| Author |
Jyrki Tasa / ARKKITEHDIT NRT; LOXIA Architectes Ingenierie s.r.o. |
| Studio |
|
| Location |
Laponská 1160/4, Praha 9 – Hloubětín |
| Investor |
YIT Stavo s.r.o. |
| Supplier |
GEMO a.s. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
February 2022 |
| Fotograf |
|
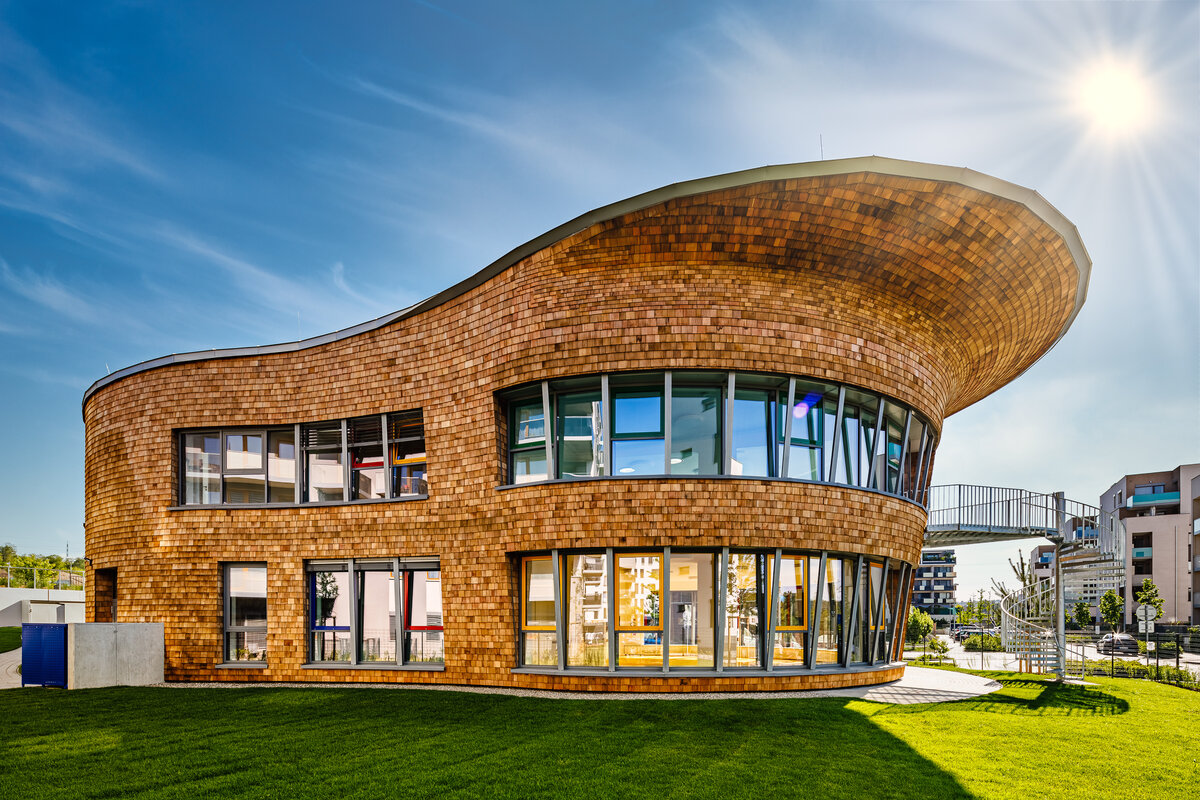
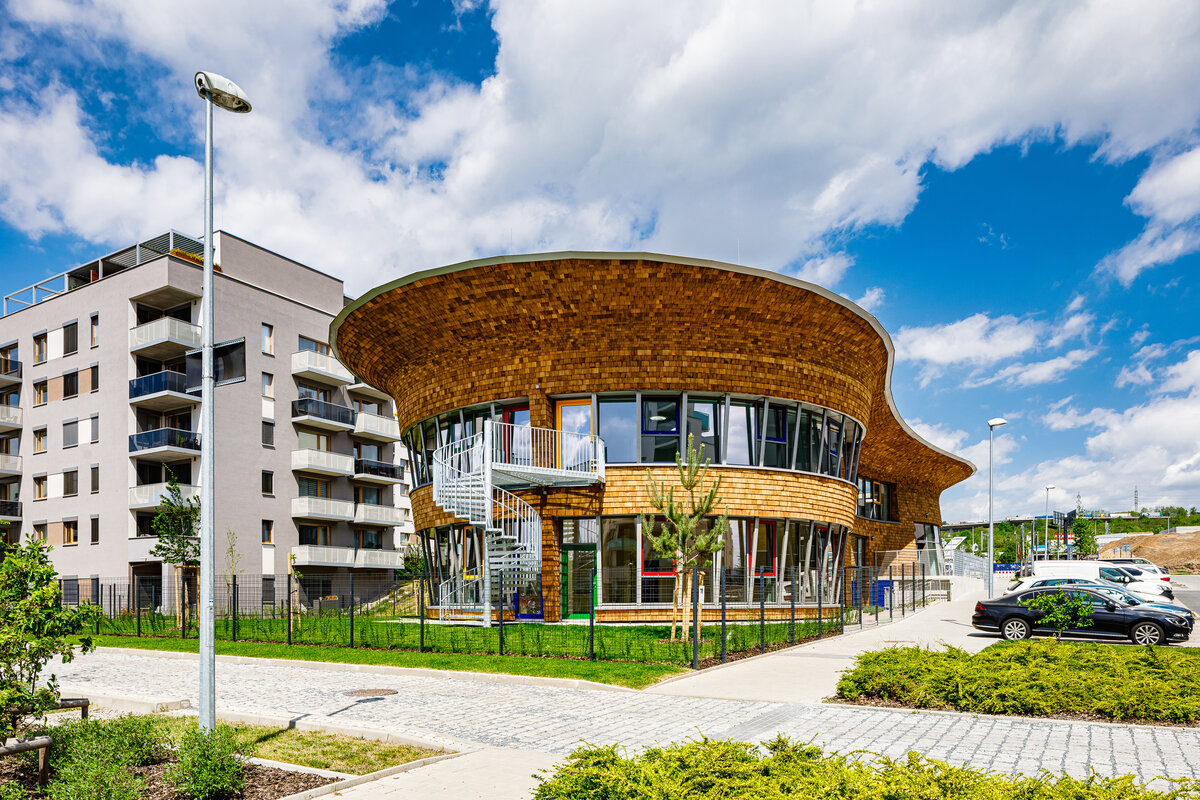
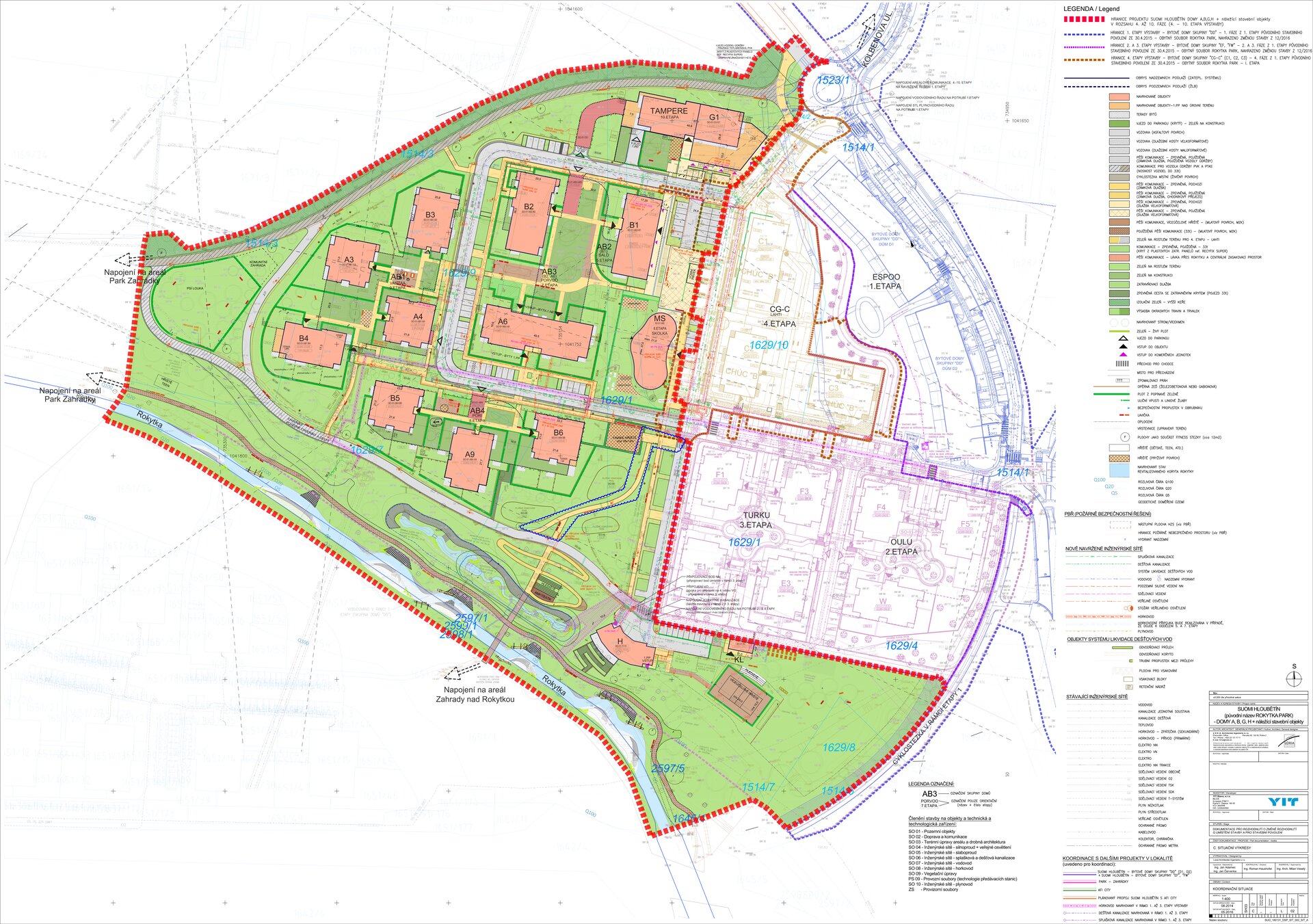
The new preschool, which will take up to about 100 children, is located in the very heart of the Suomi Hloubětín residential neighbourhood. The house itself represents a statue and is connected to the built square. The preschool should become the centre of activities and public events in the locality and its recognisable feature. The main purpose is to enrich the civic amenities of the expansive Suomi Hloubětín project. It is also the first preschool ever built by YIT Stavo.
The original architectural design and the use of imaginative materials highlights the Nordic style of construction. The renowned Finnish architect and professor Jyrki Tasa, a holder of many architectural awards, was behind its elegant design. His intention was for unusual shapes, an atypical structure and surprising details in childlike ideas to present a fairy tale that will be different every day. The preschool in Suomi Hloubětín is also characterised by the use of high-quality natural materials.
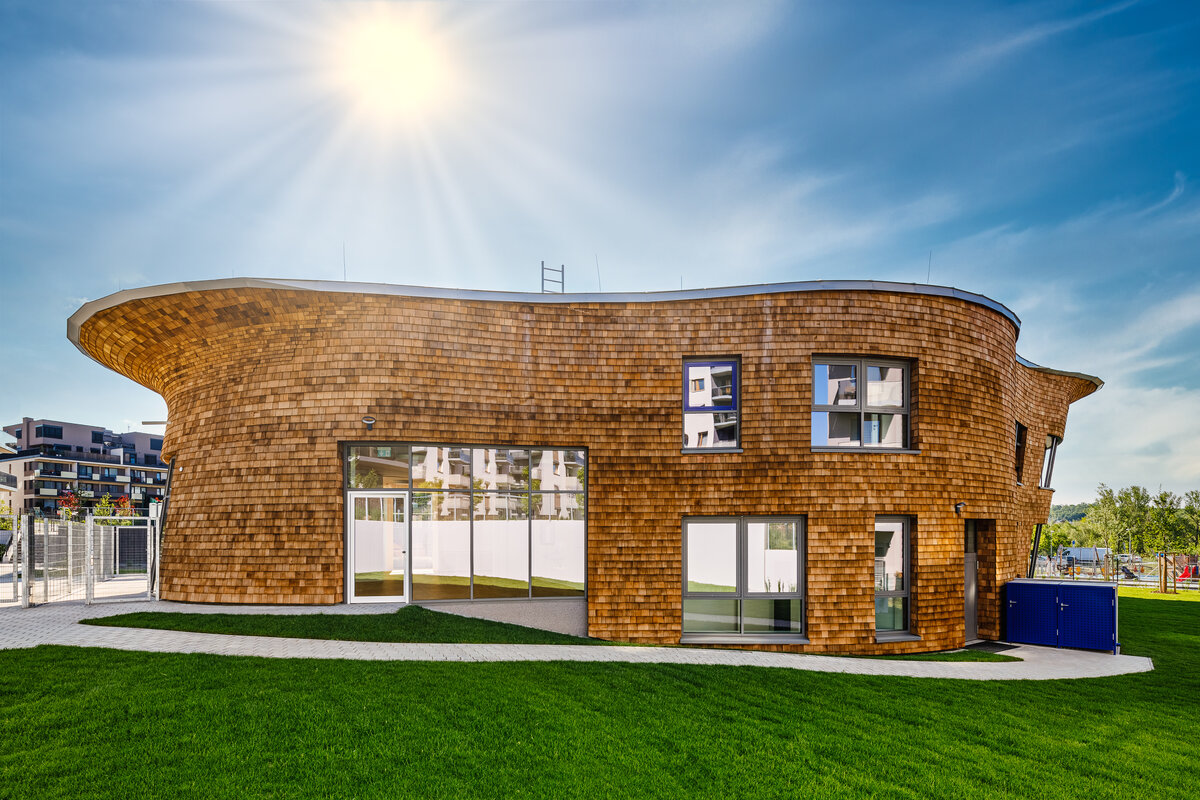
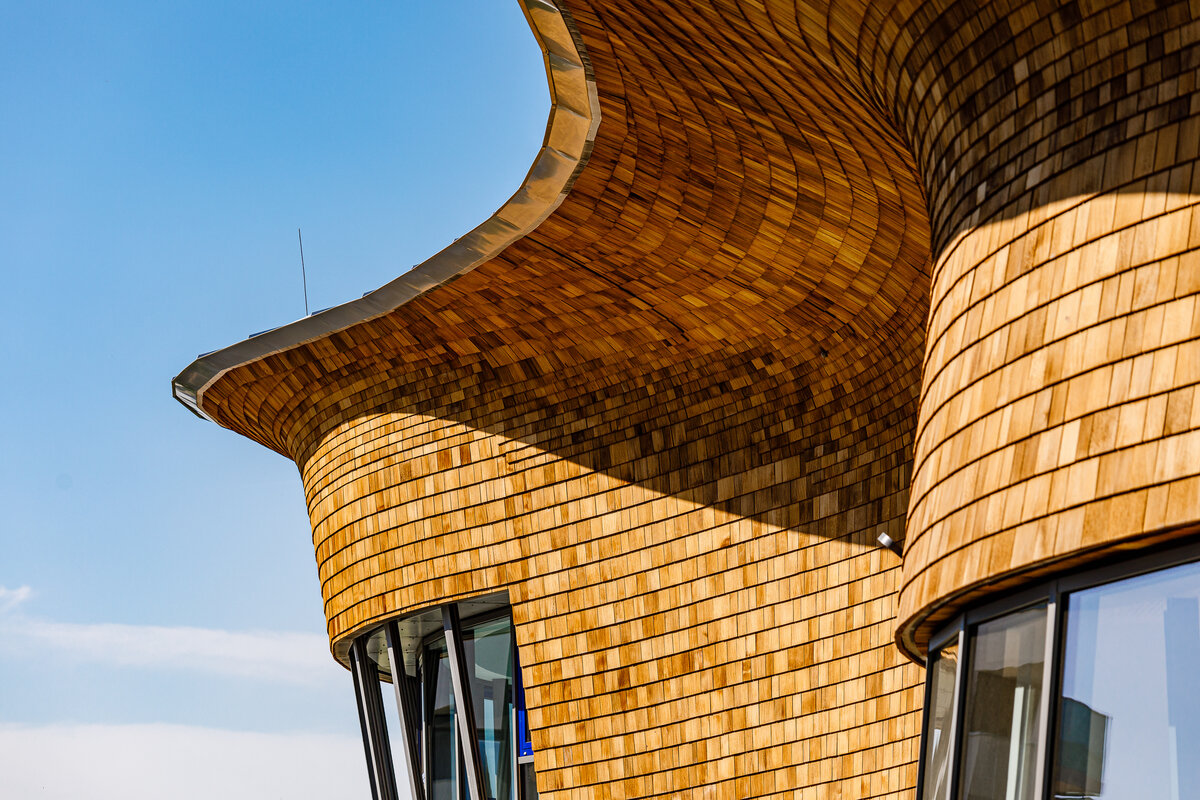
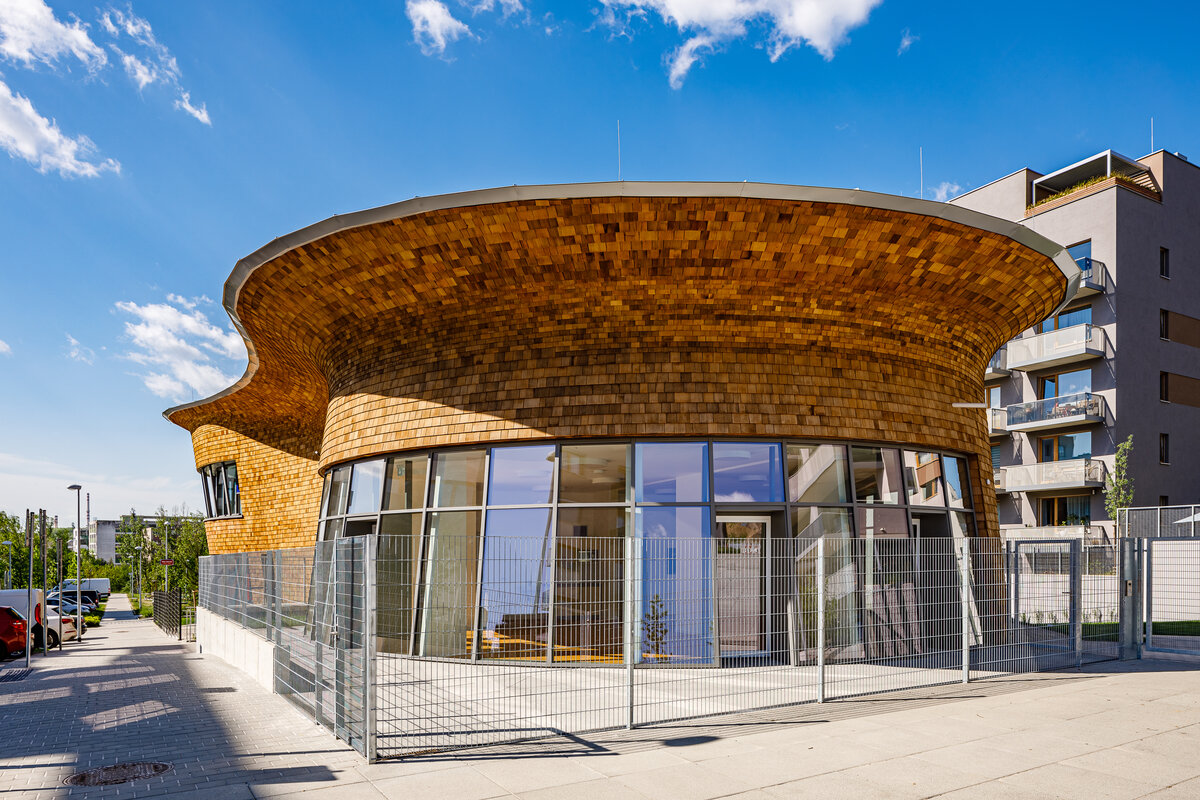
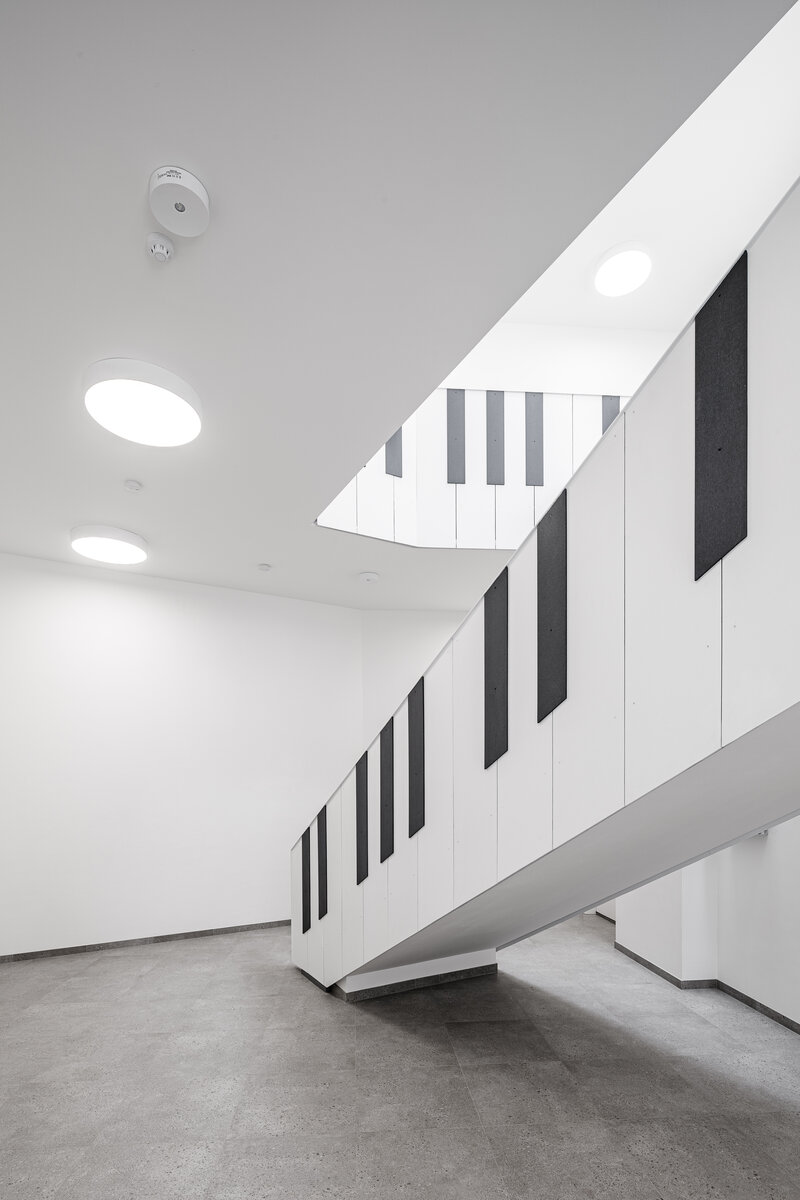
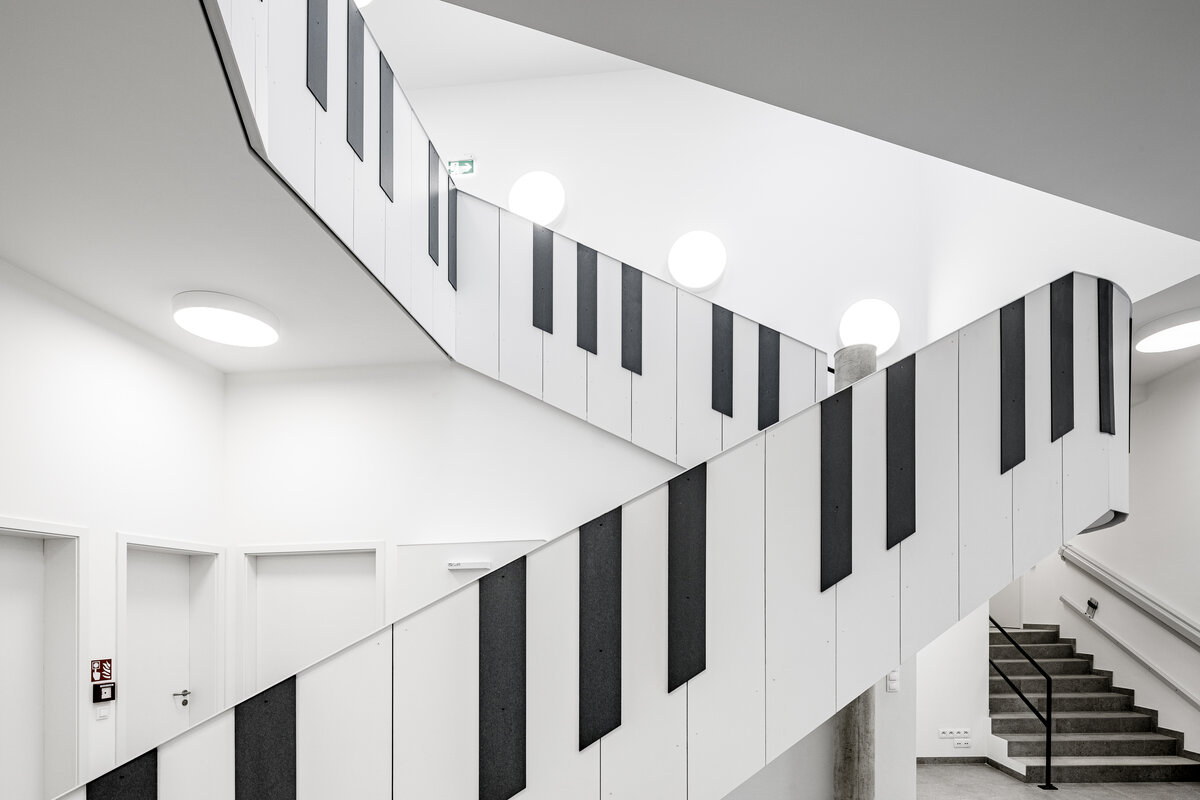
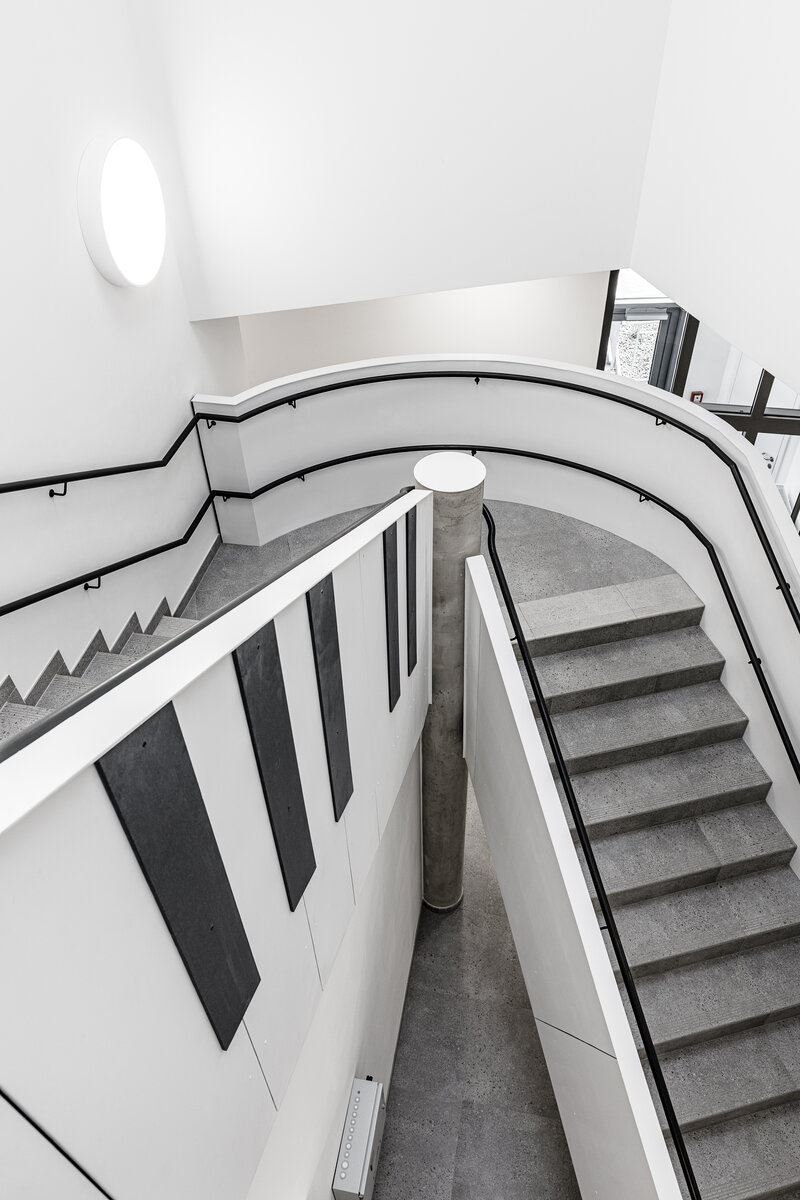
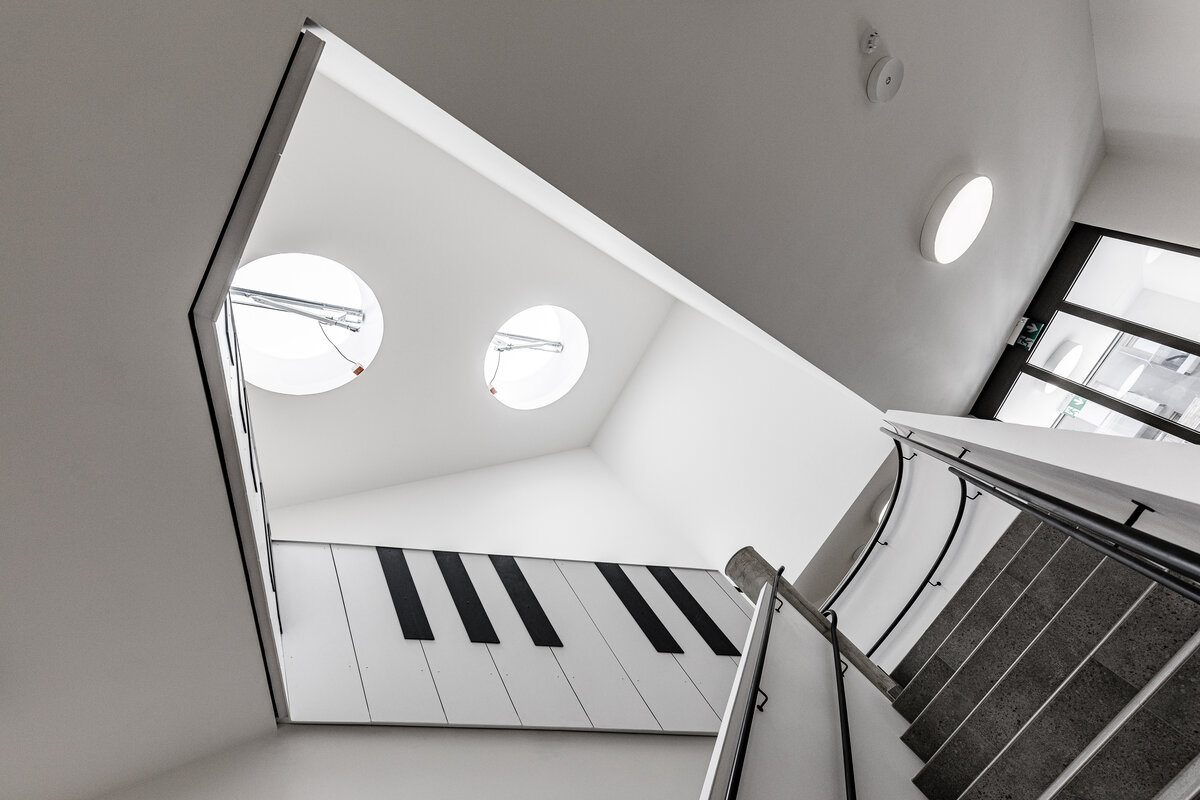
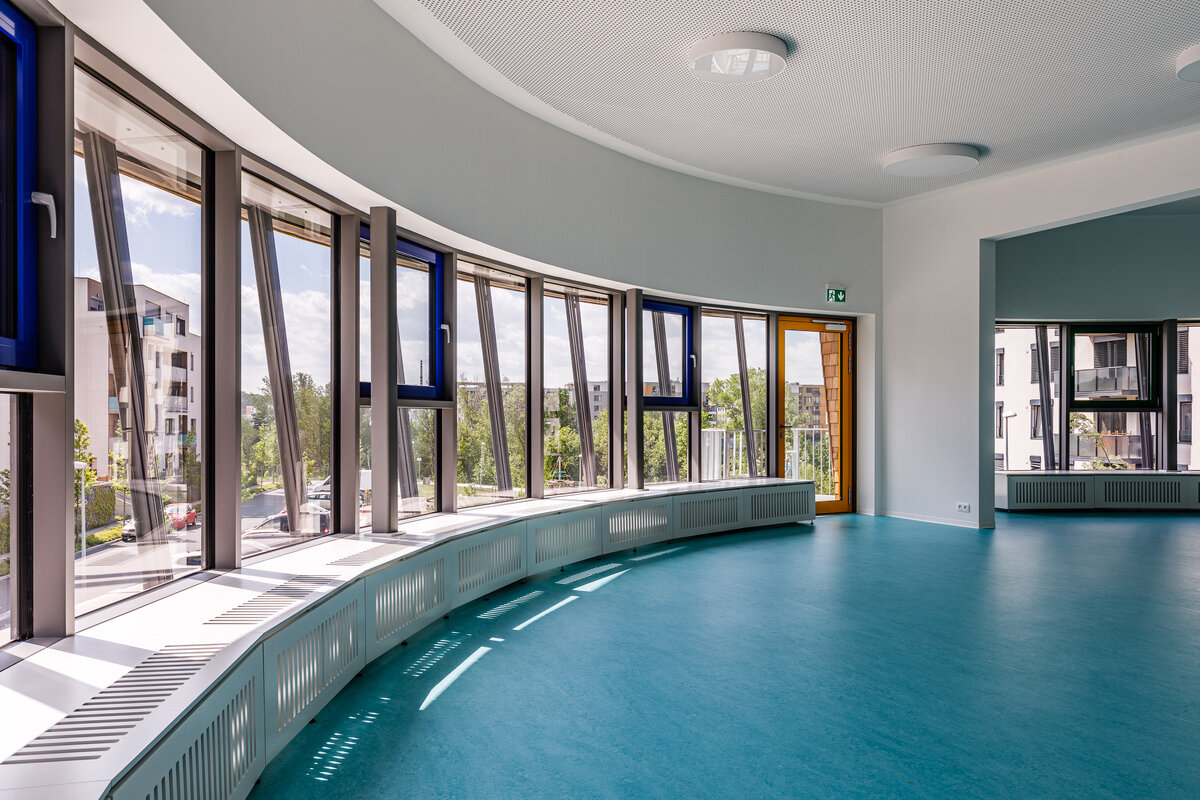
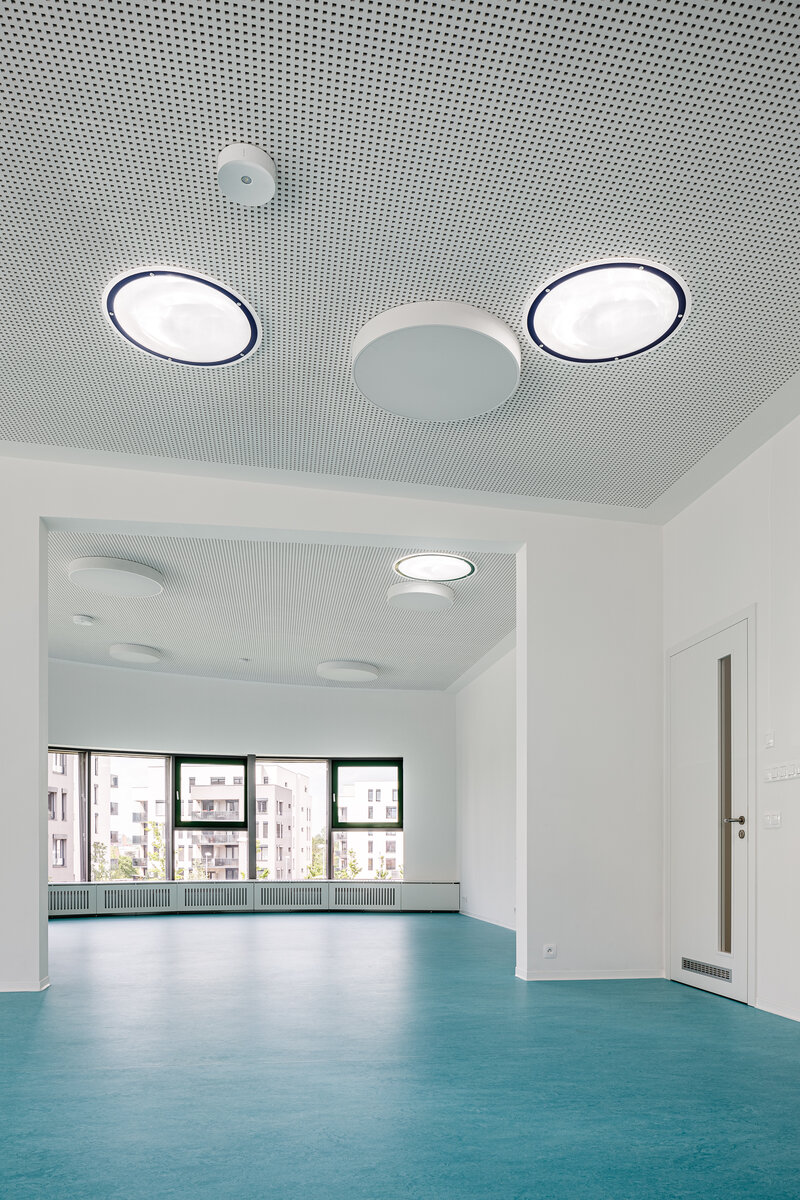
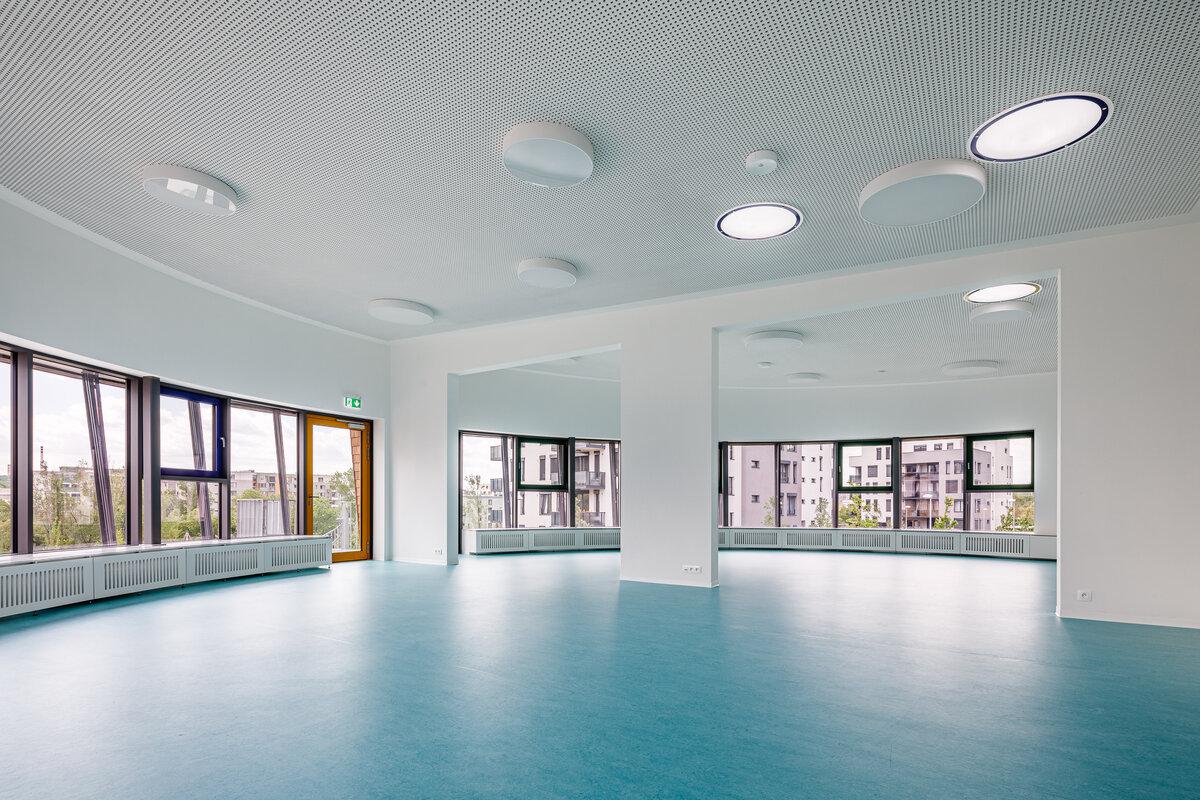
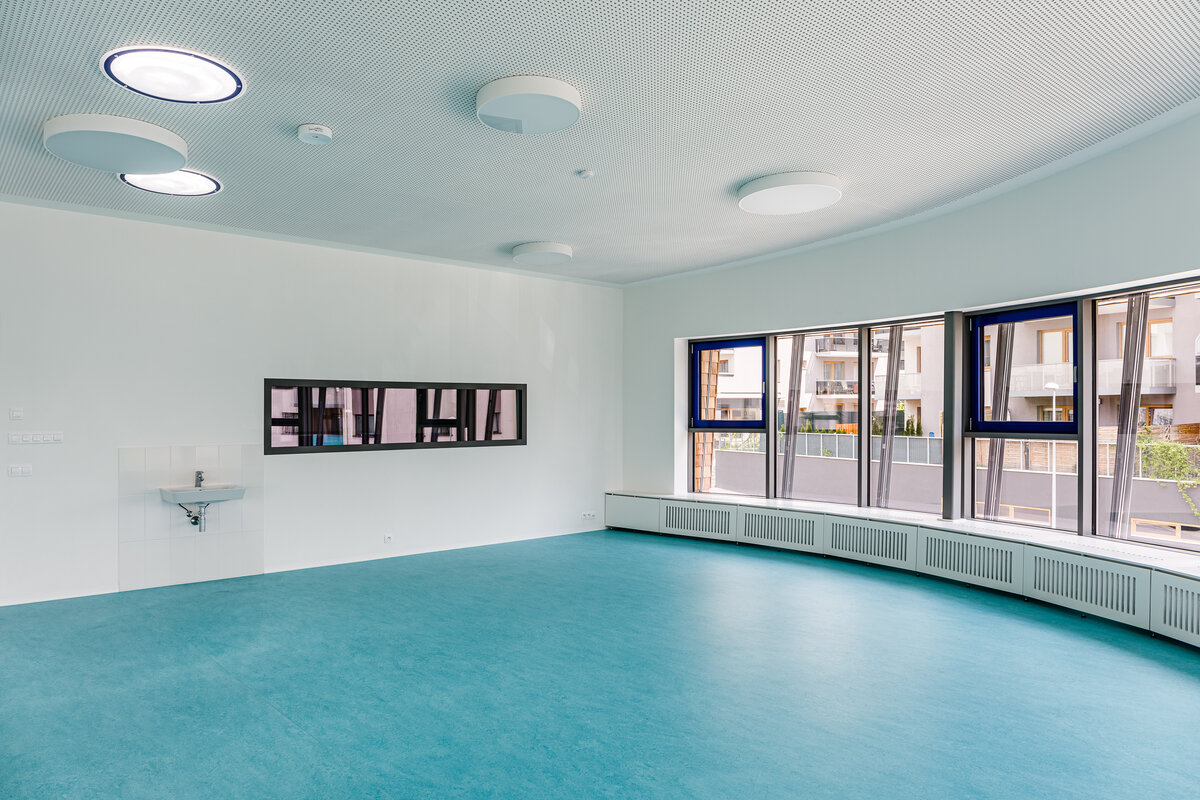
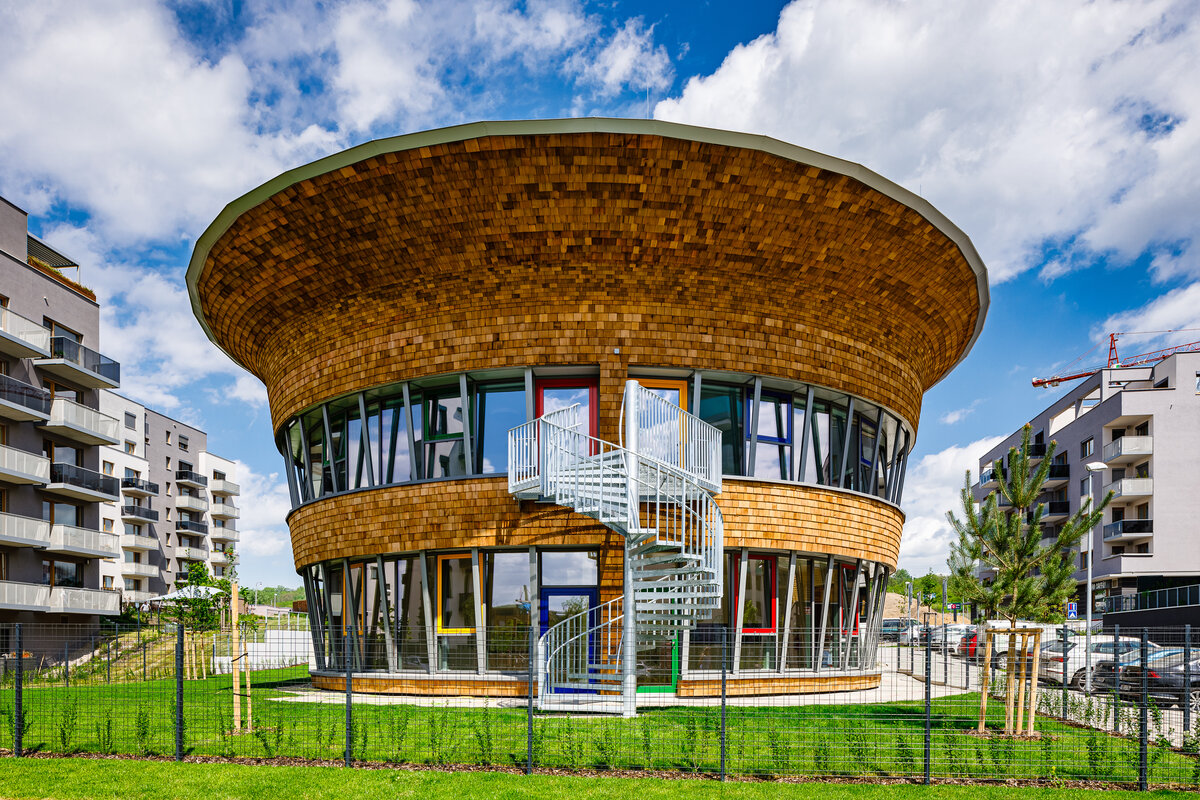
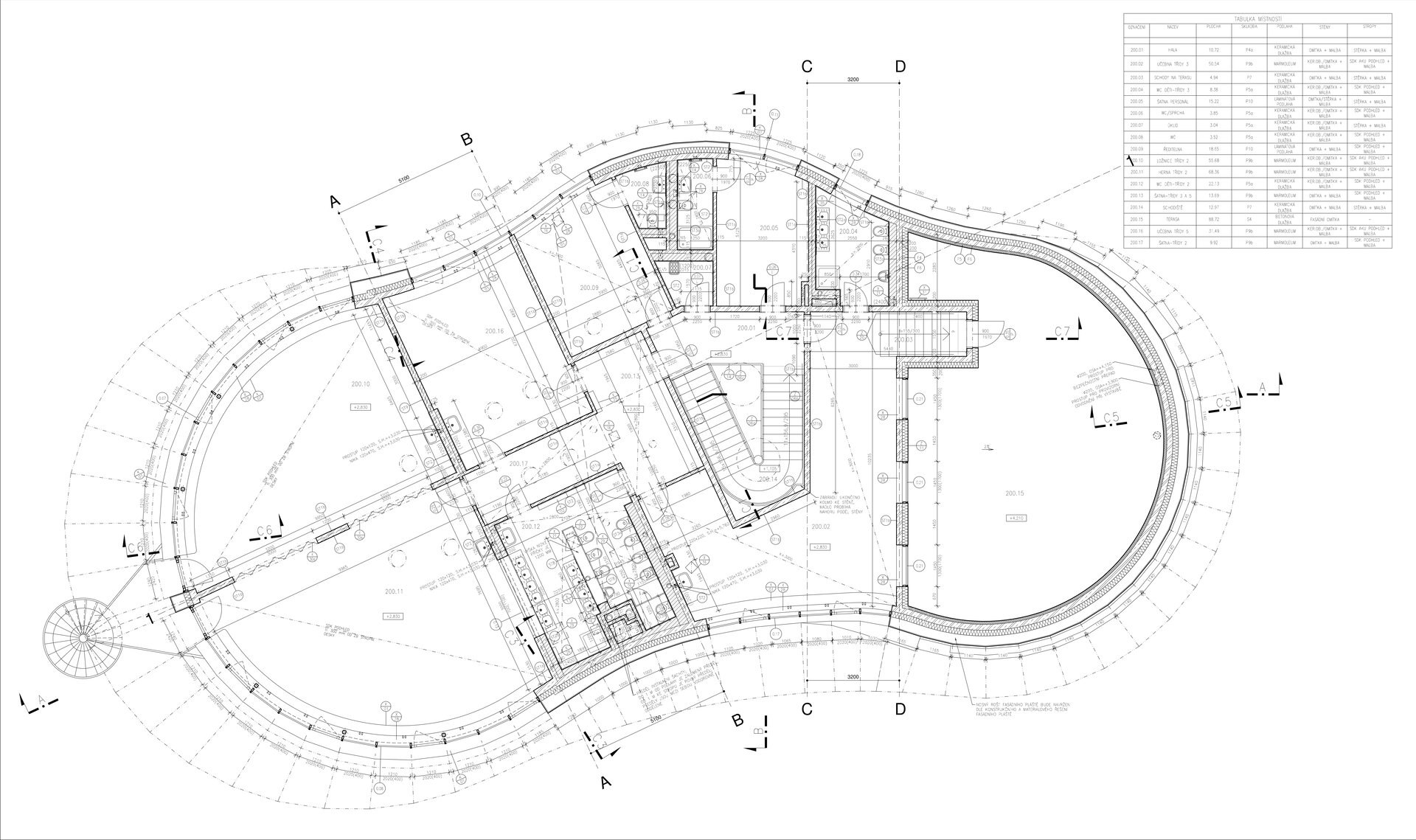
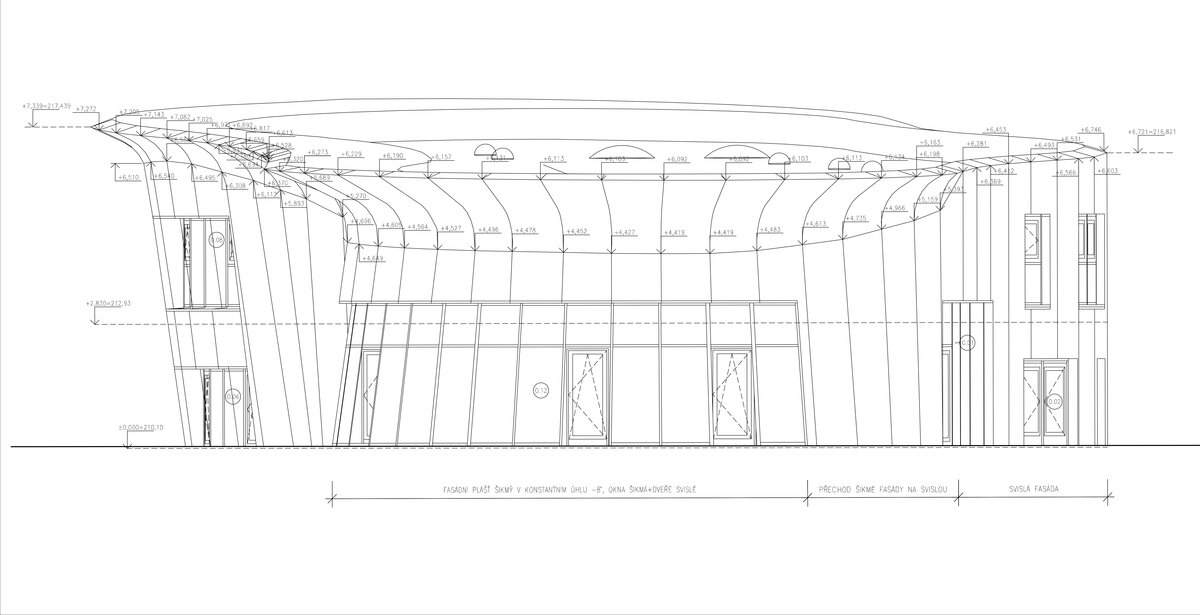
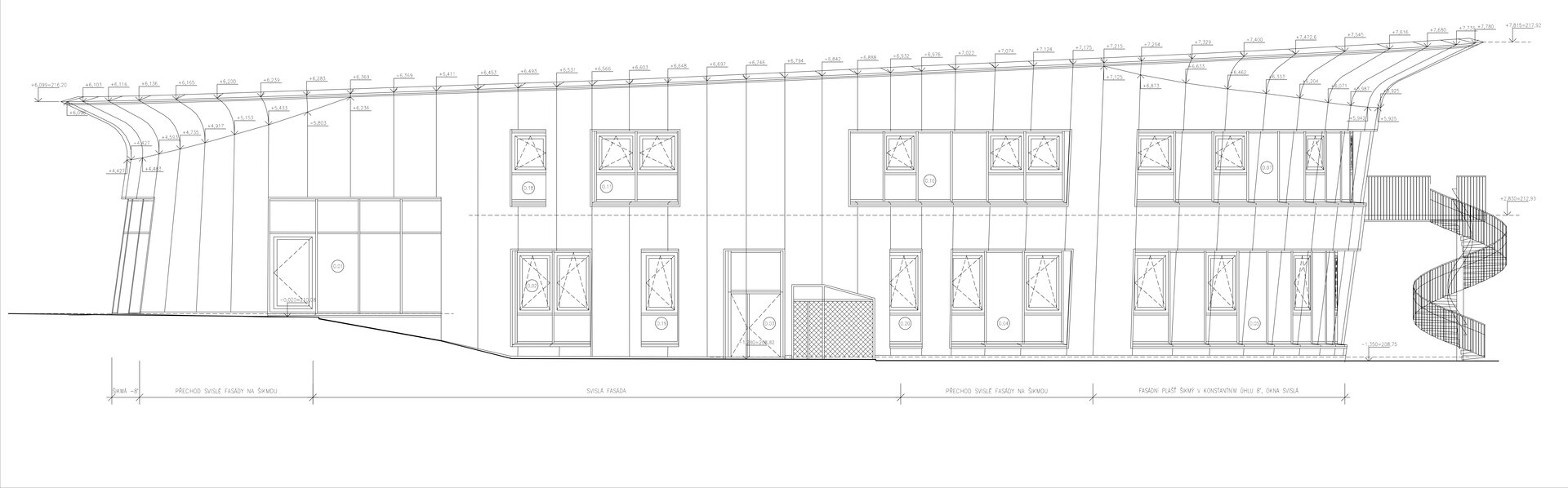
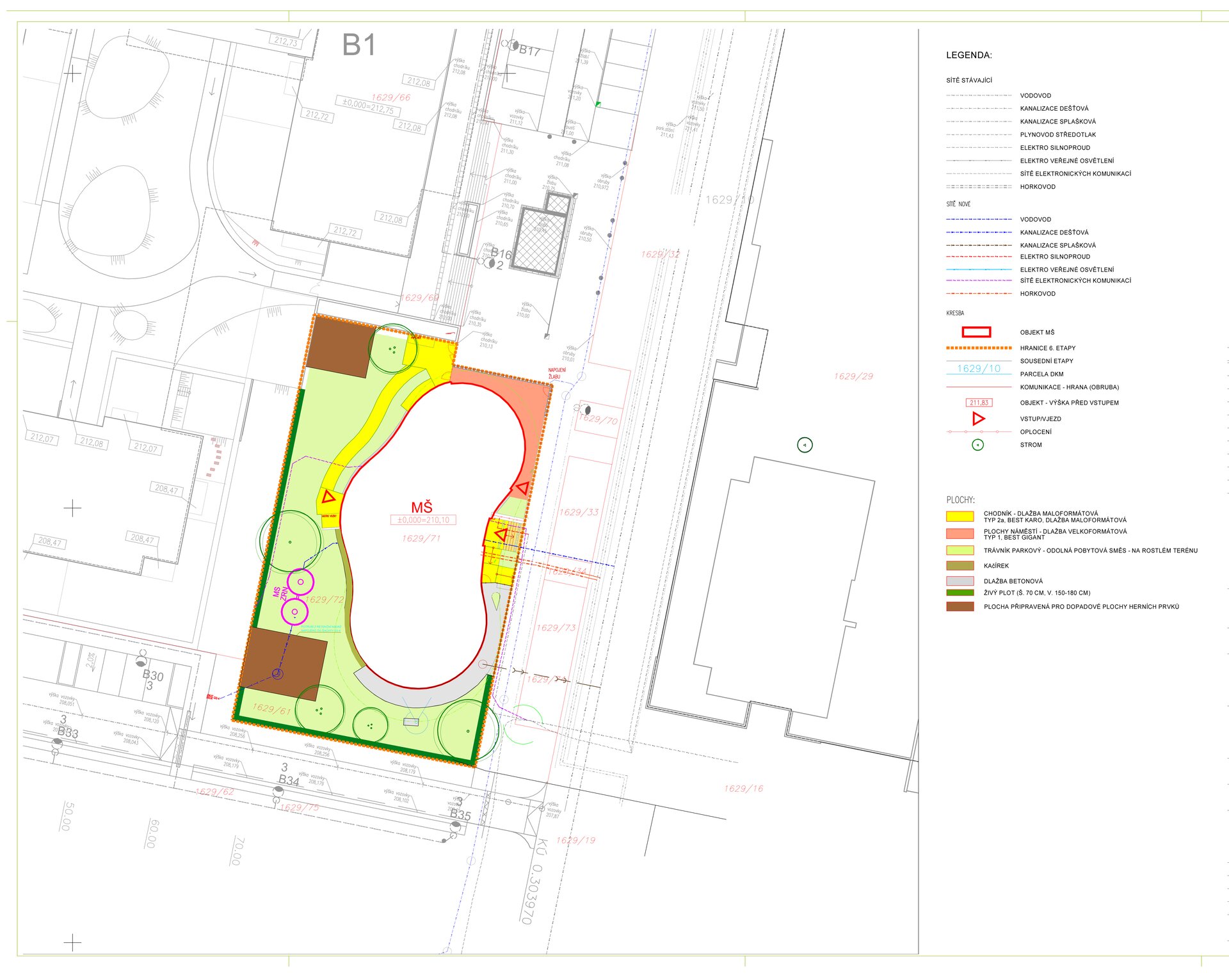
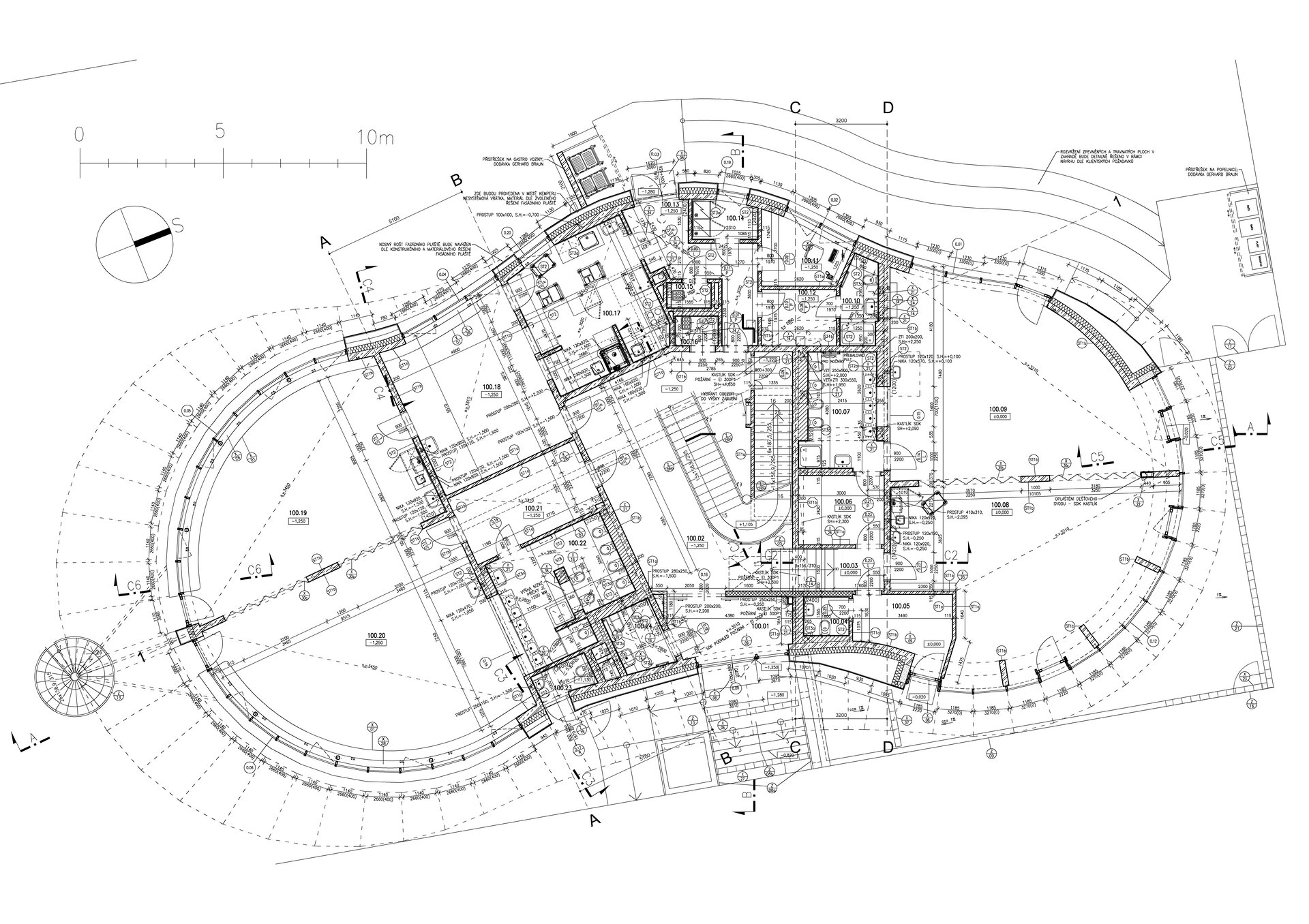
The organic geometry of the building is strikingly reminiscent of a mushroom. The façade is made of wooden shingles made of red cedar in combination with aluminium cladding. The railings of the central staircase conceived as a piano keyboard became the dominant element of the interior. An abundance of natural light is ensured not only by the large number of the building’s windows, but also the round roof window and sun tunnels. The rooms are also equipped with acoustic ceilings. The Marmoleum floors will ensure heat and sensory comfort, as well as easy maintenance. A section for children up to the age of 3 years with its own entrance is situated towards the north, while the play rooms face south. There is a spacious terrace on the second floor.
The children also have a large yard available and the preschool is also adjacent to a public park with a children's playground, from which it is only a short walk to the trail along the Rokytka Stream. In addition, YIT carried out a revitalisation of part of the stream in close cooperation with the Environmental Department of Prague City Hall in the framework of the construction of the Suomi Hloubětín residential complex. In accordance with the low-impact development concept of YIT Stavo, a system of rainwater retention was also built in the concept landscape with minimal environmental impact. Its aim is to work with rainwater to the maximum extent, to keep it in the locality and also to use it for watering greenery in the complex.
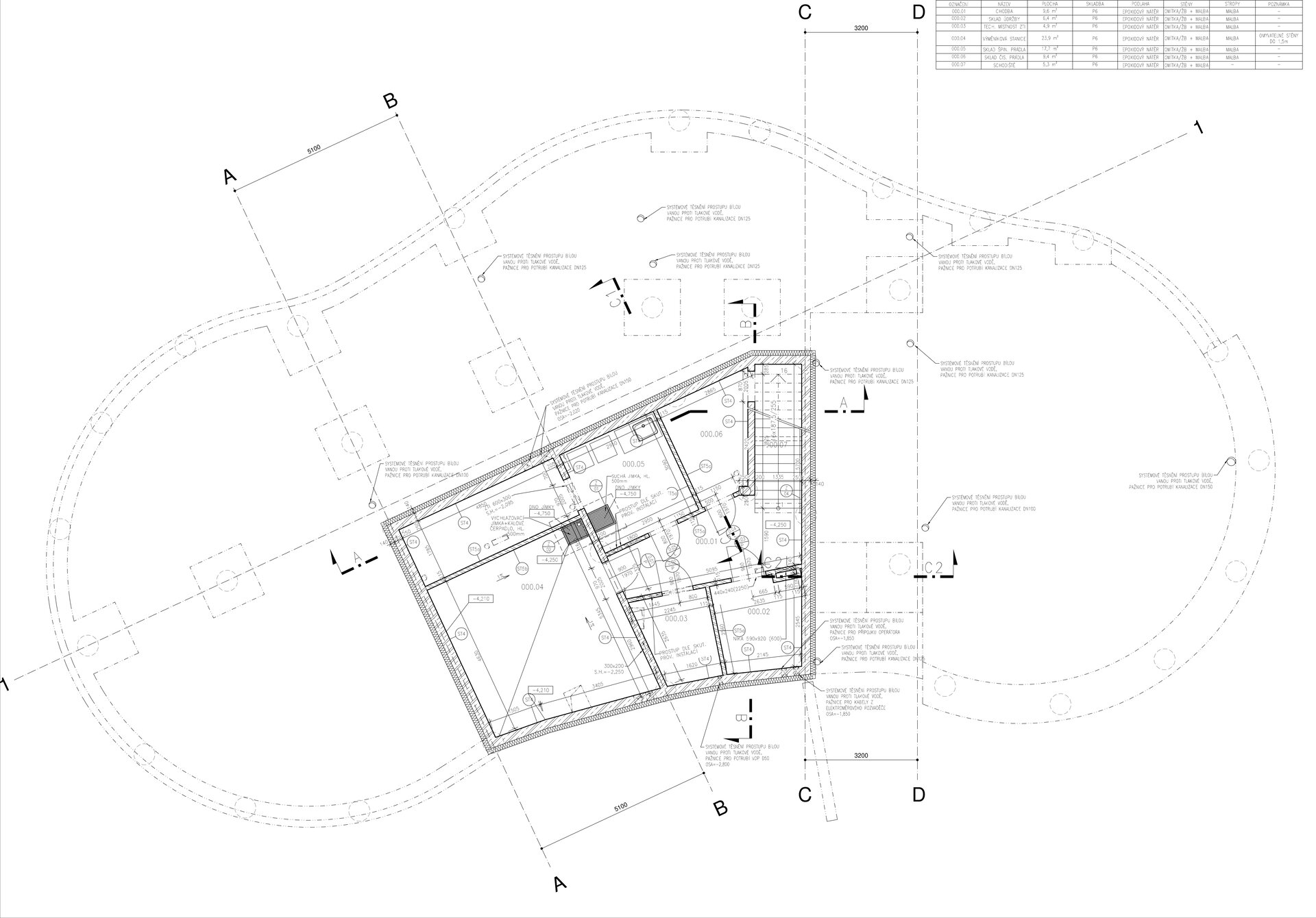
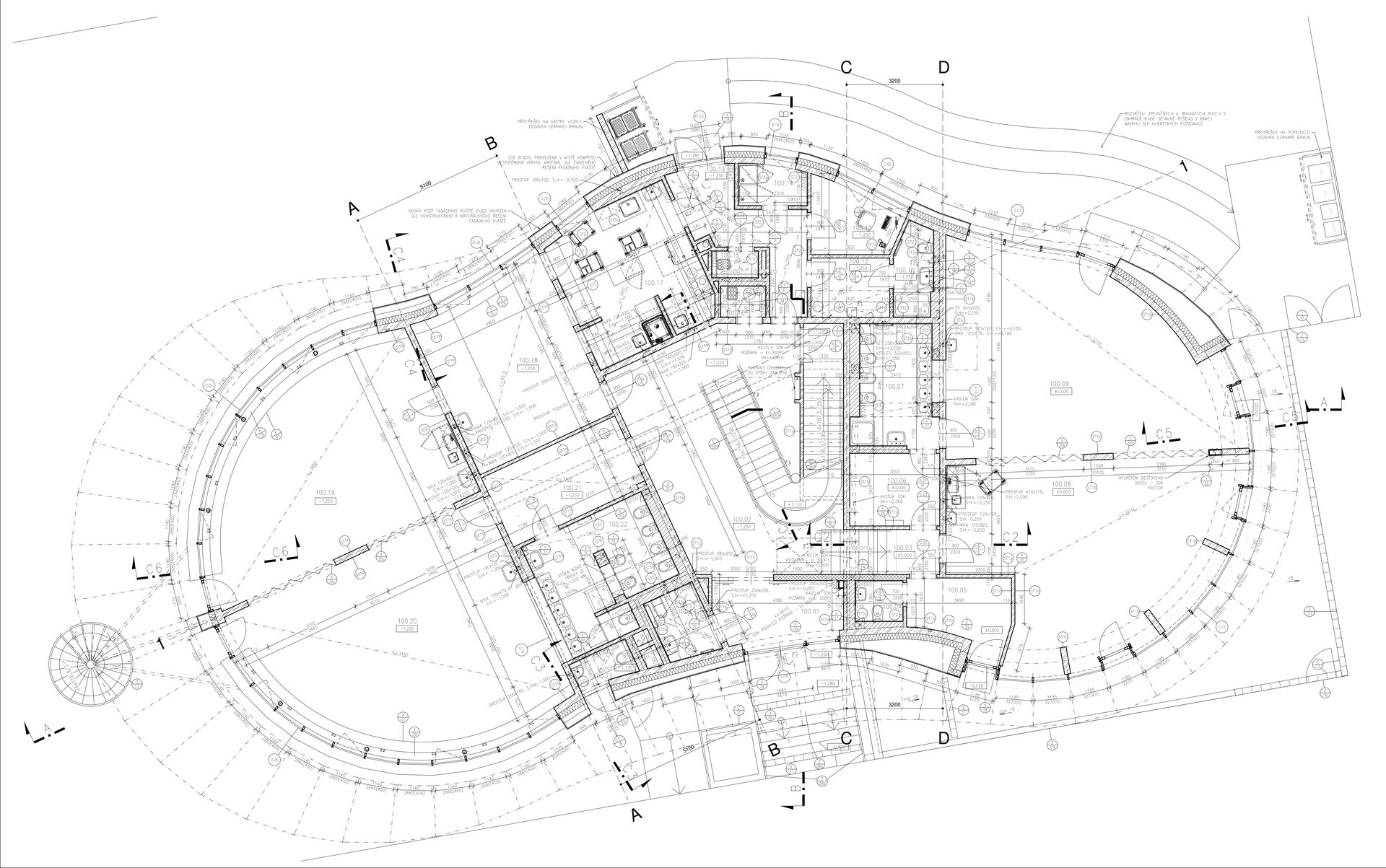
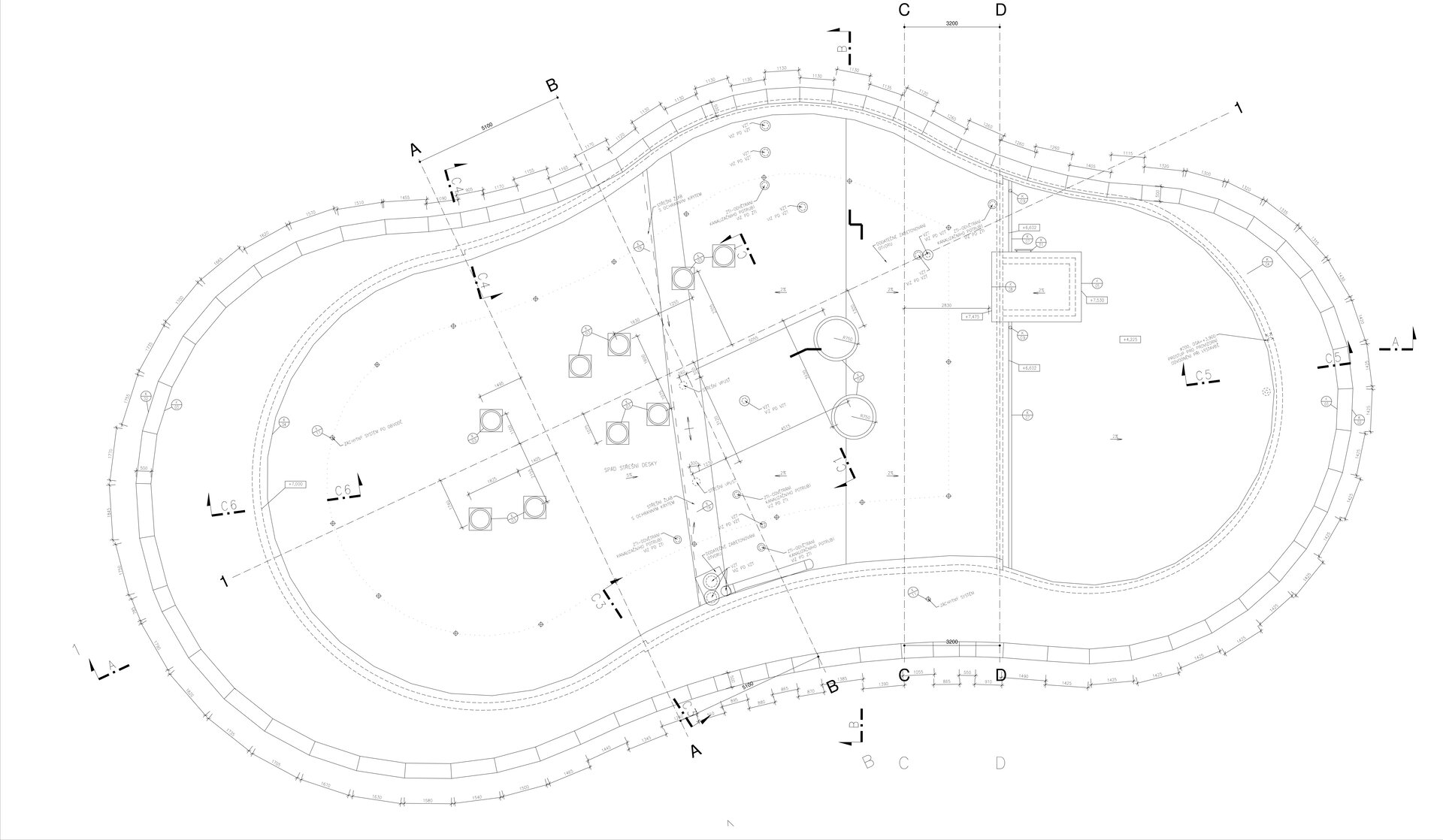
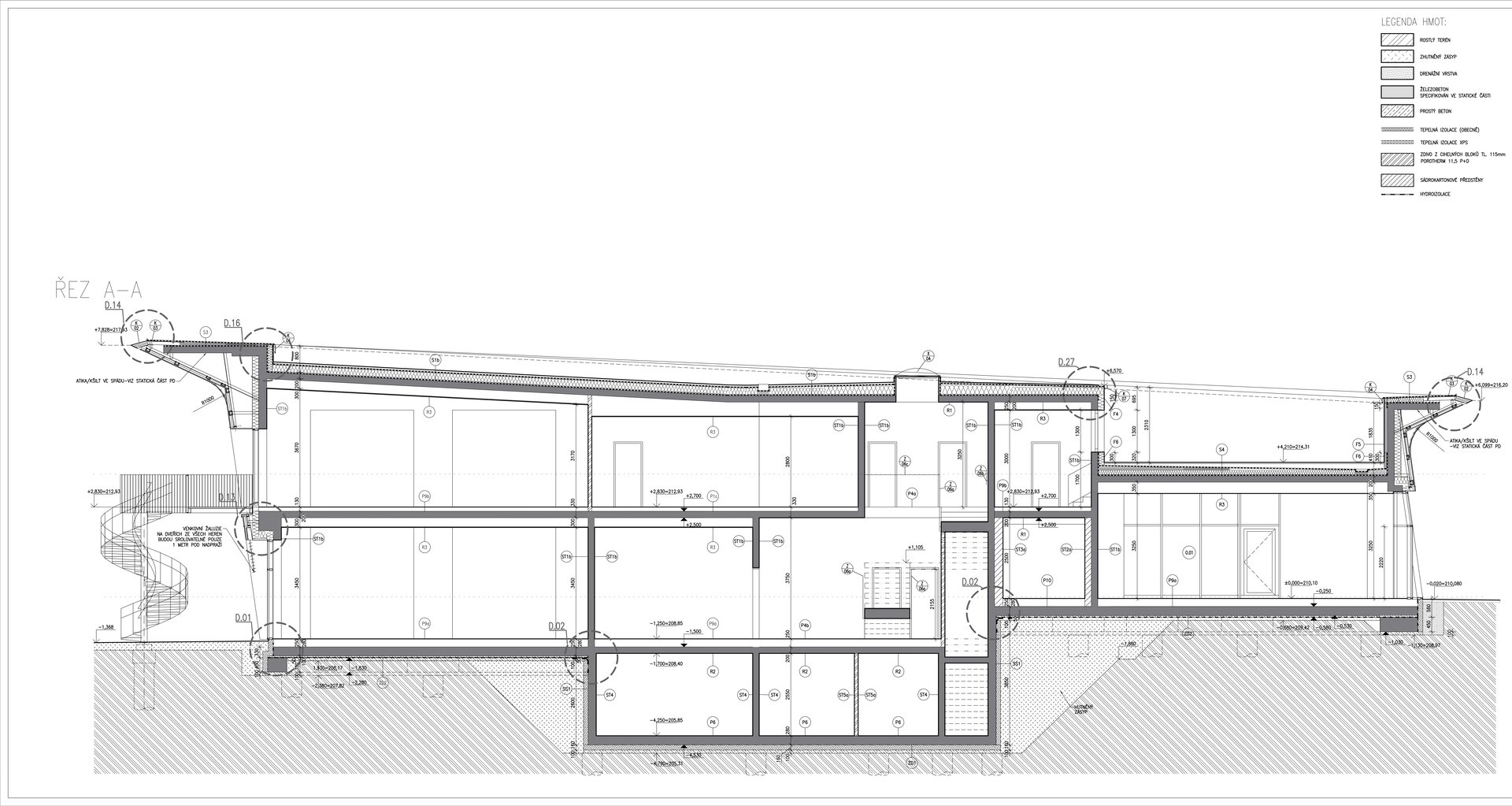
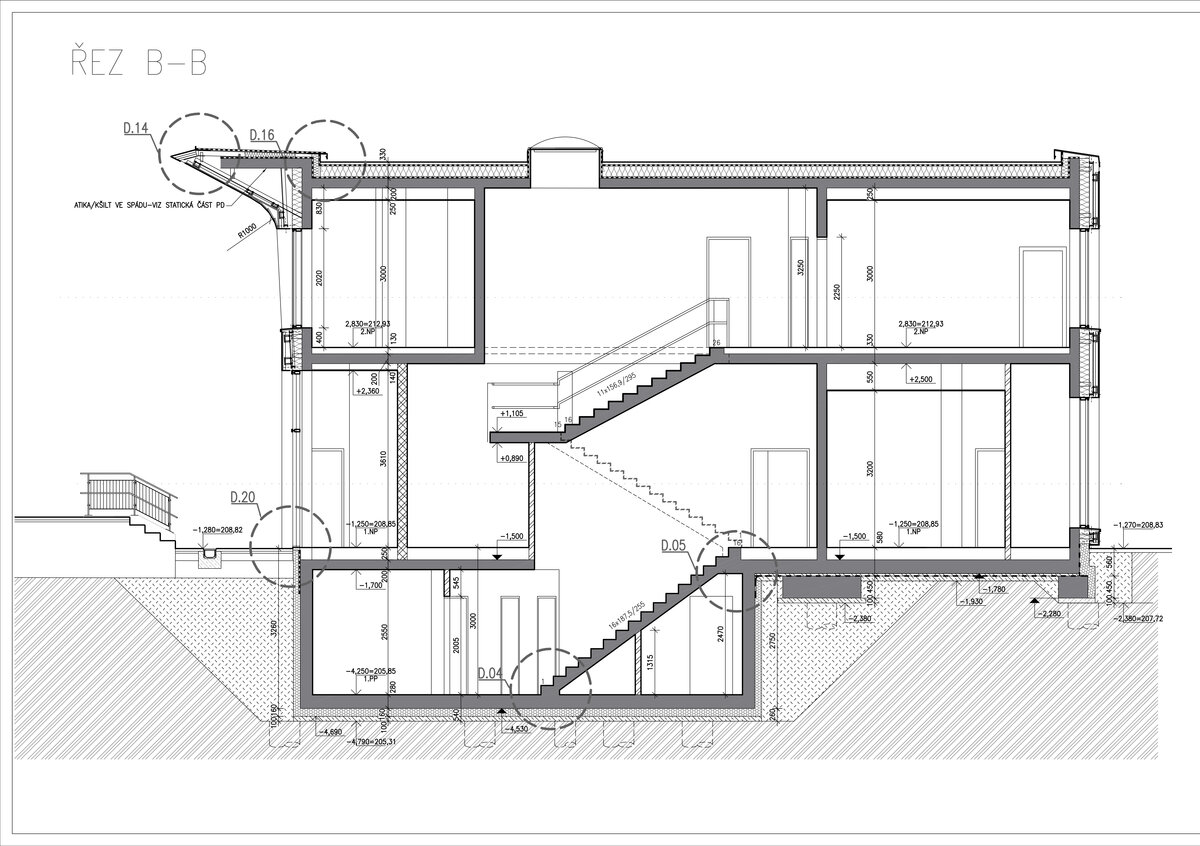
The preschool has a reinforced concrete monolithic load-bearing building construction. The substructure is designed as a “white tank”, anti-radon insulation is located under the first storey's foundation plate. The object is built on a panel supported by drilled pilots. In the first underground level the system is based on walls, while on the upper storeys there is a combination of walls and columns. The roof is a flat single shell with classic layer order. The main part of the roofing boards has a slope of about 5%. The roof is lined by an attic, which is extended in about ¾ of the perimeter by a brim.
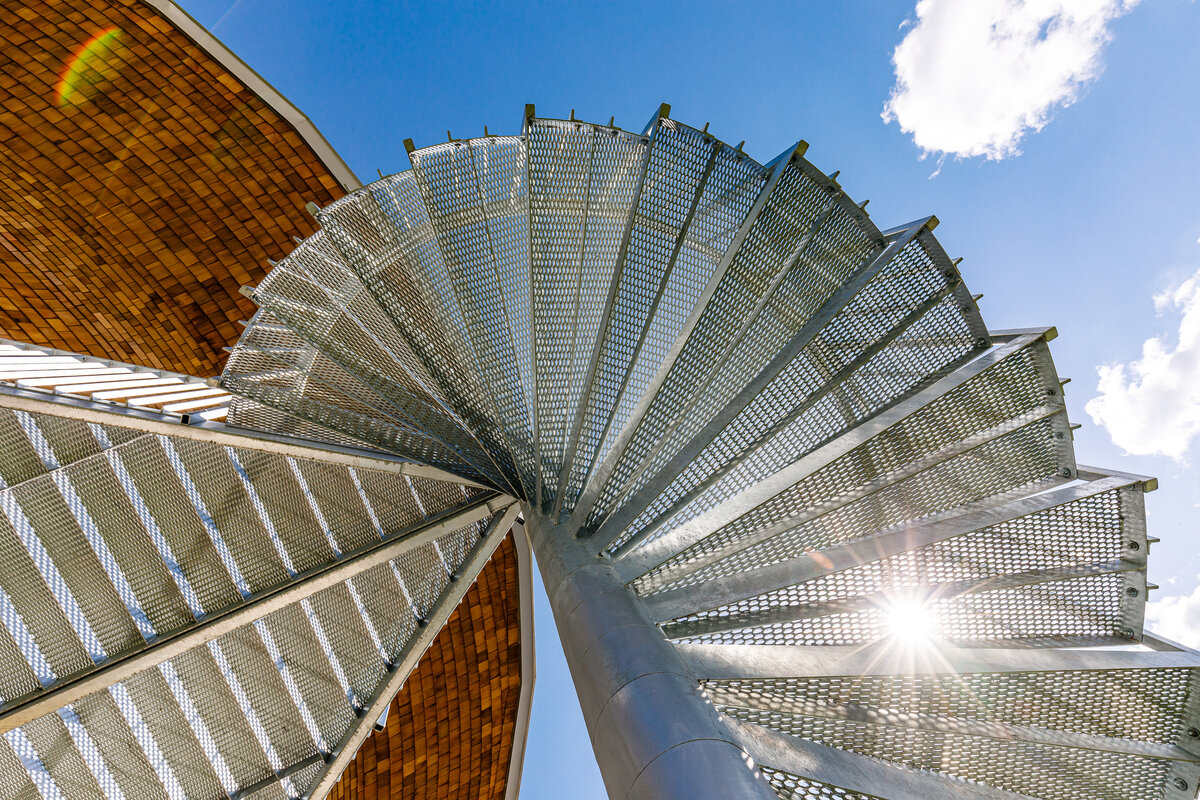
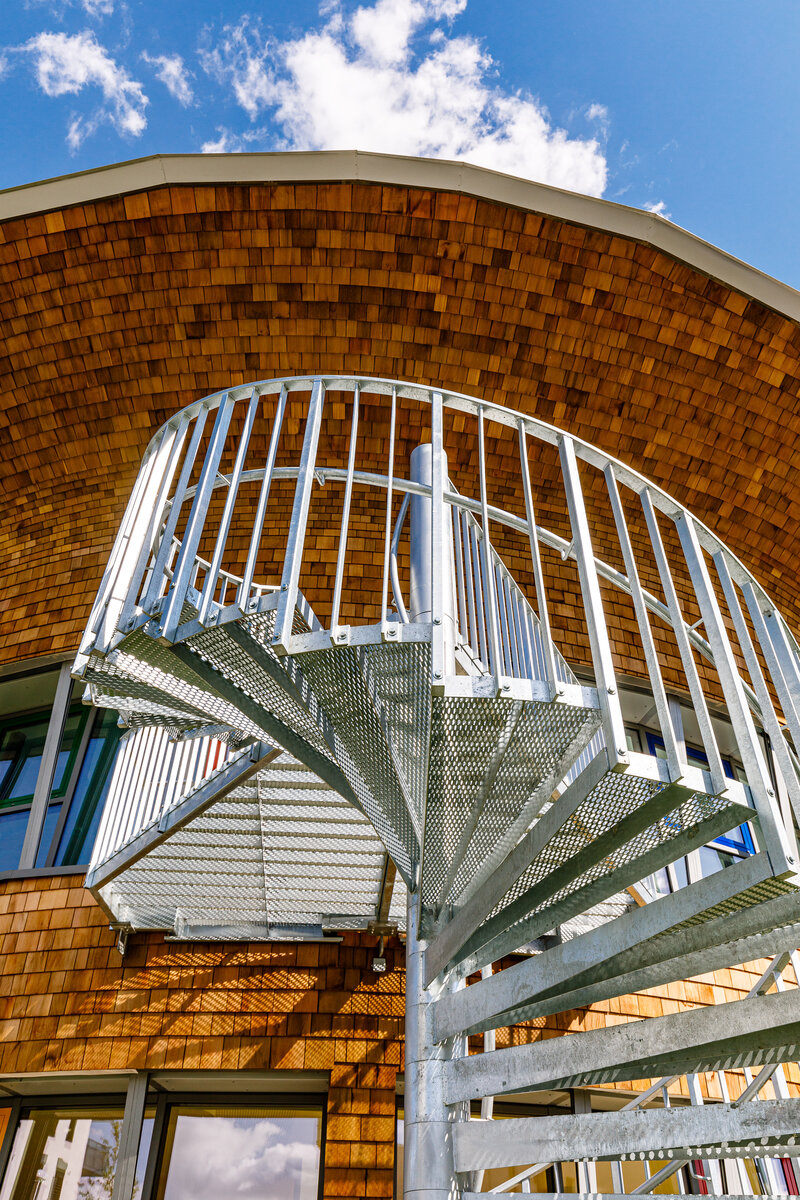
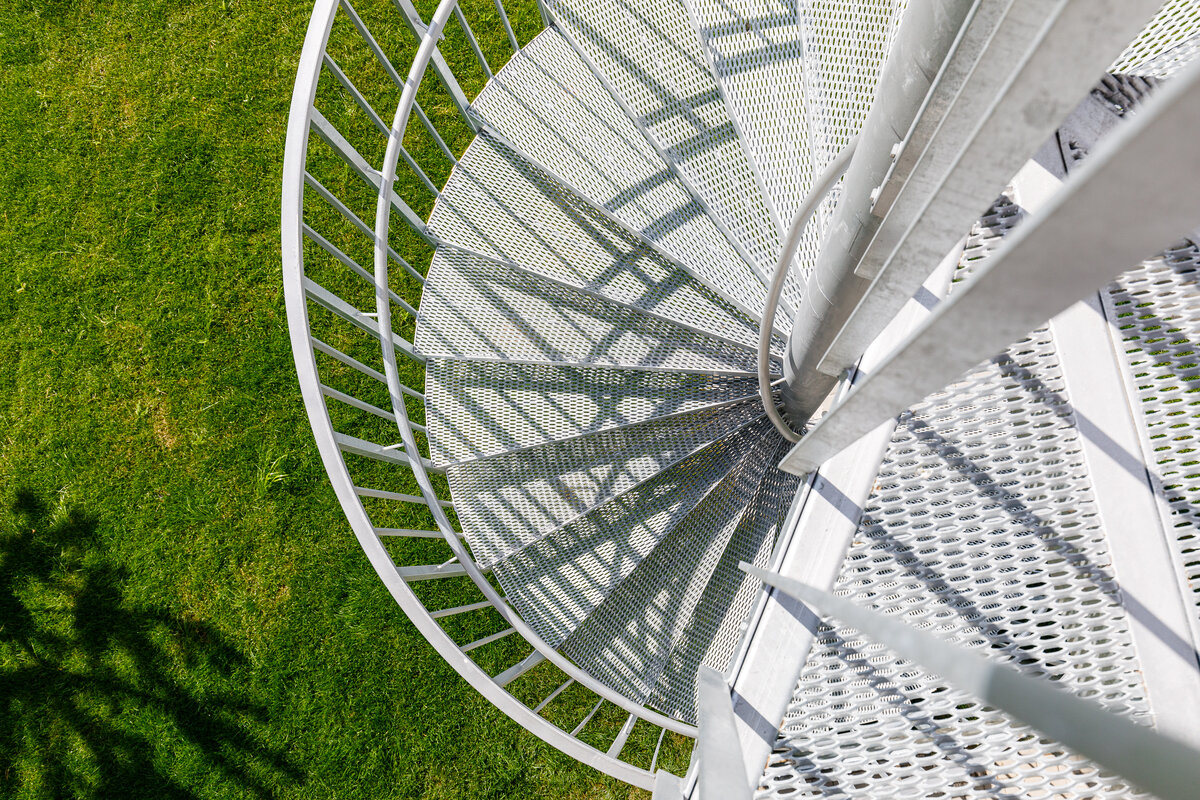
The inner staircases are monolithic, placed on lugs over acoustic pads. The main staircase railings made of steel sheet and Cembrit tiles visually represents a piano keyboard. The outer steel spiral fire escape staircase is a striking element. The internal partitions are masonry made of ceramic bricks with a thickness of 115 mm. The installation pre-walls are made of a plasterboard construction with a double joist. Bathrooms and toilets have full horizontal plasterboard ceilings. In the playrooms, bedrooms and dining room there are acoustically absorbing plasterboard ceilings. There are heavy floating floors with thermal and impact insulation under a layer of concrete screed. Marmoleum was used as a covering in the rooms used by the children. Tiles were laid in the social facilities, the kitchen and main hall, while a floating wooden floor was used in the offices.
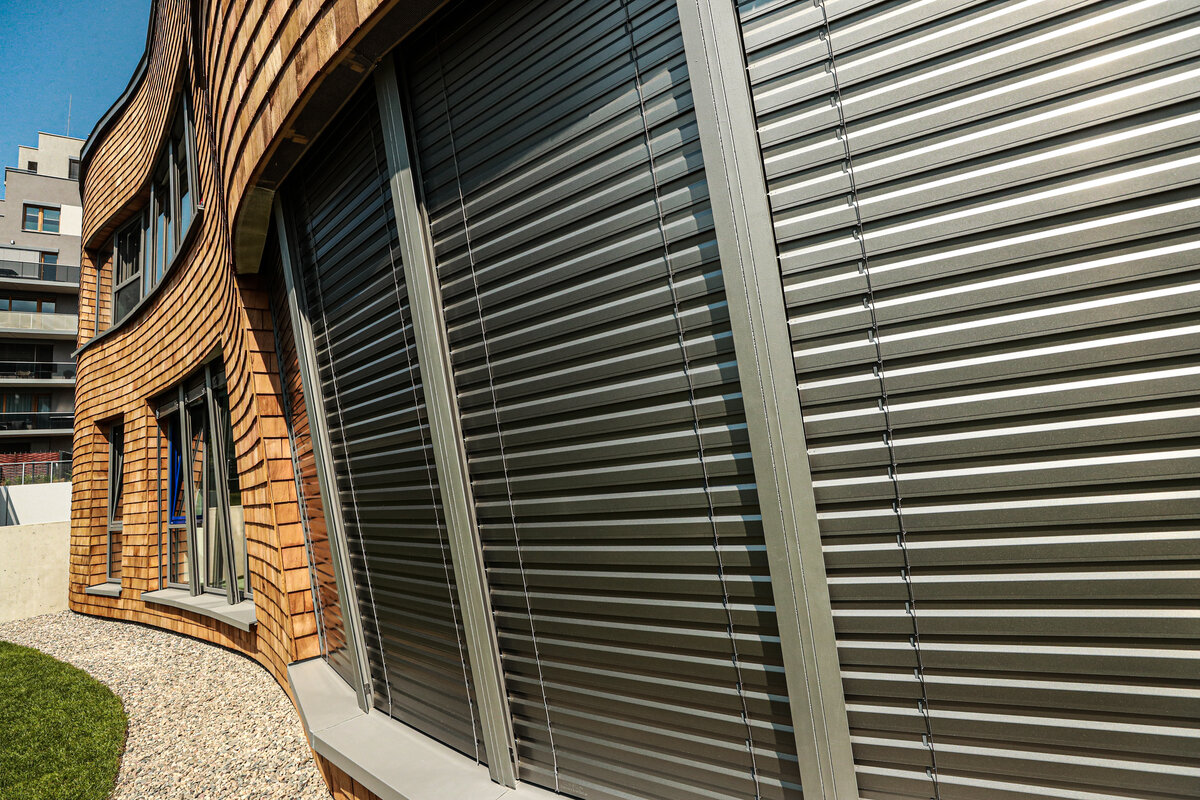
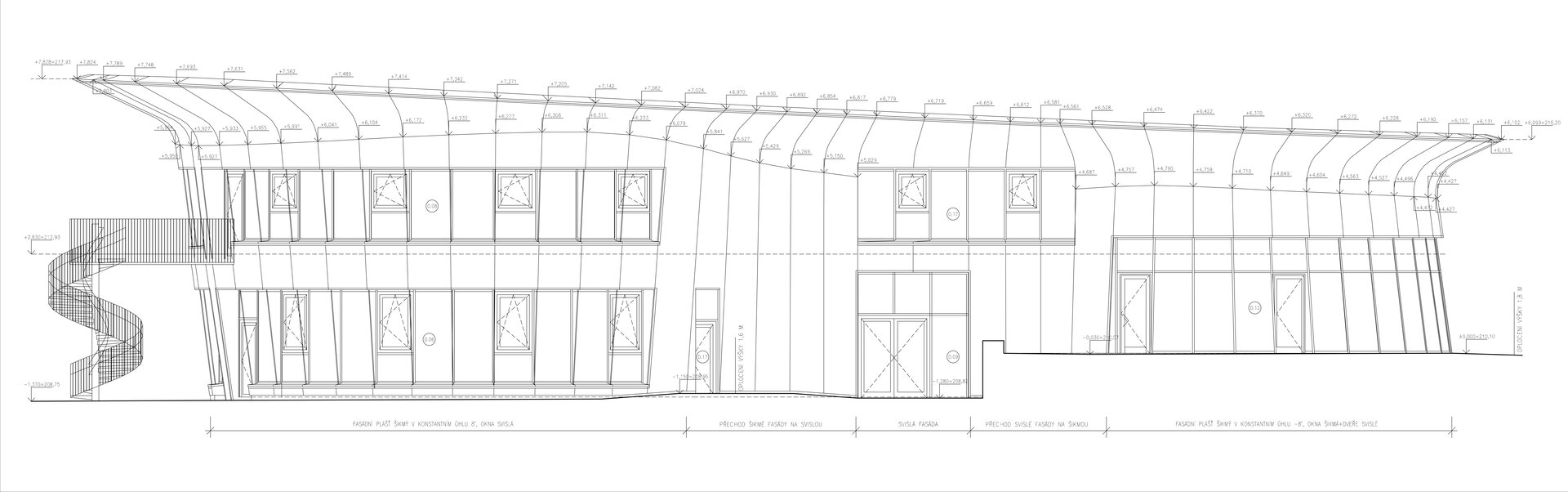
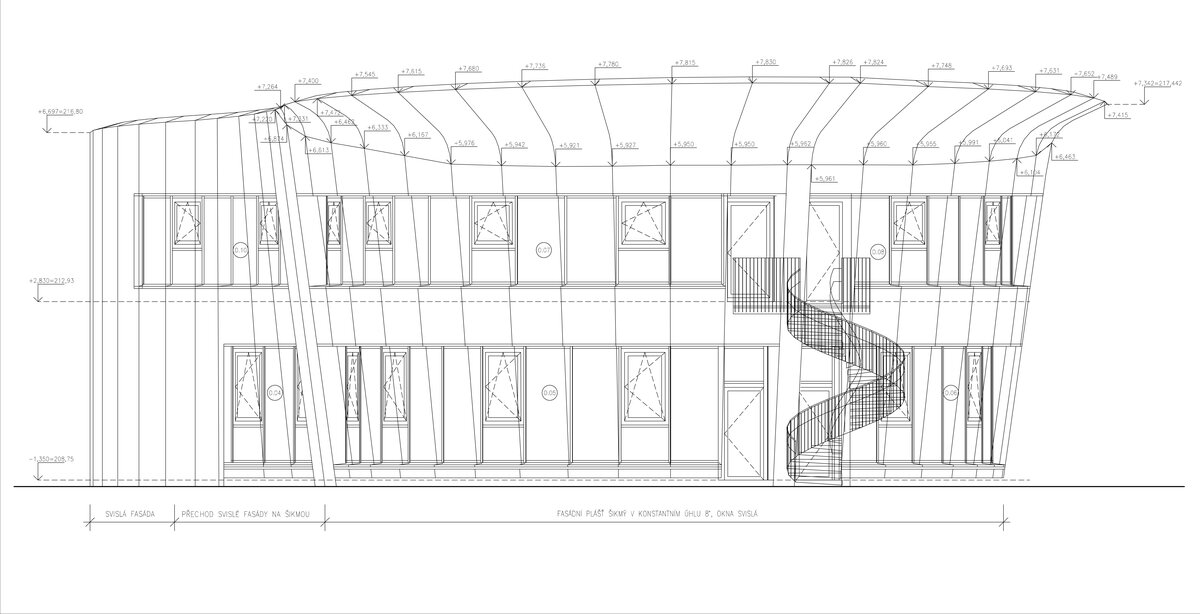
The wooden façade is double-shelled and ventilated, with a surface made of red cedar shingles. The organic shape of the façade is not only curved on the ground plan, but also along the height. The sloping façade is variable, tilted 8° away from the vertical in the south and 8° toward the vertical in the north. Above the second-storey windows, at about 3/4 of its circumference, the façade is cantilevered into a horizontal cornice, creating a brim. The ground plan of the foundation concrete structure is curved. The desired façade inclinations are achieved by the supporting ribs of the shell.
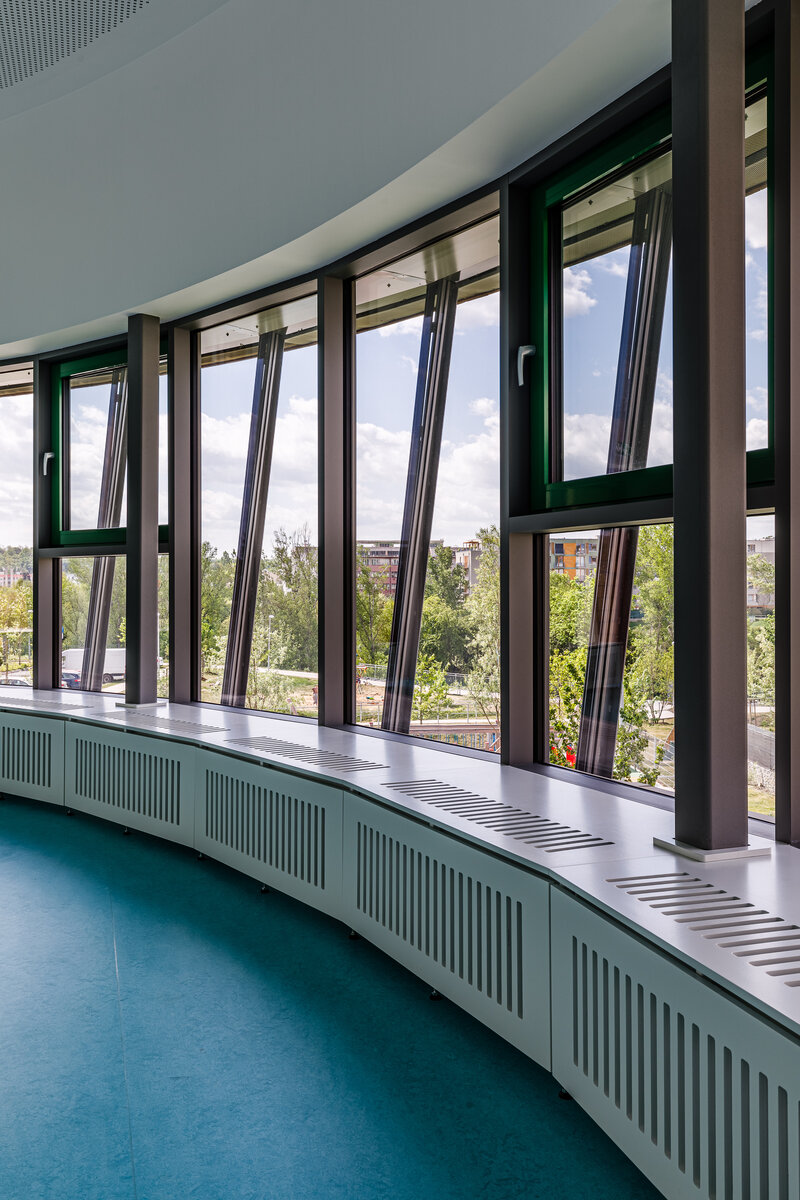
The main entrance doors and windows of the building are in the aluminium light circumferential shell system. The ribbon windows have insulating triple glazing. The glazed façade is complemented by external blinds, whose slope follows the inclination of the main surface of the façade. There are two circular skylights above the entrance hall. Light tunnels contribute to the lighting of some second-storey rooms.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
B
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|