| Author |
ateliér: atakarchitekti / autor: Ing. arch. Ing. Jiří Janďourek, Ing. arch. Ondřej Novák, spoluautor: Ing. arch. Jana Janďourková Medlíková |
| Studio |
|
| Location |
Nad Školou 278
463 11 Liberec–Vratislavice nad Nisou |
| Investor |
Městský obvod statutárního města Liberce – Vratislavice nad Nisou |
| Supplier |
B R E X, spol. s r.o. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
October 2021 |
| Fotograf |
|
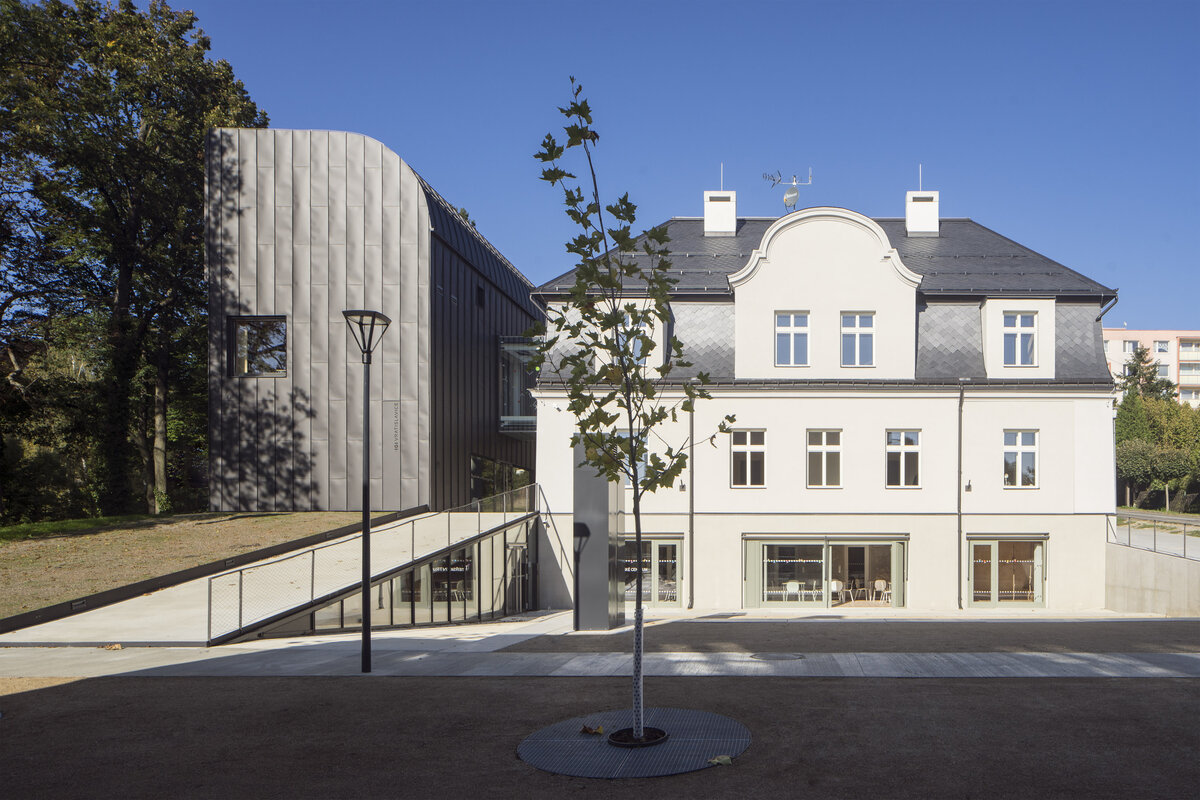
A suitable place for the new town library was the unused house of the Roman Catholic rectory, in the past also used as an orphanage, kindergarten and vocation school. In addition to the library, the municipality intended to place a multifunctional hall, facilities for clubs and a maternity centre in the house. The former rectory could not accommodate all the functions, so it was decided to extend the building with an extension.
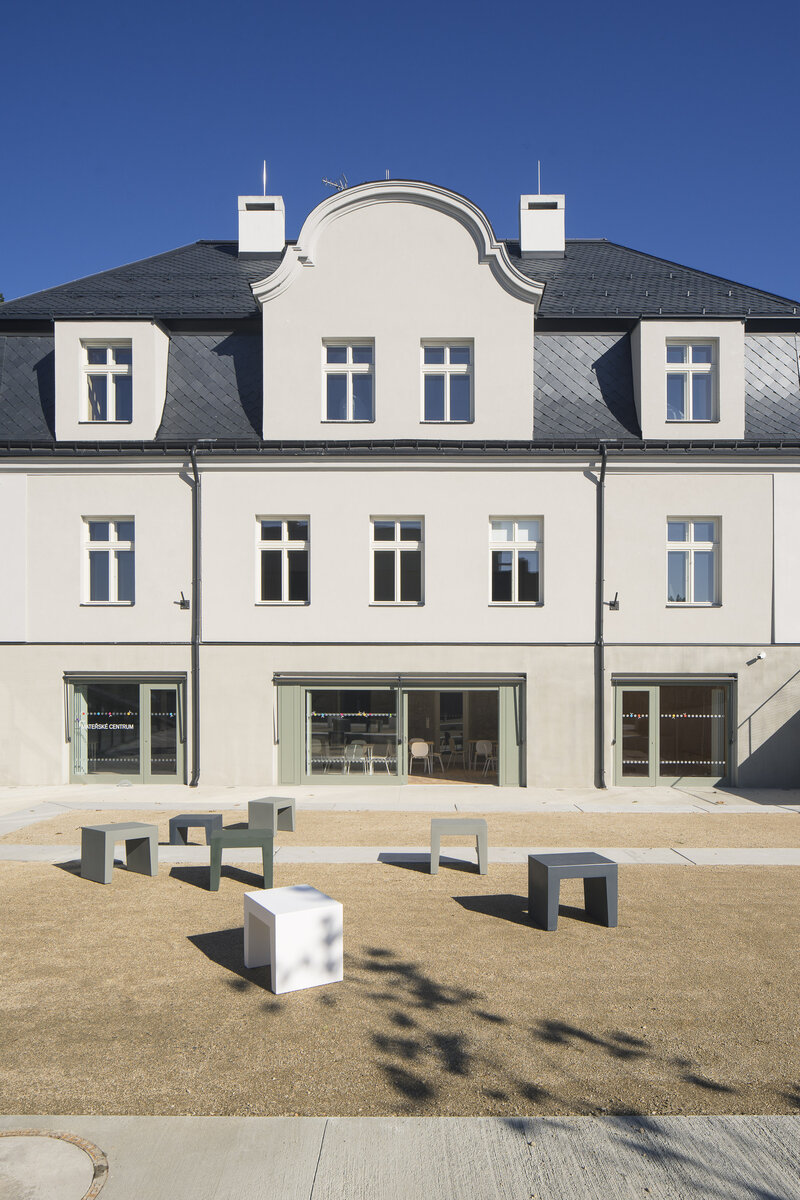
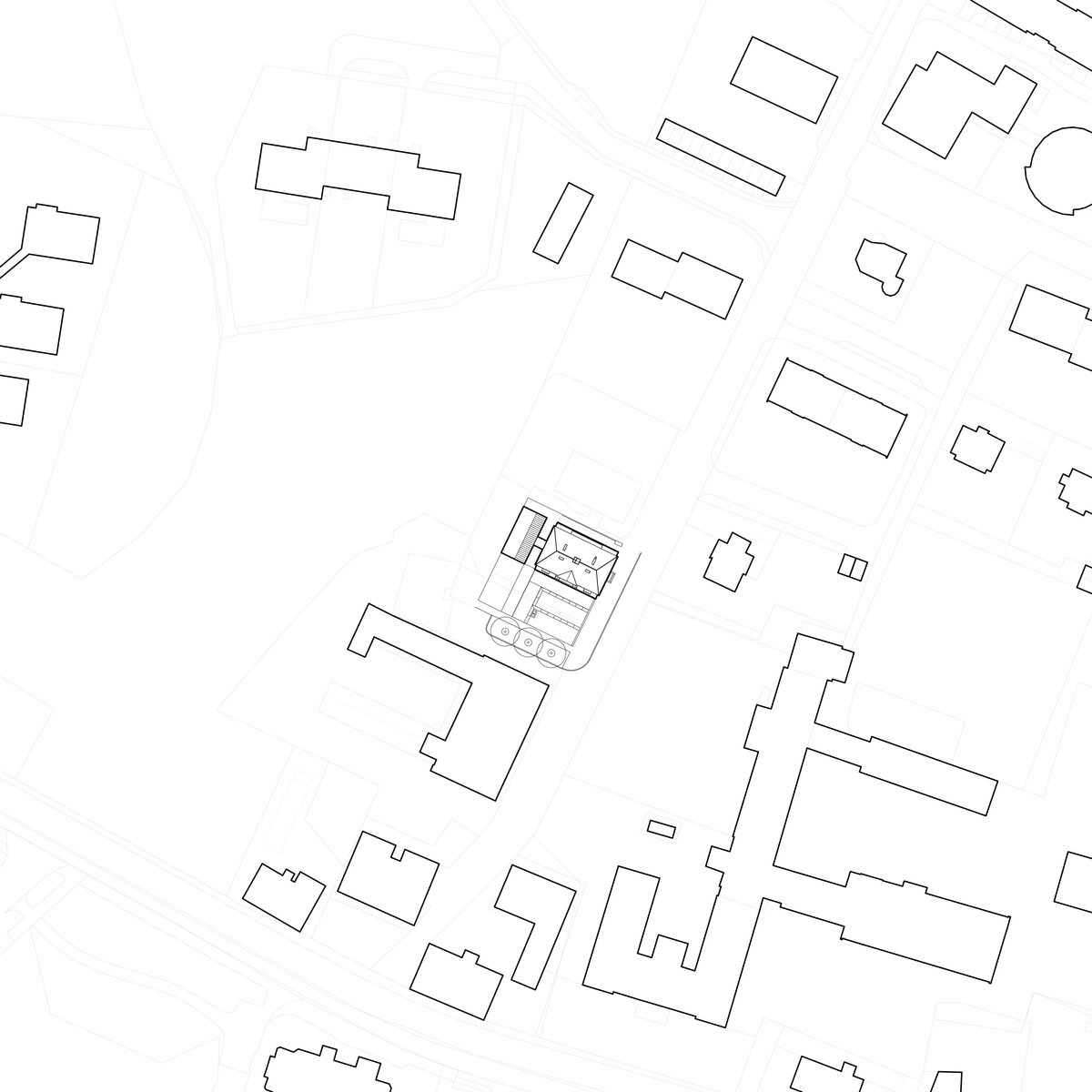
The idea of the design is to create a new public place that will connect to the existing vibrant center of Vratislavice, defined by public buildings and the château garden. A new piazzetta is being created, inspired by the rhythm of small squares in the vicinity of the public buildings.
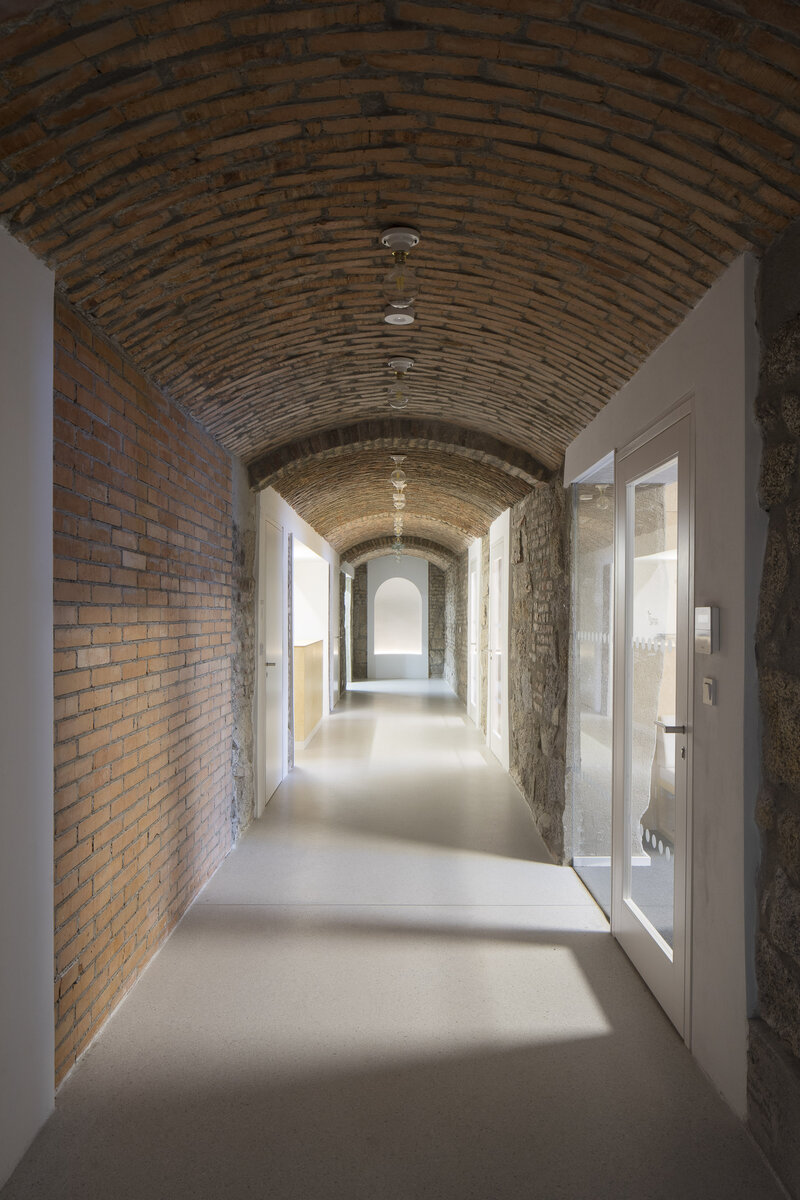
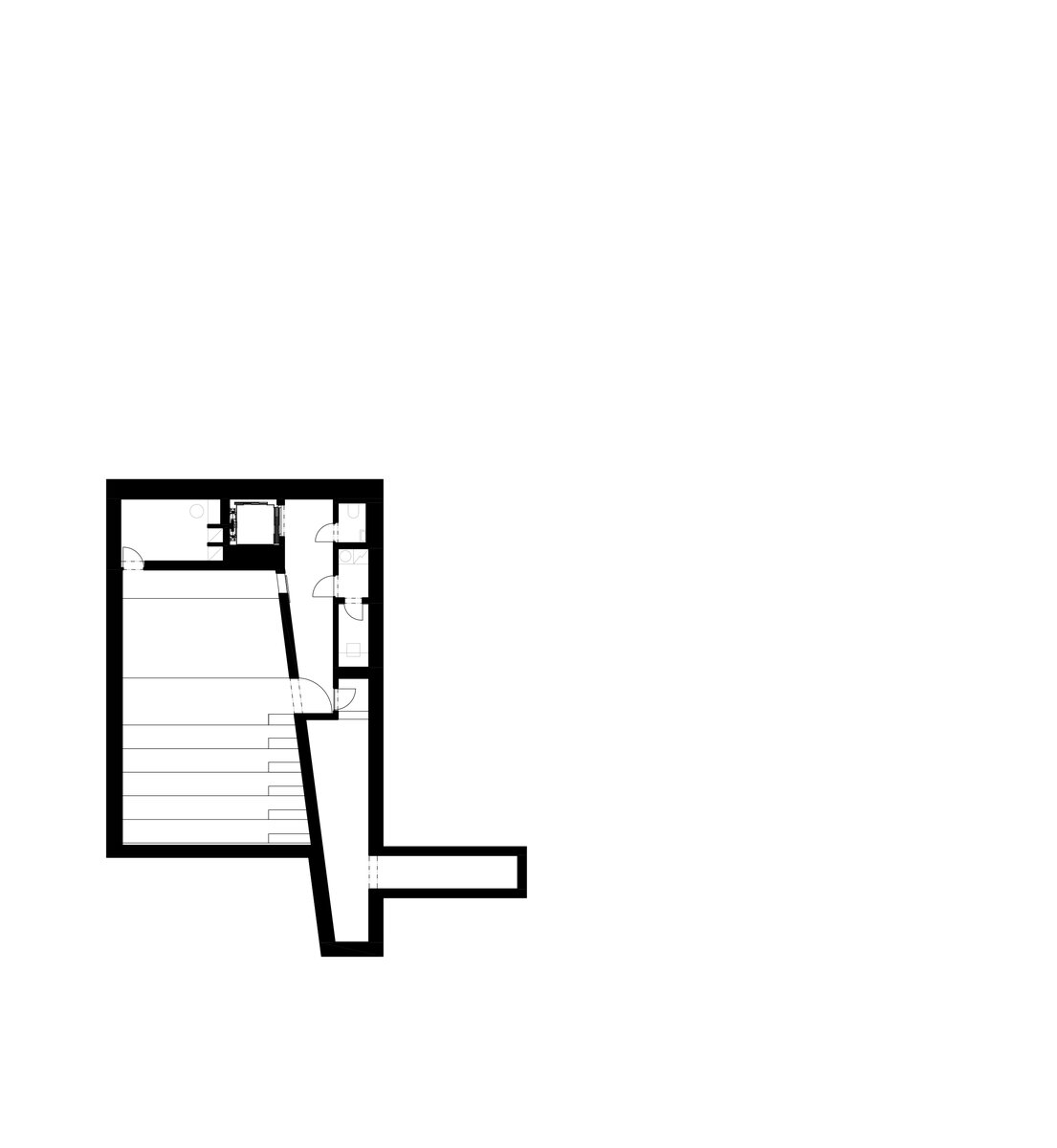
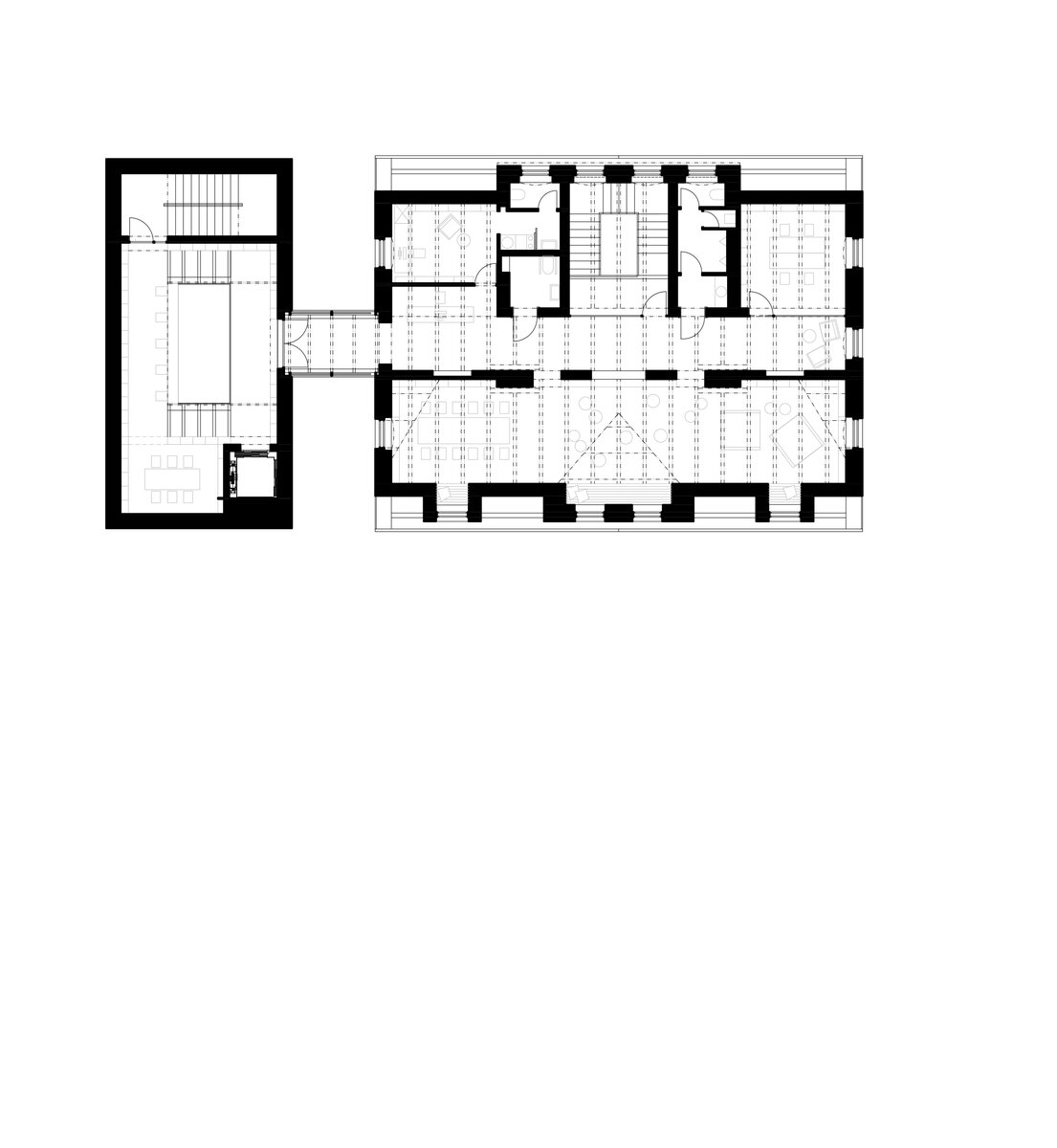
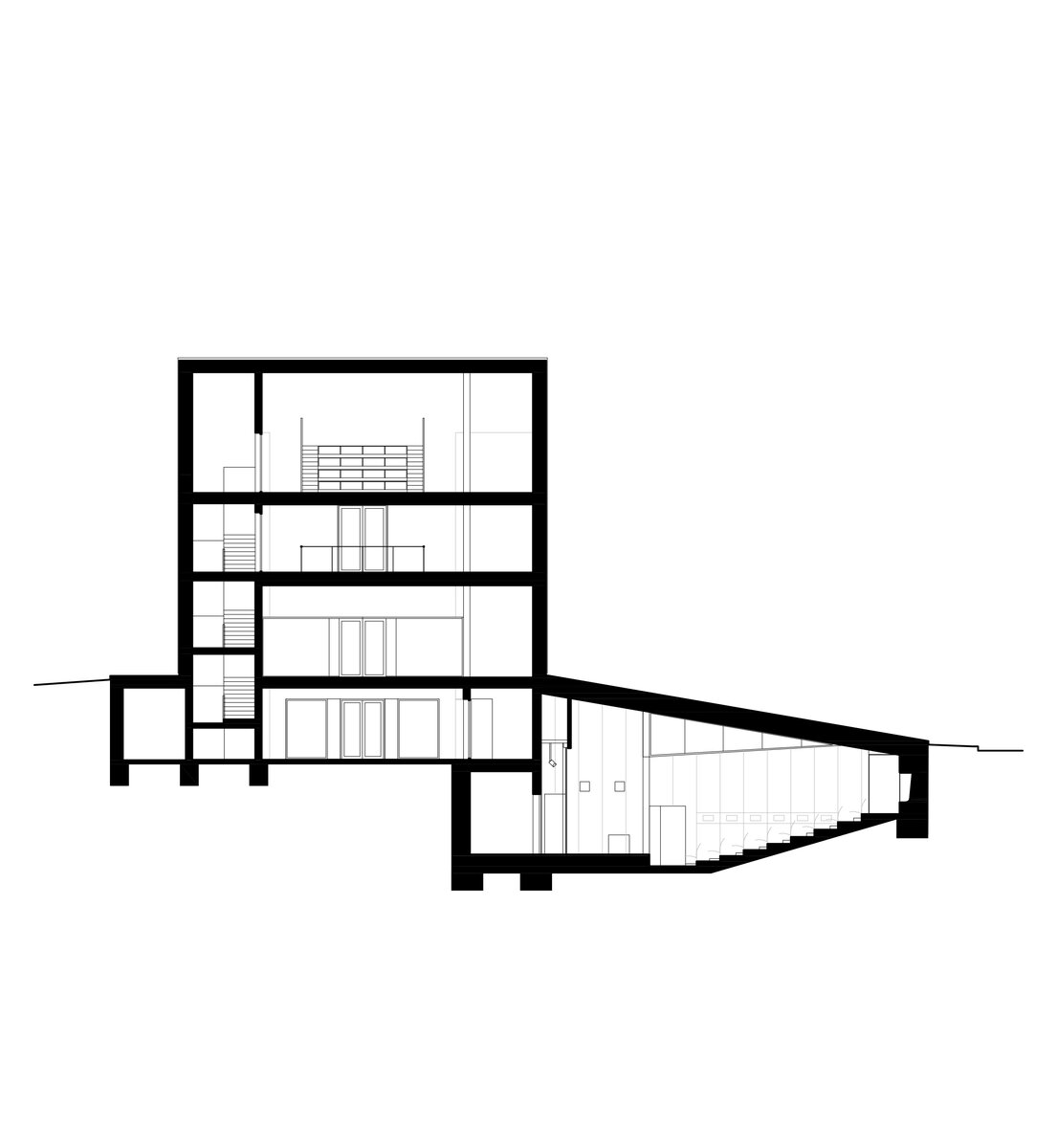
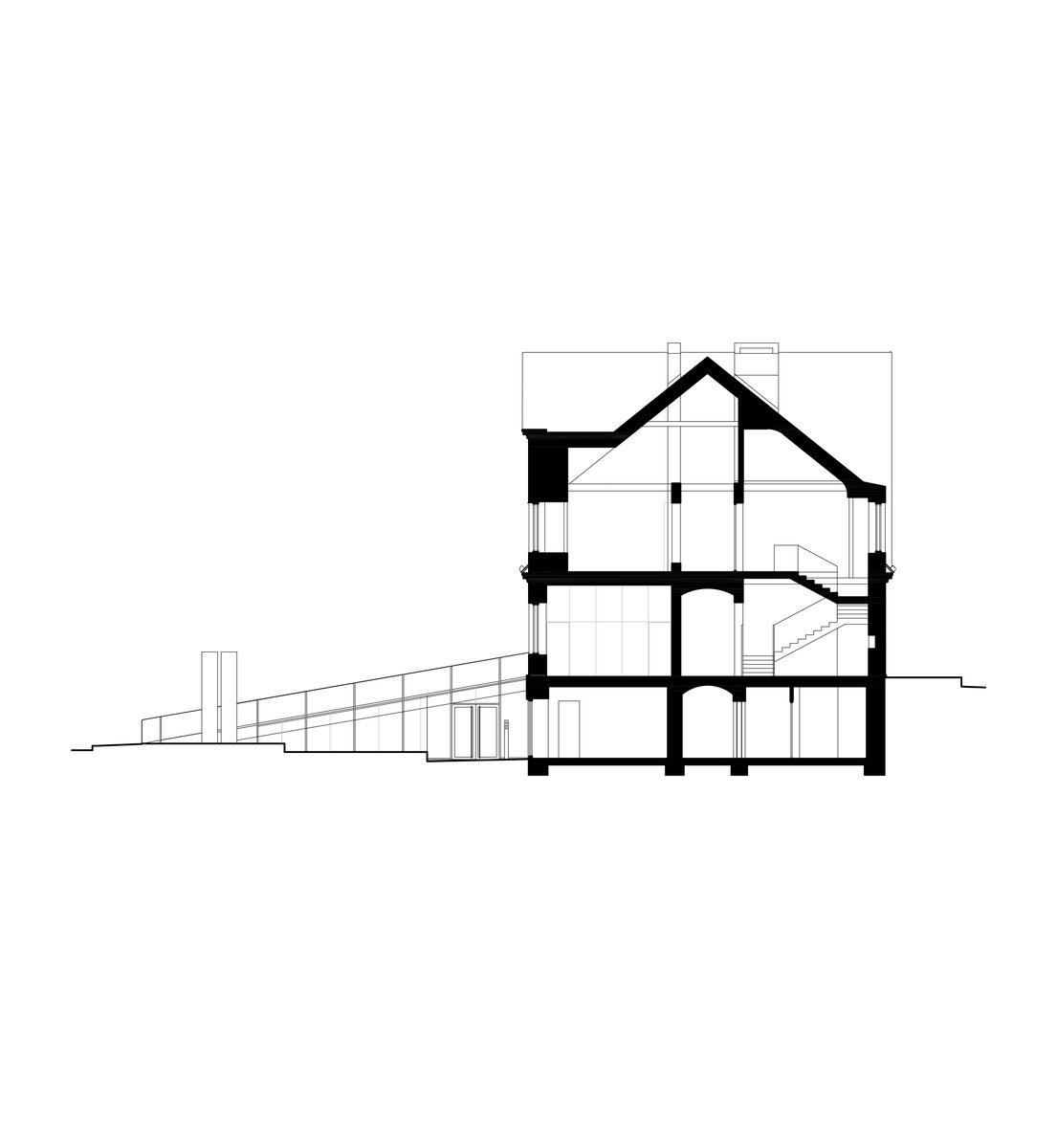
The original character of the old house has been retained – its deep foundations have allowed for a semi-recessed floor to be created by weighing off the ground. The excavation allowed daylight in through generous portals and the excavated pit formed the base of the new plaza. The ground floor has been given over to clubs and the upper floor to the children's library.
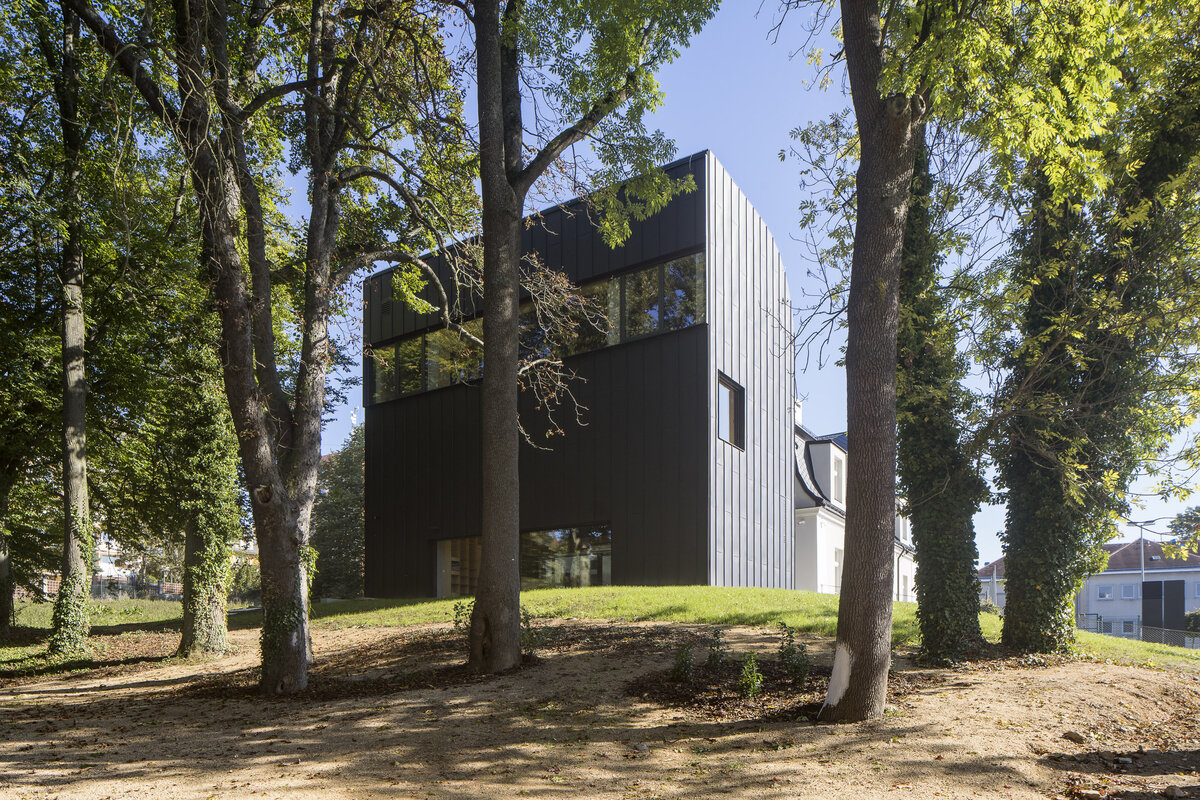
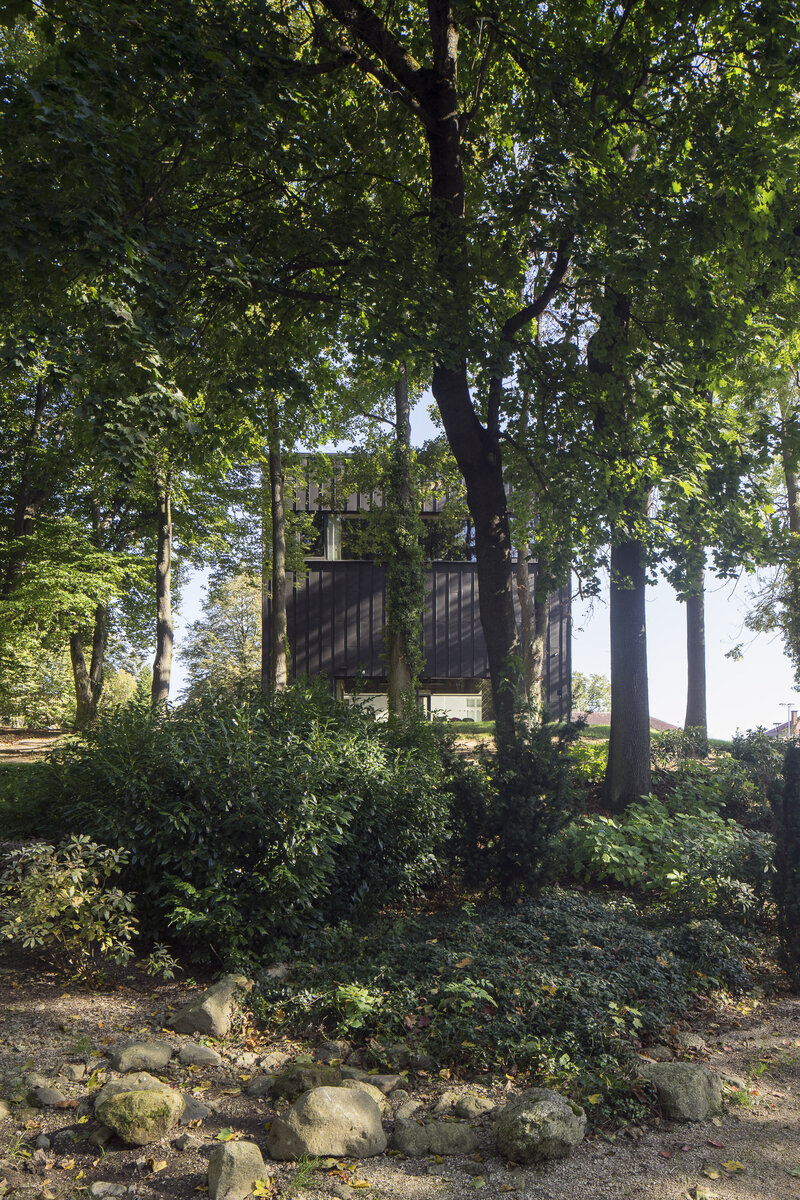
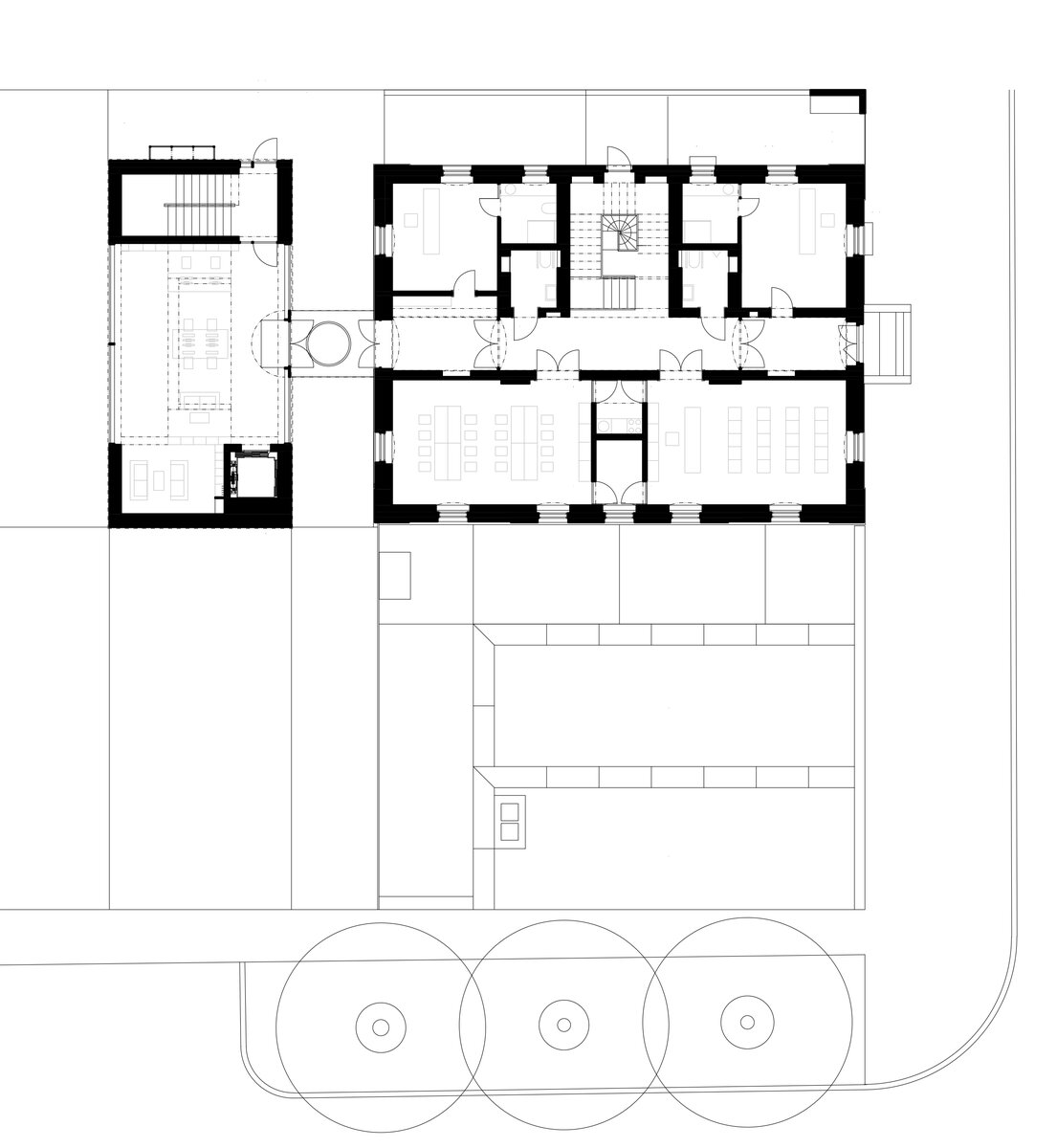
On the west side, the rectory is complemented by the contemporary-styled library structure. Both buildings are connected in the basement and also by a bridge on the first floor. Its size, shape and location are based on the context of the château garden and the rectory, as well as the tree protection zones and infrastructure network lines. The result is a building with a narrow, compact three-story upper part and a two-story basement.
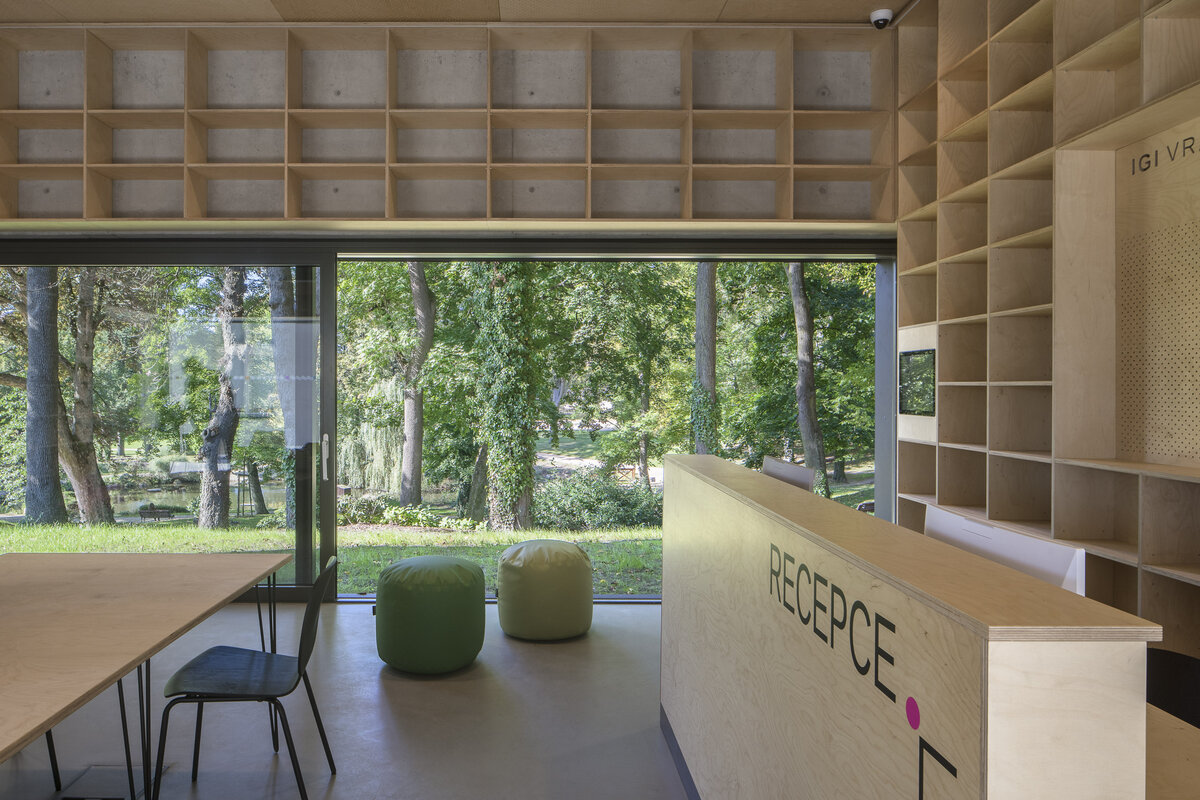
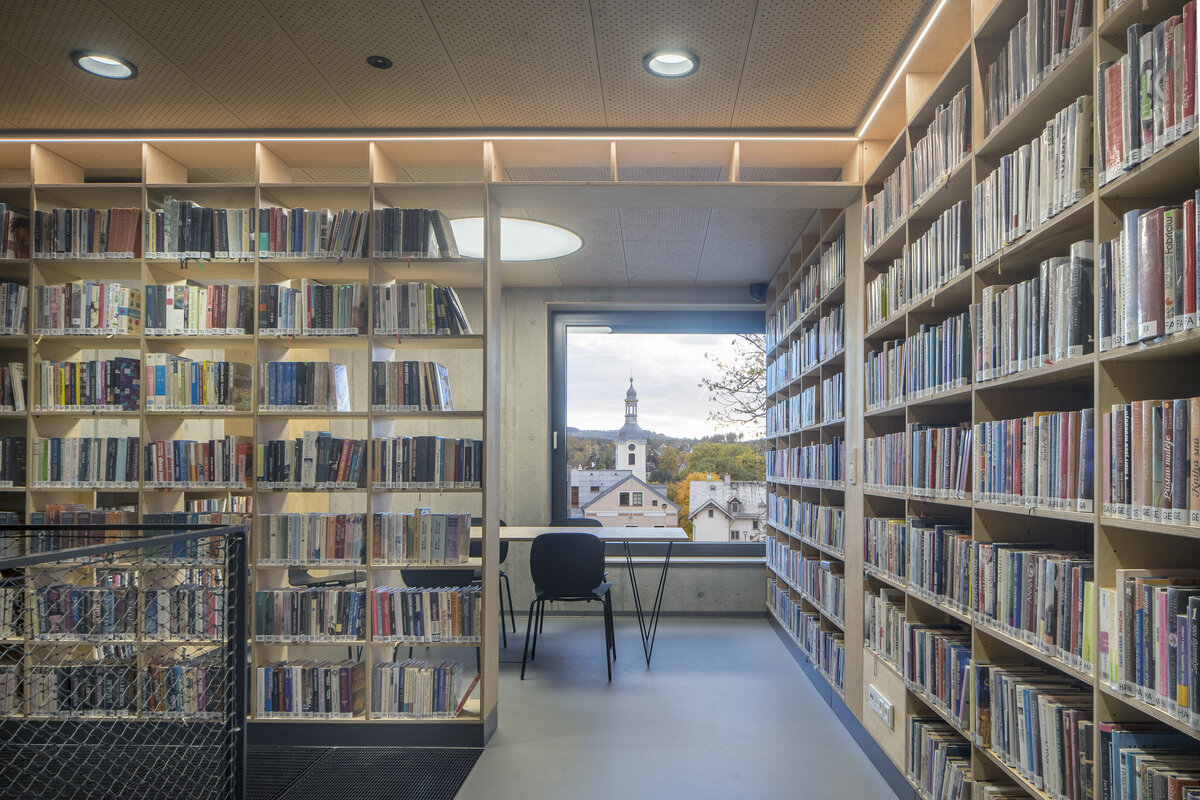
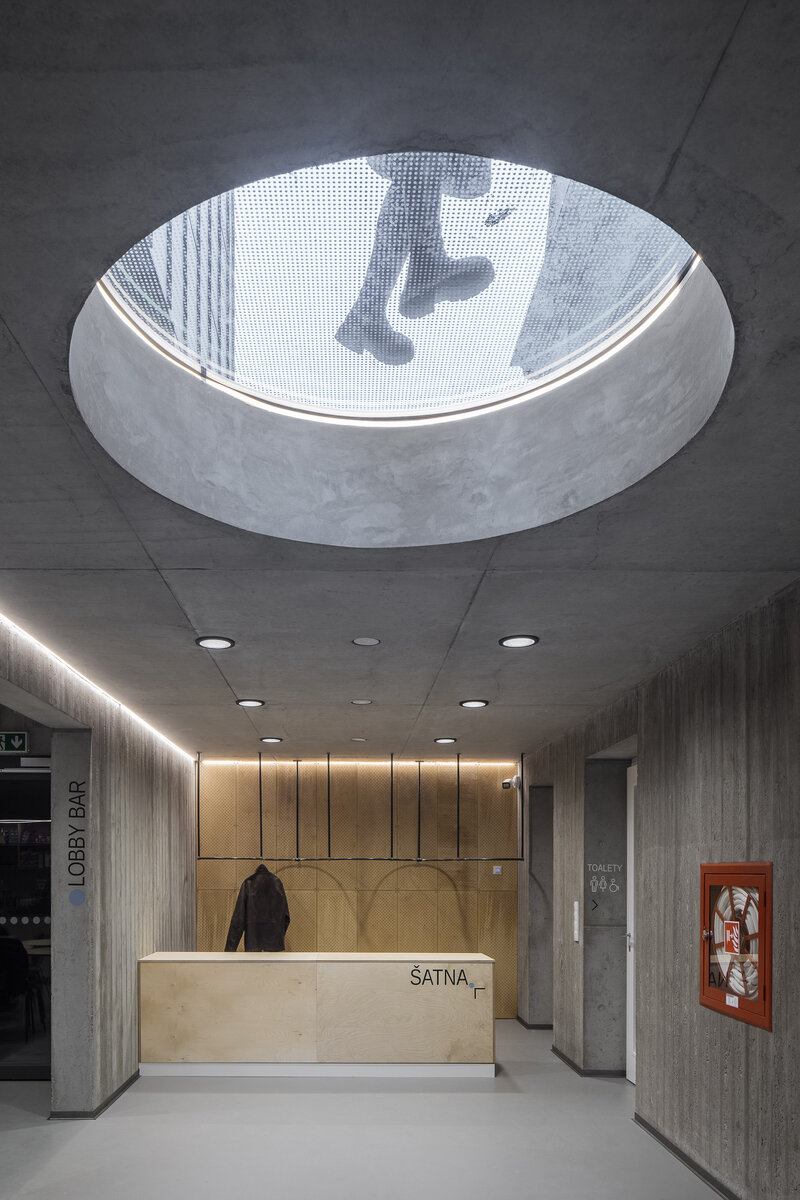
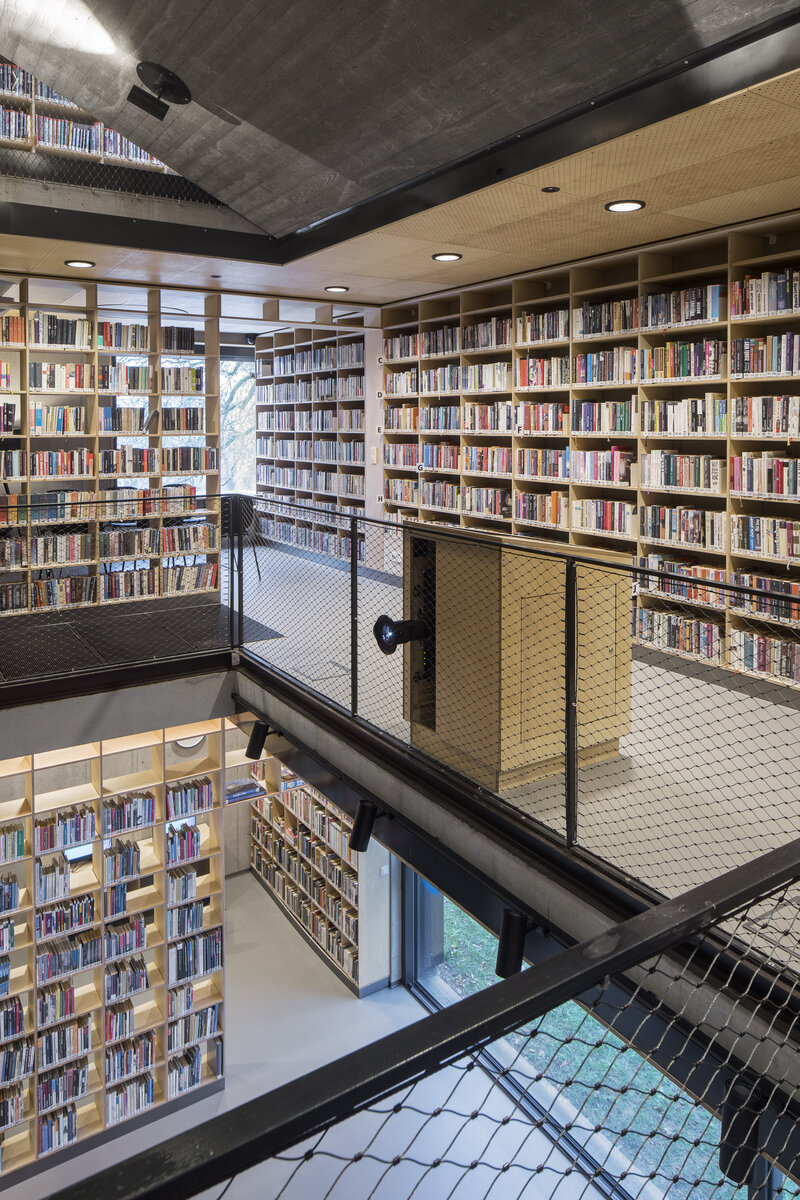
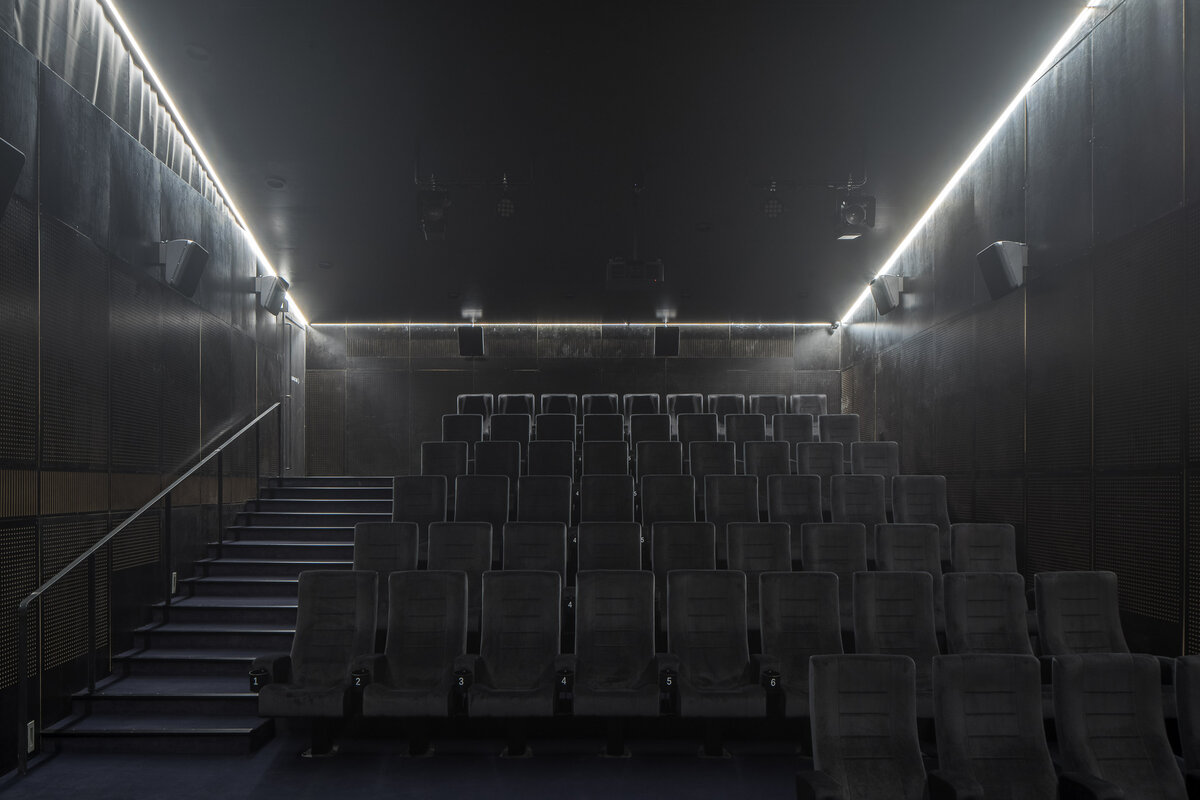
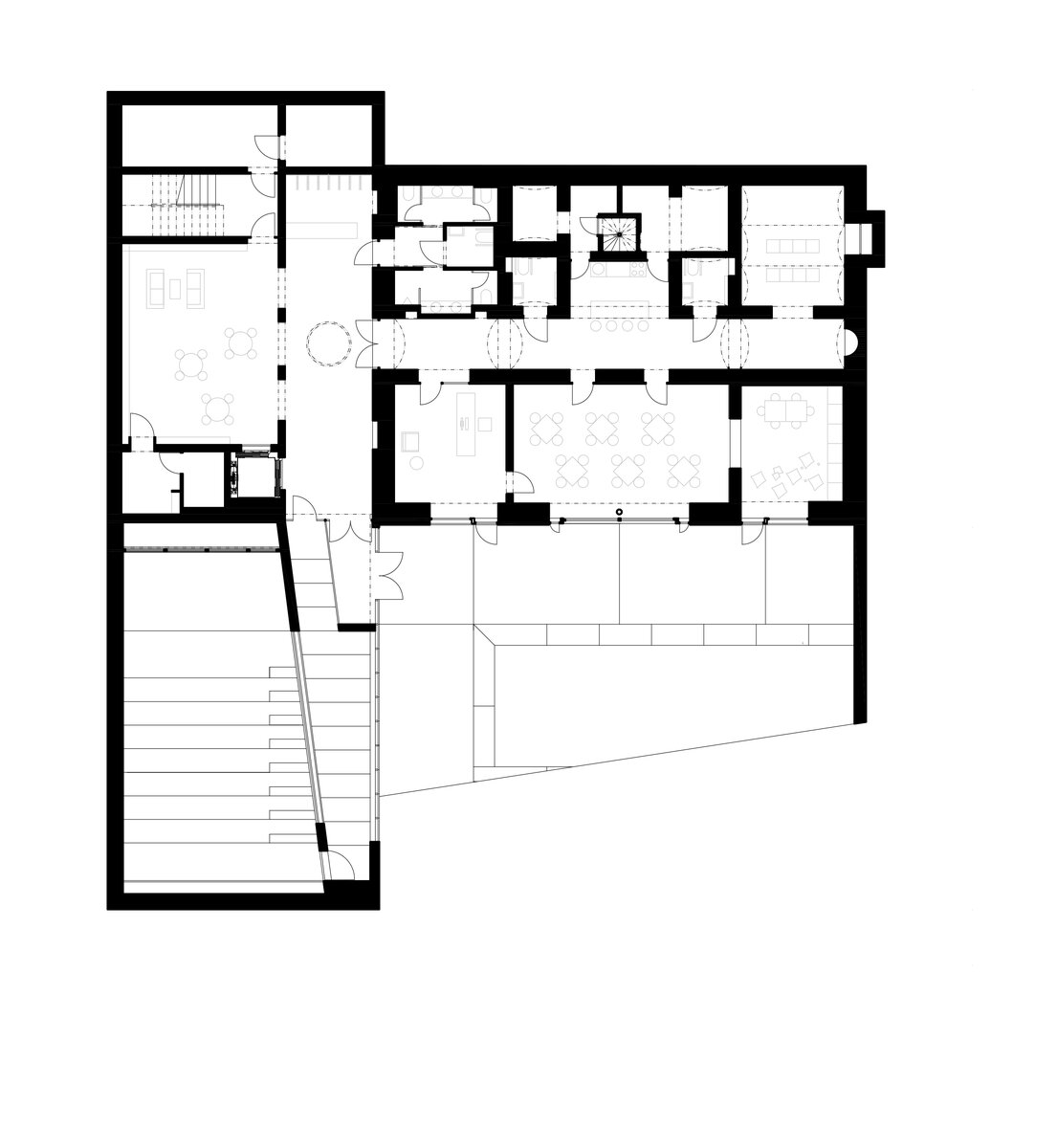
The library is integrated into the above-ground floors of the extension, whose open space principle accommodates a reception area with terrace on the ground floor, a first-floor gallery and a reading room under an arched roof. The underground floors house a multifunctional hall with a small lobby and a cloakroom in a vestibule linking the two buildings, creating a common entrance area.
Through the large glass walls on the ground and upper floors, the library makes the most out of the views of the château garden. In the reading room, the contact with trees through the panoramic window is so close that readers feel like they are sitting inside the tree crowns.
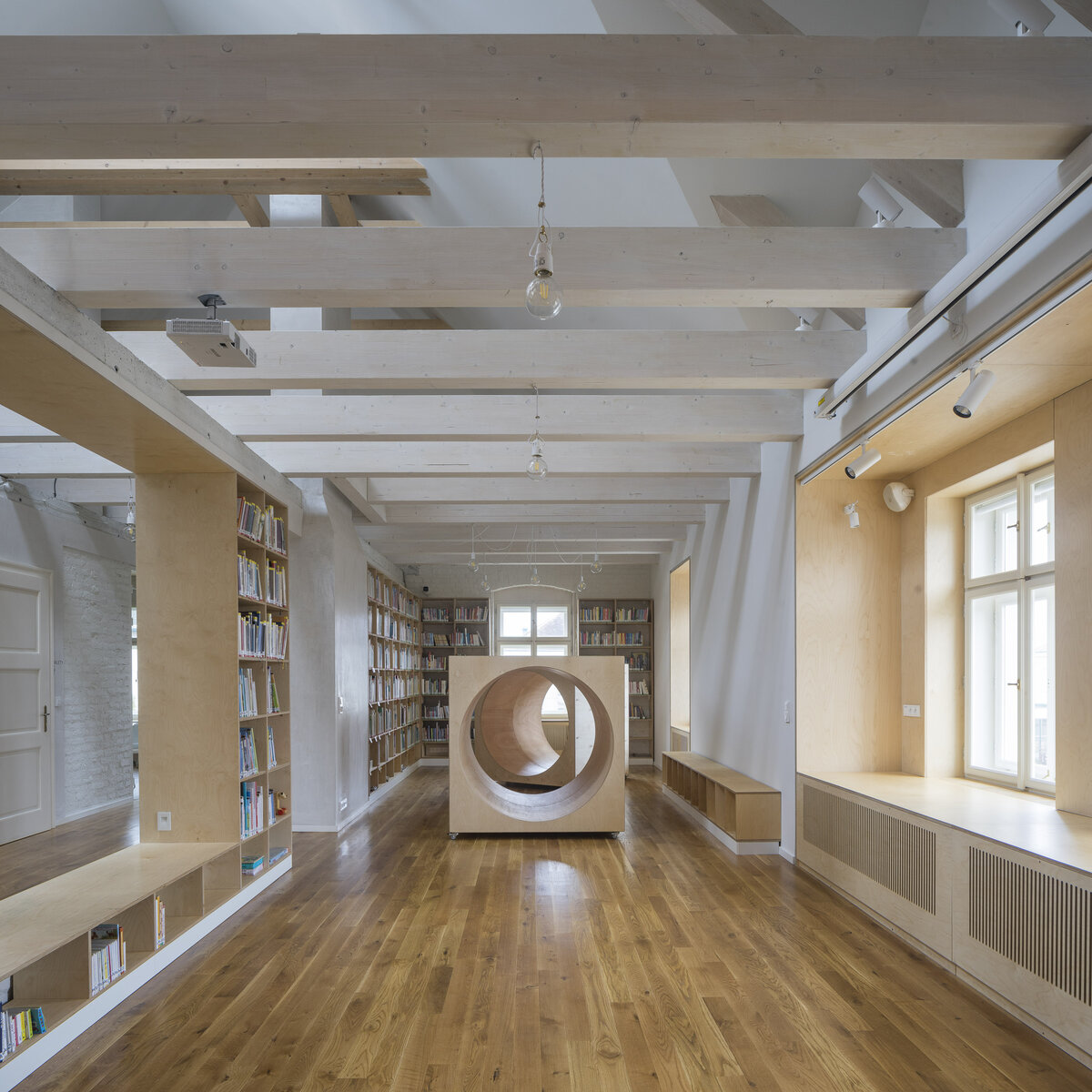
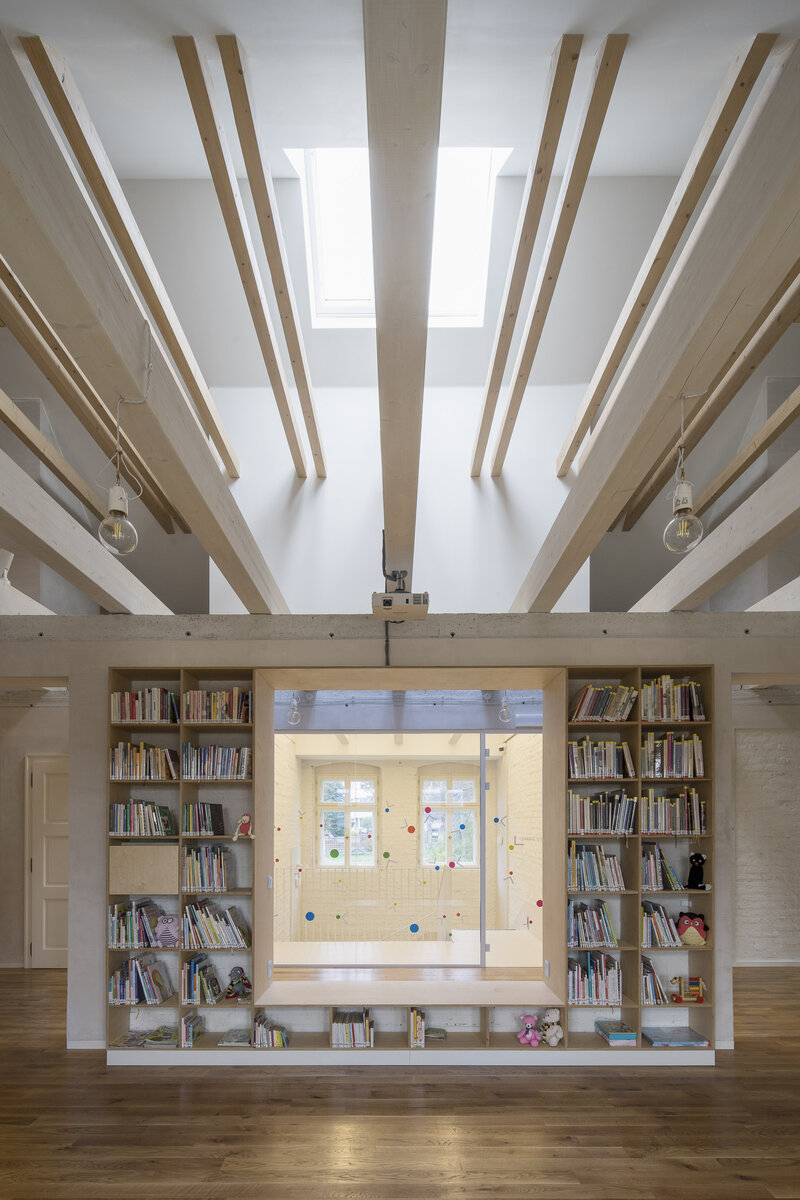
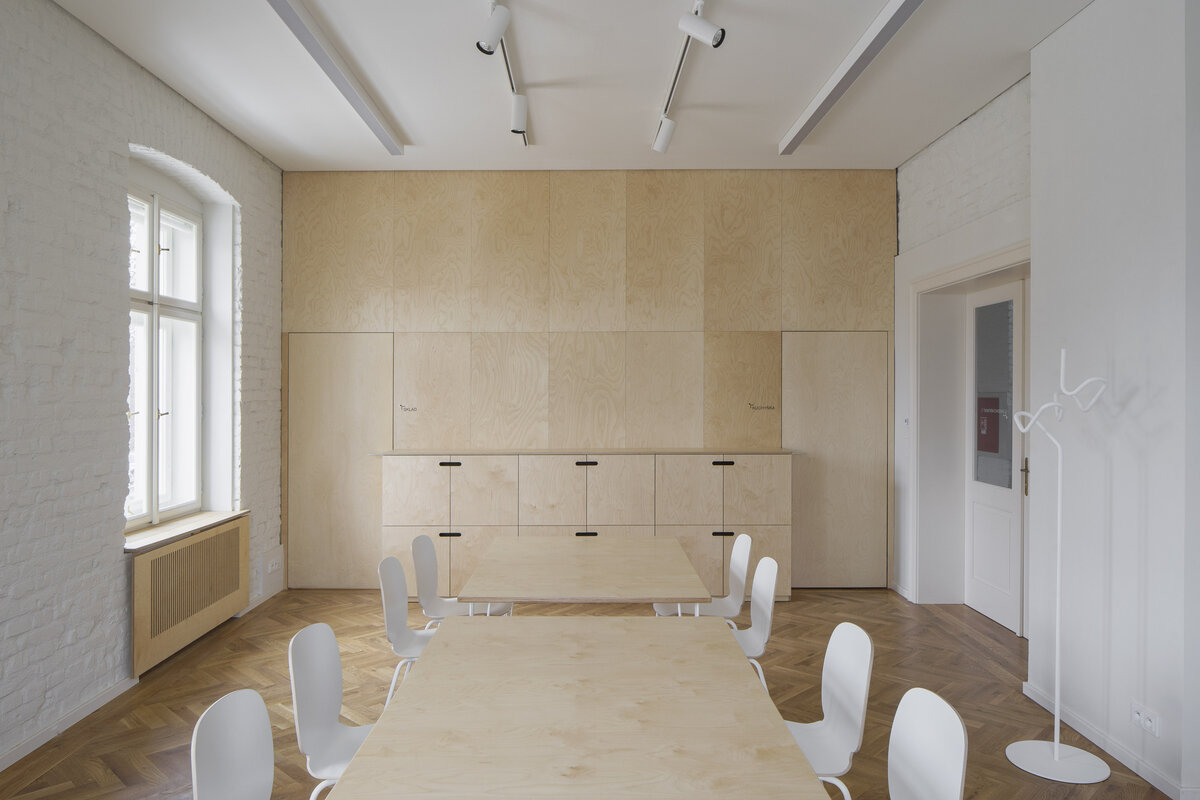
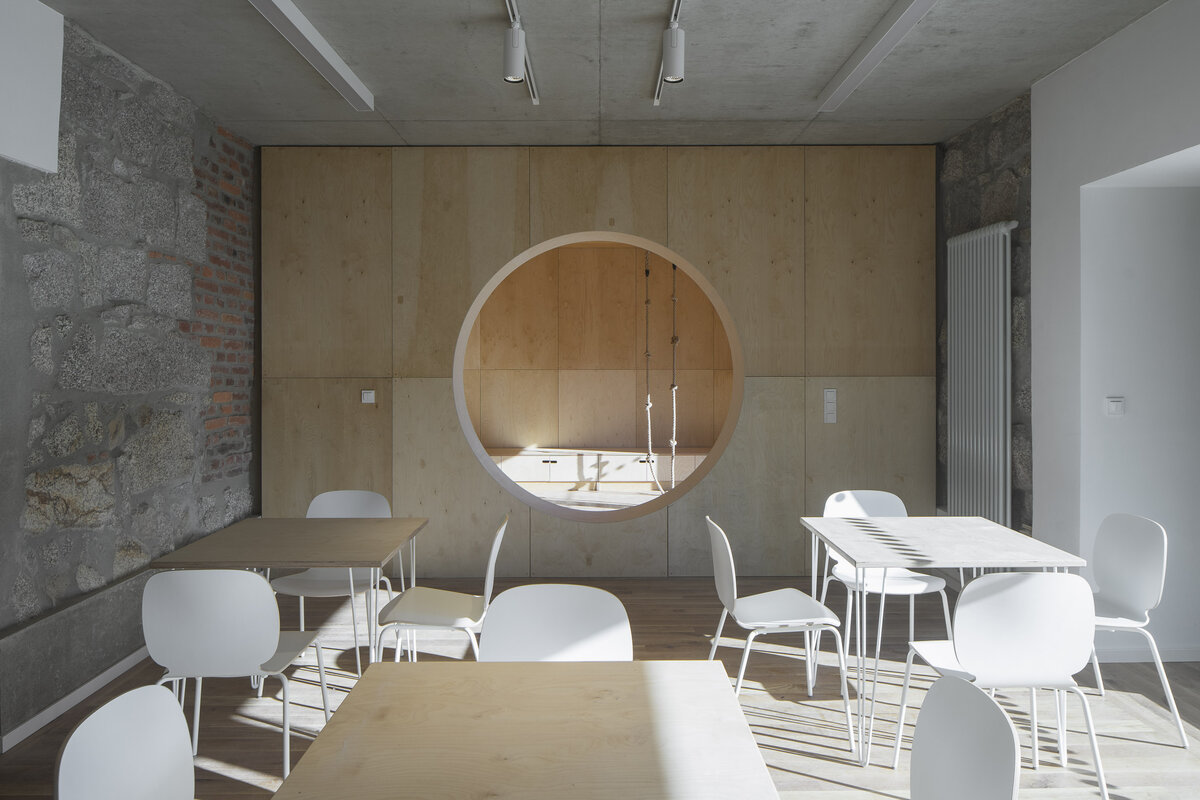
The exposed concrete and the brick and stone masonry of the interior are softly lined with wooden sedilia and bookshelves. These create all sorts of hiding places and nooks where the visitor can constantly discover something new.
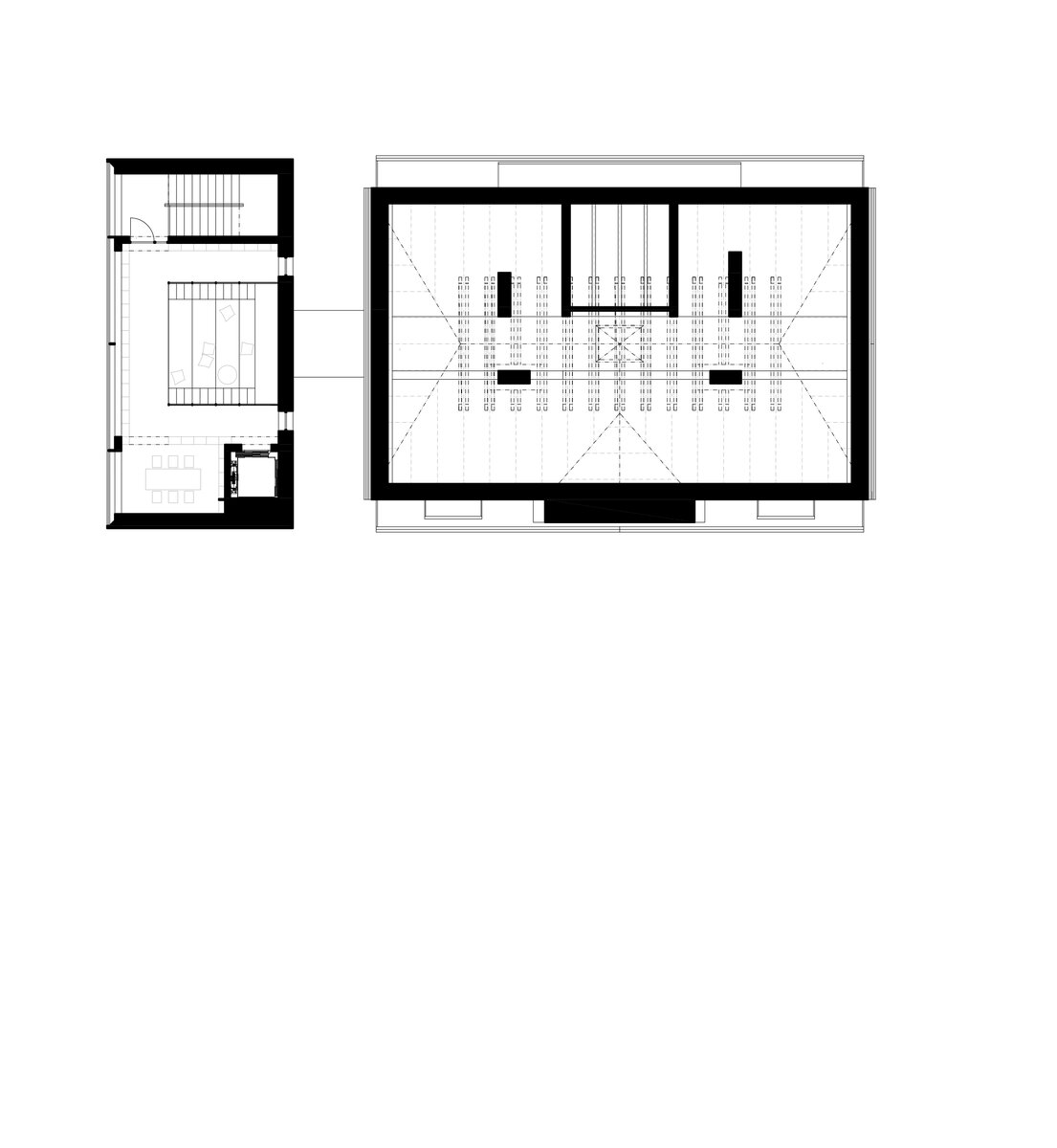
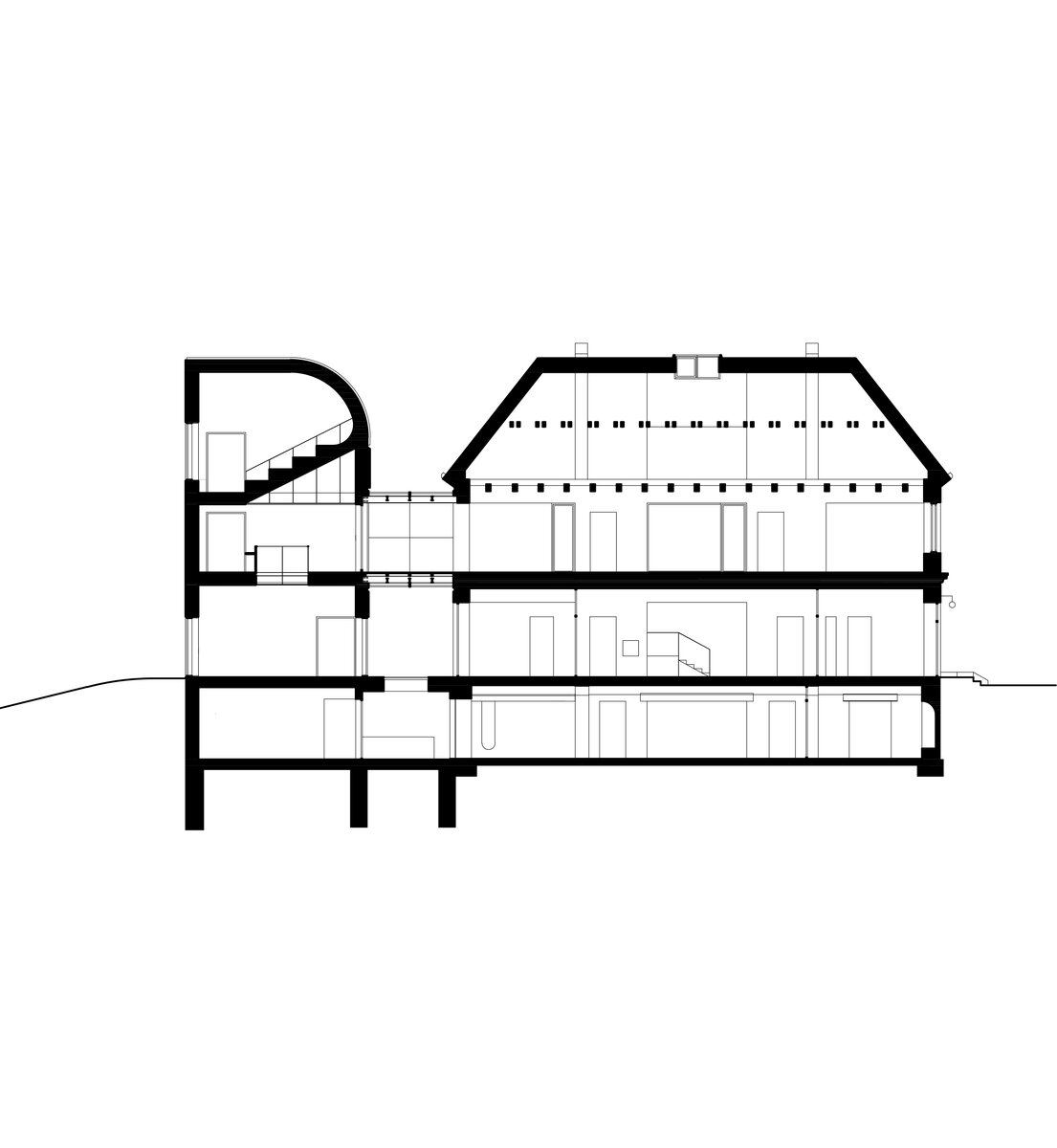
The structural system of the former rectory is made of brick masonry walls with wooden beamed ceilings. The timber trusses support a mansard roof – unfortunately, the wooden structures showed considerable signs of degradation due to high humidity and woodworm. Thus, contrary to original assumptions, no timber structures could be retained and the timber ceilings and trusses had to be removed.
The deep granite block foundations, after stripping the ground and concreting and stacking the vaults, gave rise to another usable floor, which was professionally rehabilitated after being uncovered.
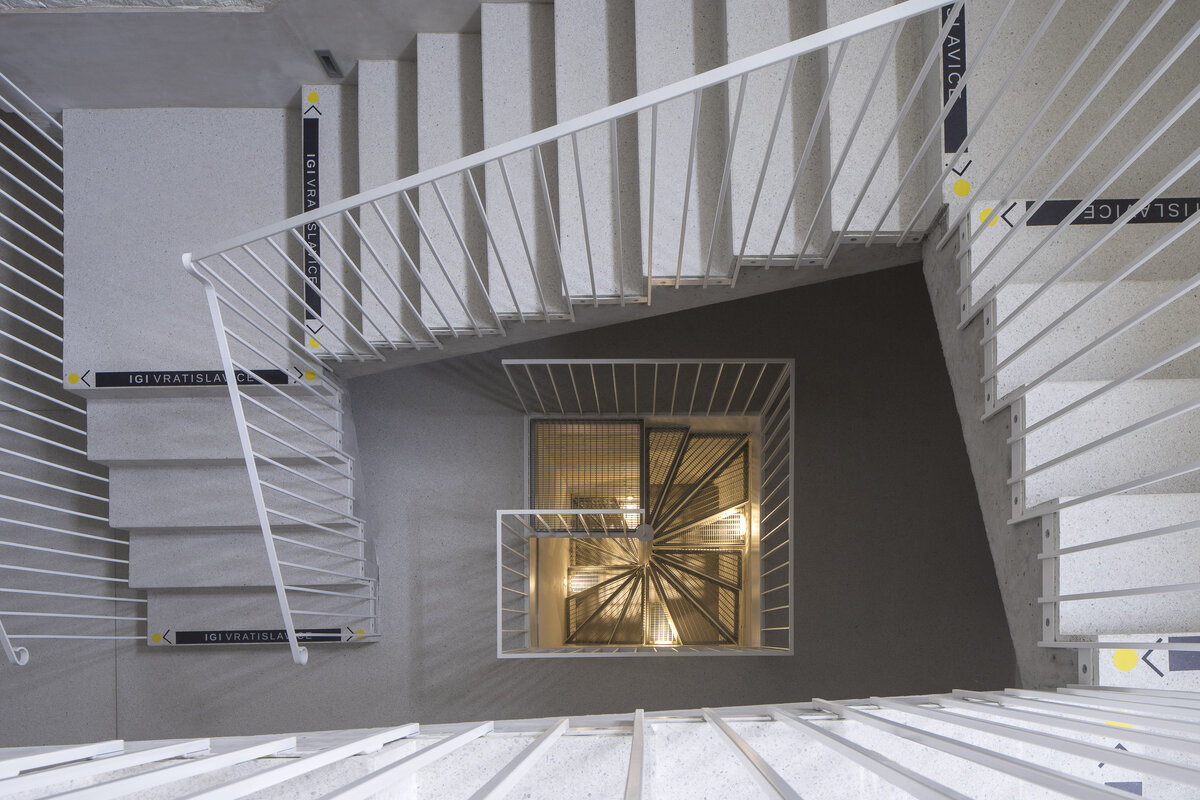
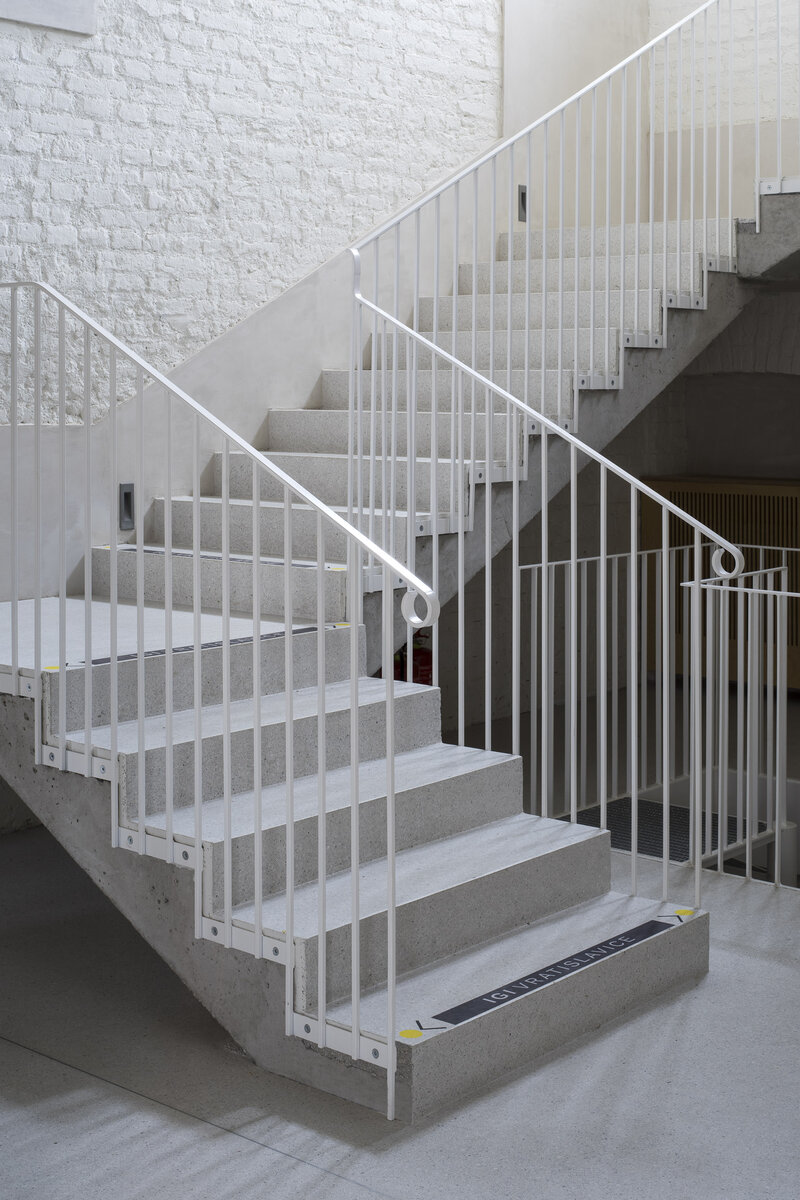
The new internal linings are made of burnt bricks, the ceiling structures are made of monolithic reinforced concrete or steel ceiling beams bonded with sheet concrete and trapezoidal sheet metal. The roof truss is replaced with a new carpentry structure that fully matches the original roof shape and is covered with natural slate templates. The building has two new internal staircases – the lower one is a steel spiral staircase with wrought metal spindles, the upper one is a four-arm staircase made of reinforced concrete monolithic plates.
While the internal layout of the house must have been significantly affected, the building envelope has been preserved almost unaltered. Insensitive deposits have been removed from the facades and, after insulation, they have been restored with historic features and details, brizolite plaster, wooden doors and copies of the casement windows.
The entire structure of the extension, including the foundations, is made of monolithic reinforced concrete. The exterior is completely contact insulated and wrapped with black folded sheet metal. The windows and glazed walls are set in minimalist aluminum frames, the connecting bridge between the buildings is designed as a prefabricated steel structure, sheathed with an isolating double glazing. The external retaining walls defining the new piazzetta are made of monolithic reinforced concrete.
The interior of the extension and the existing building retains exposed concrete, brick and stonework masonry. Plywood tiles are used in the interior and they were also used to make the library furniture.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
B
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|