| Author |
autor: Ing. arch. Petr Franta, spolupráce: Ing. arch. Petr Sobotka, Ing. arch. Štěpán Sekera, Danuše Kolenová |
| Studio |
PETR FRANTA ARCHITEKTI & ASOC., spol. s r.o. |
| Location |
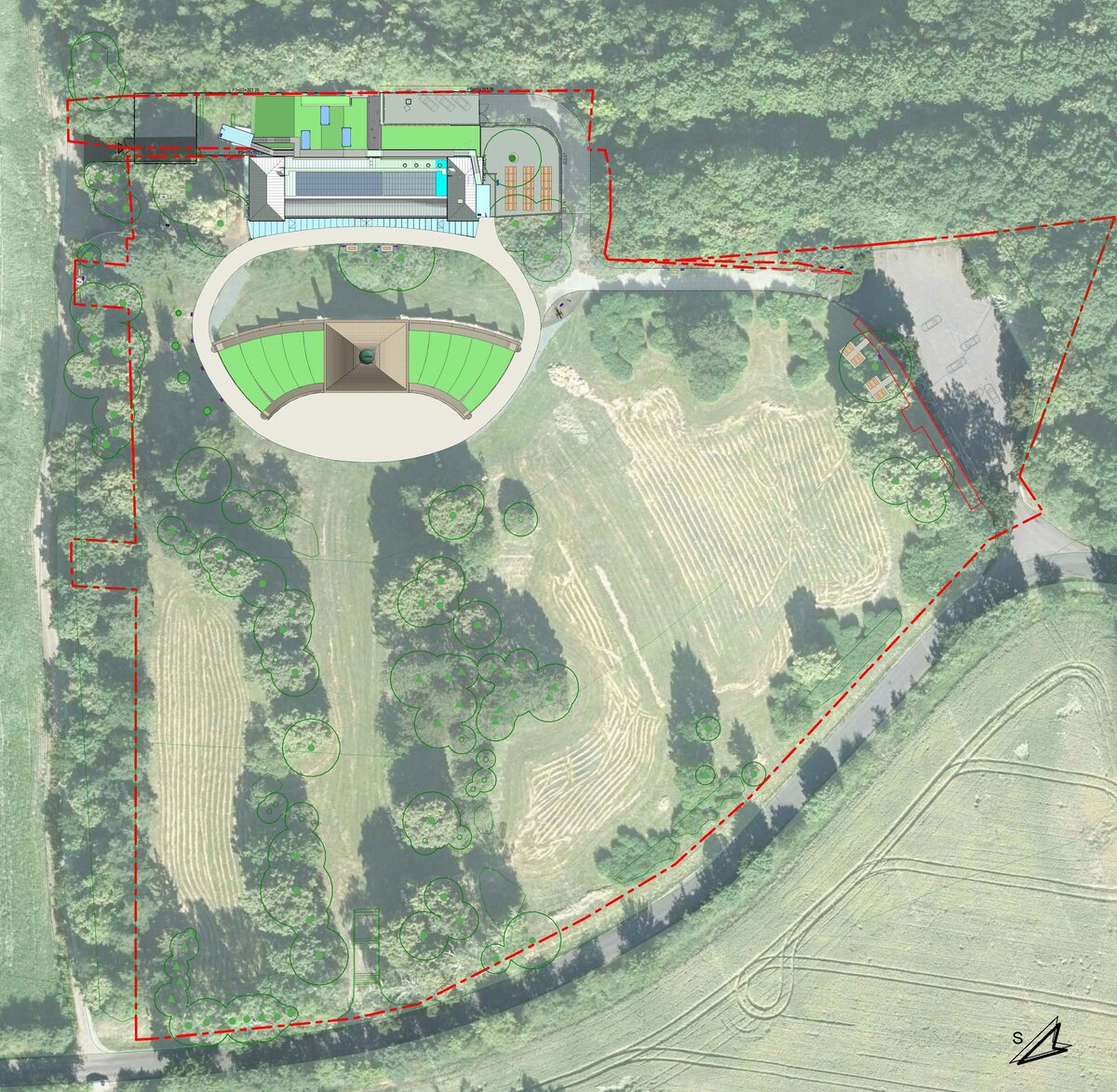
Památník Mohyla míru, Pracký kopec u obce Prace, K Mohyle míru 200, 664 58 Prace |
| Collaborating professions |
Statika skla a ocelových konstrukcí: Ing. Miroslav Špaček; technika prostření Ing. Jan Červenák; zeleň, parkové úpravy: Vratislav Brabenec |
| Investor |
Muzeum Brněnska, příspěvková organizace, Předklášteří, Porta coeli 1001, PSČ 602 00, ředitel Ing. ThLic. Evžen Martinec, Ph.D., MBA; Ing. Jana Klusoňová
Jihomoravský kraj, Žerotínovo nám. 449/3, Brno, 601 82 |
| Supplier |
WELLCO Brno s.r.o., Příkop 843/4, budova IBC, Brno, Ing. Jan Šenkýř, jednatel společnosti |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
April 2024 |
| Fotograf |
Petr Franta, Michaela Glezgová, Štěpán Sekera |
THE MUSEUM OF THE CAIRN OF PEACE MEMORIAL – ARCHITECTURE OF MEMORY AND THE AUSTERLITZ BATTLEFIELD
The main idea of the project was to commemorate the first Peace memorial in Europe, which was built out of piety for all fallen soldiers, regardless of nationality or religion.
Our primary task was to unite historical and contemporary architecture in a historical and landscape context.
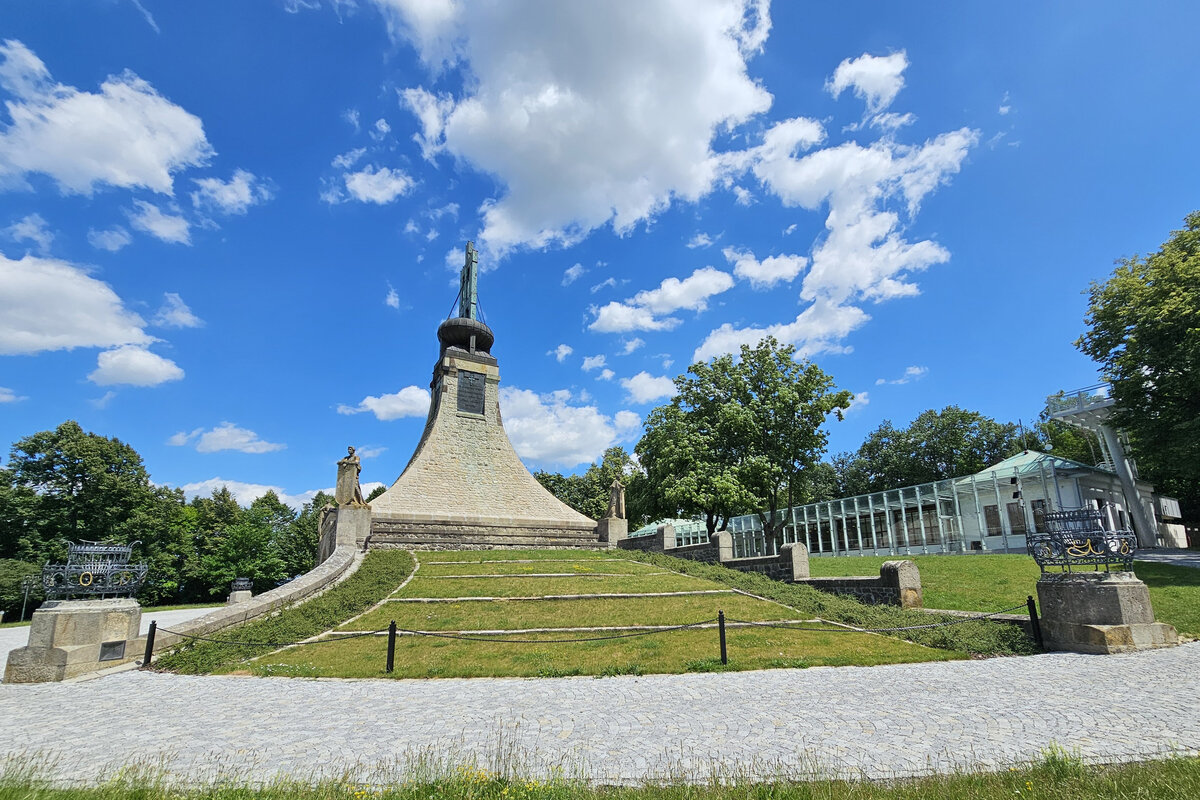
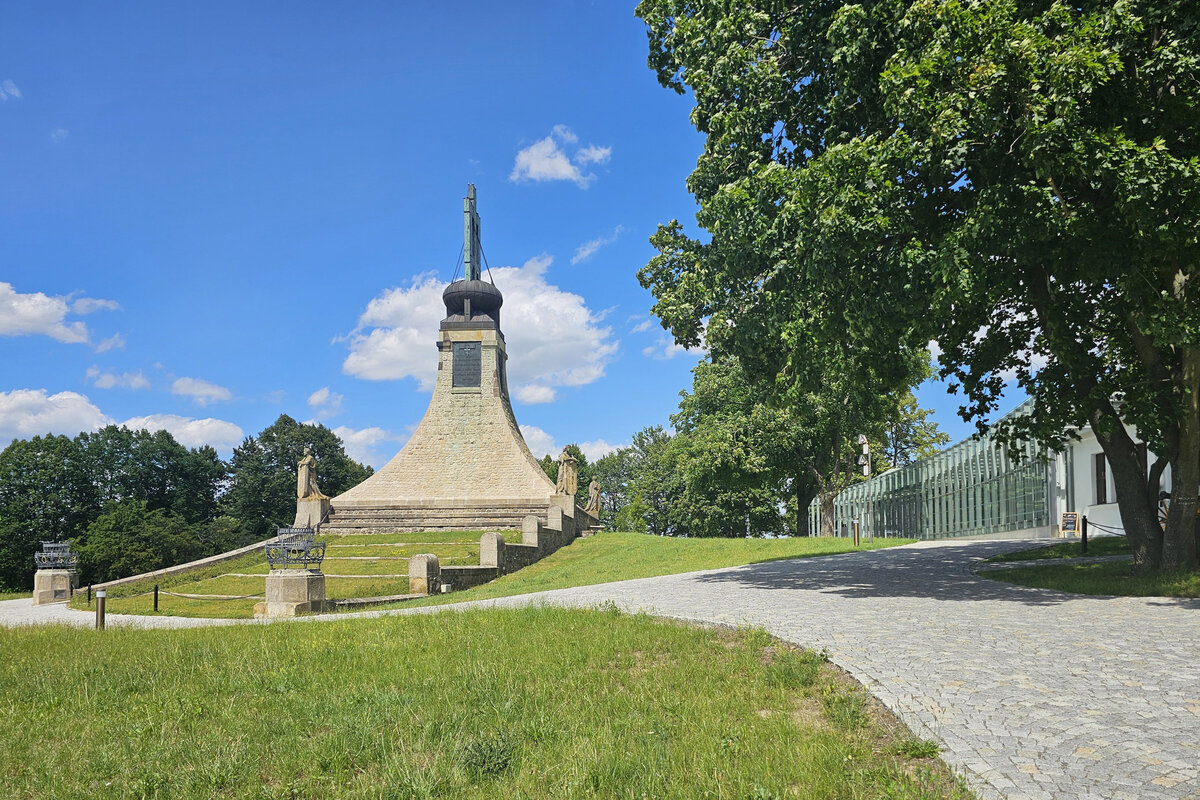
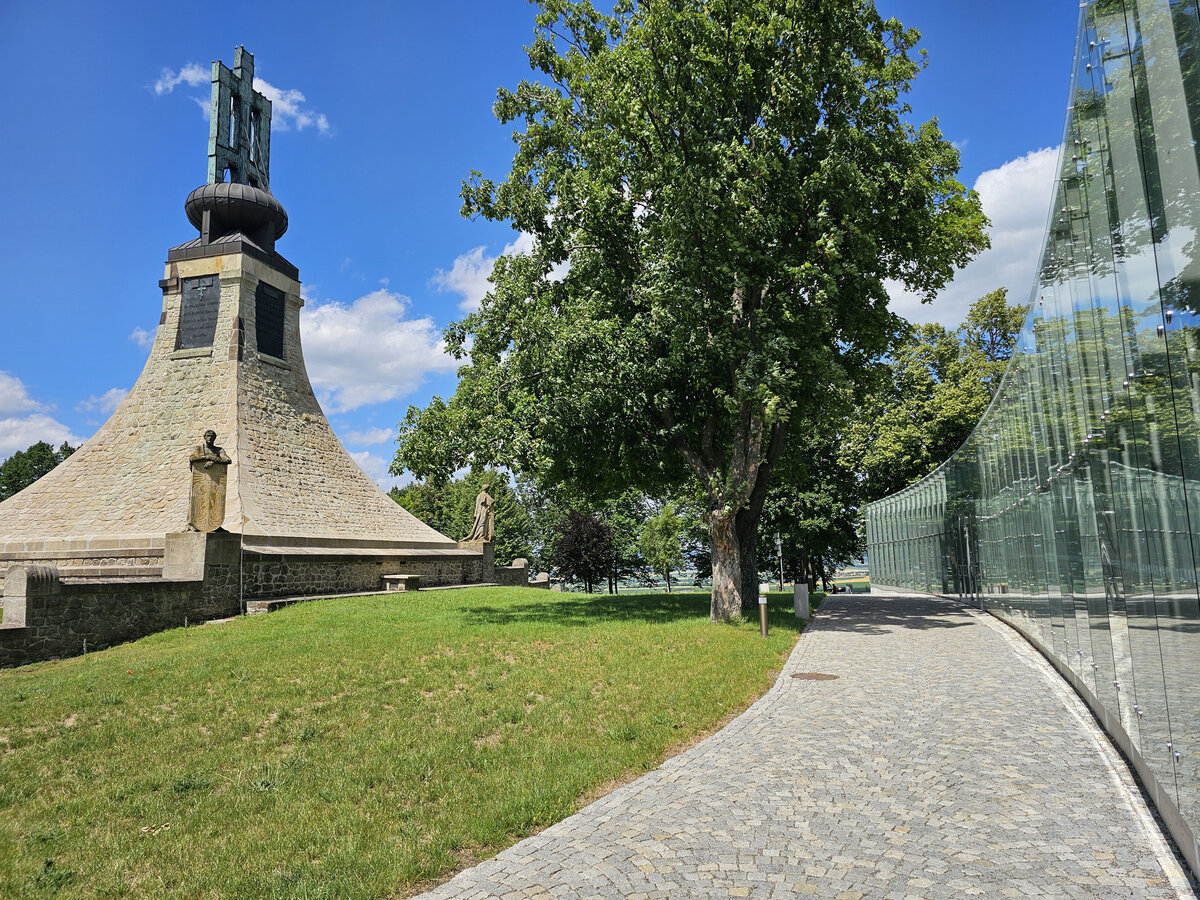
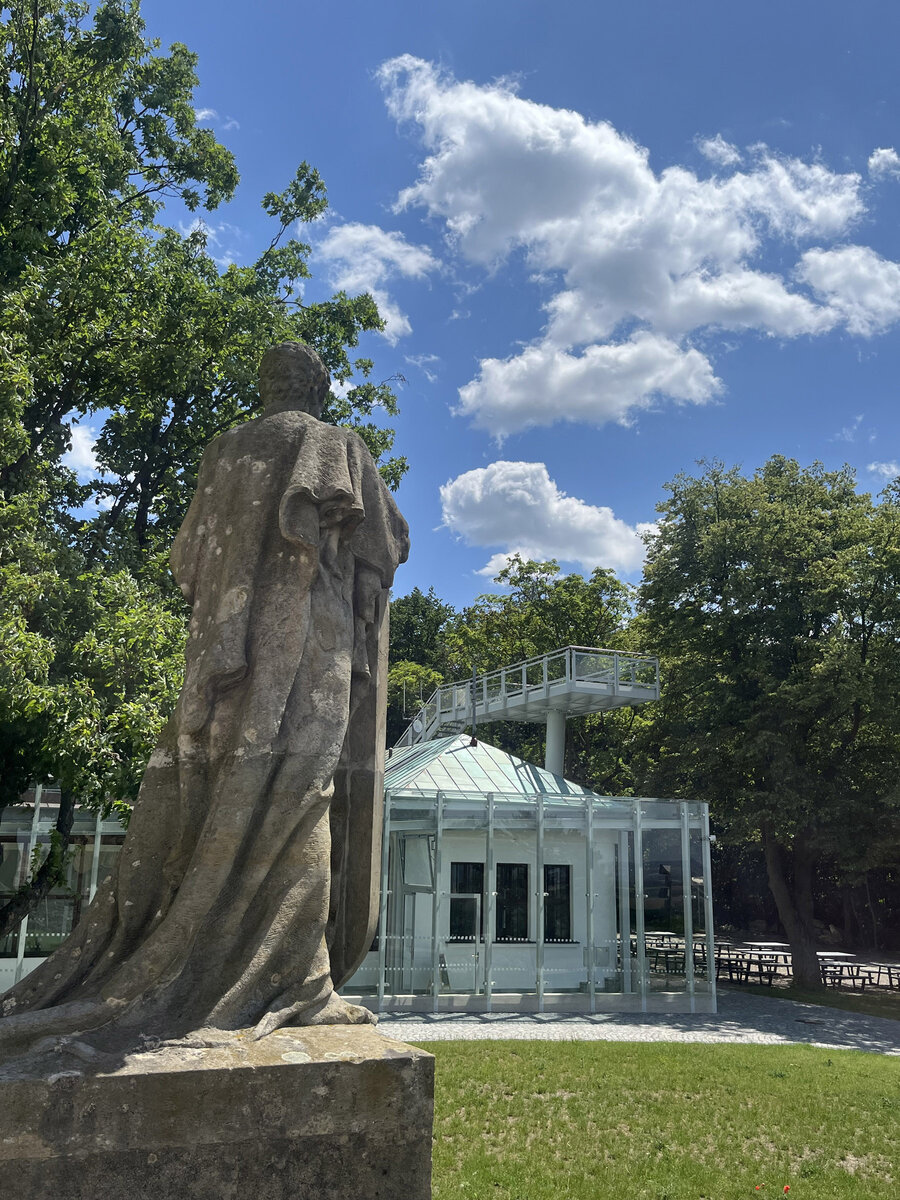
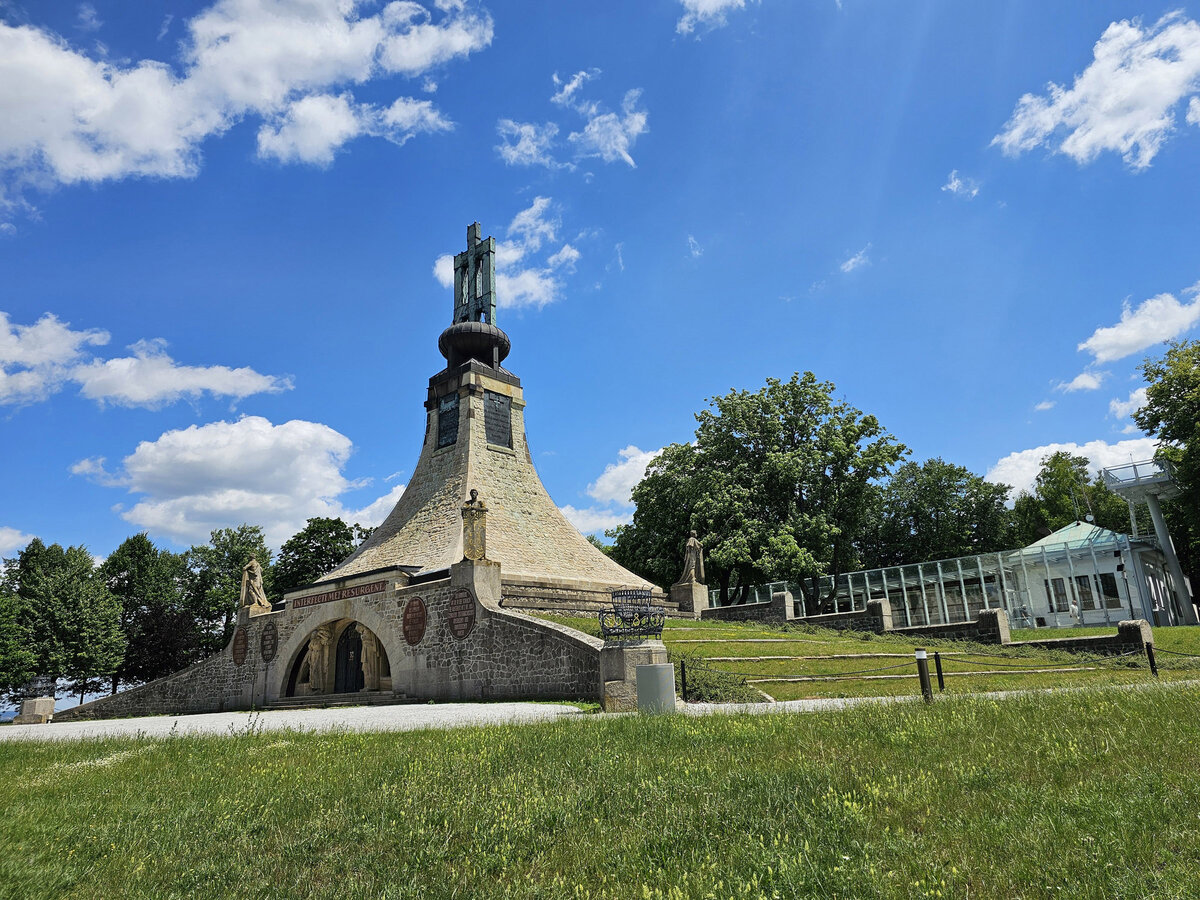
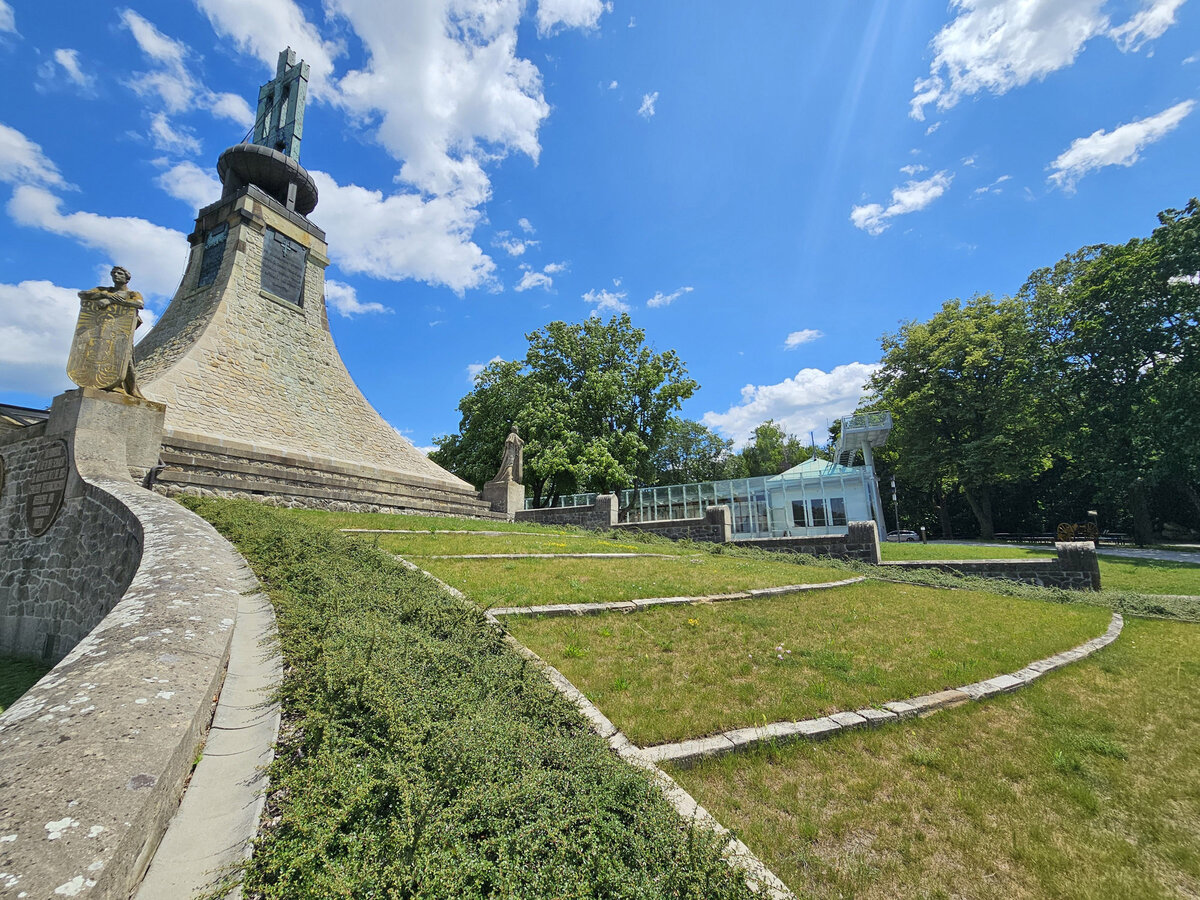
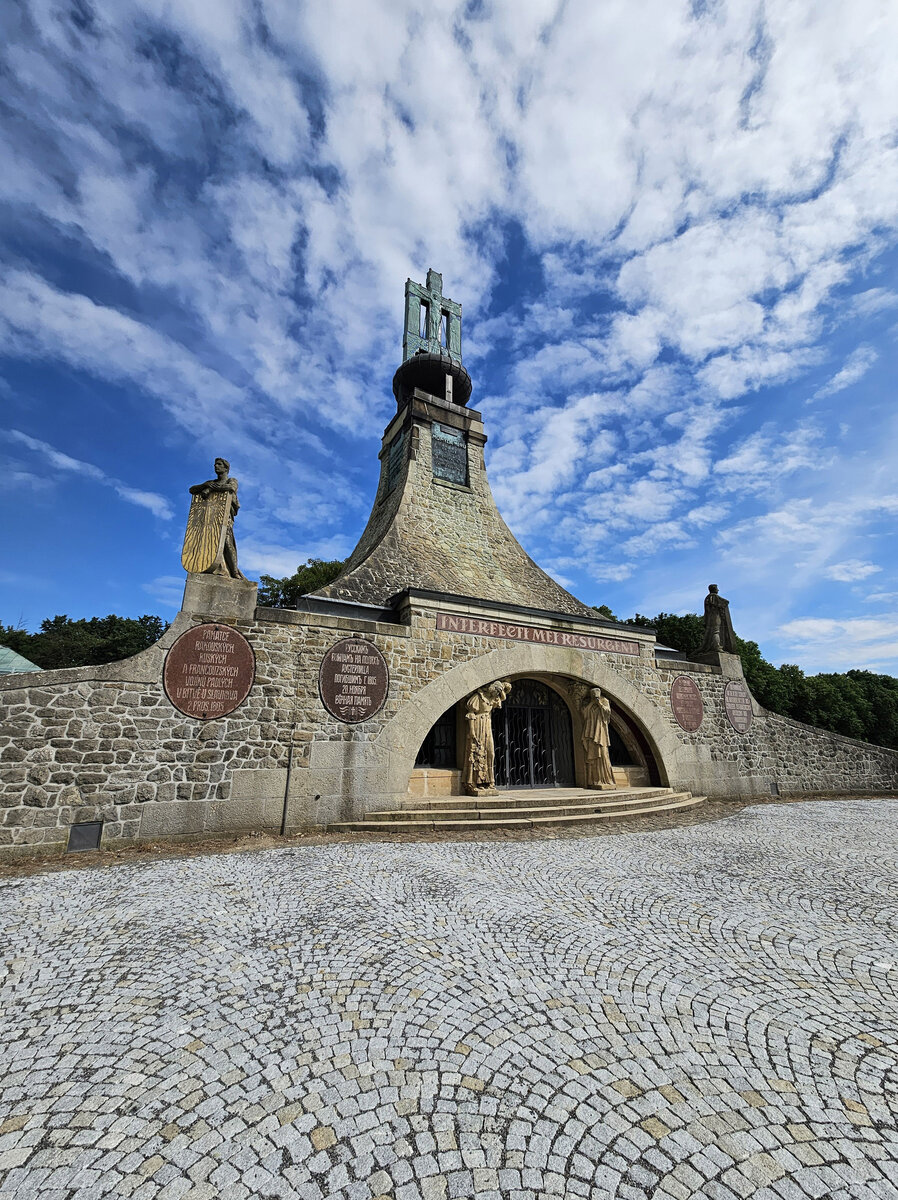
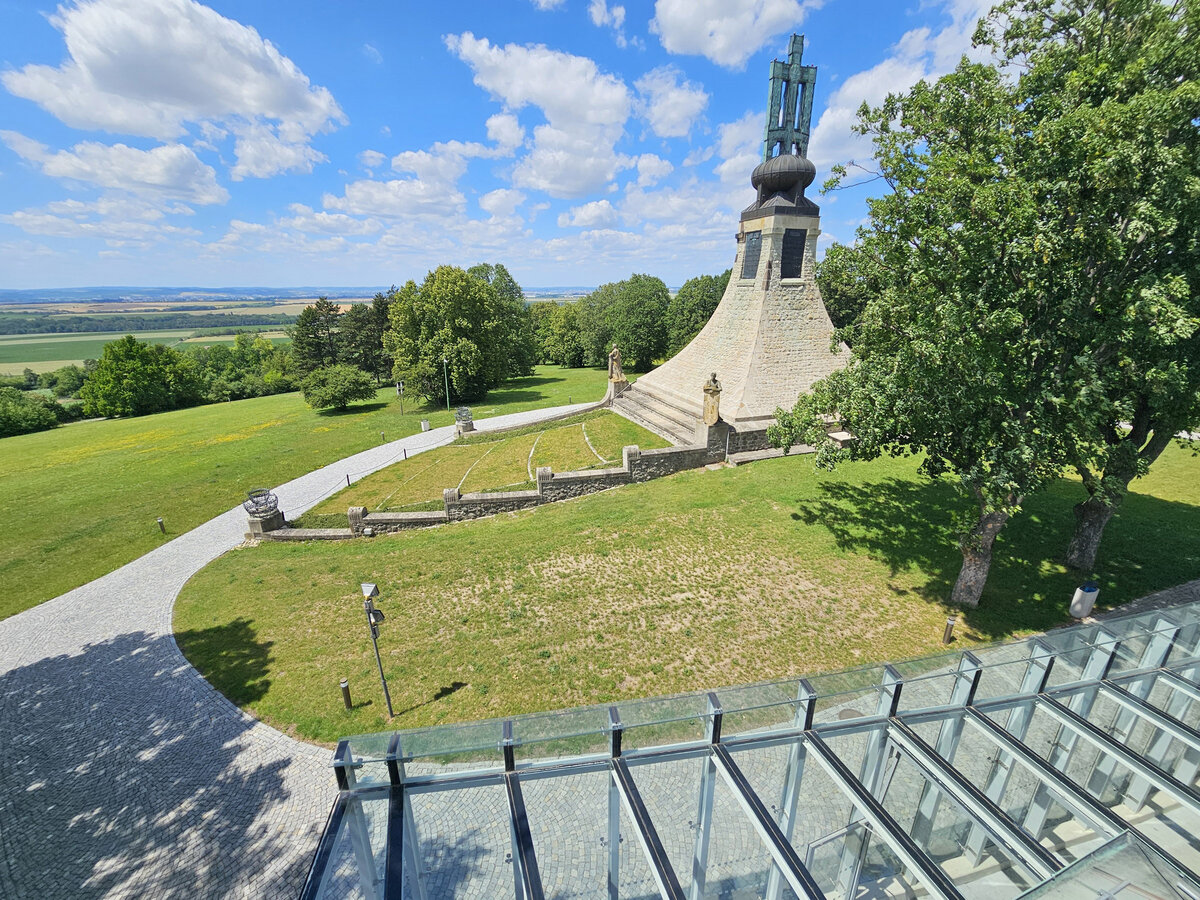
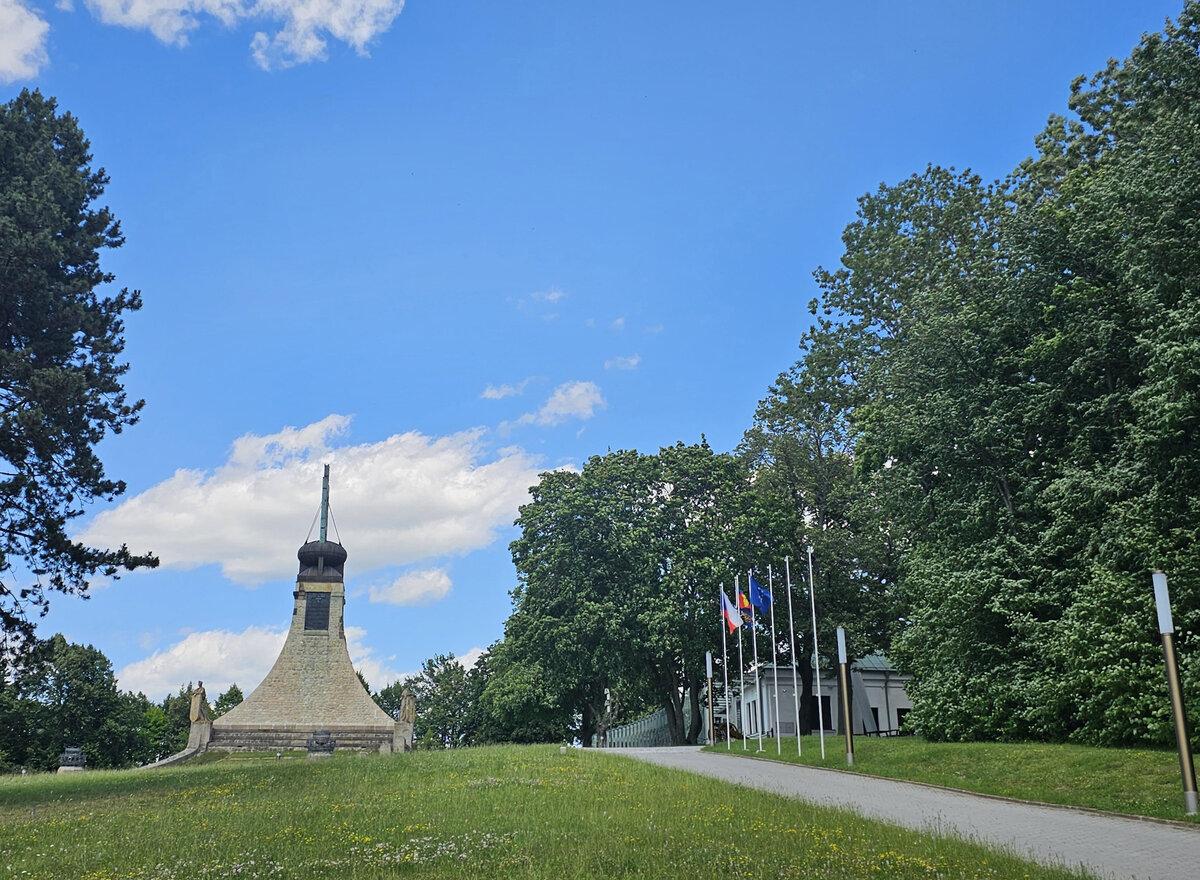
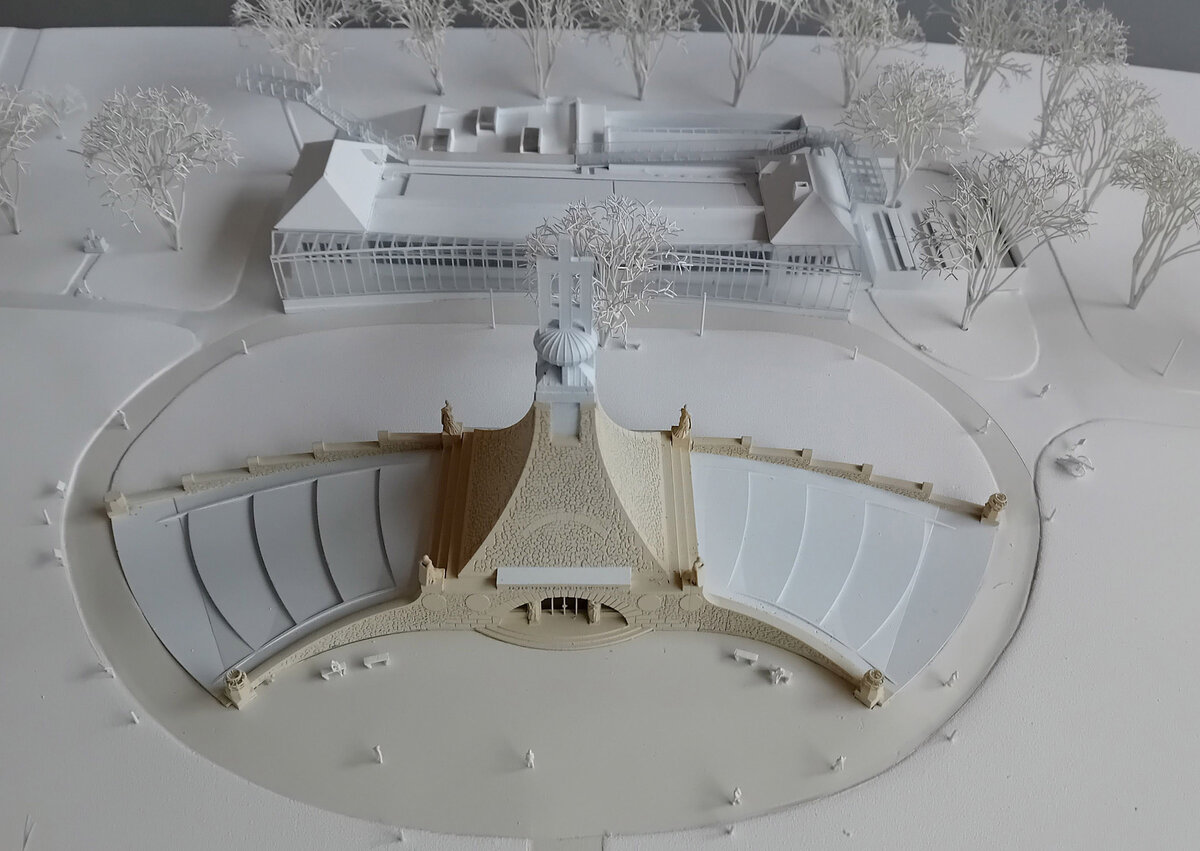
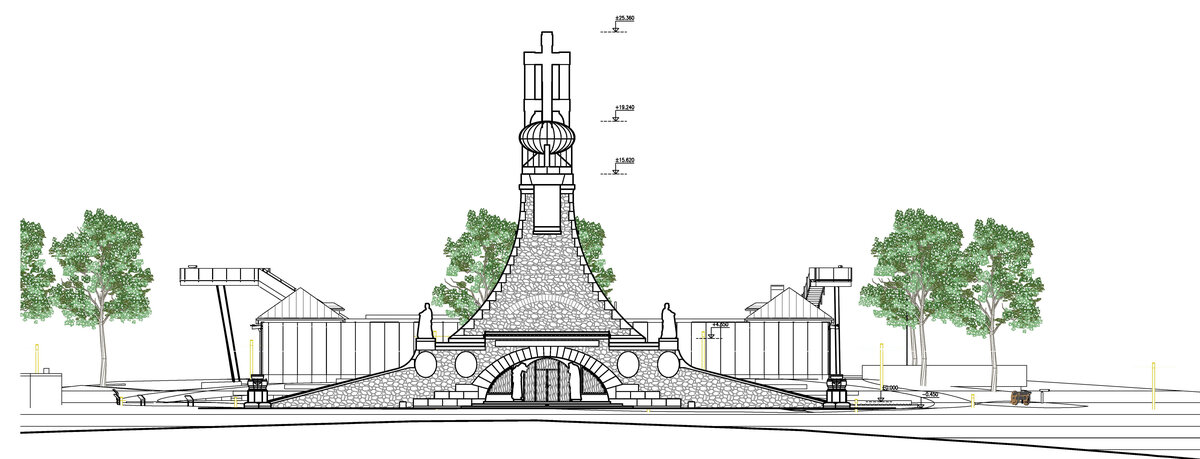
The Cairn of Peace, designed in 1907 by architect Josef Fanta, is on the Central List of Cultural Monuments and is also located in the landscape conservation zone of the Austerlitz Battlefield.
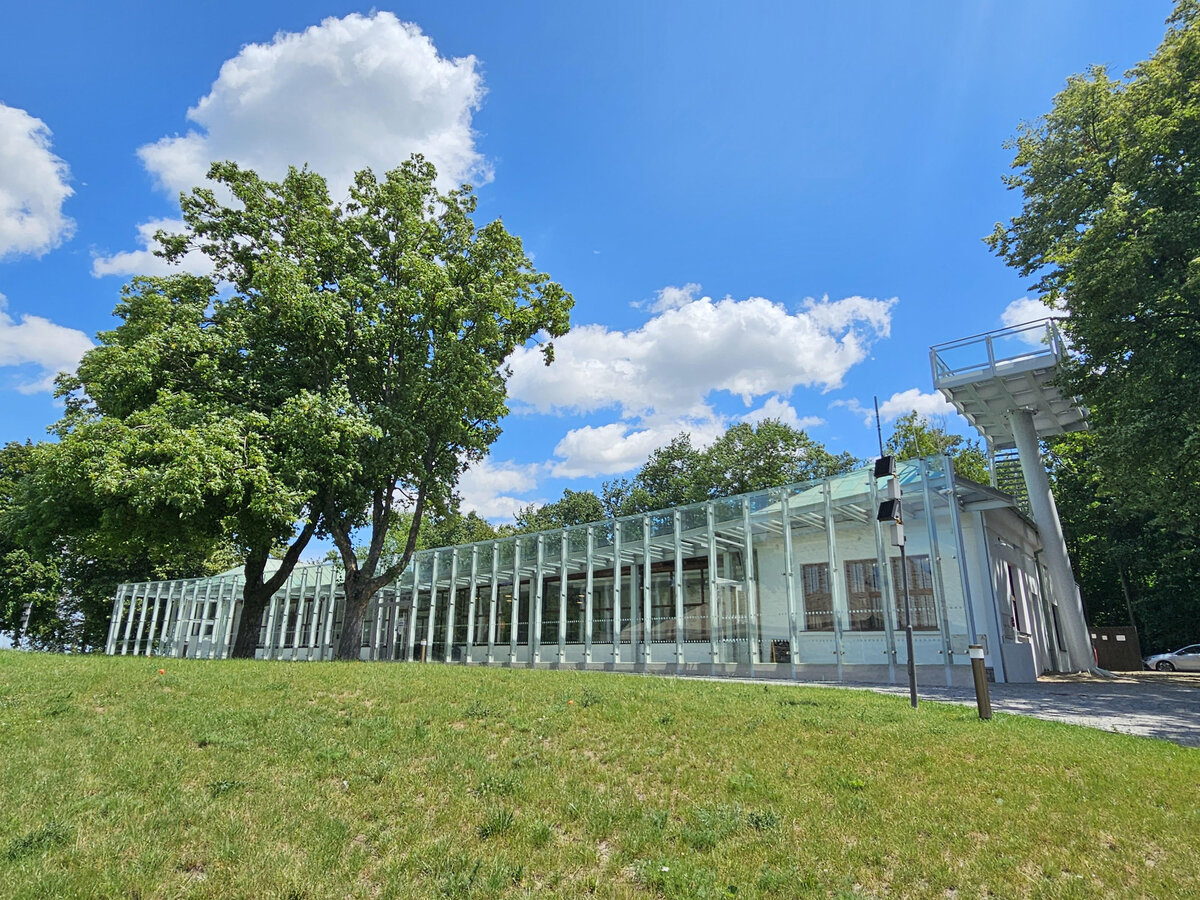
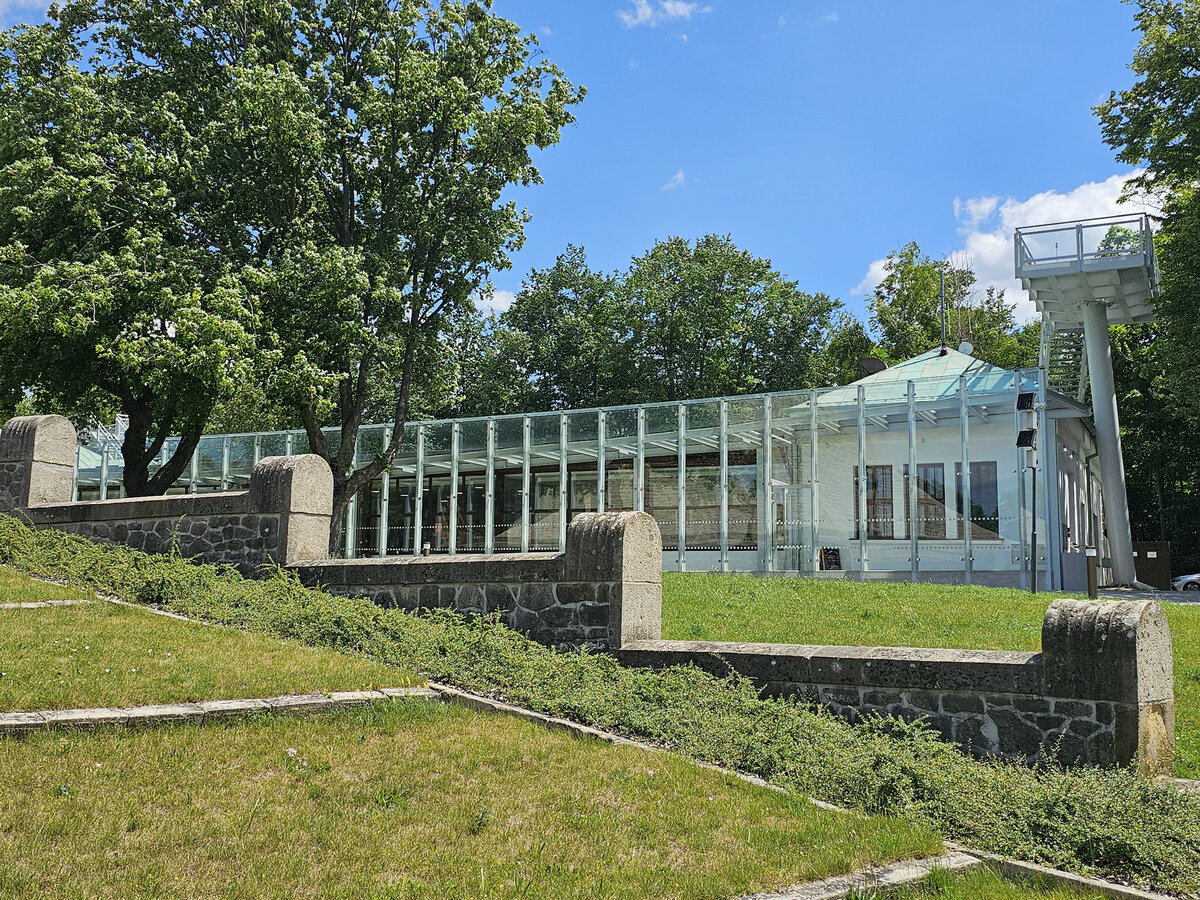
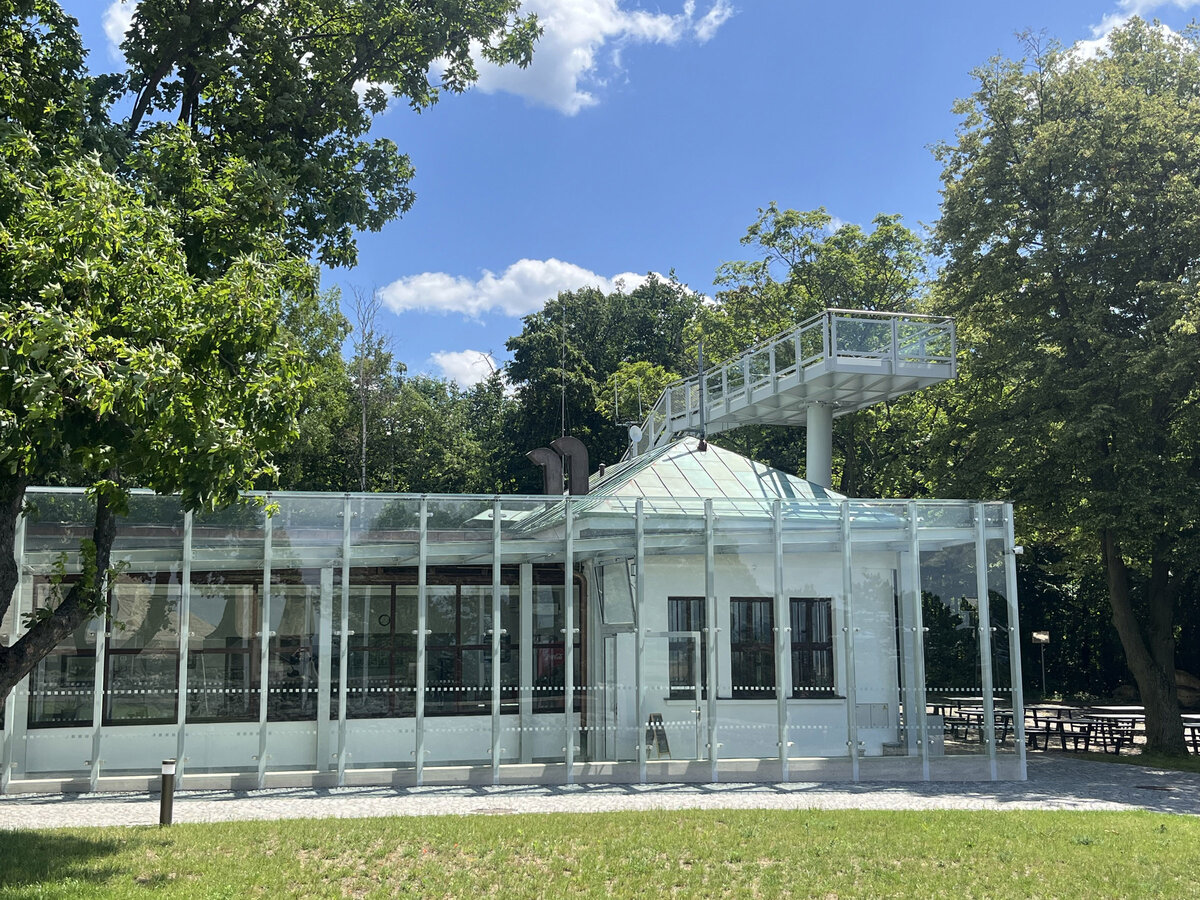
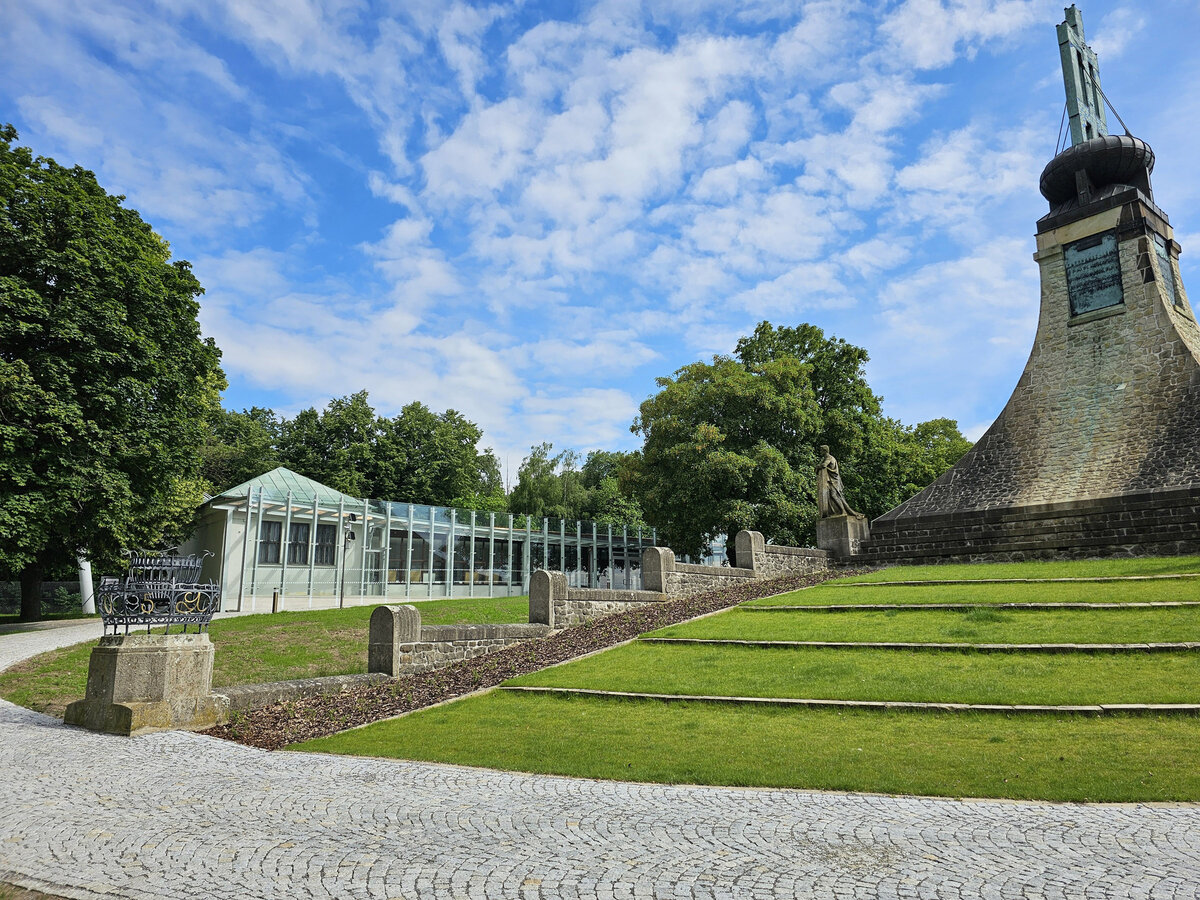
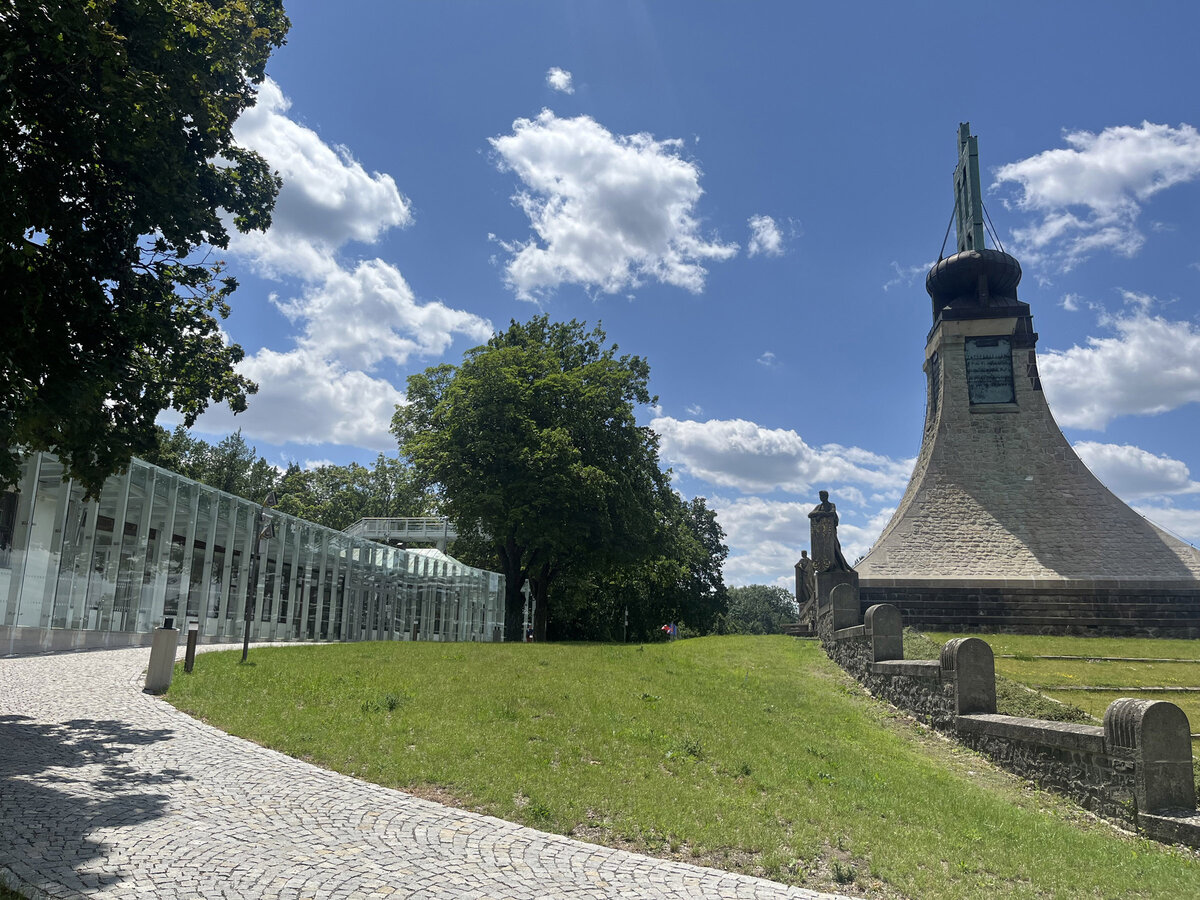
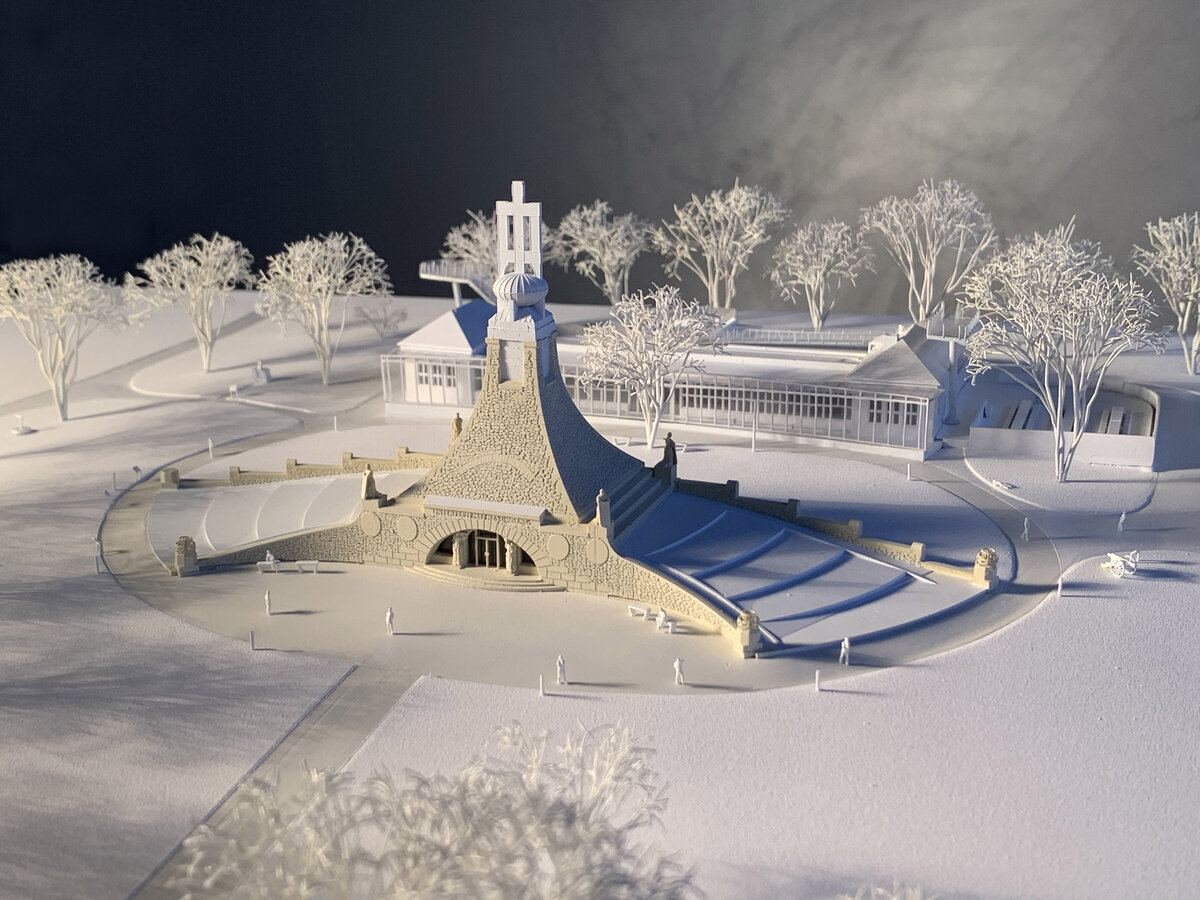
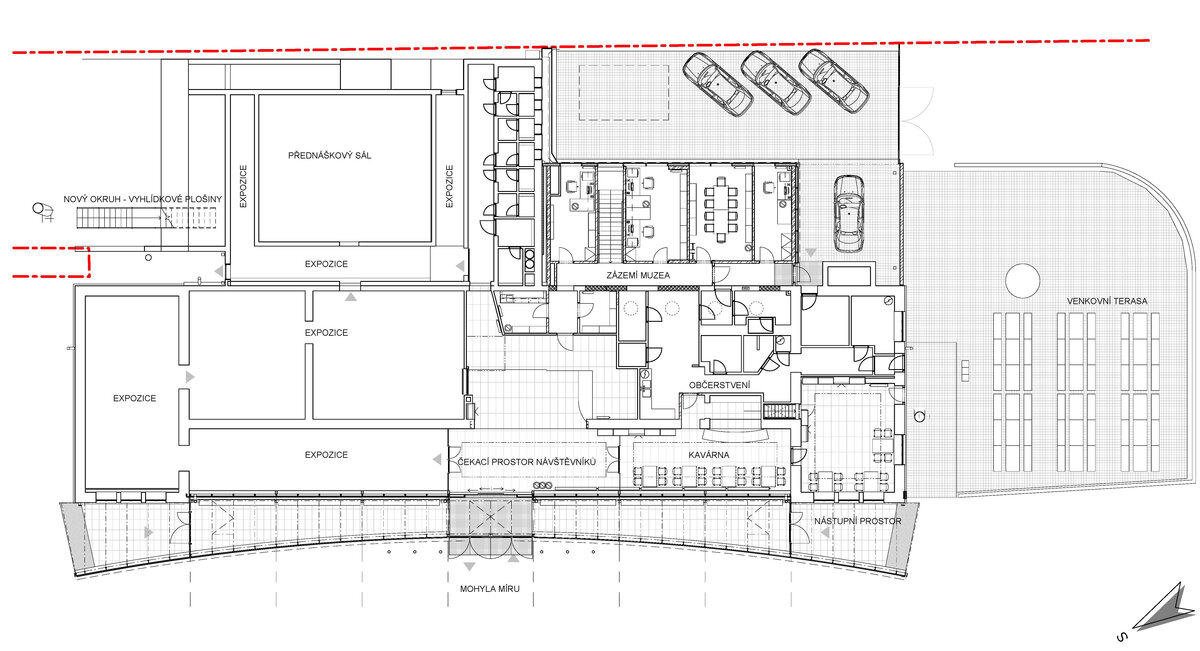
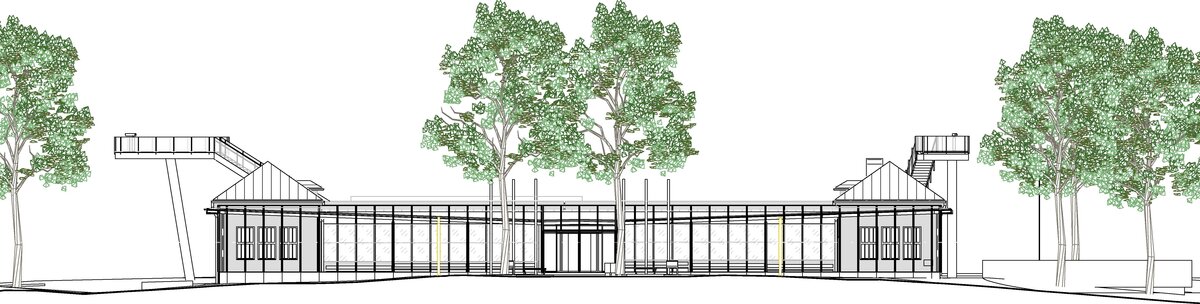
The principal aim was to sensitively connect the existing museum pavilion with the new infrastructure, i.e. with the museum's facilities – the curators' rooms and offices, depositories and visitors' cafe.
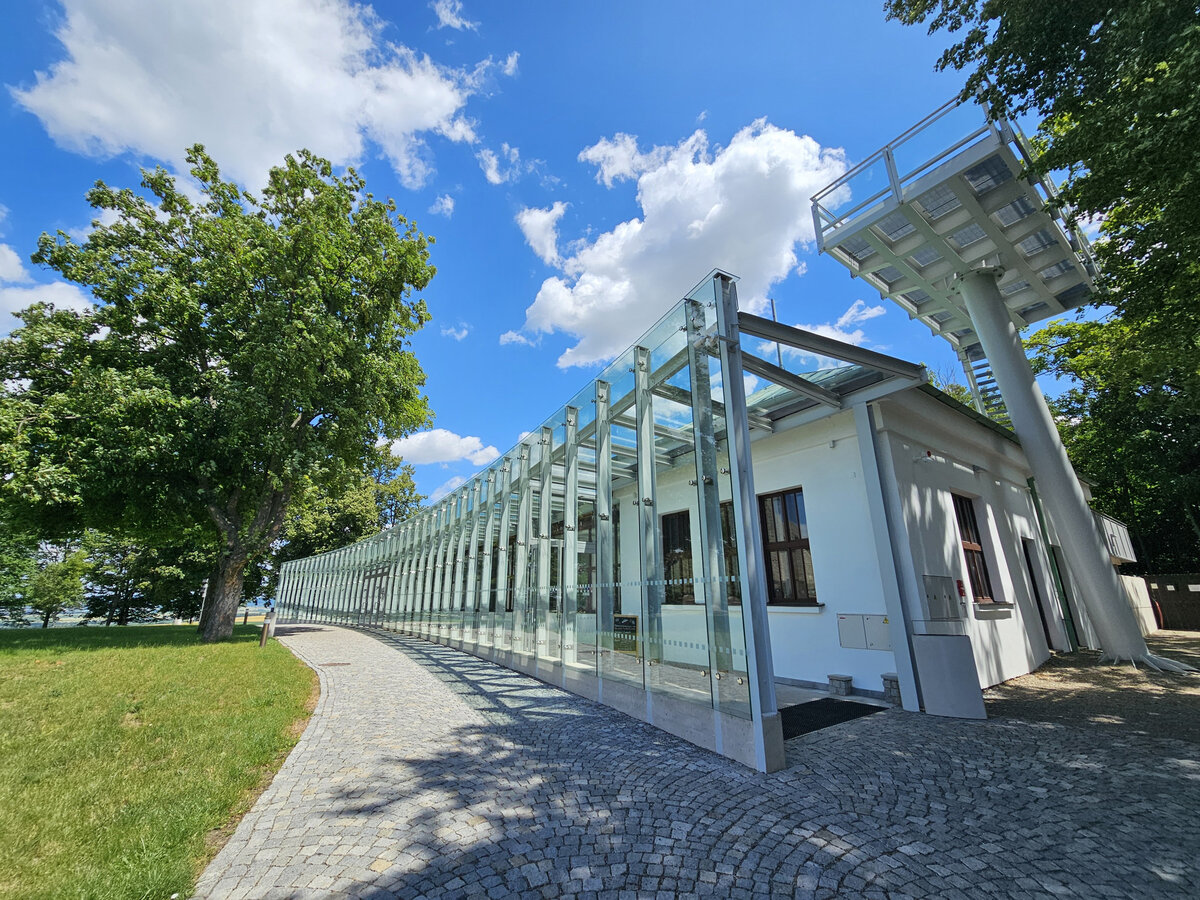
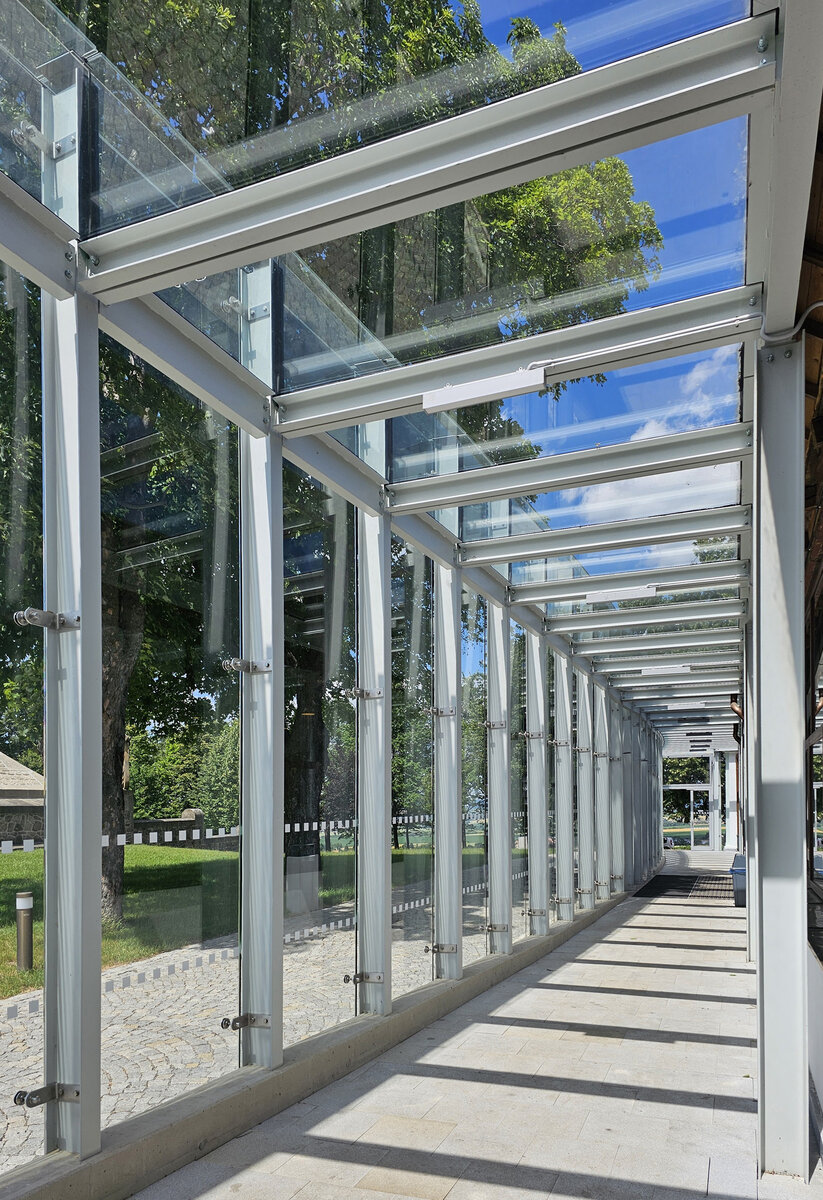
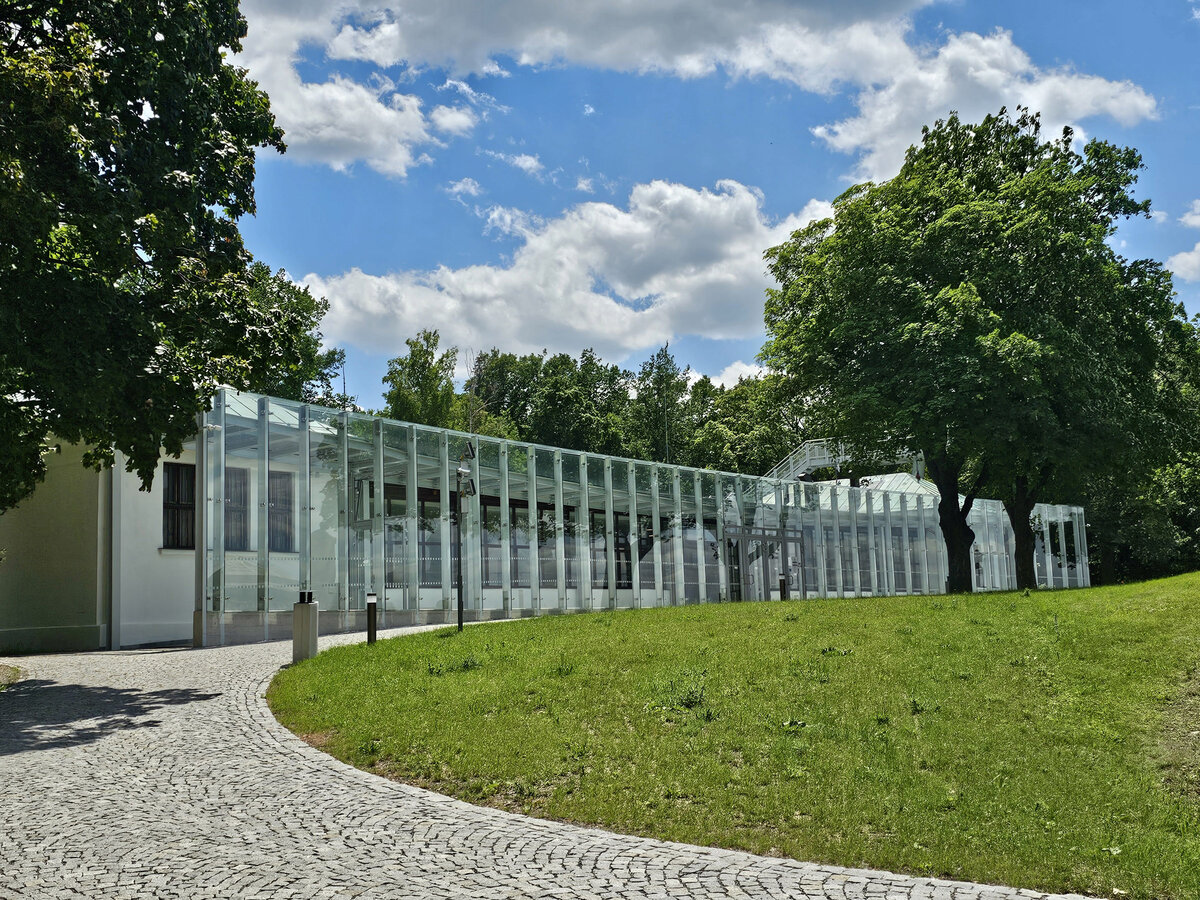
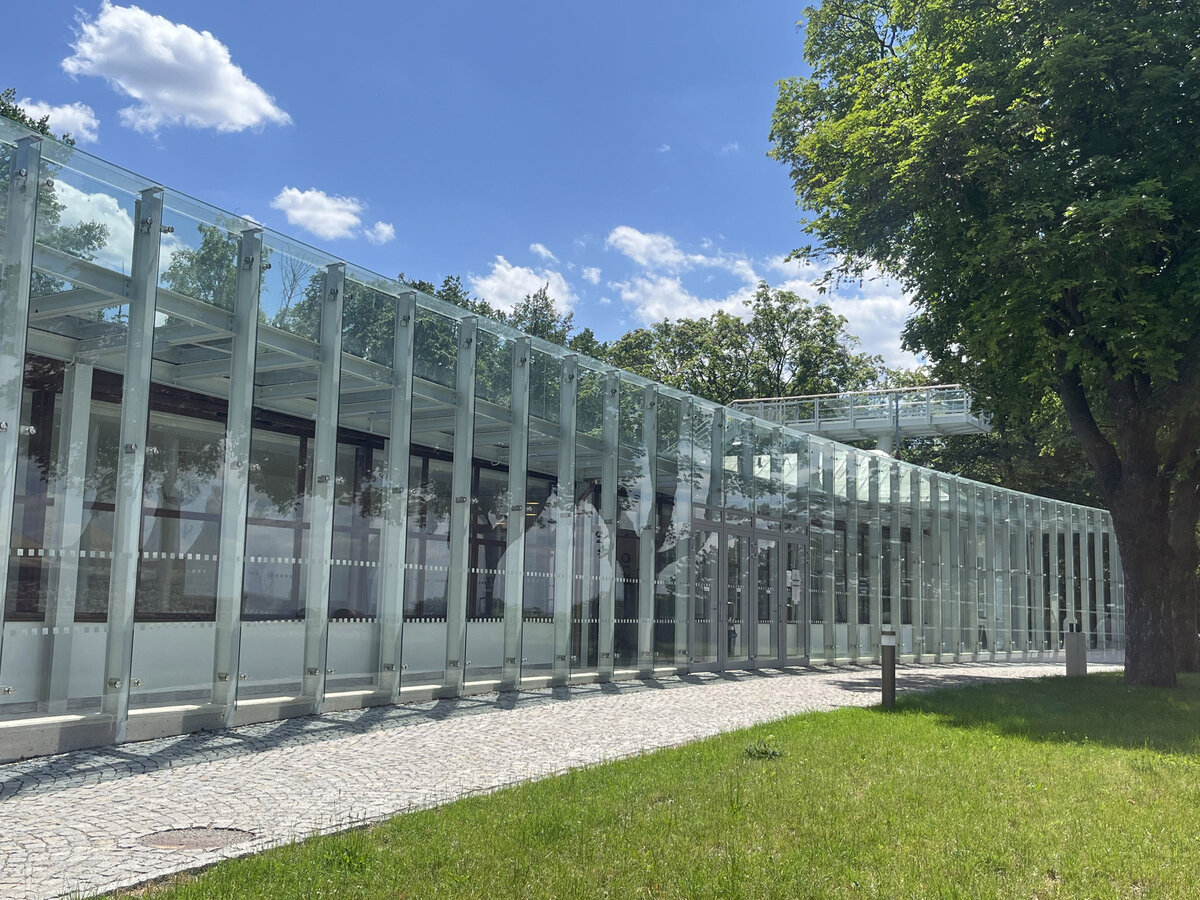
The all-glass vestibule wall, that forms an arch in which the Cairn of Peace Memorial is mirrored, seemed ideal.
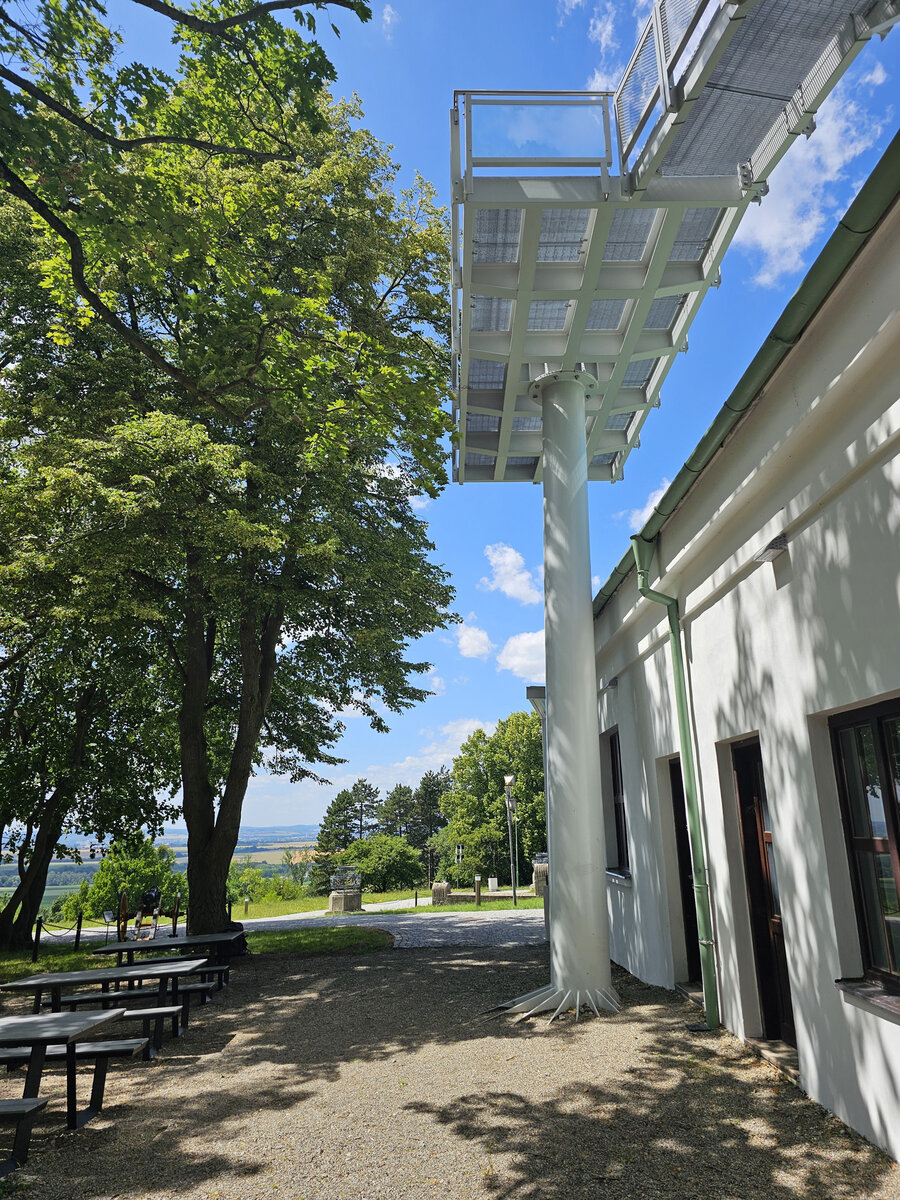
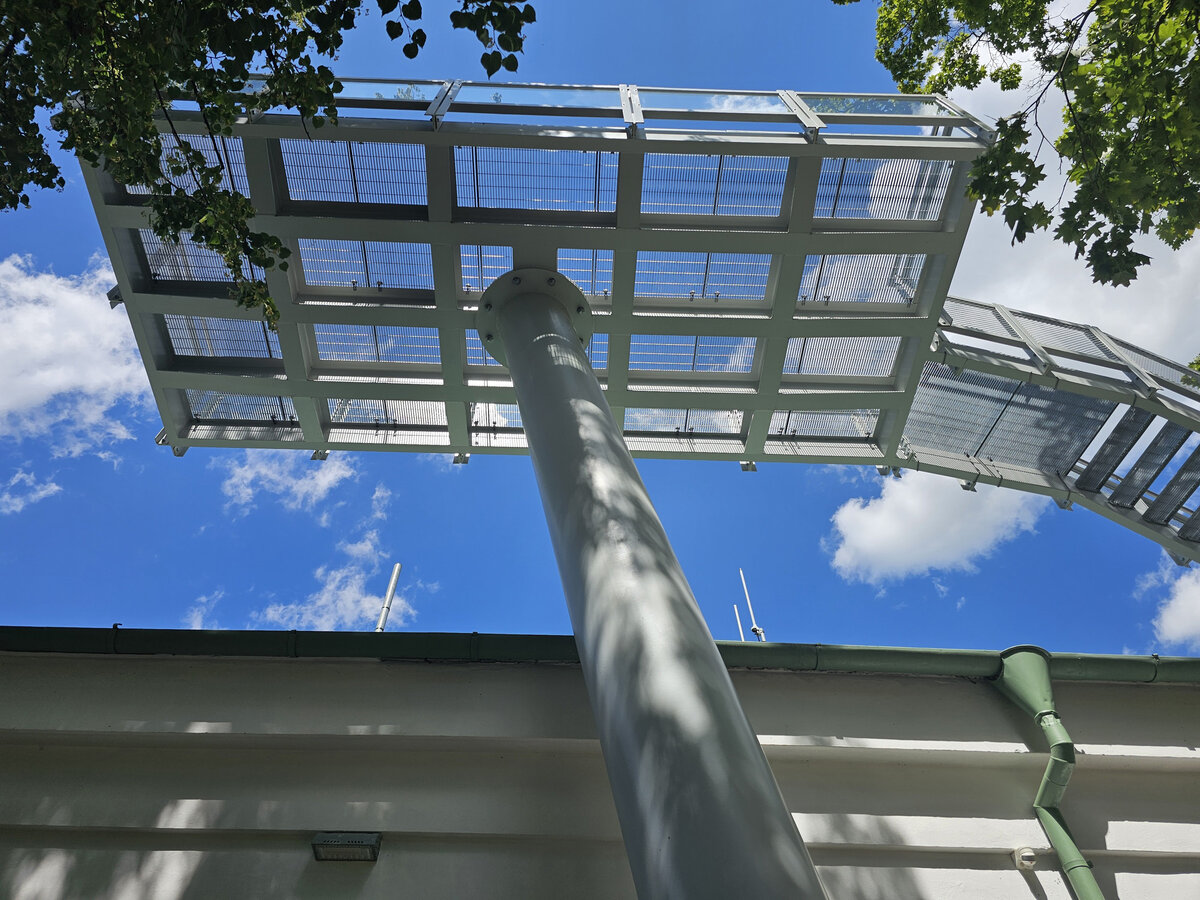
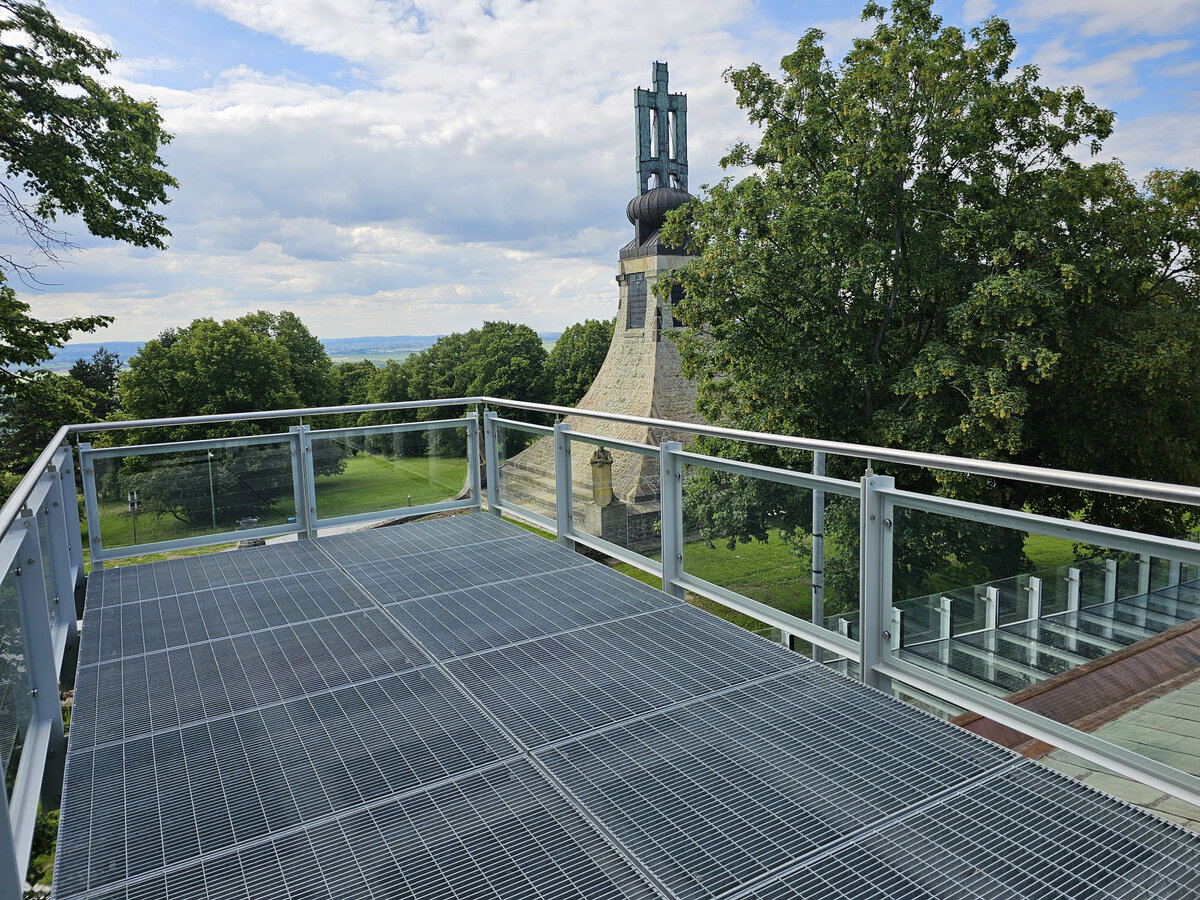
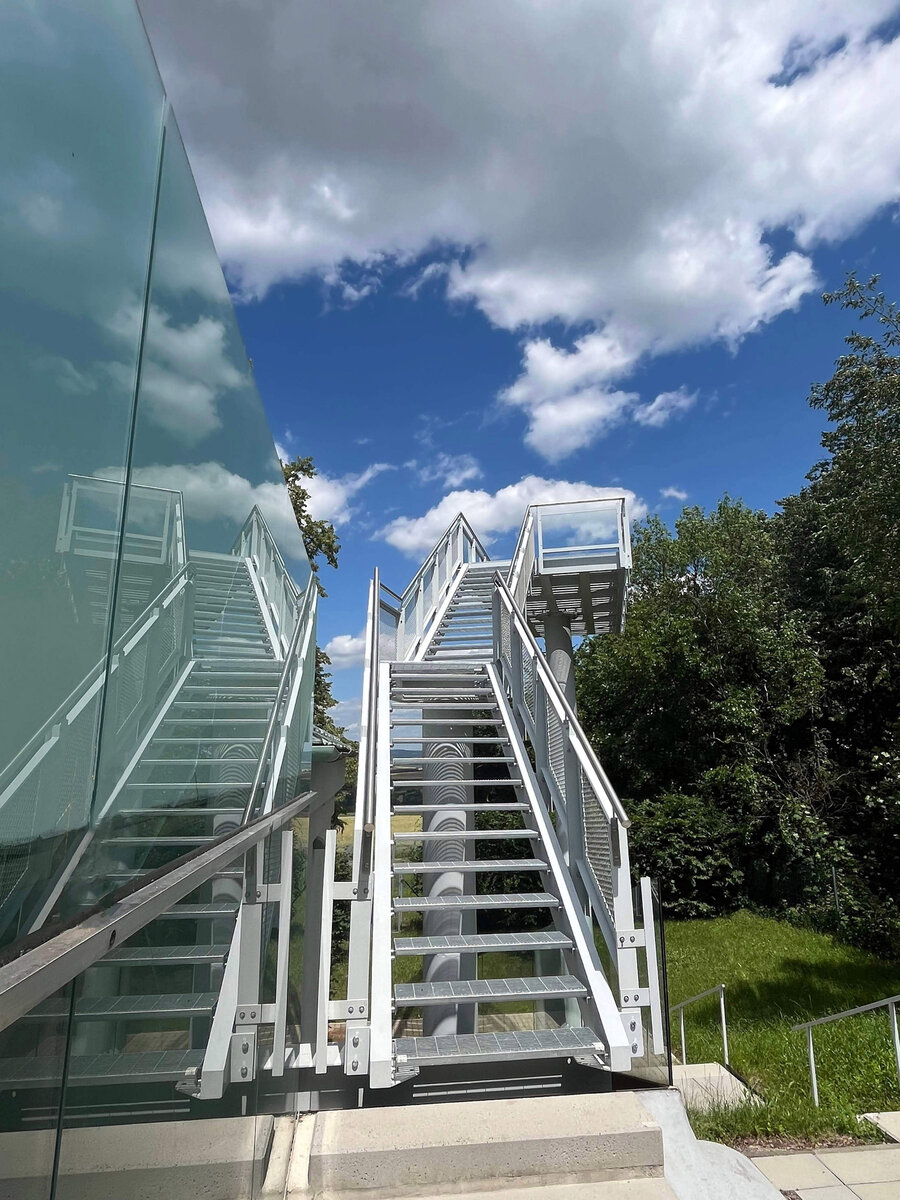
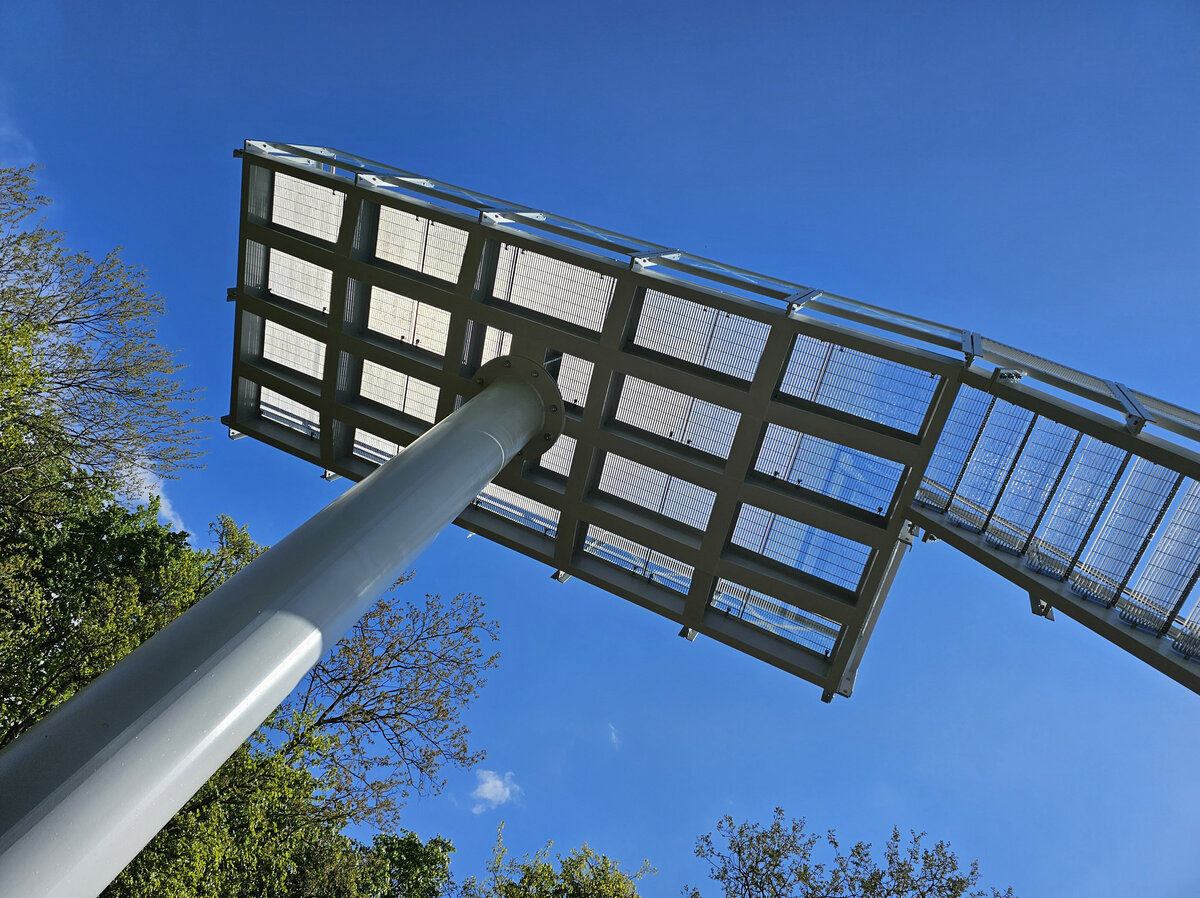
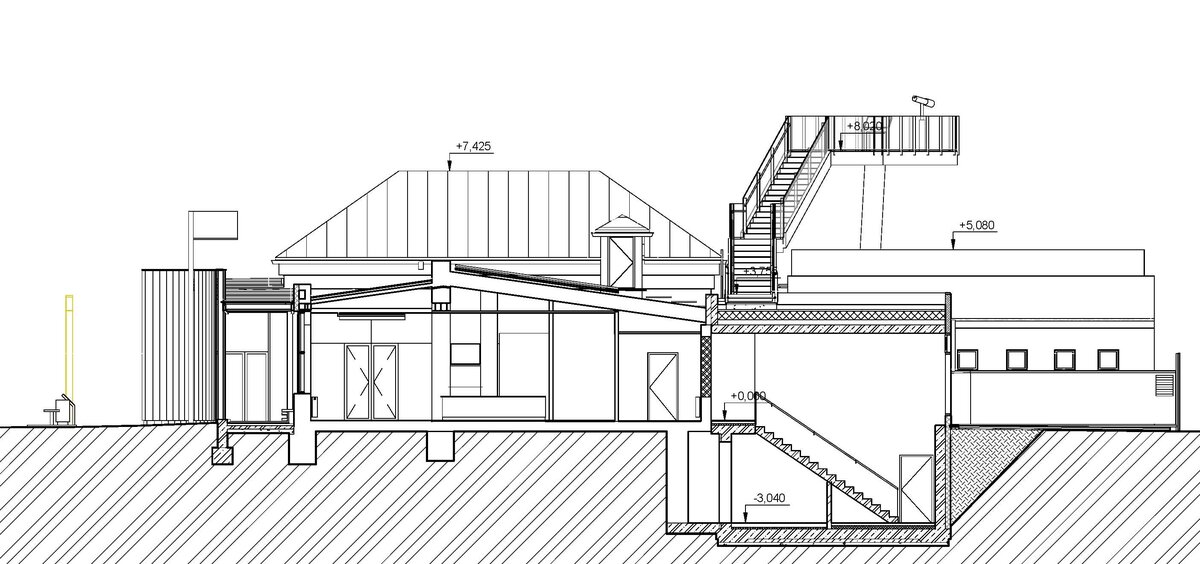
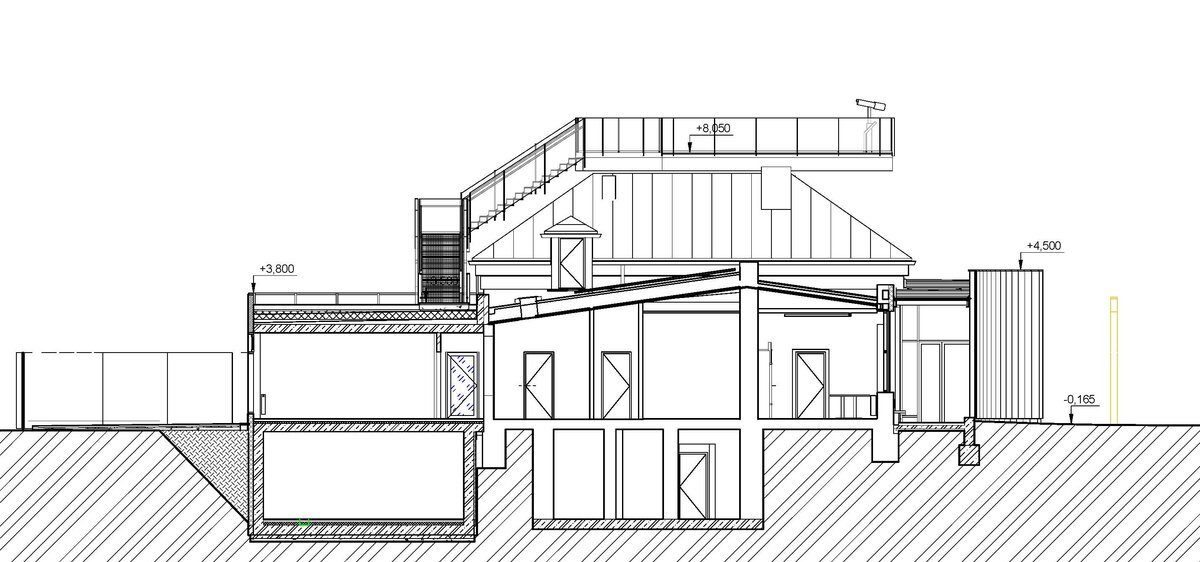
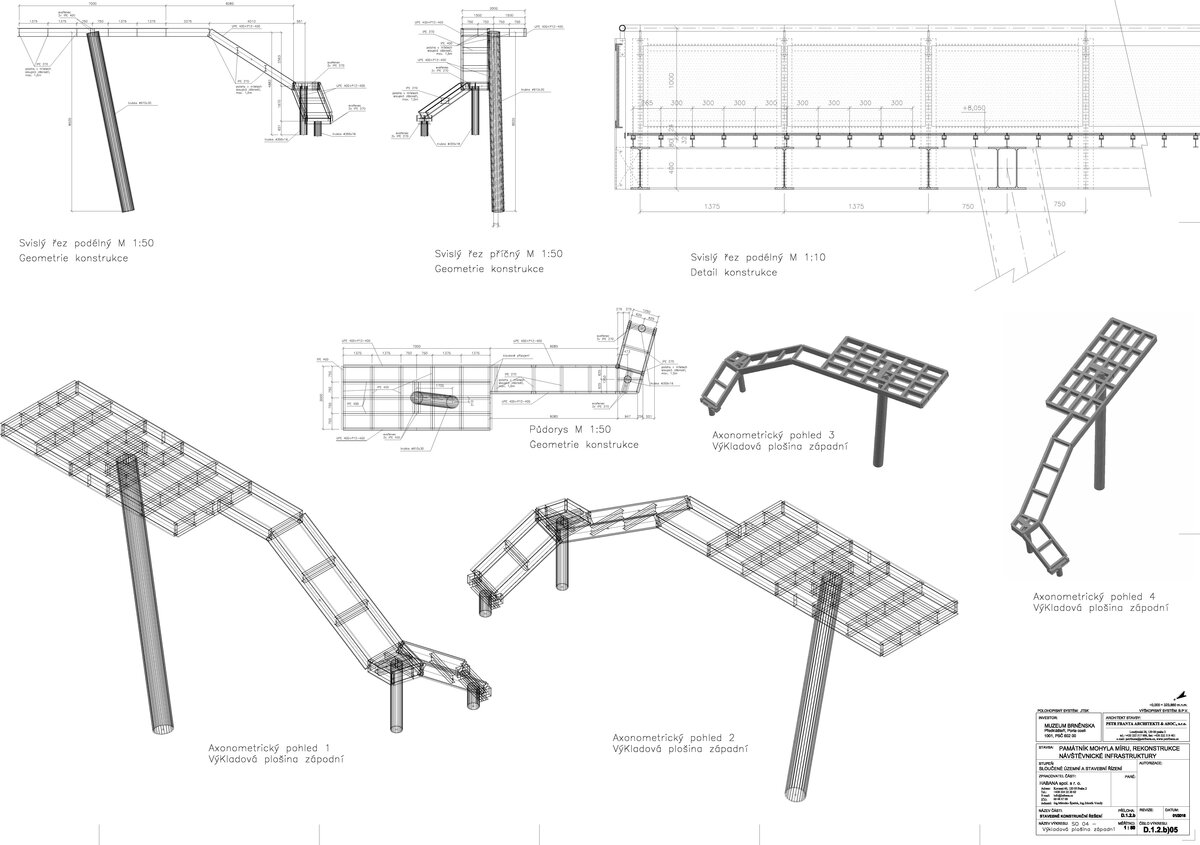
We added two eight-metre high observation platforms – newly designed lookout towers, which Fanta's project originally envisaged, and from which it is possible to oversee the entire Austerlitz Battlefield.
At present, the entire surroundings of the Cairn of Peace Memorial have been reconstructed with an oval pattern of paths as well as a new stone paving of the piazzetta in front of the Chapel.
The whole area has been illuminated with pylon luminaires. We have also managed to restore the original beds of “Cotoneaster Dammeri” shrubs on the slopes of the chapel, which bear their fruits in the colour of a drop of blood on the anniversary of the battle.
With entire project we have aimed to contribute to the centenary of the completion of the Cairn of Peace Memorial Museum and present it as a living reminder of the cost of wars around us in this century. We believe that it is possible to place contemporary architecture in a historical, even sacred, context one that could perhaps help initiate new dialogues in the effort to preserve peace.
RECONSTRUCTION OF VISITOR INFRASTRUCTURE: reconstruction and extension of the museum, design of observation towers, glass wall vestibule, energy efficiency, environmental friendly design.
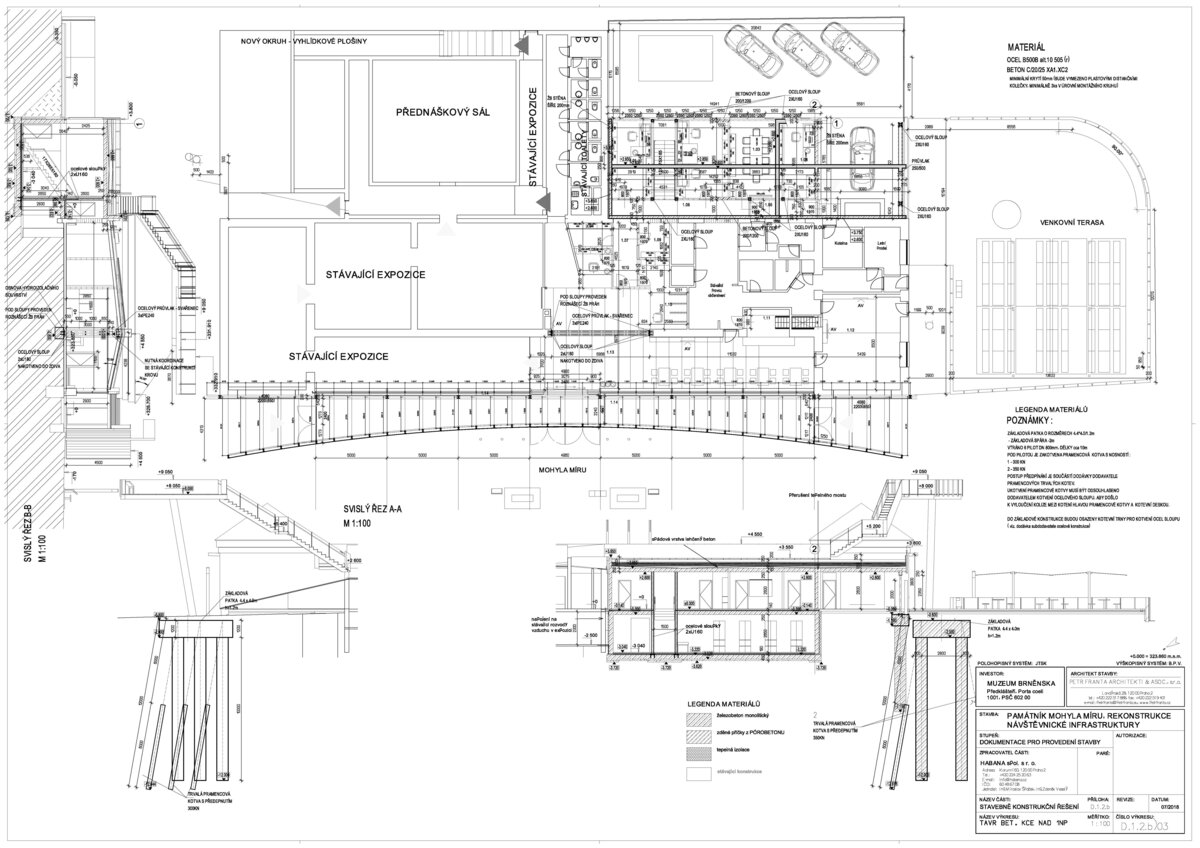
- A all-glass vestibule wall and roof across the entire length and height of the museum pavilion building (length 50 m, height 4.5 m) designed in a gentle curve following the oval of paths around the Cairn of Peace Memorial. Individual panes of glass in a 1.5 x 4.5 m module - stainless steel target holders on a steel structure.
- Design of the New Visitor Circuit, structural static solution of the observation towers and platforms: steel hot-dip galvanized structure - platform grating on steel grid with glass safety railing on inclined steel pillars - Ø 800 mm, length 8 m from the ground - with a flat base on a pile bar anchored with a permanent spring anchor with tensioning.
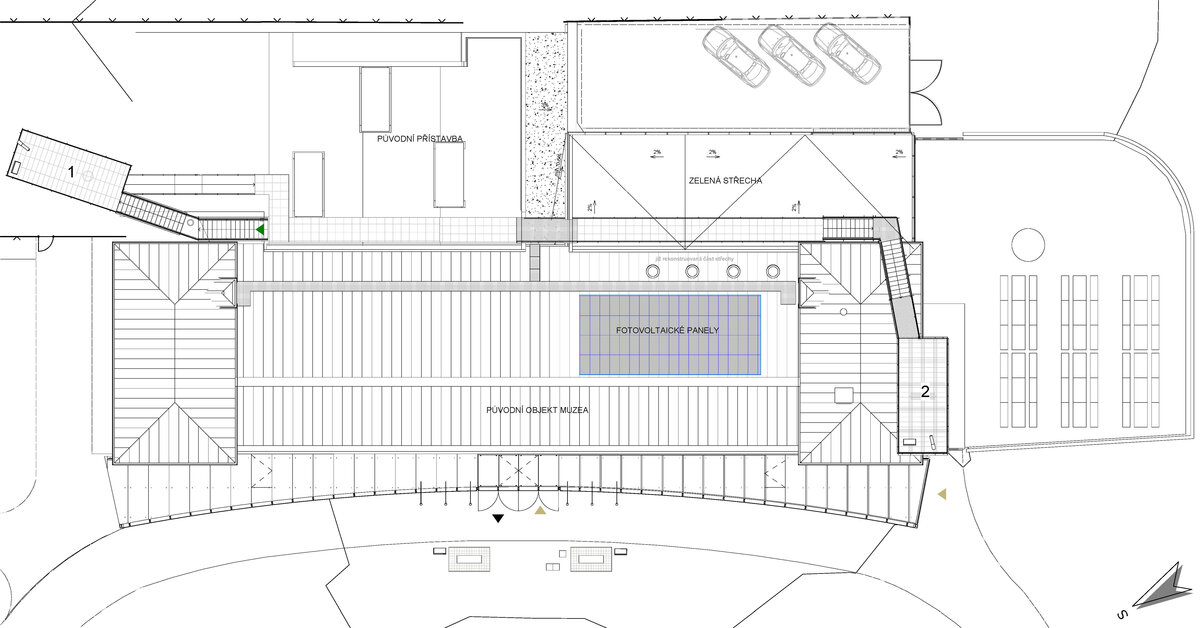
- An annex with one above-ground and one underground floor was built into the existing courtyard. Concrete insulated wall construction with aluminium facade cladding with insulating glass, providing the necessary extension to the museum and restaurant facilities. On the ground floor of the extension, curators' offices are accessible from the hall and also via a separate entrance. A depository and indoor climate technology equipment are located underground.
- The roof of the annex is designed as a green roof with a walkway, which is part of the outdoor circuit accessible from the exhibition. The roofs of the new annex have vegetation layers, planted with dry-loving plants.
- The existing photovoltaic system located on the roof and in the basement of the museum was reconstructed. Electricity generated from the photovoltaic panels is used to control the climate of the chapel area located in the Peace Memorial. The ventilated spaces have fully automatic control and heat recovery.
- According to the original plan of the architect Josef Fanta, the original terracing is reverently restored in the surroundings of the Cairn of Peace, and the edges of the sloping areas of the hillside are planted with the red berry-bearing shrubs (Cotoneaster dammeri Skogholm).
- The rainwater from all the roofs of the museum is used for watering the greenery on the hillside of the Cairn of Peace and its surroundings, or is drained on the grounds of the Memorial.
- The lighting of the entire area and access roads is designed with ecological LED pylon directional luminaires with protection against light smog.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|