| Author |
Ing. arch. Libor Žák / Atic.Zak |
| Studio |
|
| Location |
Průmyslová zóna Kuřim, Blanenská 1288/27, 664 34 Kuřim |
| Investor |
Jihomoravský kraj, Žerotínovo nám. 449/3, 601 82 Brno |
| Supplier |
Winning PS - stavební firma s.r.o., Křižíkova 2960/72, Brno |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
February 2021 |
| Fotograf |
|
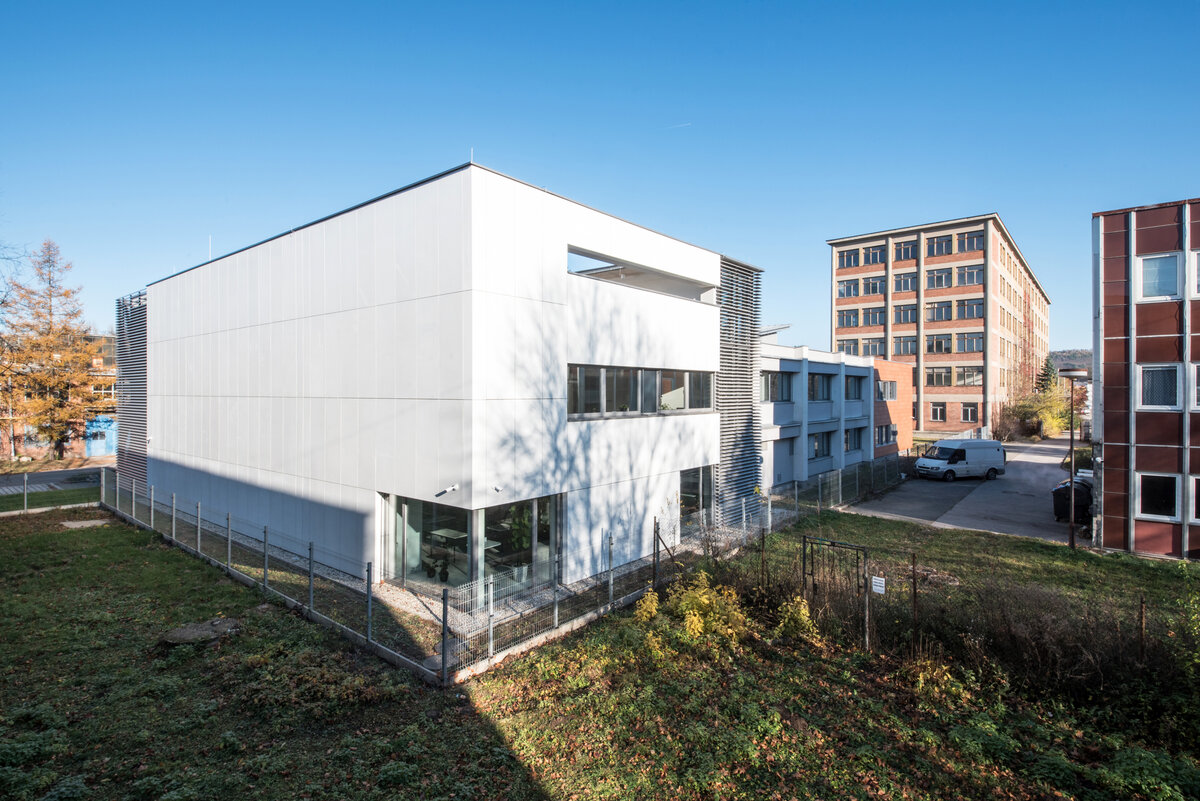
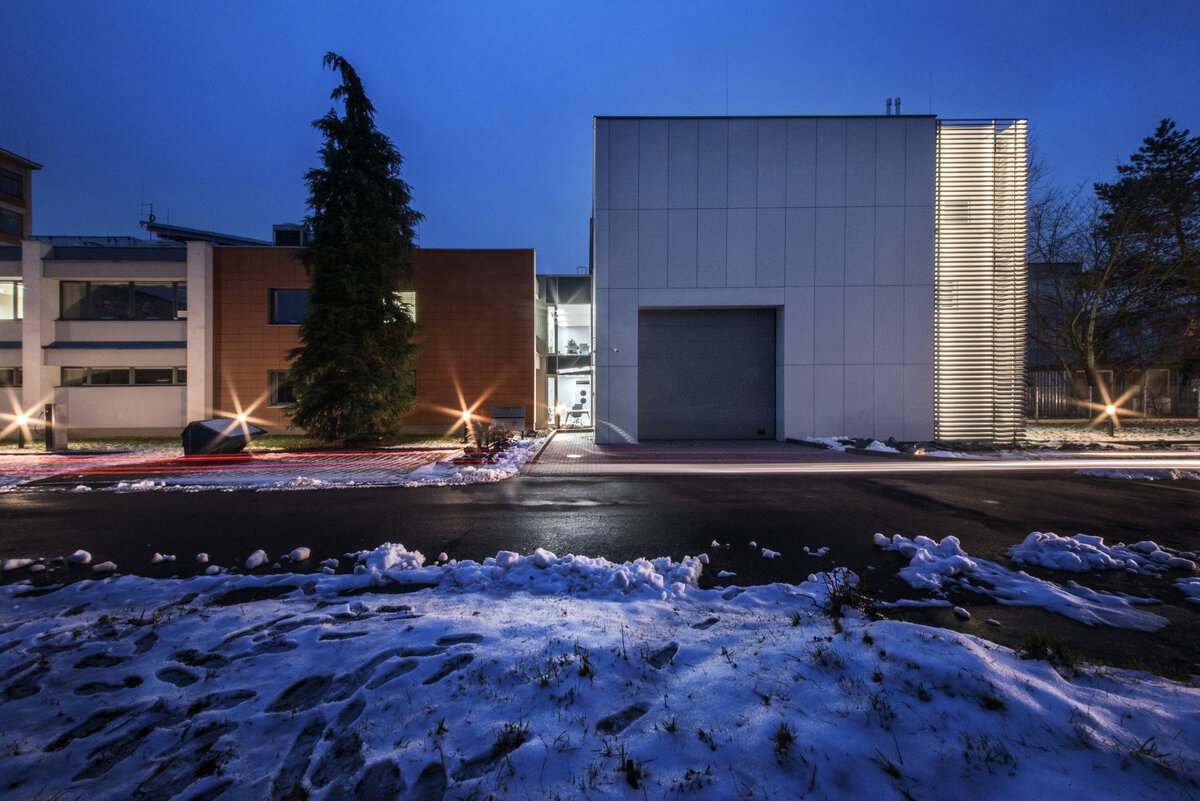
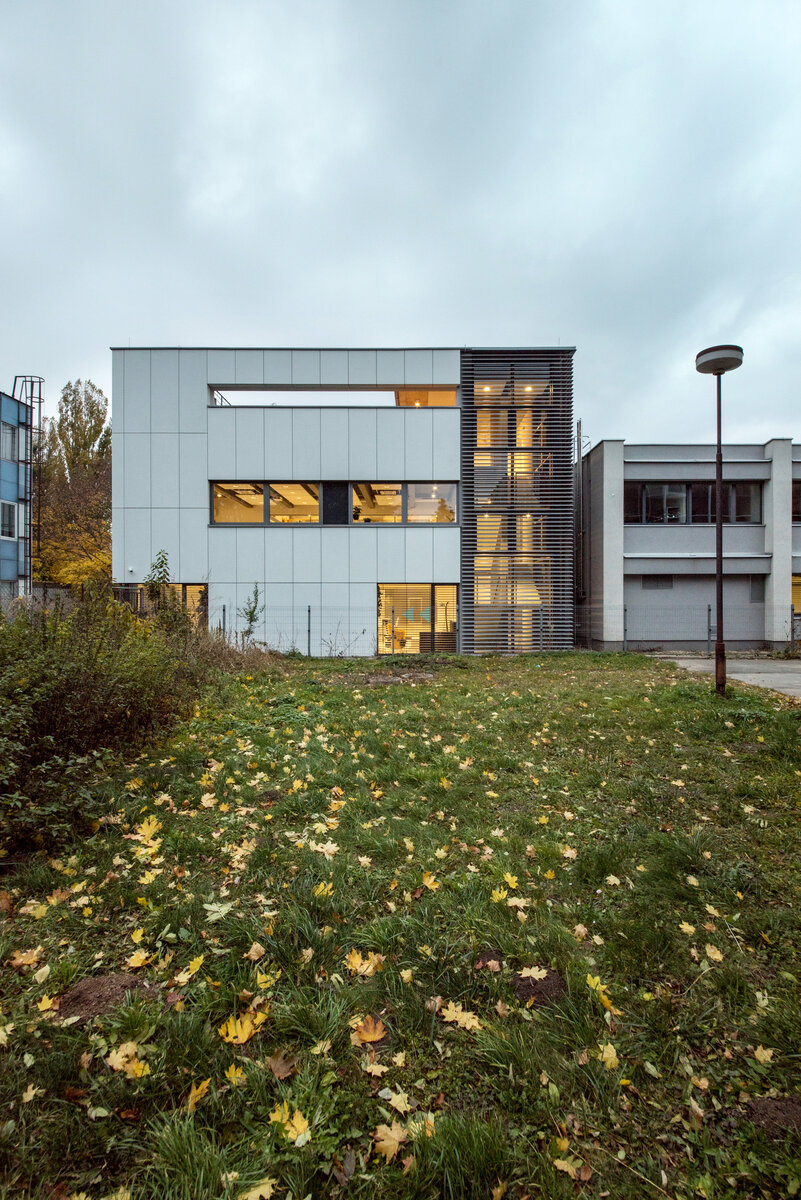
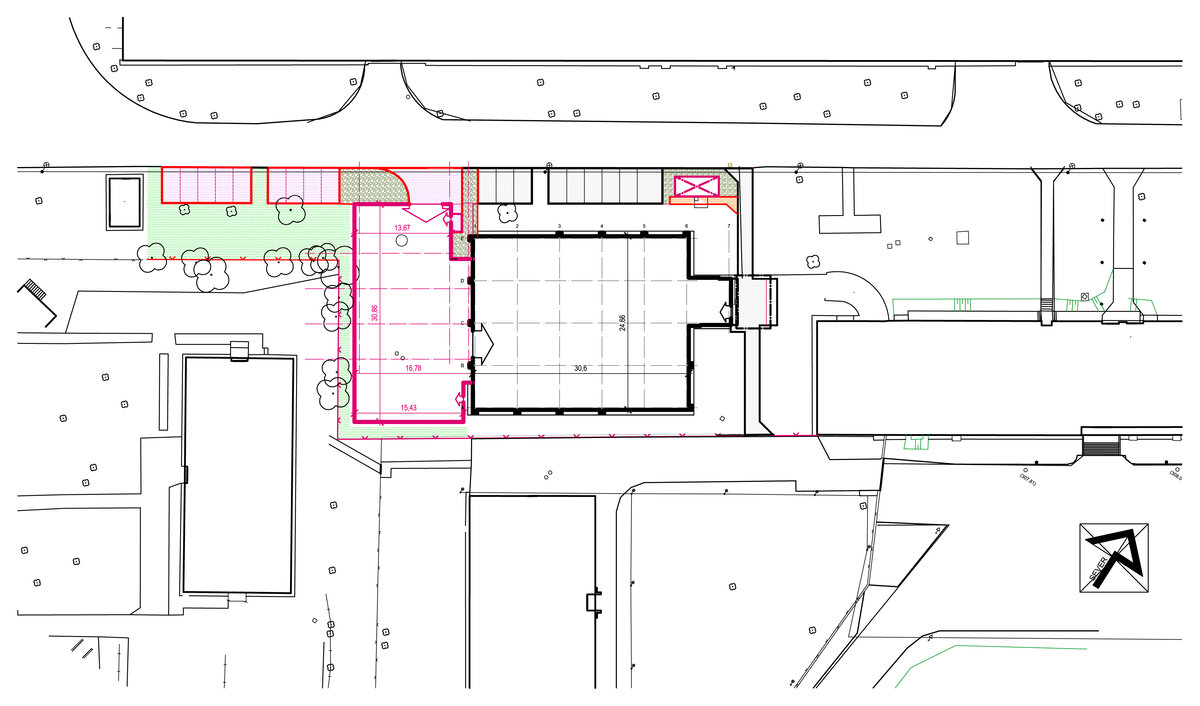
The INTEMAC modern research and innovation center is located on the industrial estate in Kuřim. The area in question is located along Blanenská Street, which forms a divide between the large plot of the engineering company TOS Kuřim and the new part of the industrial estate. The existing part of the center is a reconstructed building from 2013 (by the same author), which has been followed by the presented implementation of the INTEMAC center extension. The innovation and science park promotes modern technologies in engineering production. The project was supported by the South Moravian Region in cooperation with the JIC, an interest association of legal entities in partnership with the Brno University of Technology and major engineering companies.
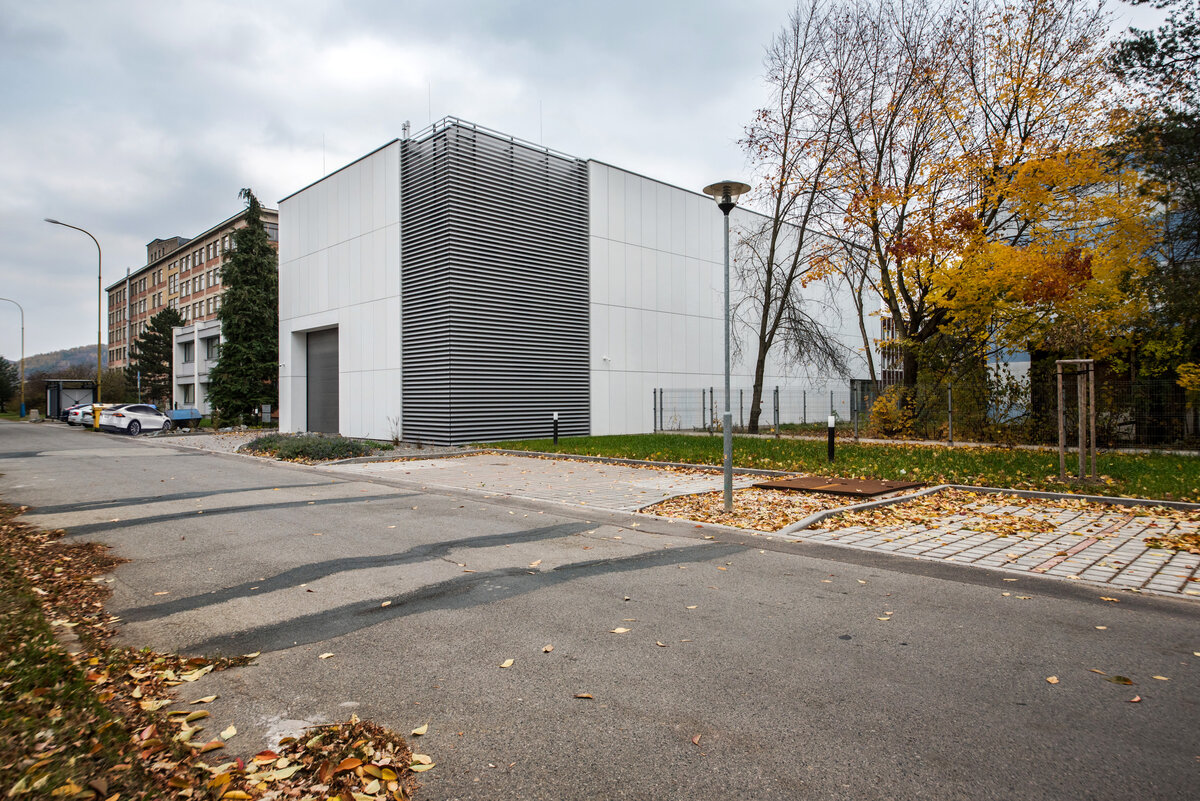
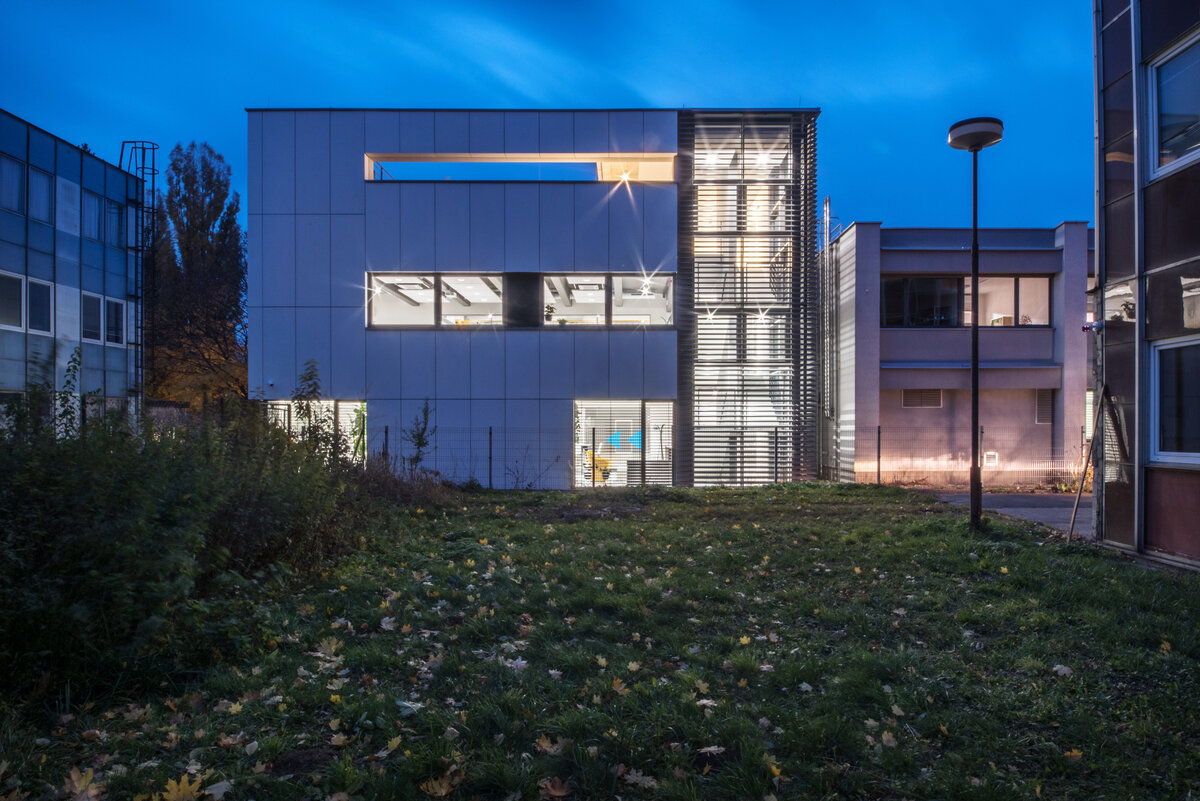
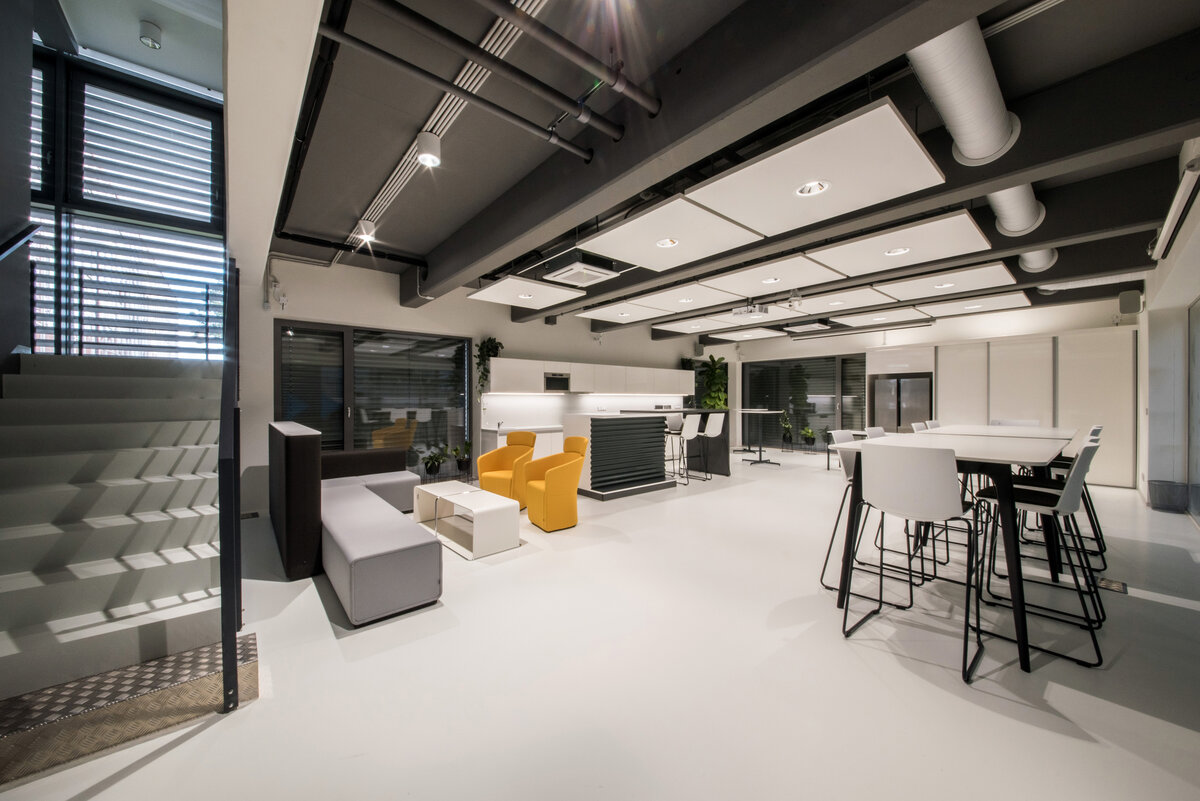
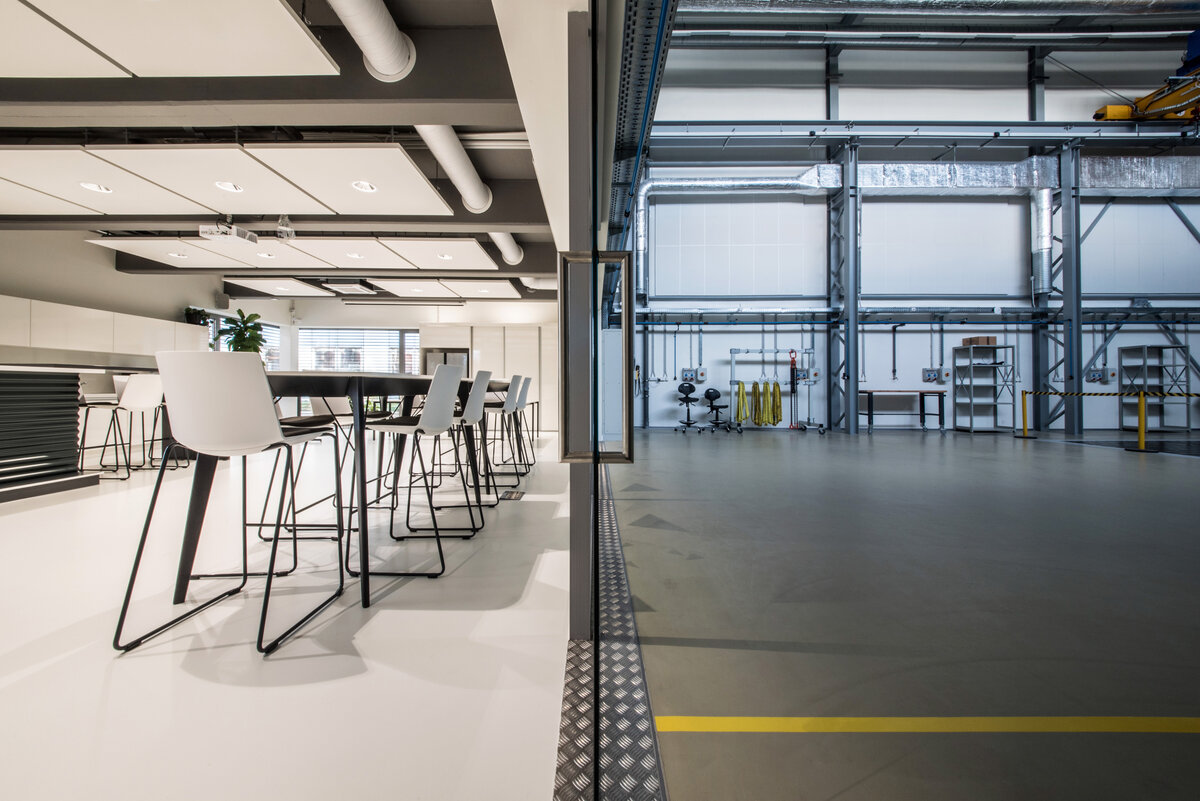
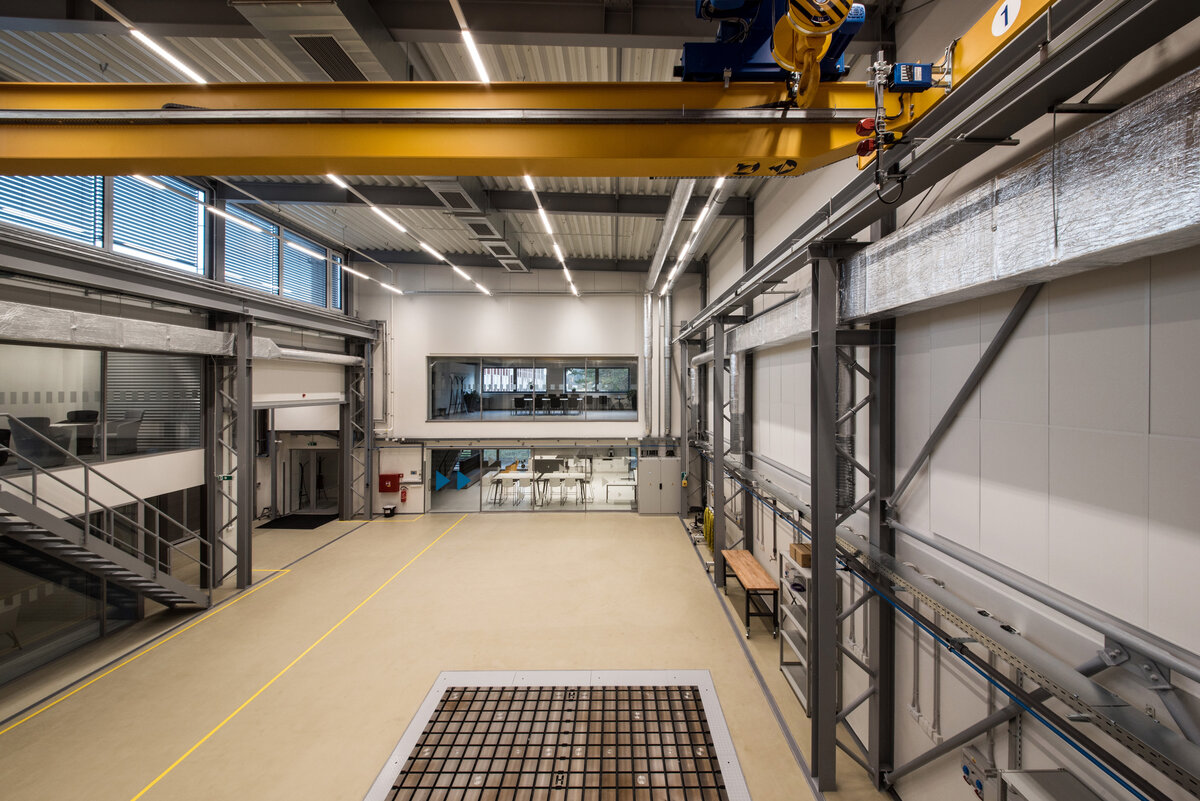
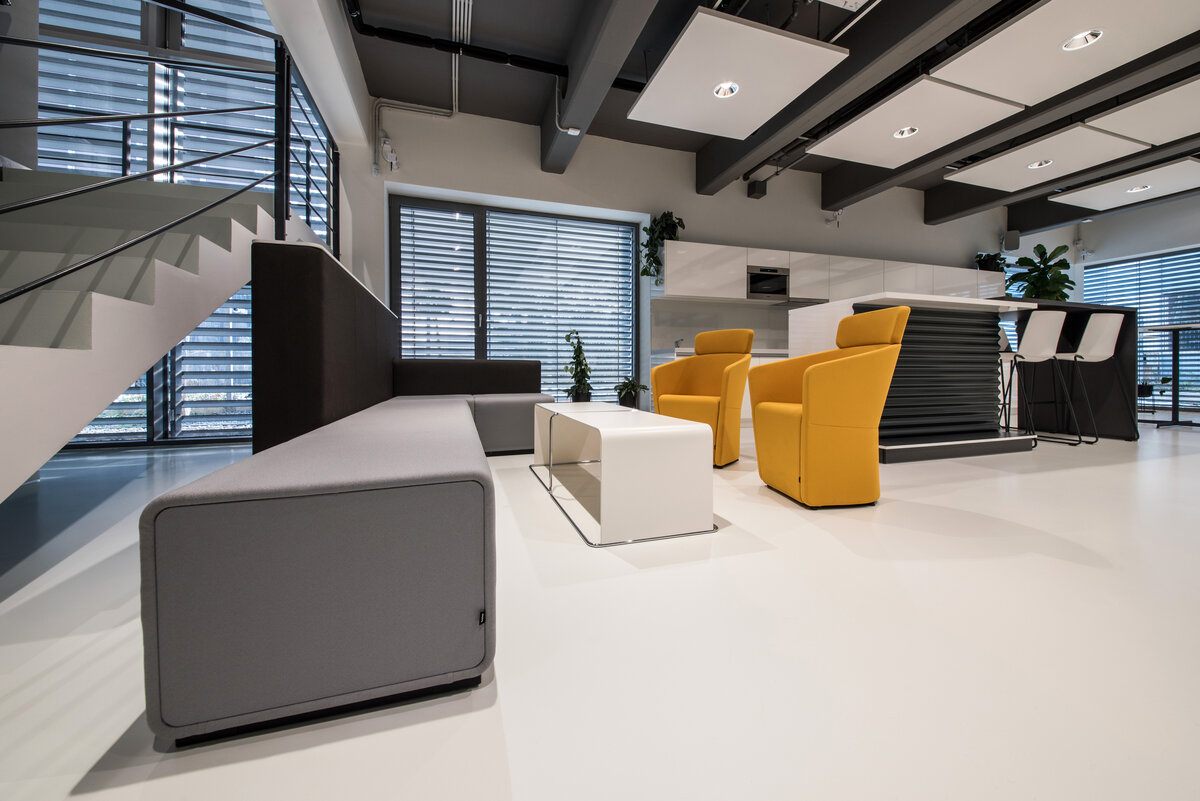
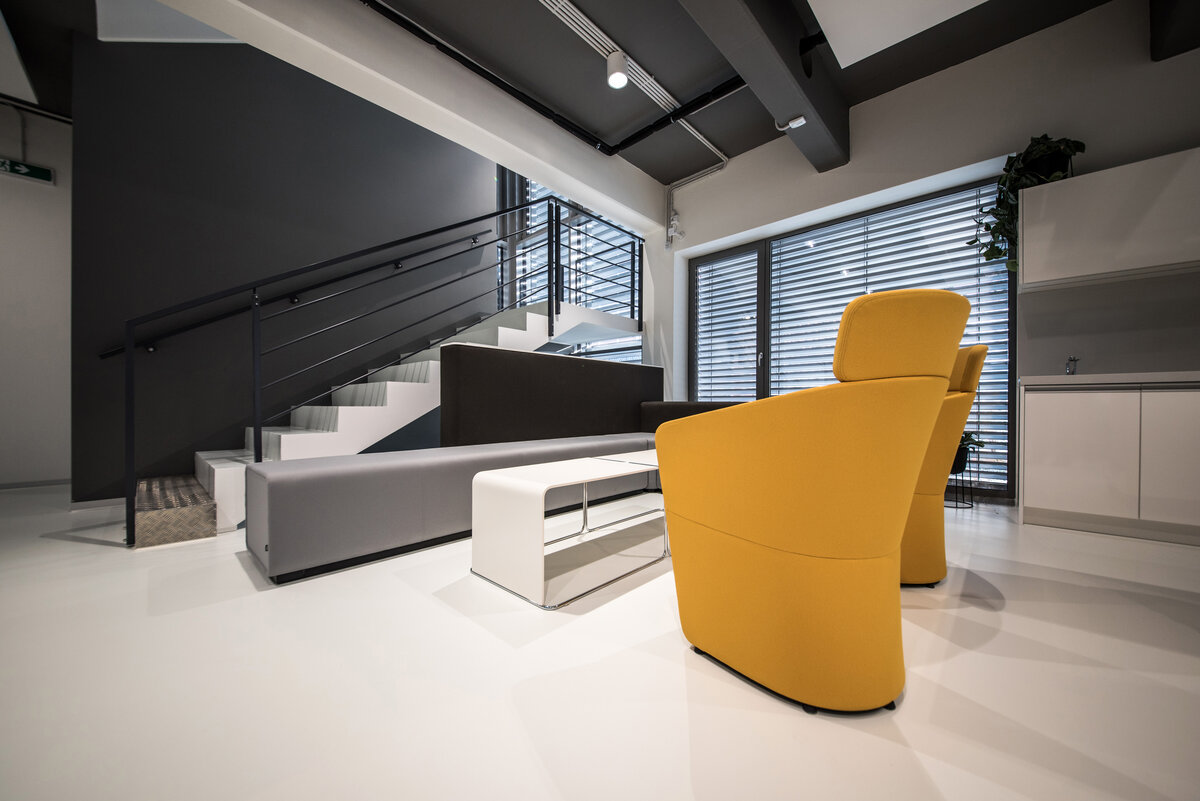
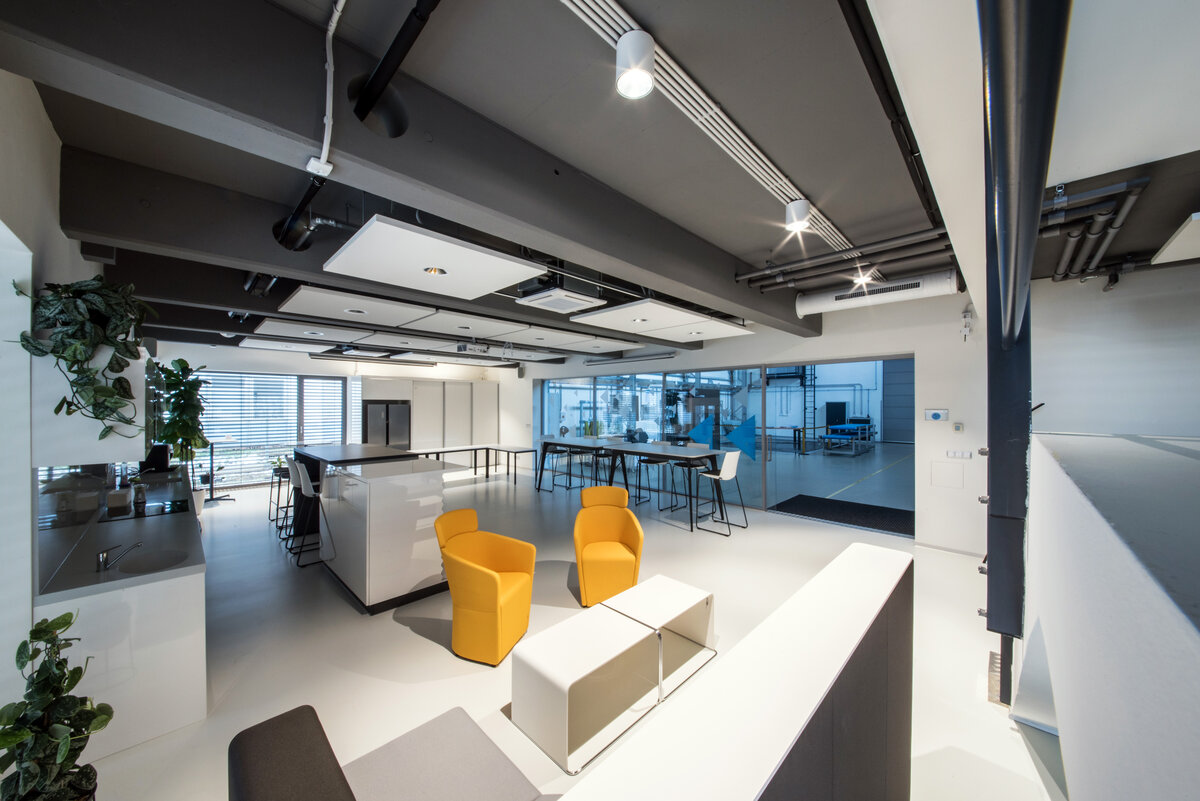
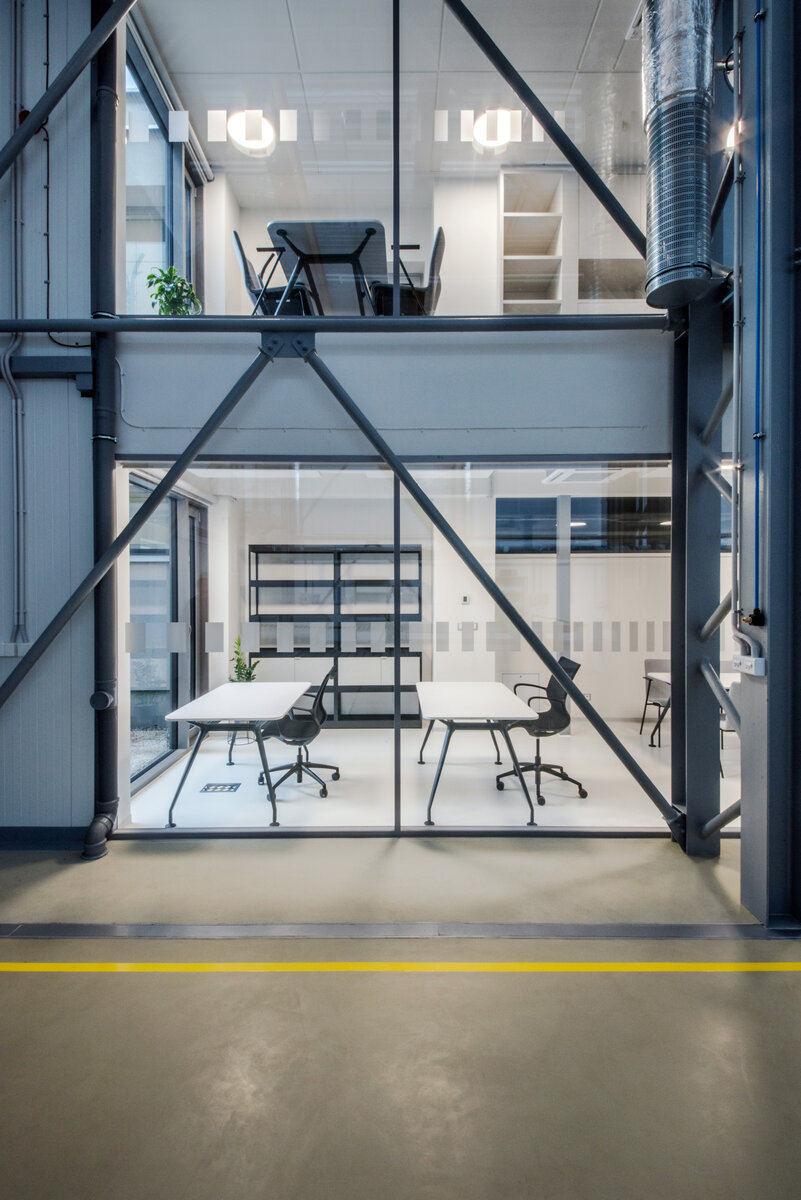
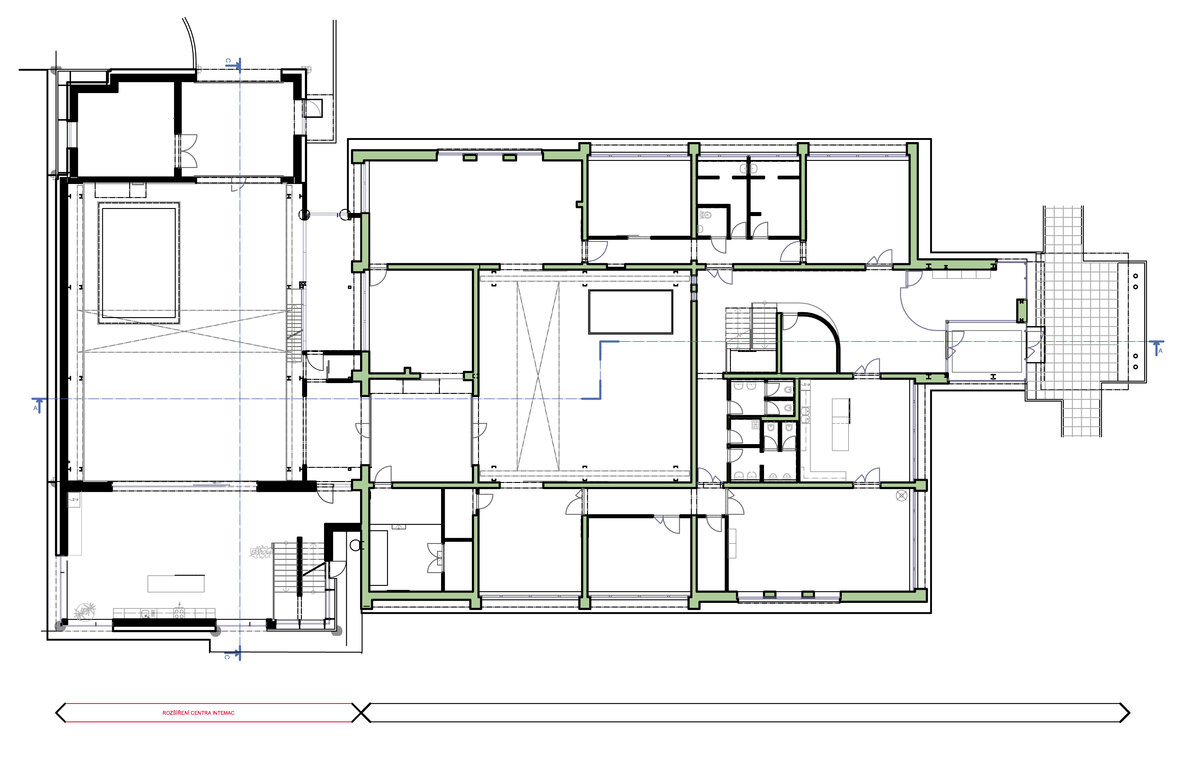
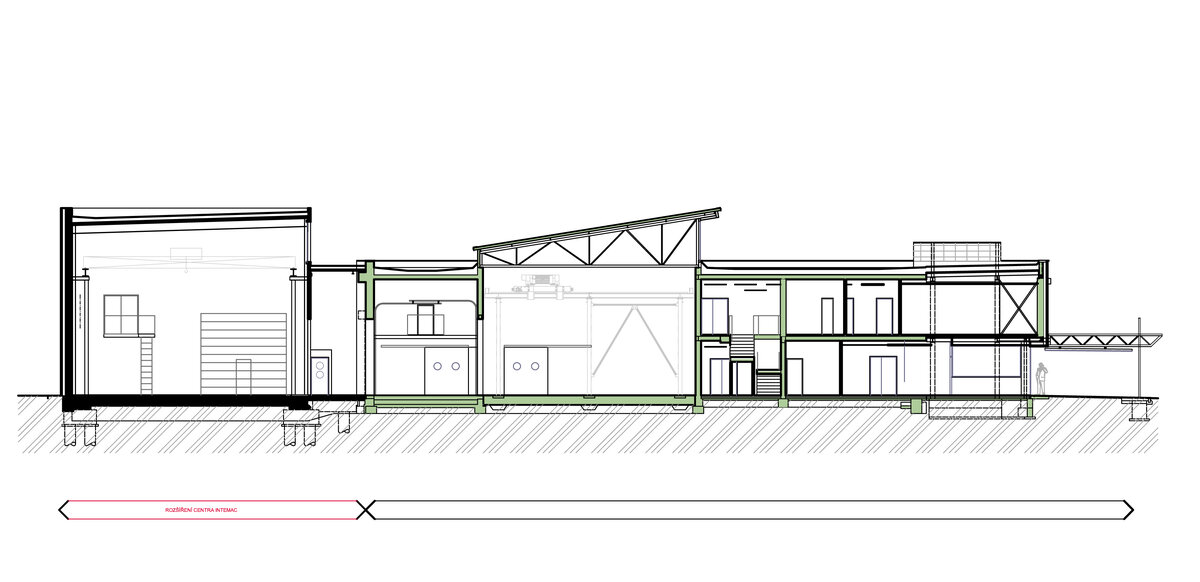
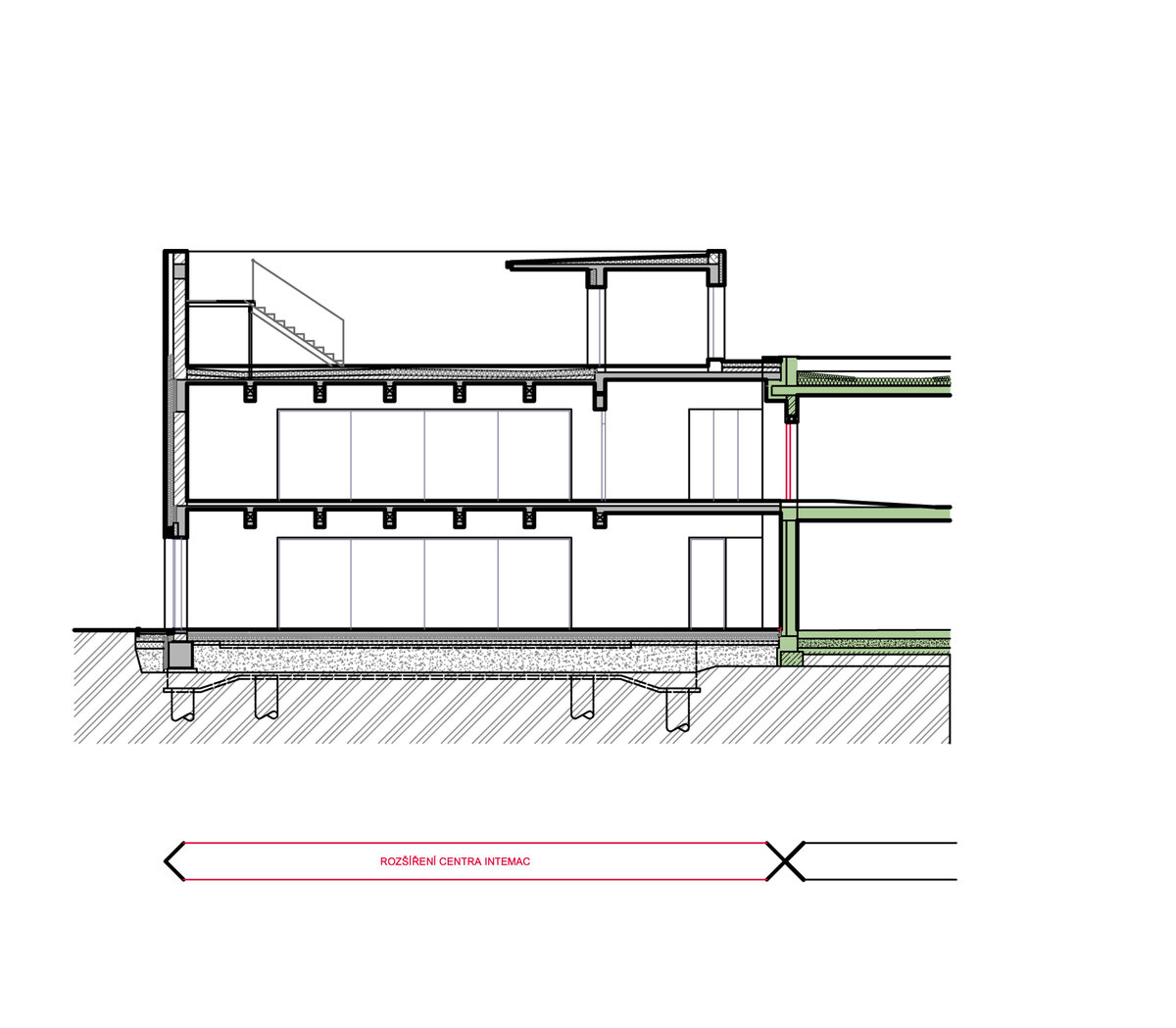
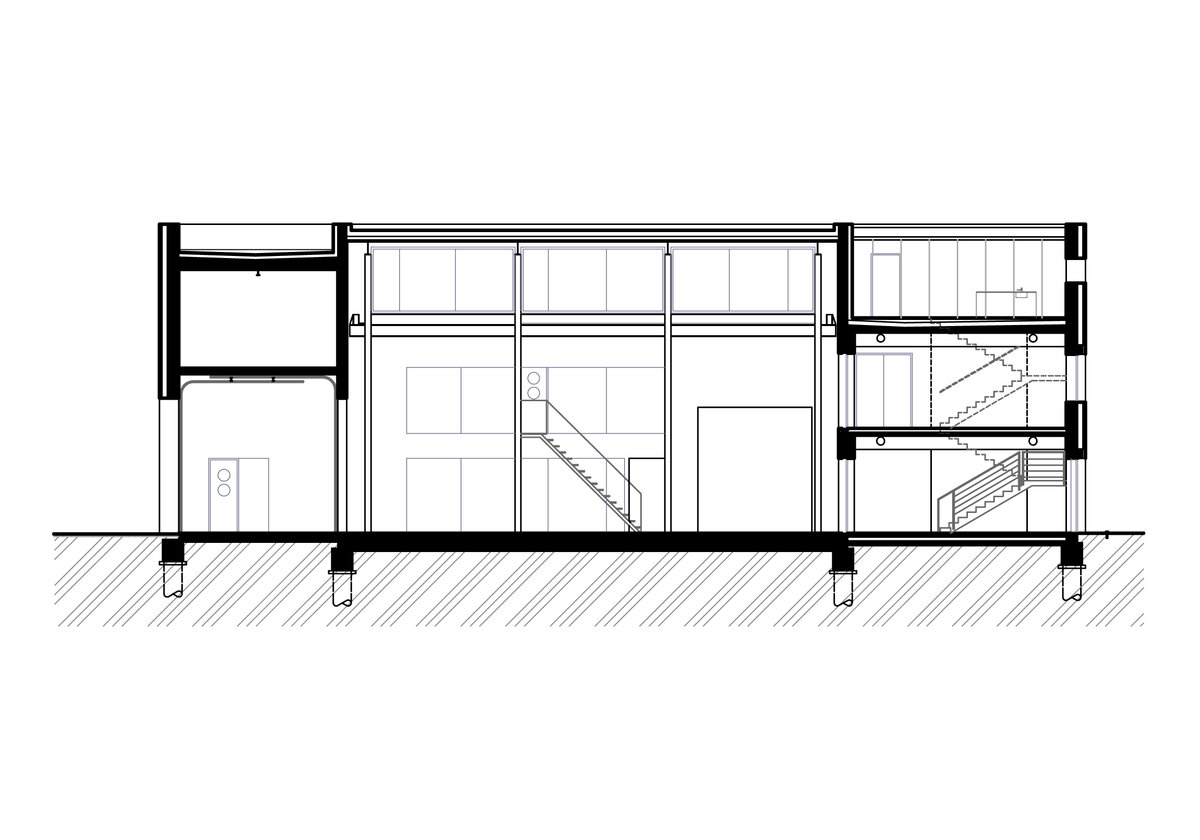
The overall placement and urban design respects the existing volume as a solitary building. The new extension connects with the old building with necessary distance. The intention of the architectural solution was to meet the requirement of a combination of unusual operations. Engineering laboratories modeling real production processes with concentrated activities in the background and the possibility of presentations for a larger number of clients and visitors. Emphasis is placed on the technical character of the building, which also integrates a number of technical media in a small space. The innovative character of the adjoining spaces was the defining motive for the design of the interior. The motives of production and technology are central to the overall design language. At the same time, the spaces are variably designed for demanding presentations. The exterior of the building is an elementary cubic volume. The individually produced white concrete slabs create the building’s cladding. The extension complements the existing building and at the same time creates a contrast by intentional expression of shift in time and technology. The central hall is naturally lit by a ribbon window from the northeast and further through the glass walls.
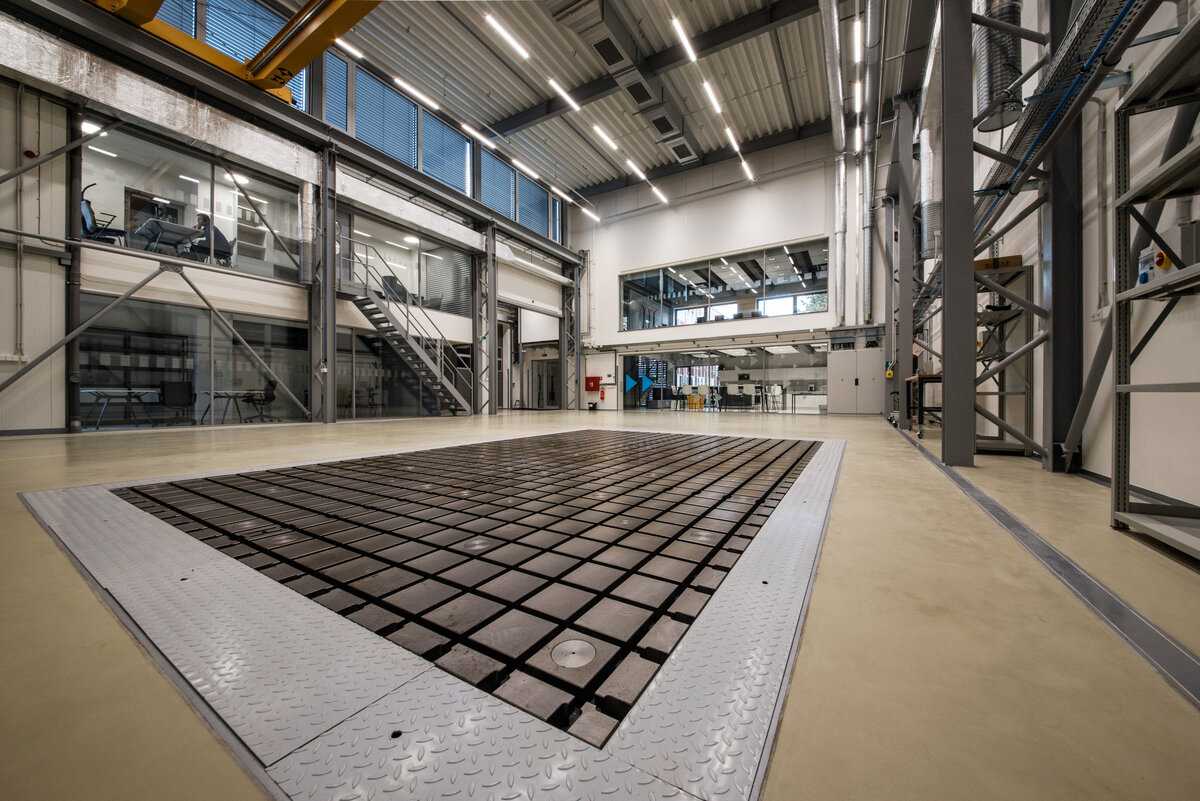
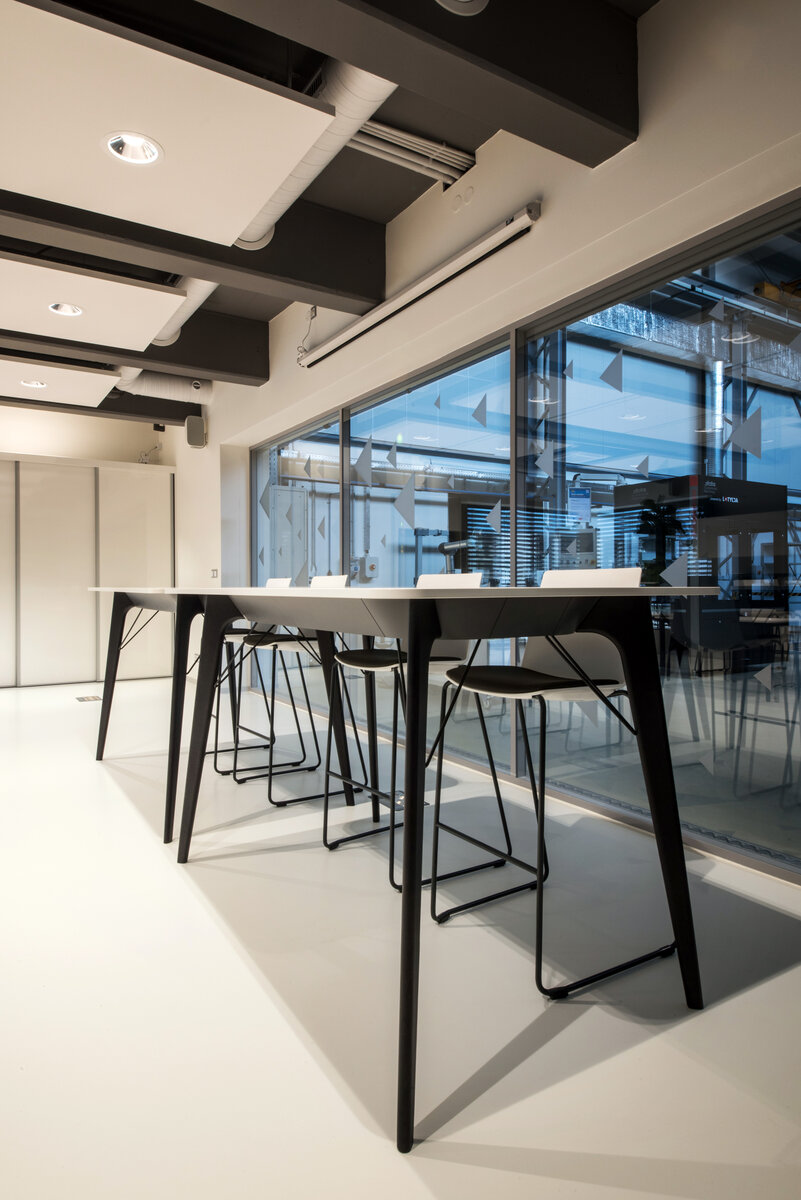
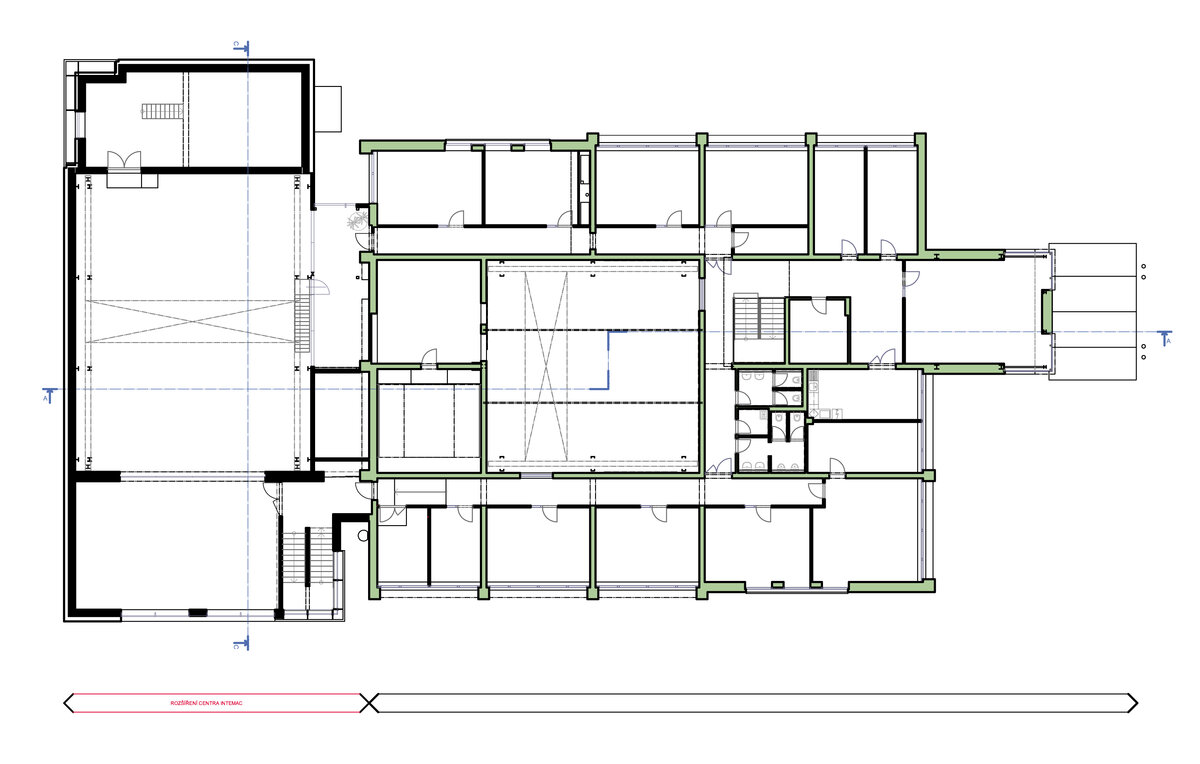
On the second floor there is the presentation room overlooking the main laboratory. Structure of the hallway space is formed by truss columns made of steel with crane tracks and plate steel rafters. A new connection to the existing building was added here. The connecting corridor between the original building and the new building used the most of the tight conditions of the given construction site. Despite the need to design a gap due to the establishment of a heavy duty hall with an extreme load bearing floor, it was possible to use the offered gap for a workshop and offices on both floors next to the connecting corridor. Above the entrance there is also a room organized in two different levels with extensive utility and technology content.
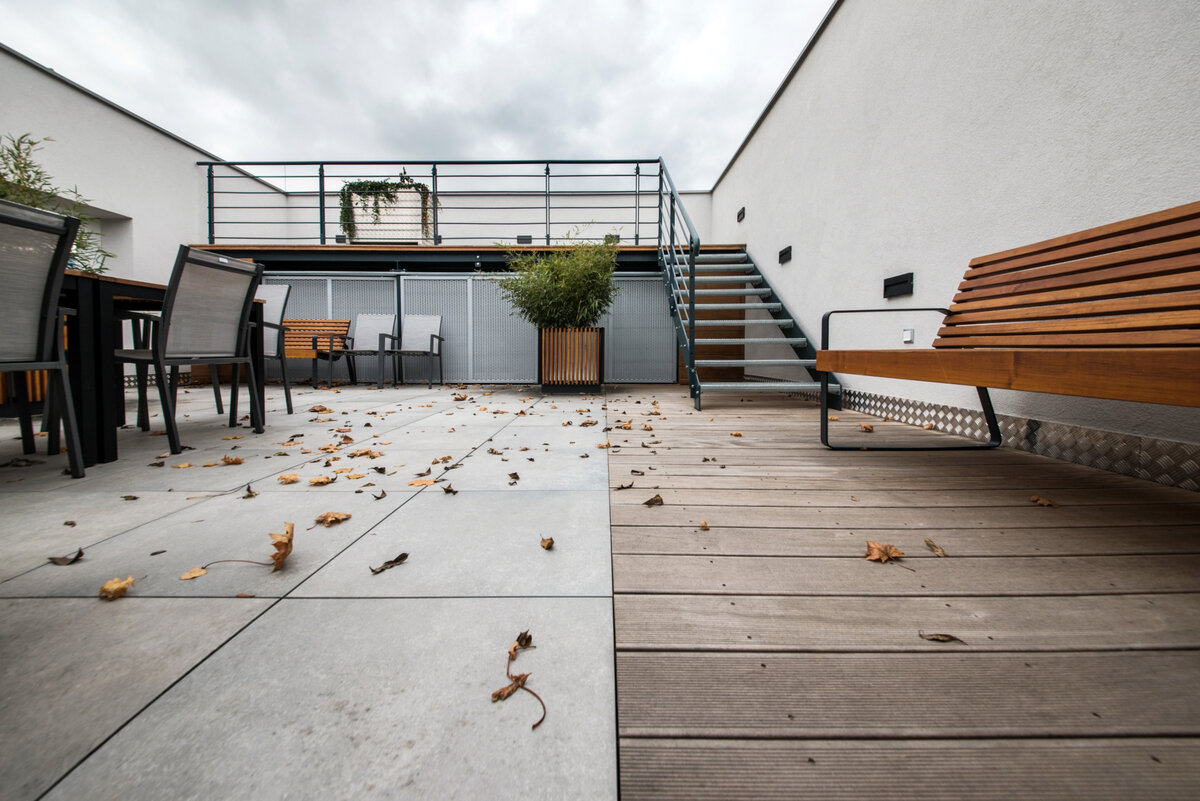
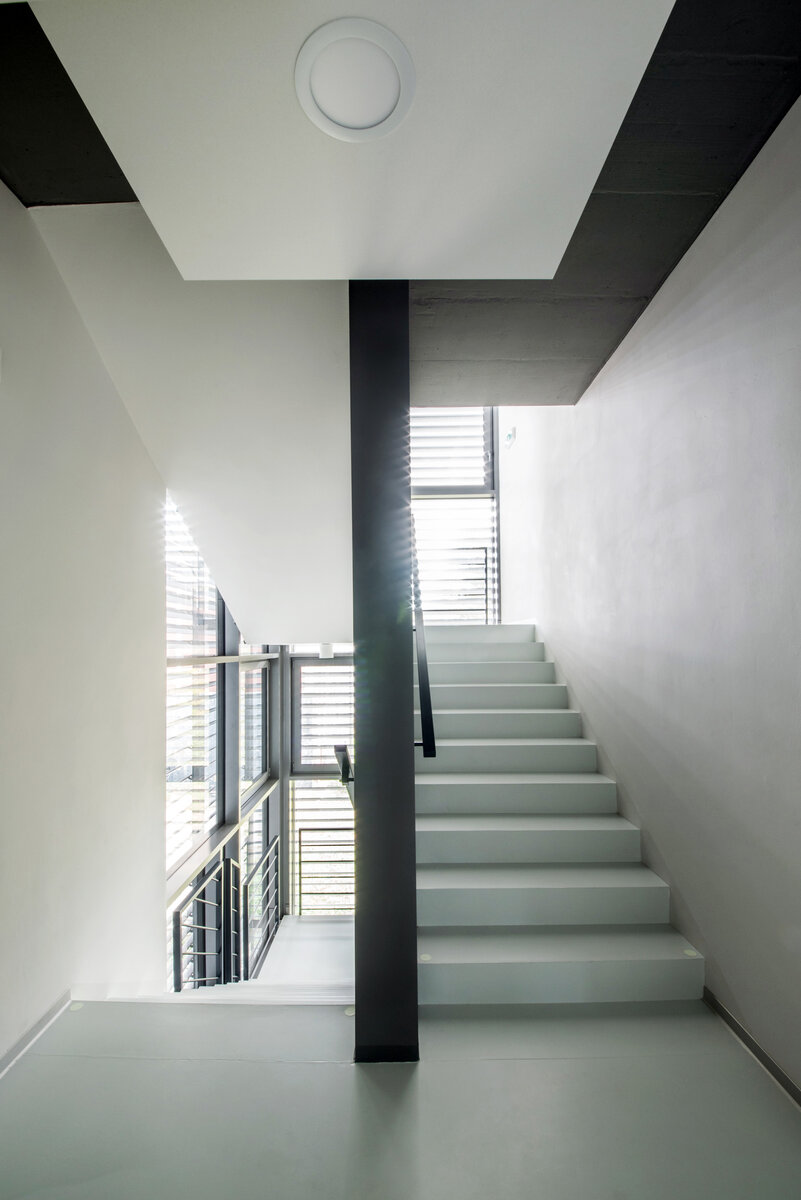
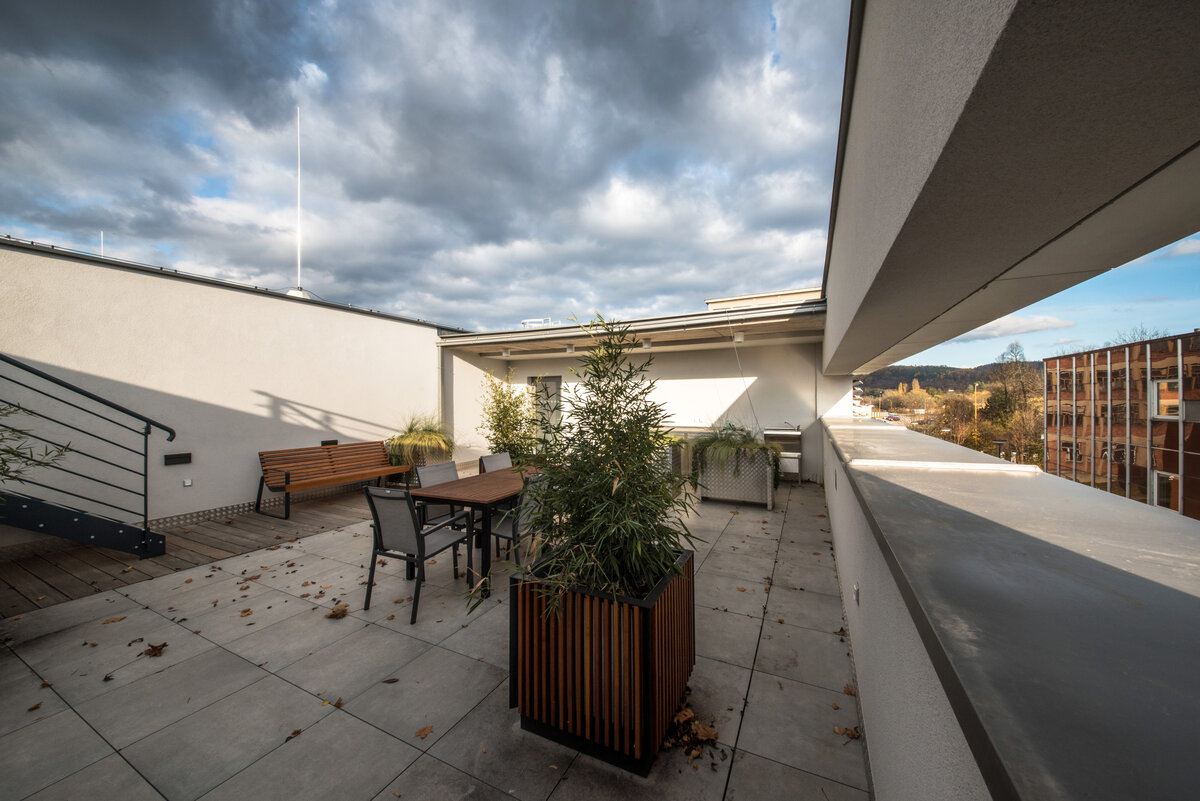
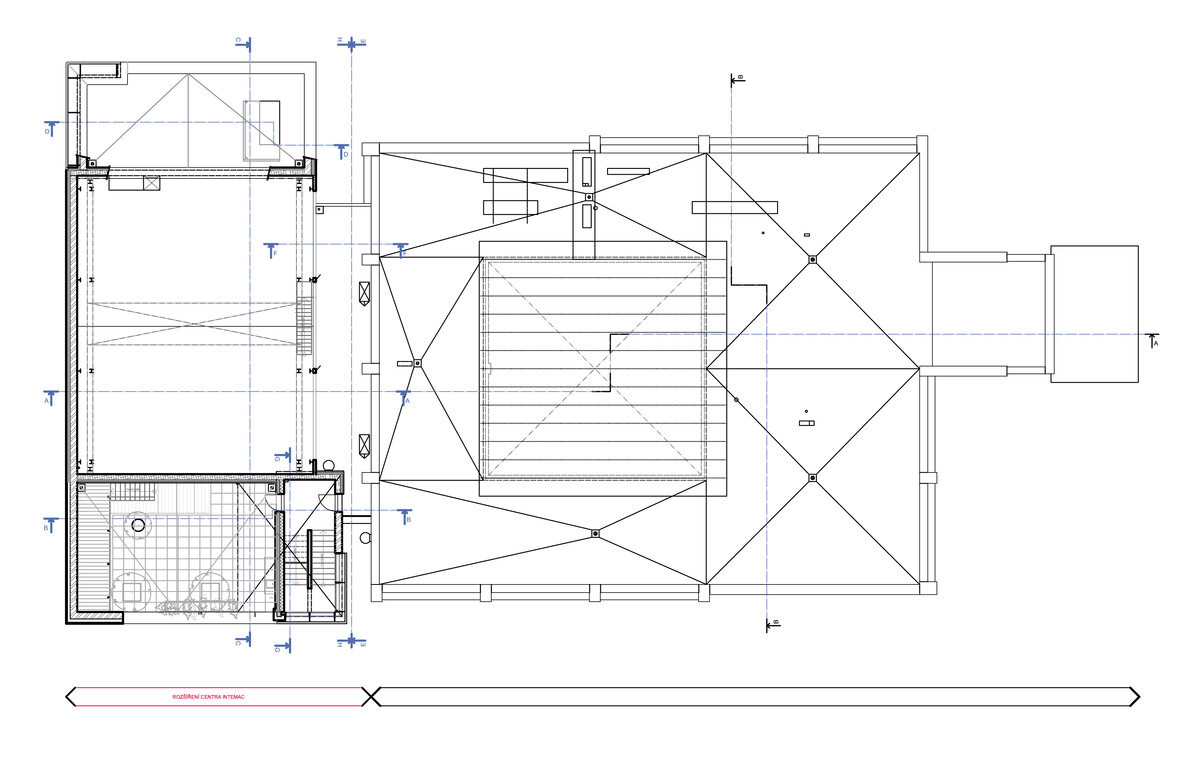
The third floor consists of a roof terrace and a staircase exit. The terrace is designed as an employee relaxation area. The sanitary facilities have been placed in the original building volume, these facilities include changing rooms, toilets, another laboratory, offices and a rehearsal room.
Due to heat accumulation, brick walls with thermal insulation under ventilated facade were designed. The connecting corridor has a separate lightweight steel construction. The utility room above the entrance and the administrative part have a monolithic reinforced concrete structure. The floor surfaces of the administrative part are as cast floors.
The space of the main laboratory is used for very precise machining and measurements, there are increased demands on the parameters of the indoor environment, especially the stability of the room temperature.
The stable operating conditions of the building are ensured by a sophisticated solution of air conditioning, ventilation and recuperation. An air-water heat pump and a solar thermal system are also used. The building is equipped with RTLS - Real time locating system.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
A
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|