| Author |
Jiří Knesl, Jakub Kynčl |
| Studio |
knesl kynčl architekti s.r.o. |
| Location |
5. května 123/1, Třešť |
| Investor |
Město Třešť |
| Supplier |
STARKON a.s. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
February 2023 |
| Fotograf |
Radek Brunecký / ATELIÉR BRUNECKÝ |
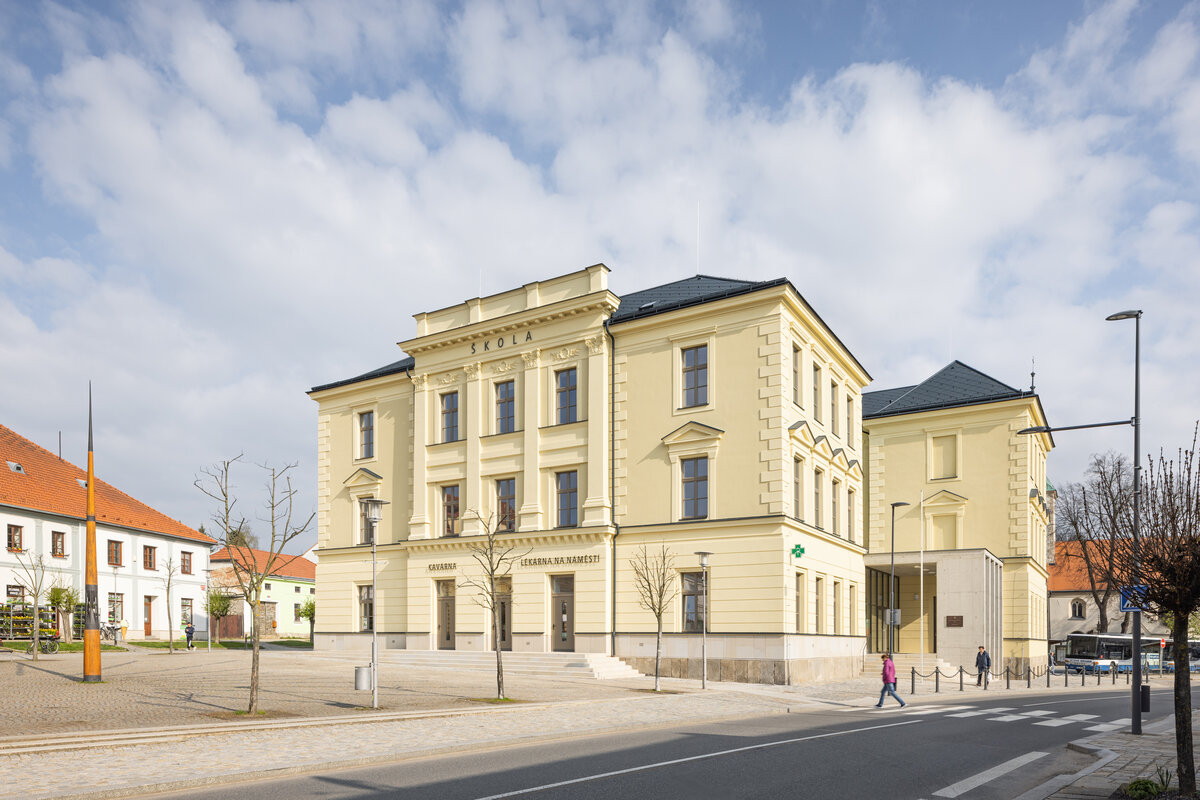
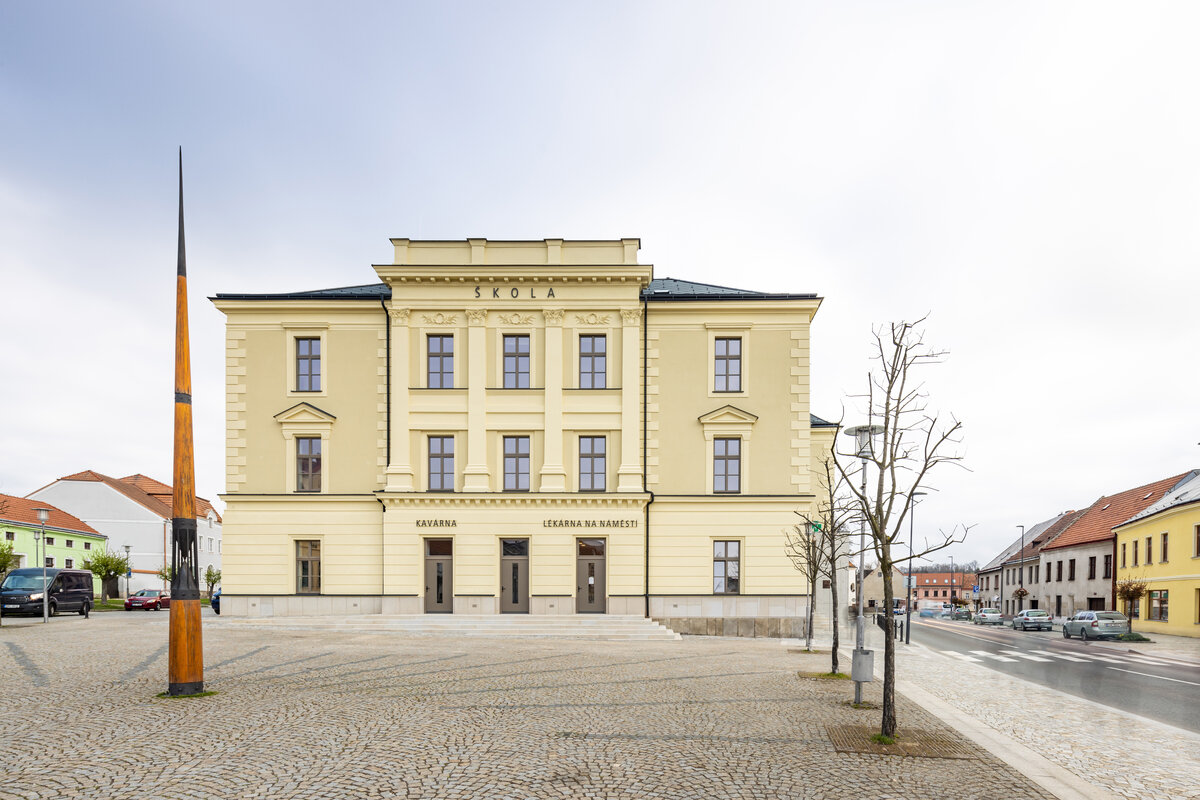
The building of the so-called old school occupies a unique place at the head of the main square of Třešt'. Its importance is underlined by the situation where the square is shaped like an isosceles triangle and the school building is located in the centre of its elevated base.
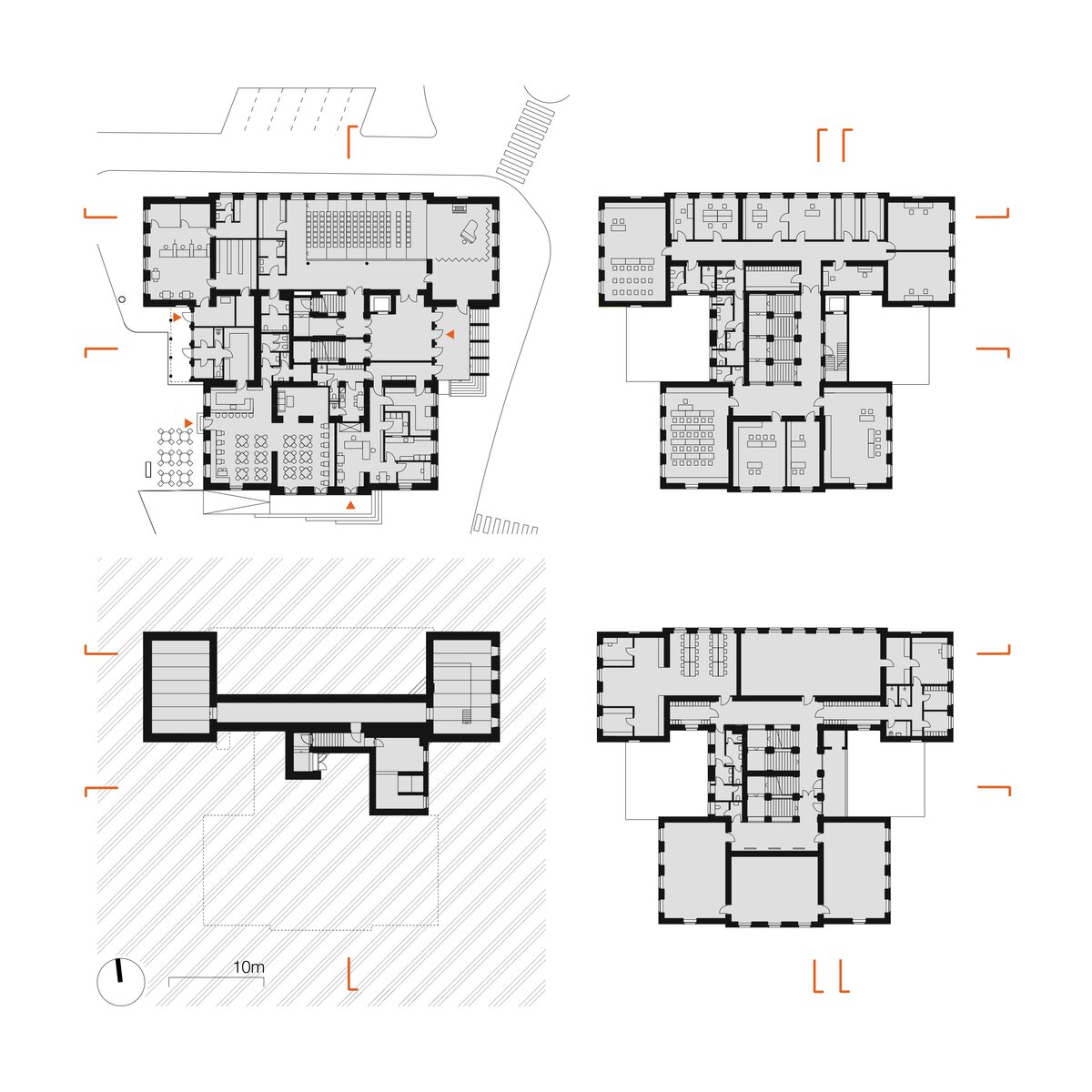
The building was designed by architect Václav Tebich and built by his brother Antonín Tebich. The historic old school building was built in two phases between 1890 and 1901. In 1890, the southern part of the building was opened to serve as a boys' common and burgher school. The building had an inverted T-shaped plan with classrooms facing the square and a back room with a staircase to the north. In 1901 the northern extension of the girls' part of the school was completed. The extension was again T-shaped and mirrored the original school.
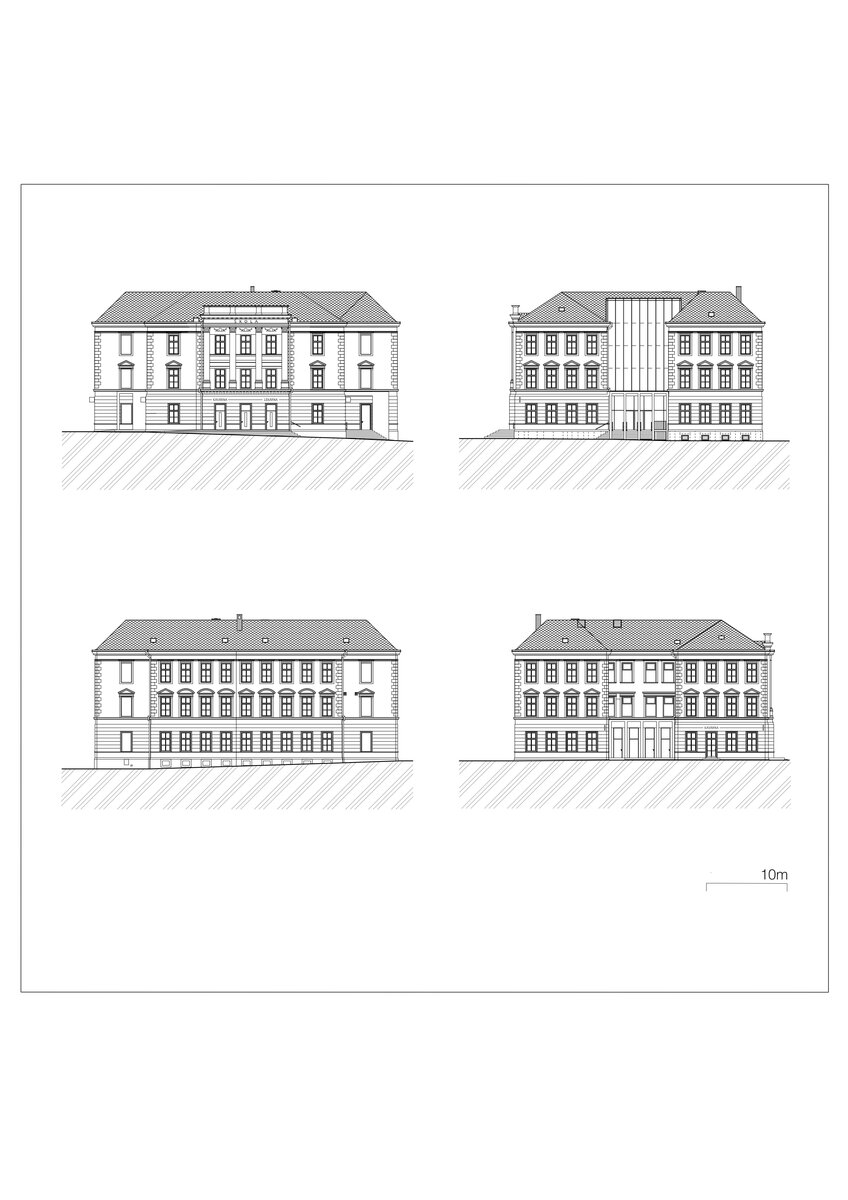
The complex construction development was reflected in the atypical positioning of the building on the square, where the southern most facade of the building would have been the logical place to create the main entrance, yet there were only classroom windows and the main entrance was from the beginning located on the eastern facade facing 5 May Street. The solution of the entrances and the new "connection" of the building to the square was one of the main objectives.
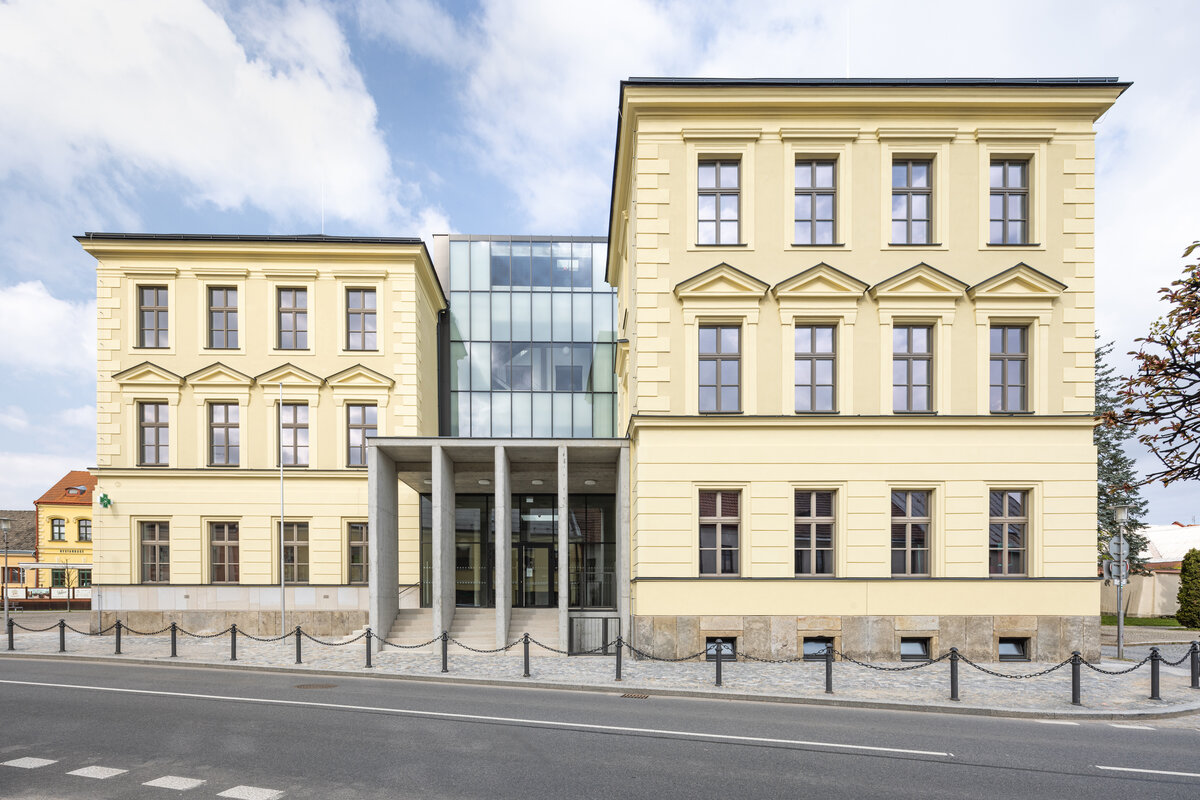
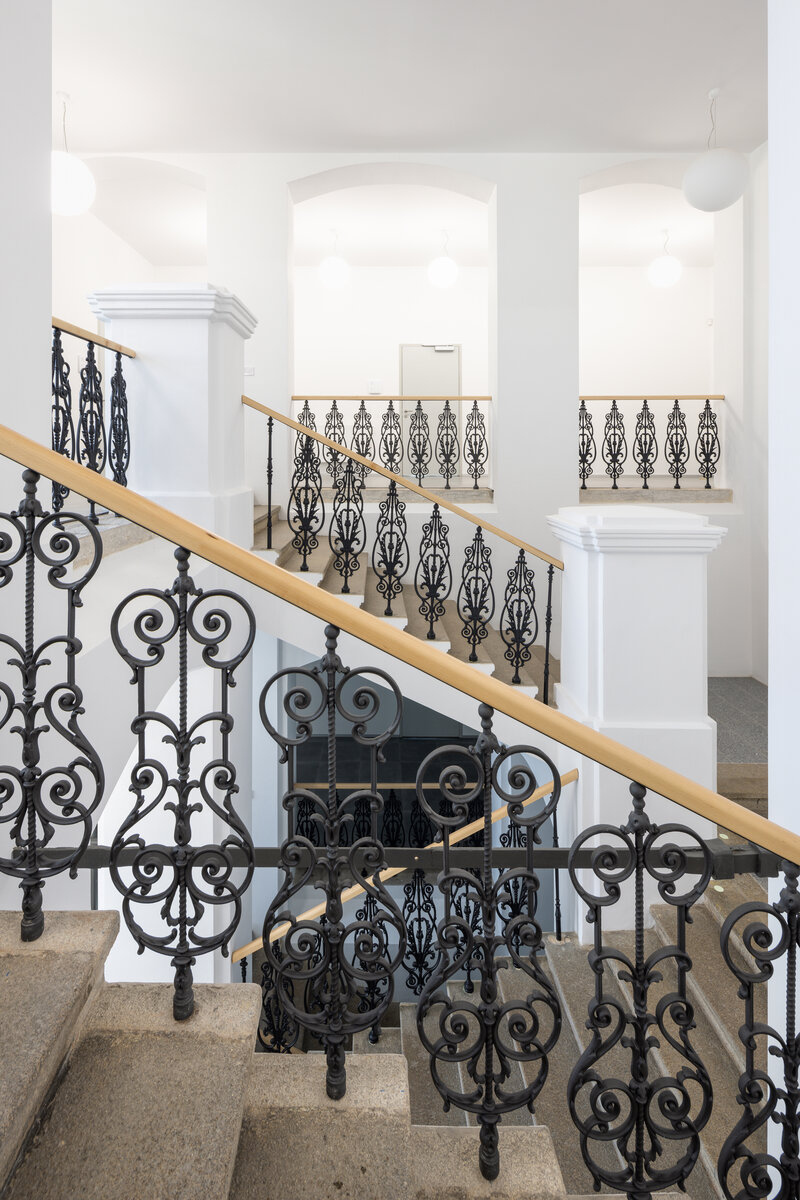
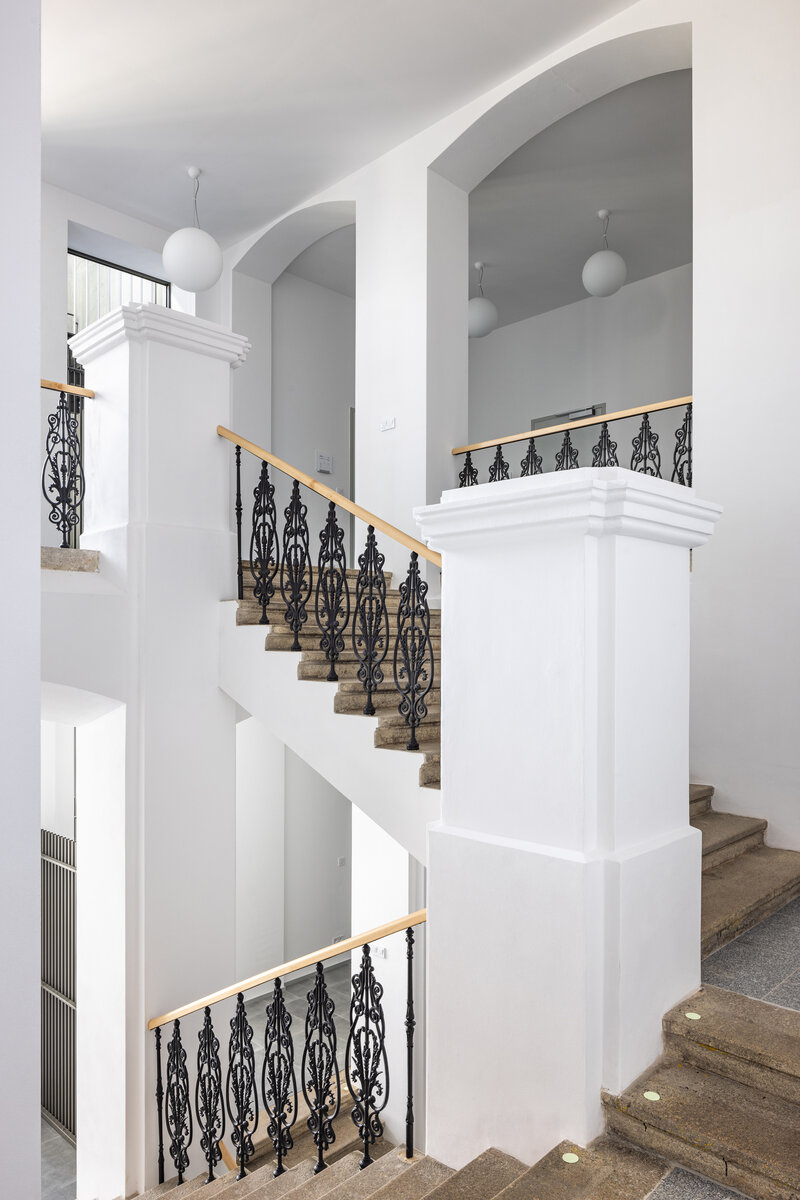
The historic building has been cleaned of the unwanted part of the later interventions and the facade has been restored to its original form (restoration of pilaster footings, bosses, profiles, etc.), including the preservation of the individual historic layers. As the original infillings of the openings have not survived, they are all replaced with new ones in the spirit of the historic building.
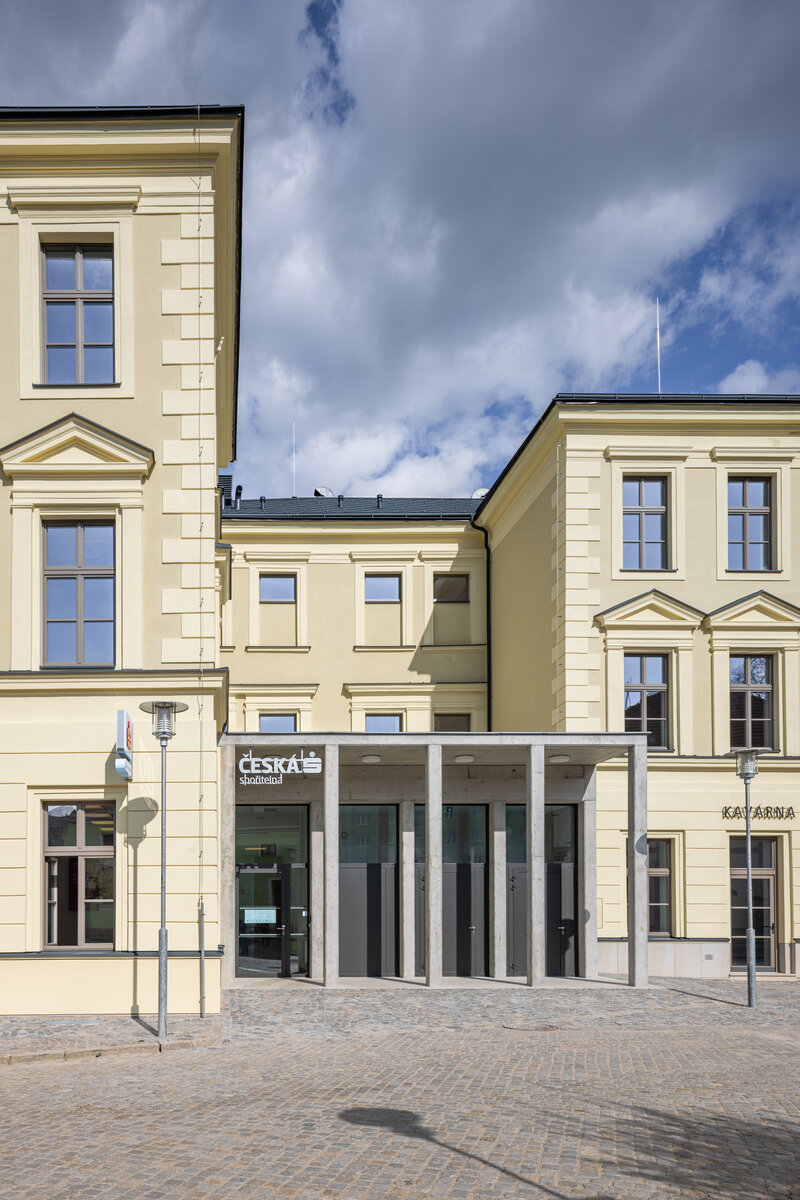
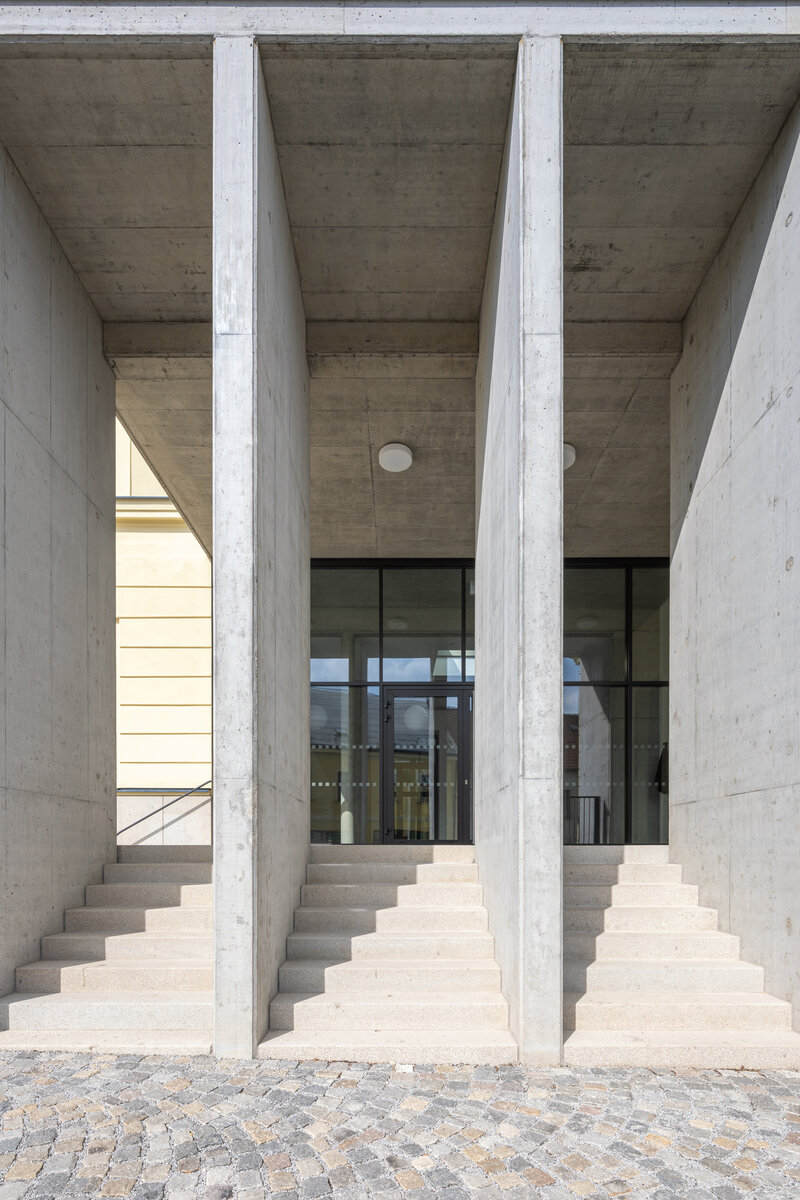
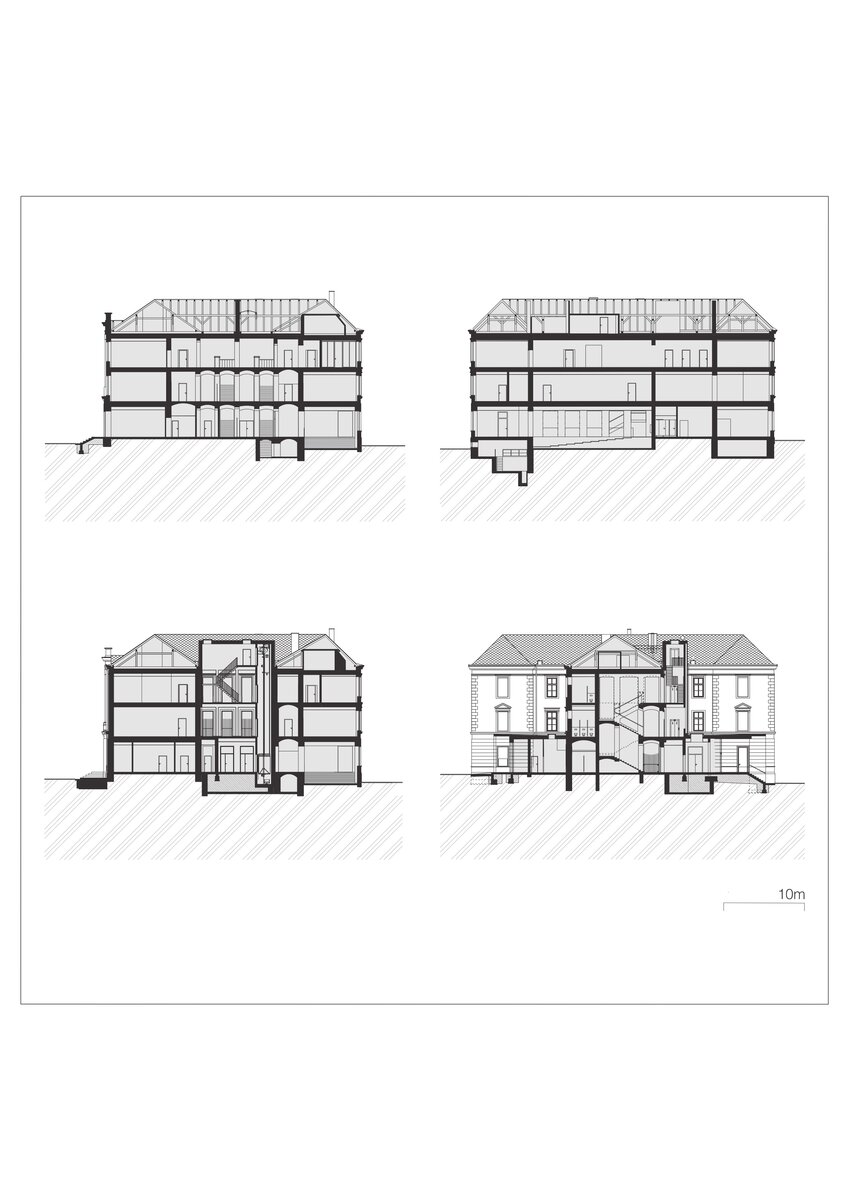
The new entrances in the extensions, sandwiched between the north and south wings, are clearly distinguished from the historic part of the building in terms of form and materials by the use of exposed reinforced concrete and aluminium profiles with large-format glazing of the new openings.
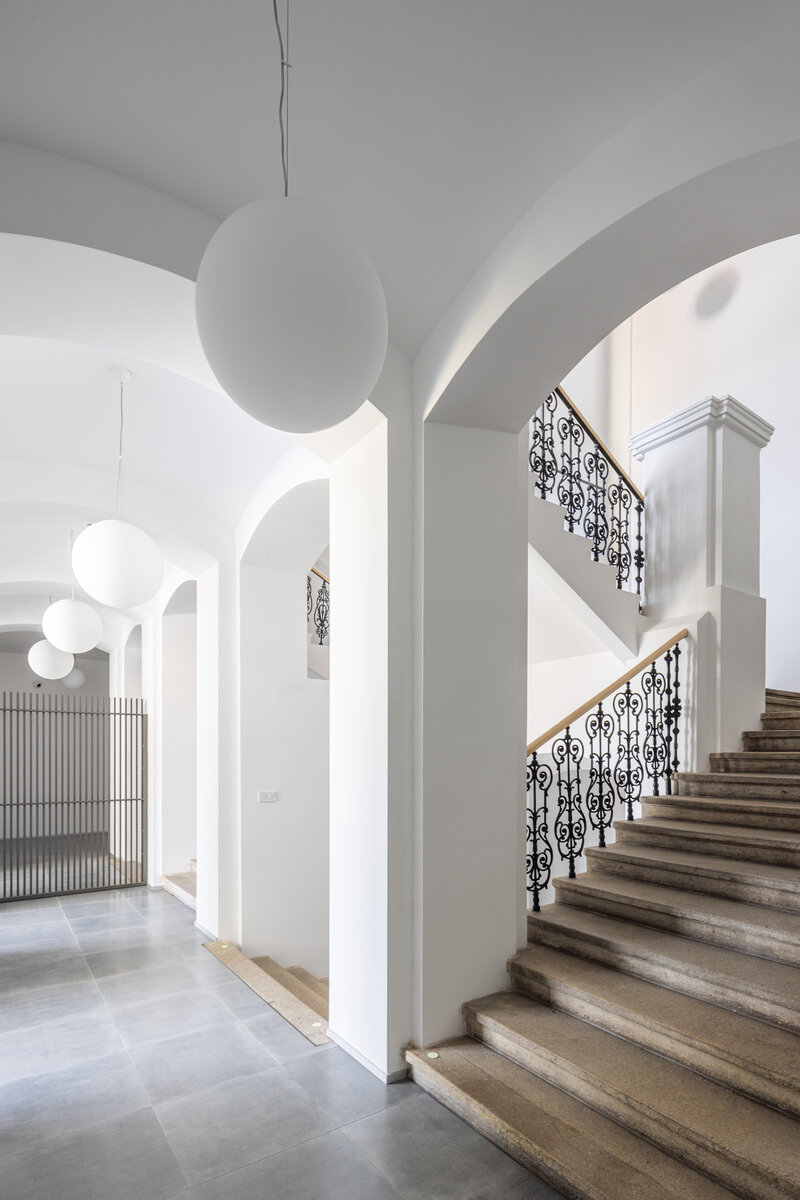
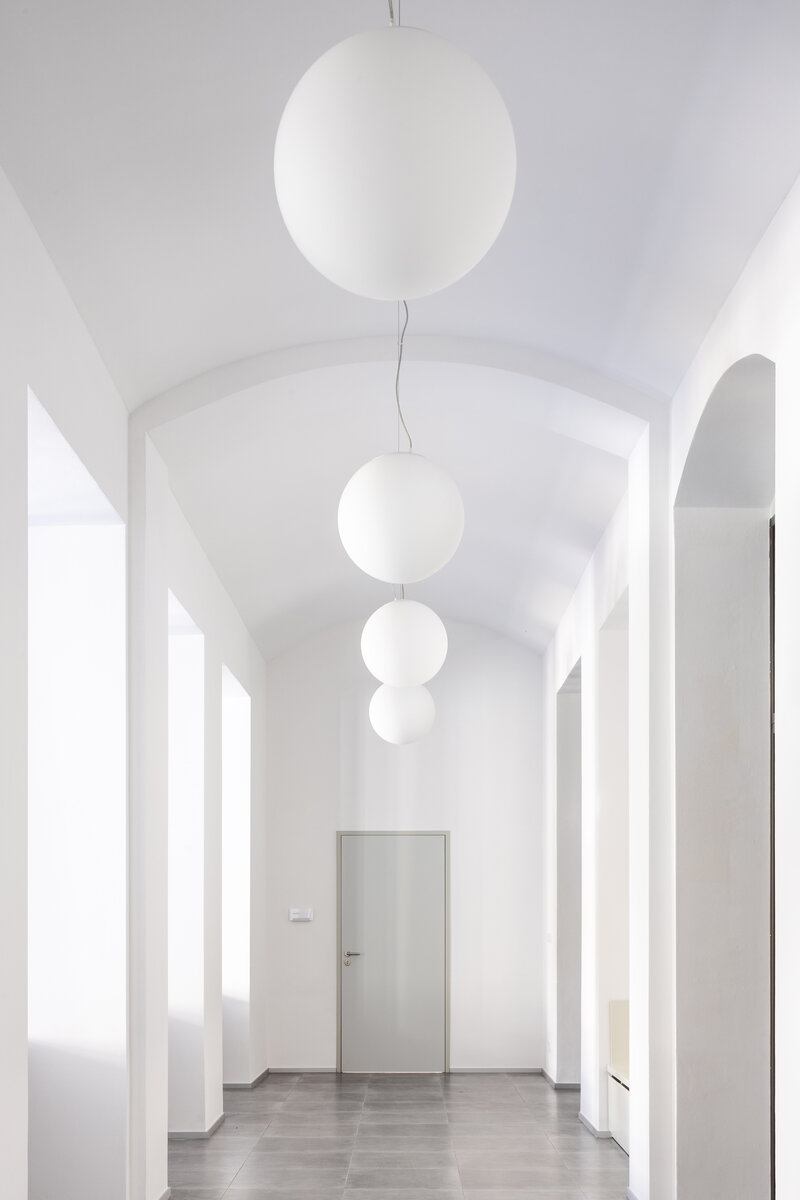
The ground floor of the building now houses three commercial units accessible directly from the ground floor. The other parts of the building are accessible through the main entrance from the eastern part, through the foyer in the new extension. The foyer also provides access to the historic staircases.
The attic is newly accessed by a staircase and lift and is used primarily for the technical facilities of the building.
The proposed extensions are made of exposed concrete with large-format fillings in aluminium profiles. The original building has been sensitively adapted in a traditional manner, particularly with regard to the external and internal plasterwork, stone cladding and the restoration of the original railings. Only some of the partitioning structures are new, made of lightweight plasterboards, the acoustic elements in the interior (acoustic plasterboards with an absorbent layer), the wooden windows, the floors (OSB boards on a beamed structure with a surface layer of either vinyl boards or ceramic tiles, or baltisol. Newly added ceilings, partly plasterboard, partly acoustic.
Great attention was paid to the roof structure, where part of the roof trusses were replaced with new elements, the original trusses having been severely degraded, mainly by leakage. The roof covering was replaced, the original ceramic tiles were replaced by Prefa roofing tiles.
The building modifications covered the complete technical equipment, complete reconstruction of sewage and rainwater drainage, cold and hot water distribution, electrical wiring, low-current distribution and heating. The air-conditioning facilities were completely new, which are designed for the operation of the café, the pharmacy and all social facilities. Cooling is done locally and is designed for the café and pharmacy. The mechanical rooms are located in the truss area of the building or on the flat roofs of the additions.
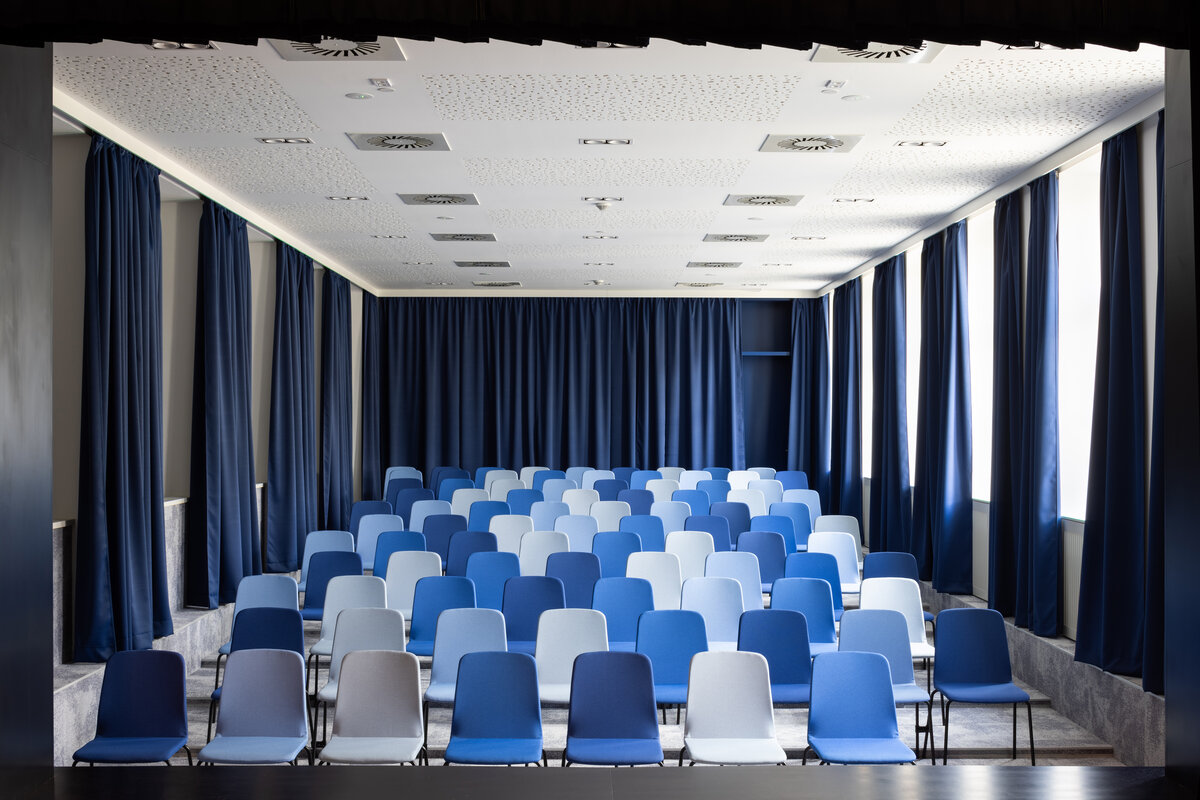
In the multi-purpose hall, the sound system and stage lighting are partially implemented and preparations are made for additional additions according to the needs of the school. The implementation includes sound and light direction.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
E
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|