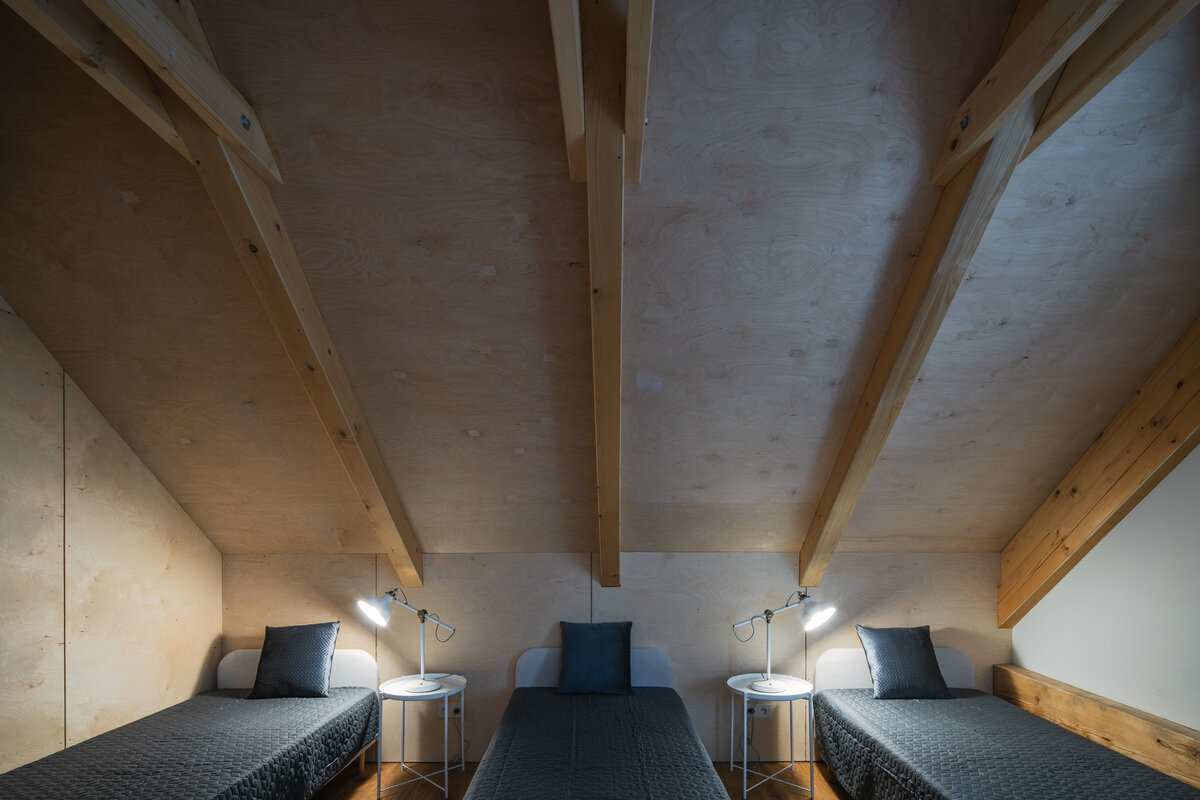
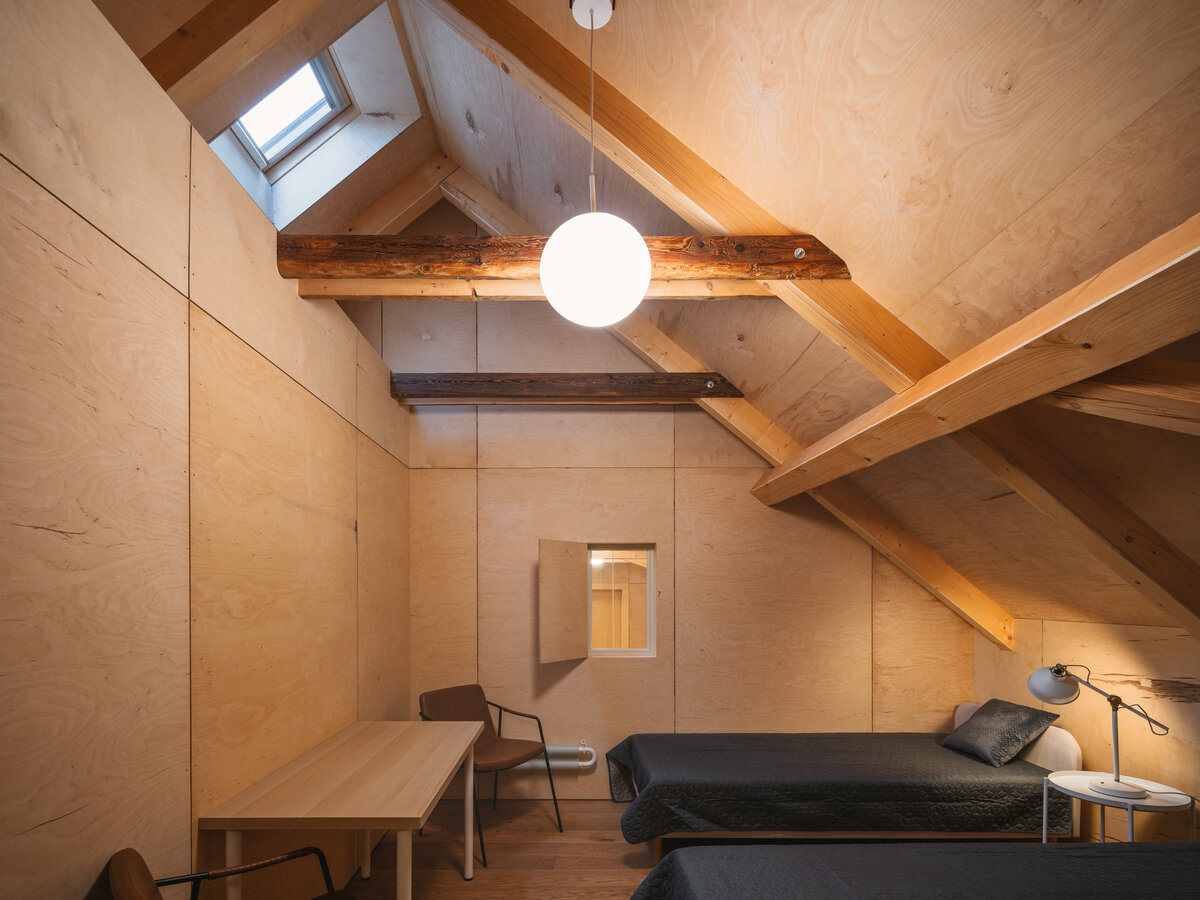
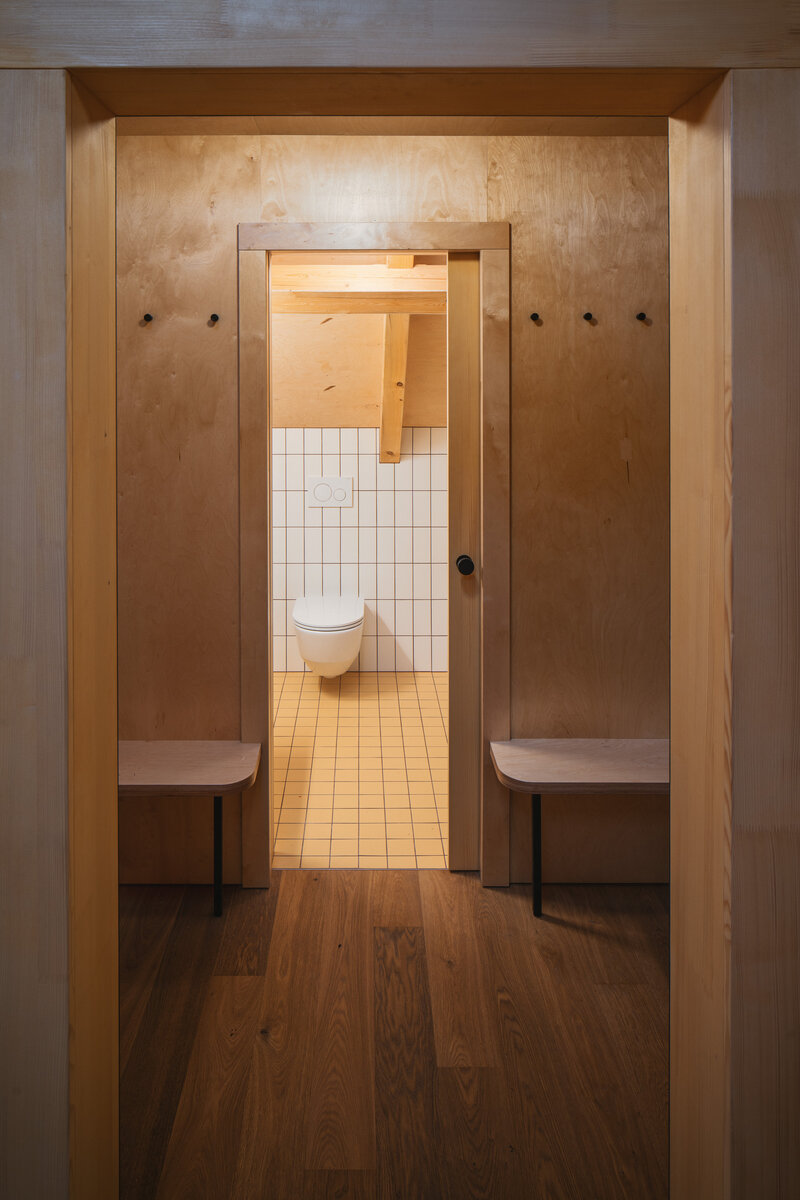
In the attic of the house, simple accommodation with facilities and an office of the site keeper was created. The layout of the attic is served by a corridor. The access is granted by a new external staircase adjacent to the gable wall. In the centre of the floor, an elevated gallery space with a kitchen is created.
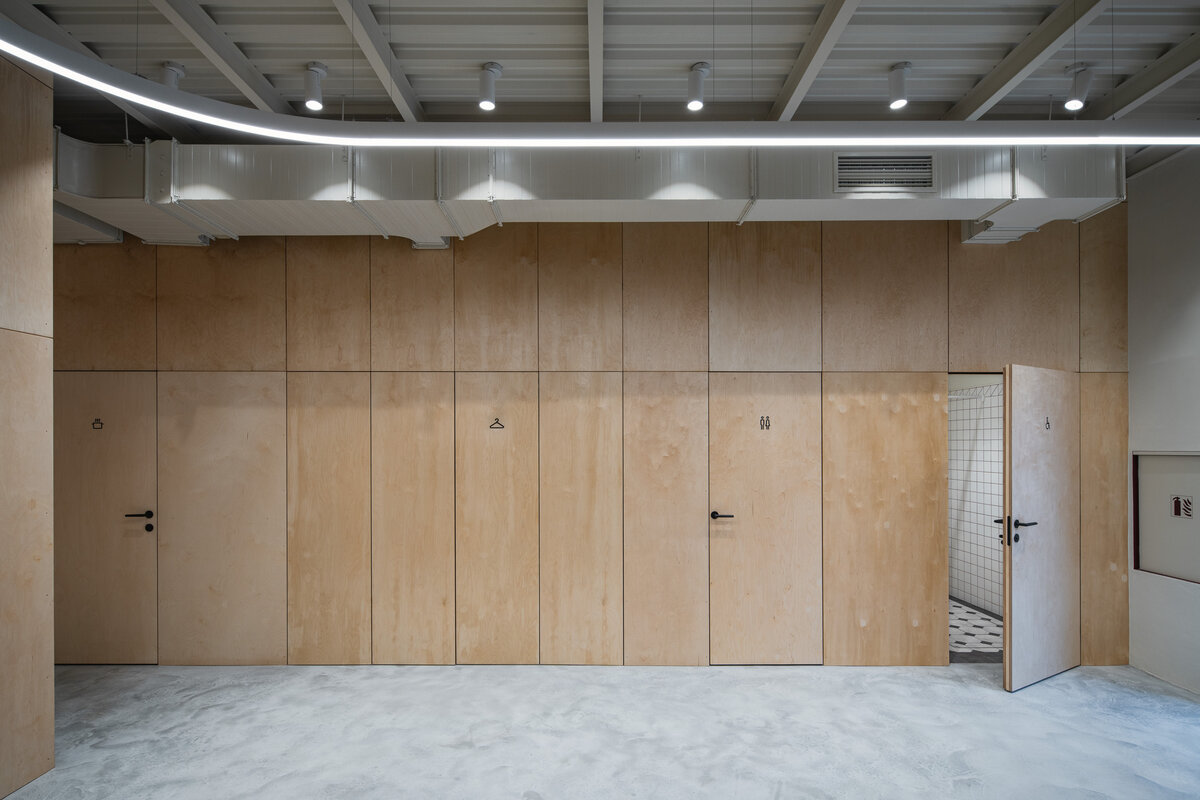
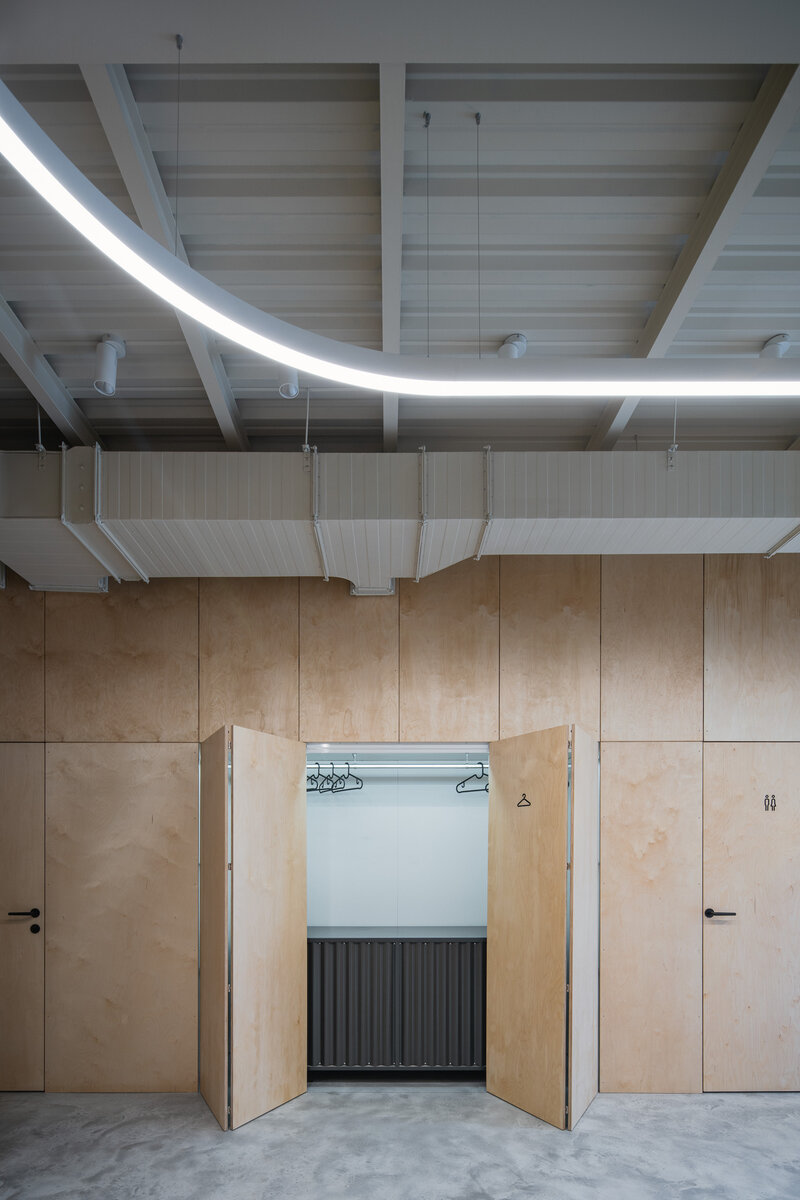
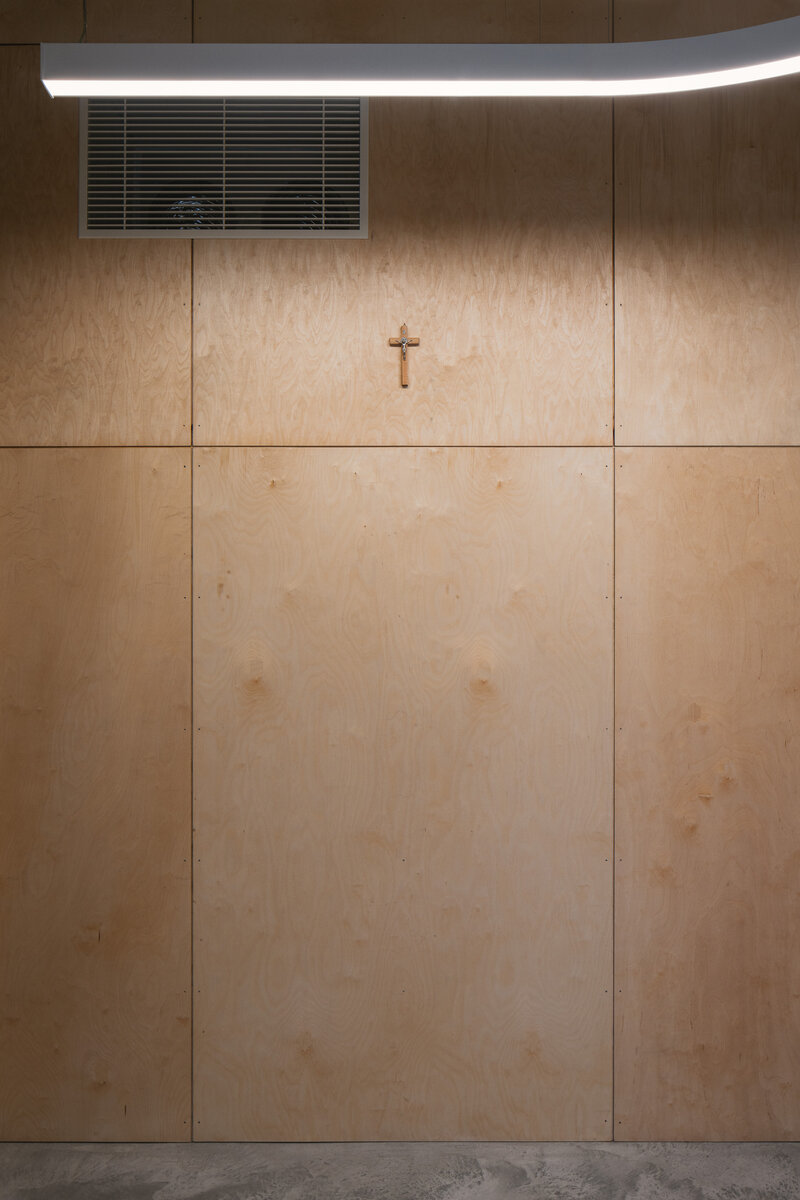
During the renovation of the house, inappropriate building layers were replaced. Materials used for the restoration of the building are related to the period of its original construction. The main feature of the interior is wood. Mild coloured steel construction with new plastering of the original walls brings a contemporary layer to the building.
The contrast of old and new highlights the qualities of the historic house, admits the interventions and reflects the contemporary architecture.
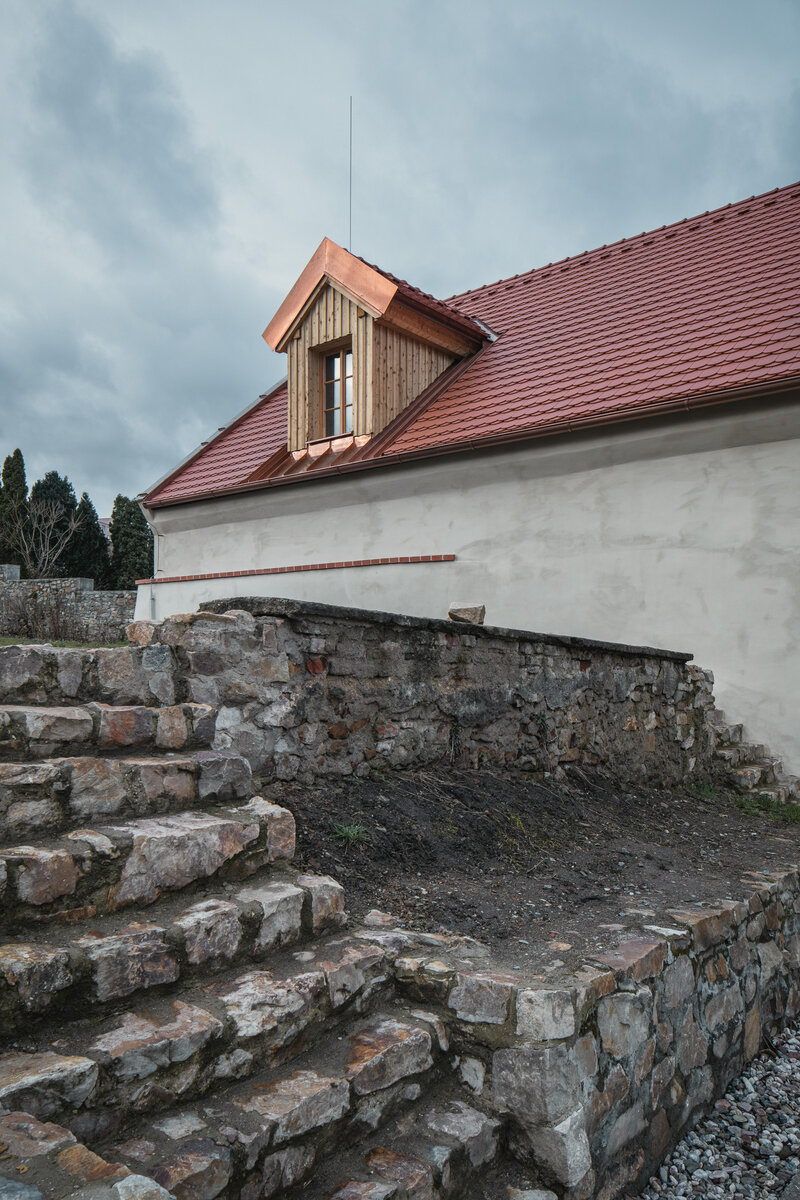
The reconstructed building uses a combined structural system. The existing foundation has been preserved with local repairs. Foundation pads were added under of new load-bearing steel columns.
The existing combined structural system, consisting of load-bearing masonry and steel columns on the ground floor, has been preserved in the southern part of the ground floor. A few new openings were created in the walls. The original windows were replaced with replicas. The steel structure and the Hurdis ceiling structure on the ground floor were preserved only above the southern part. The partition walls above the ground floor were removed. The ceiling structure above the northern part of the ground floor was removed to because of a change in height arrangement and was replaced with a composite steel-concrete slab structure on trapezoidal sheeting, supported by steel beams installed into openings in the perimeter walls.
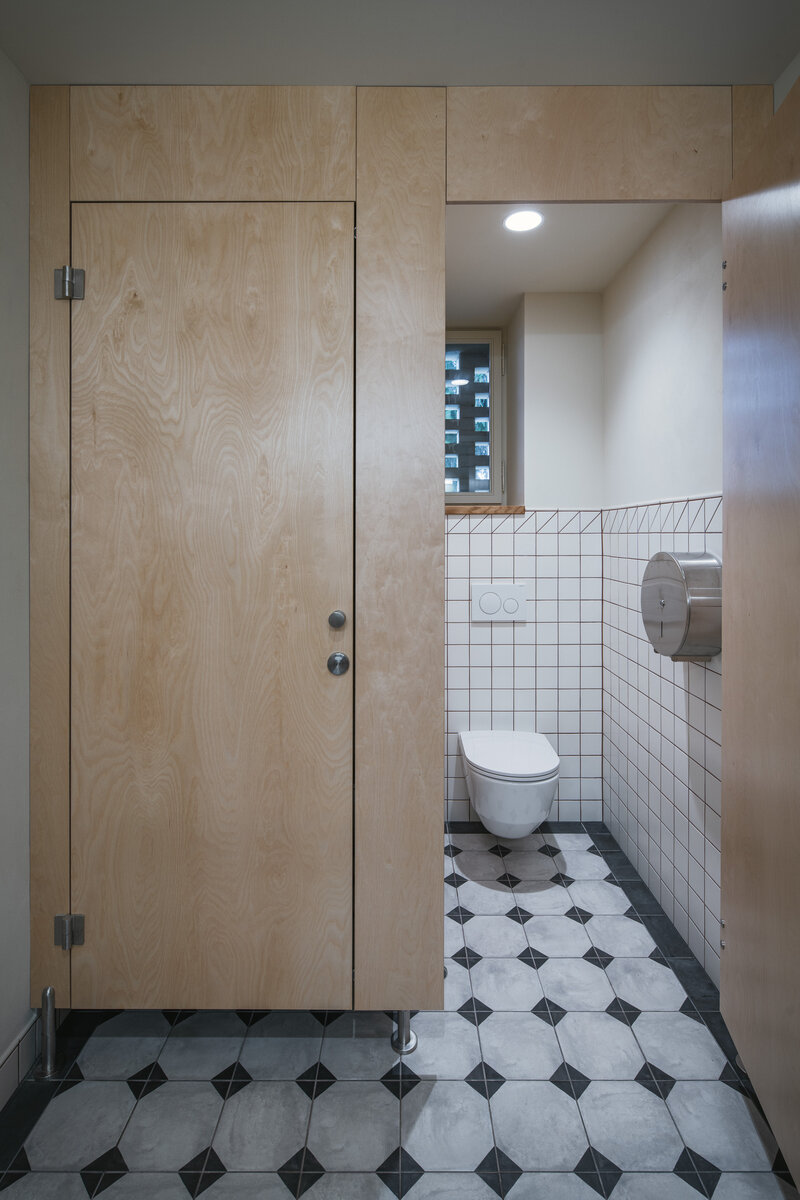
Partition walls on the ground floor are made of brick blocks. The finishing of the individual masonry structures includes gypsum plaster, ceramic tiles, or a light coating applied directly to the masonry. The partitions between individual functional units and common areas on the first floor are made of drywall. In dry operational areas, the visible layer is made of birch plywood.
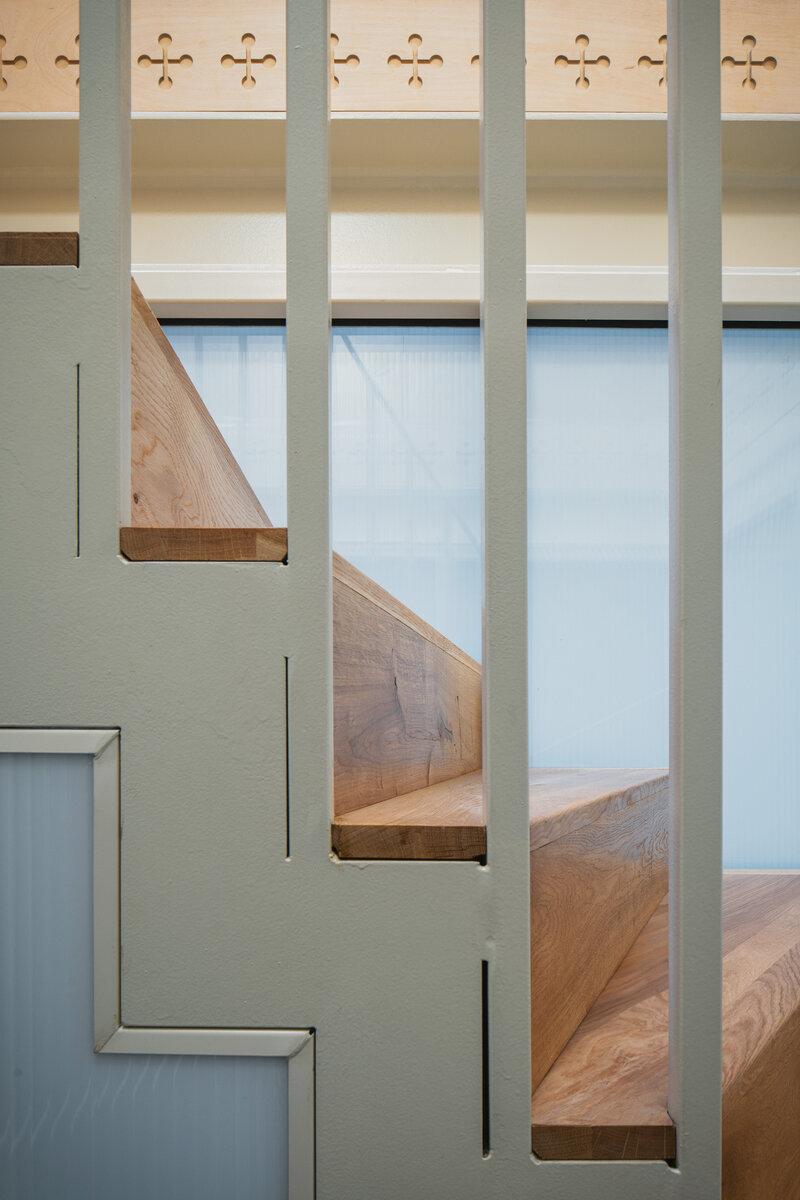
The original steel staircase in the central space was removed and replaced with a clad steel staircase in the center of the layout, ensuring both operational and acoustic separation between floors. The cladding of the interior staircase consists of steel beams with a multi-layer construction of glass and polycarbonate panels.
The original roof truss, which was largely infested with fungi and insects, could not be preserved, and was replaced with a replica. The new roof truss replicates not only the profiles of the original truss's structural system but also the original carpentry joints. This approach preserves the authenticity of the new structure in relation to the original design. Healthy, unaffected structural elements of the original truss were incorporated into the new structure. The truss is covered along its entire length with birch plywood and insulated above the rafters with PIR boards. The roofing consists of traditional ceramic tiles.
Heating is provided by an air-water heat pump, with heat distributed throughout the building.
Ventilation and air quality in the multi-purpose hall are ensured by an HVAC unit with heat recovery.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate | - |
|---|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? | |
|---|---|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? | |
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? | |
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? | |
|---|---|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? | |
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? | |
| Is artificial lighting automated? | |
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? | |
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? | |
|---|---|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? | |
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? | |
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building | B |
|---|---|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? | |
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? | |
|---|---|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? | |
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |