| Author |
Ing. arch. Pavel Pekár, Ing. arch. Martin Pončík, Ing. Pavel Matonoha, Ing. Marek Holán, Blanka Ponížilová |
| Studio |
P.P. Architects s.r.o. |
| Location |
Koněprusy č.p. 101, 266 01 Beroun |
| Collaborating professions |
Ing. Pavel Hladík, Radim Staviař, Ing. Miloslava Henešová, Ing. Marek Nos, Bc. Jakub Kaplan, Ing. Zdeněk Tulis, Petr Zpěvák, Ing. Karel Alexa, Rostislav Beneš, Ing. Milan Kramoliš |
| Investor |
Správa jeskyní České republiky |
| Supplier |
DCI Czech a.s. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
March 2024 |
| Fotograf |
Ota Nepilý |
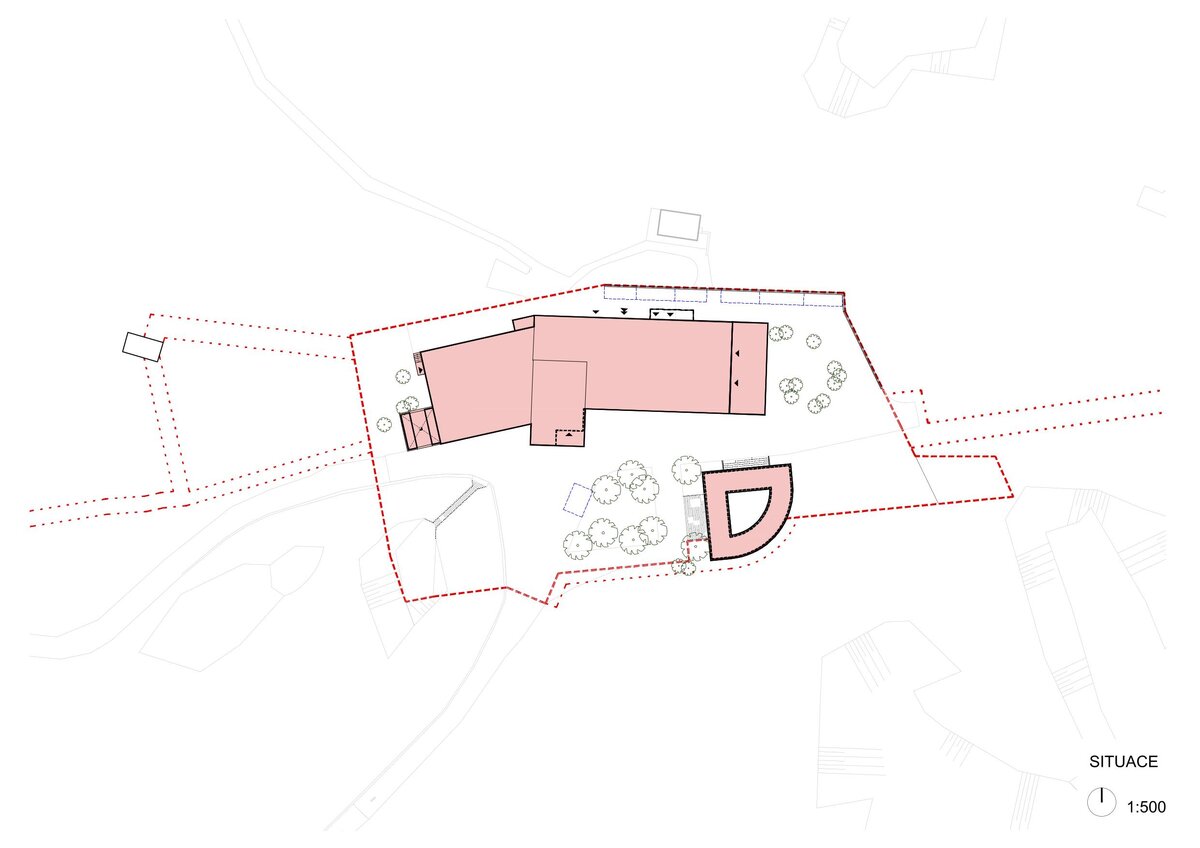
The area in question is located above the village of Koněprusy in the Bohemian Karst Protected Landscape Area. It is a slightly sloping land located in close proximity to the forest.
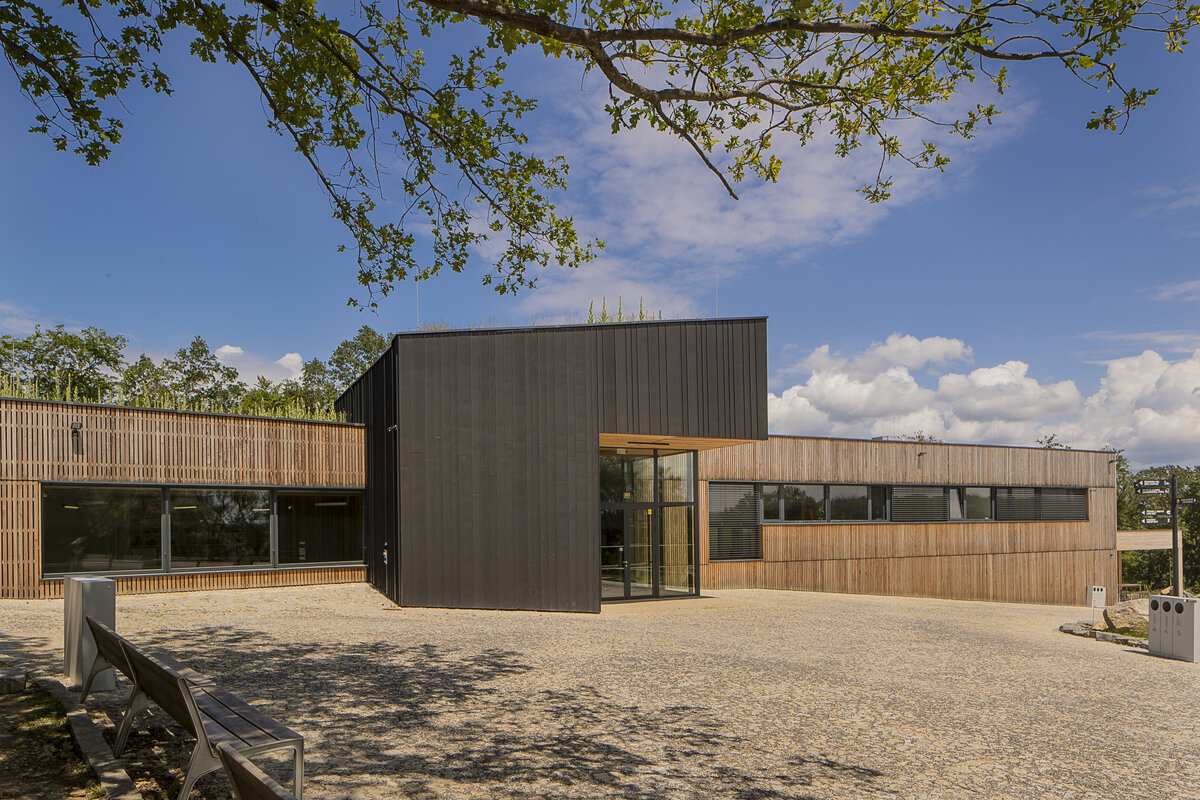
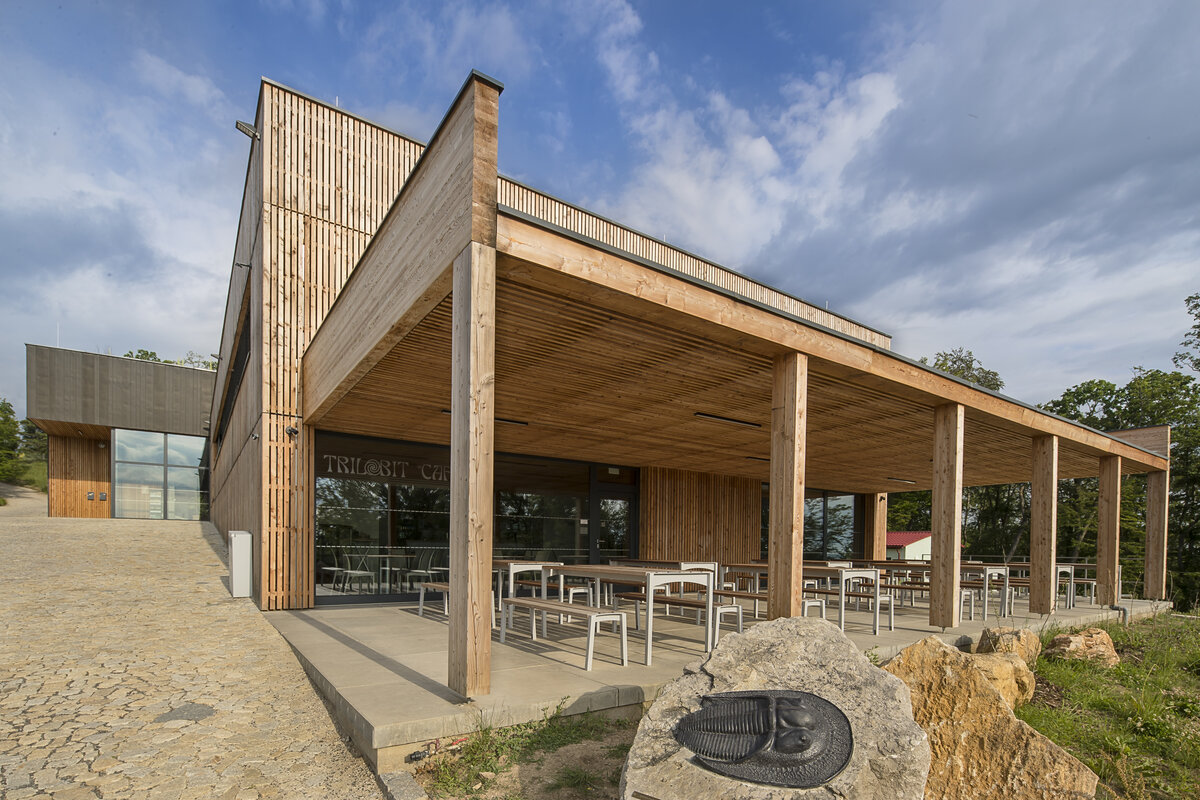
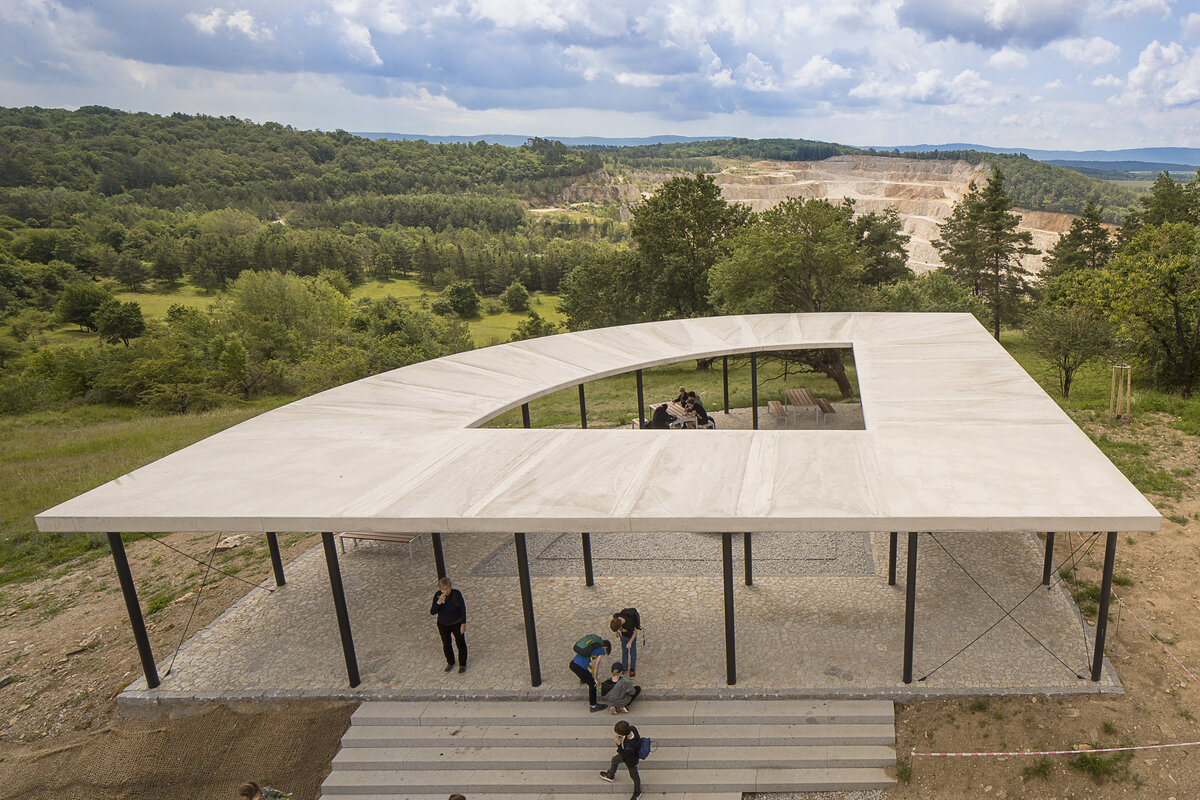
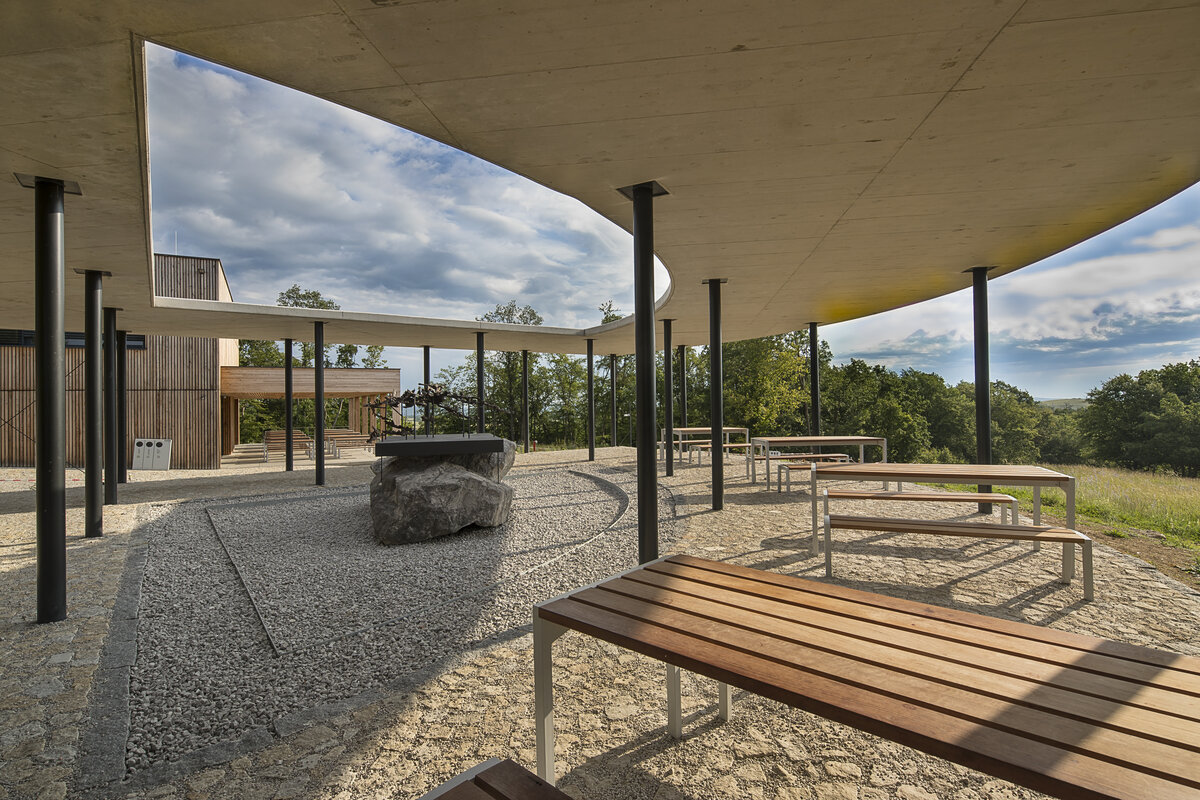
The House of Nature of the Bohemian Karst was built, including an exposition, a gazebo, modifications of the adjacent outdoor areas and an outdoor staircase in front of the entrance to the caves.
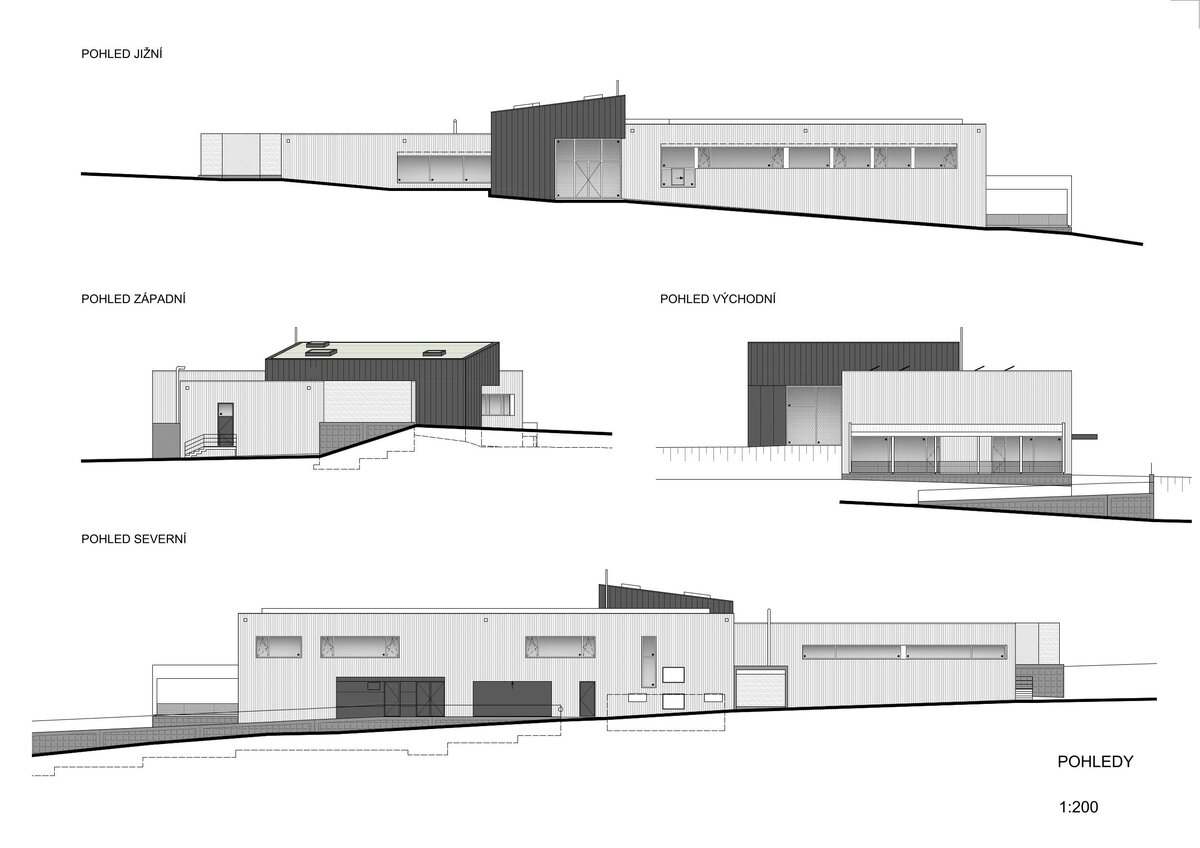
The building is positioned at the northern boundary of the site so as to interfere as little as possible with the open space and thus not interfere with walking and viewing routes. Its architectural form is based on a simple and rational massing based on the adjacent surroundings, operational constraints and the economic requirements of the client. The two rectangular masses intended for the exhibition and the administrative building with technical and operational facilities are connected by a central entrance hall oriented both to the open space and to the existing footpath from Koněprusy. This functional division is furthermore supported by the material solution of the facade.
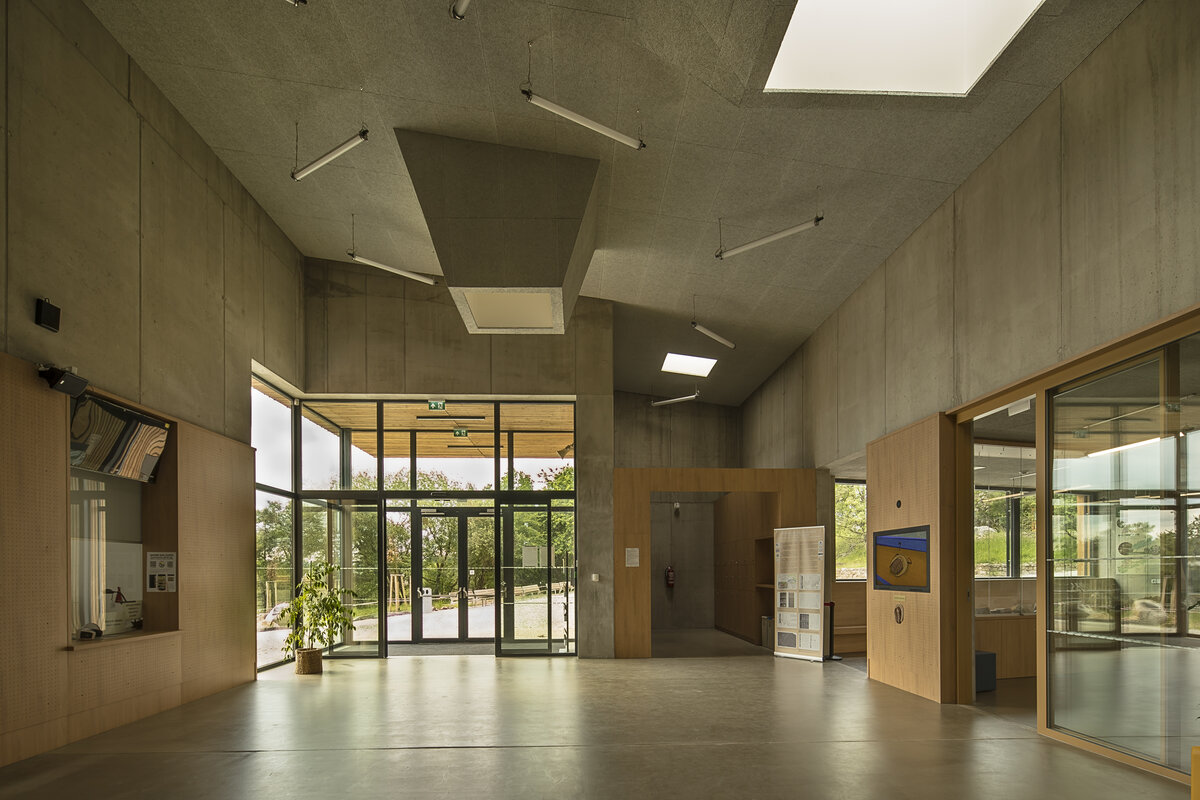
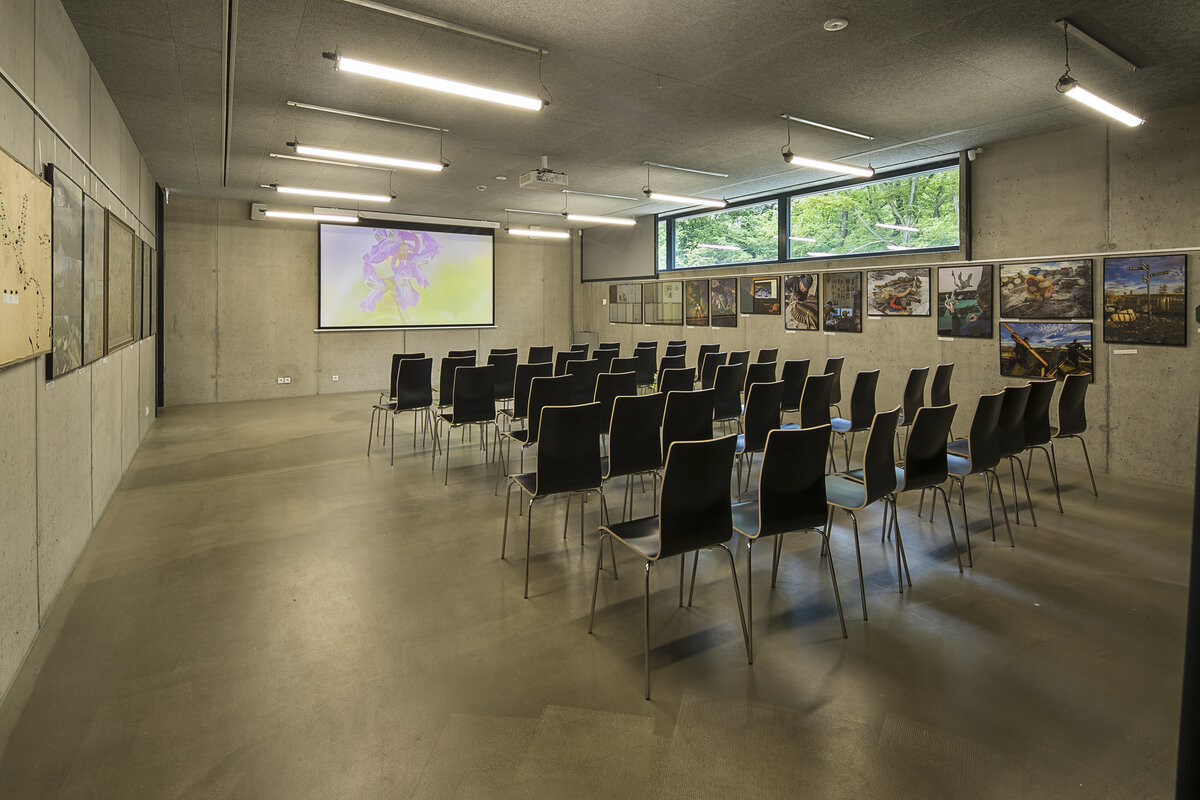
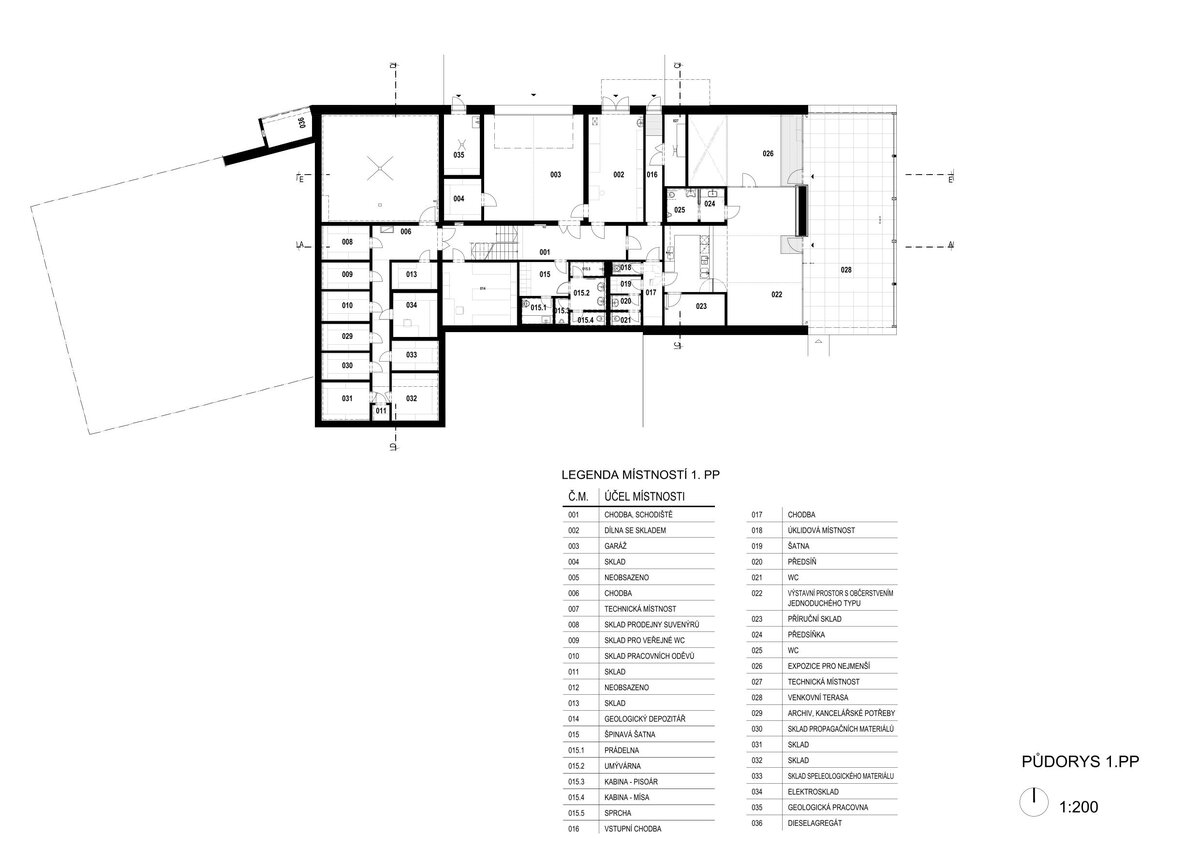
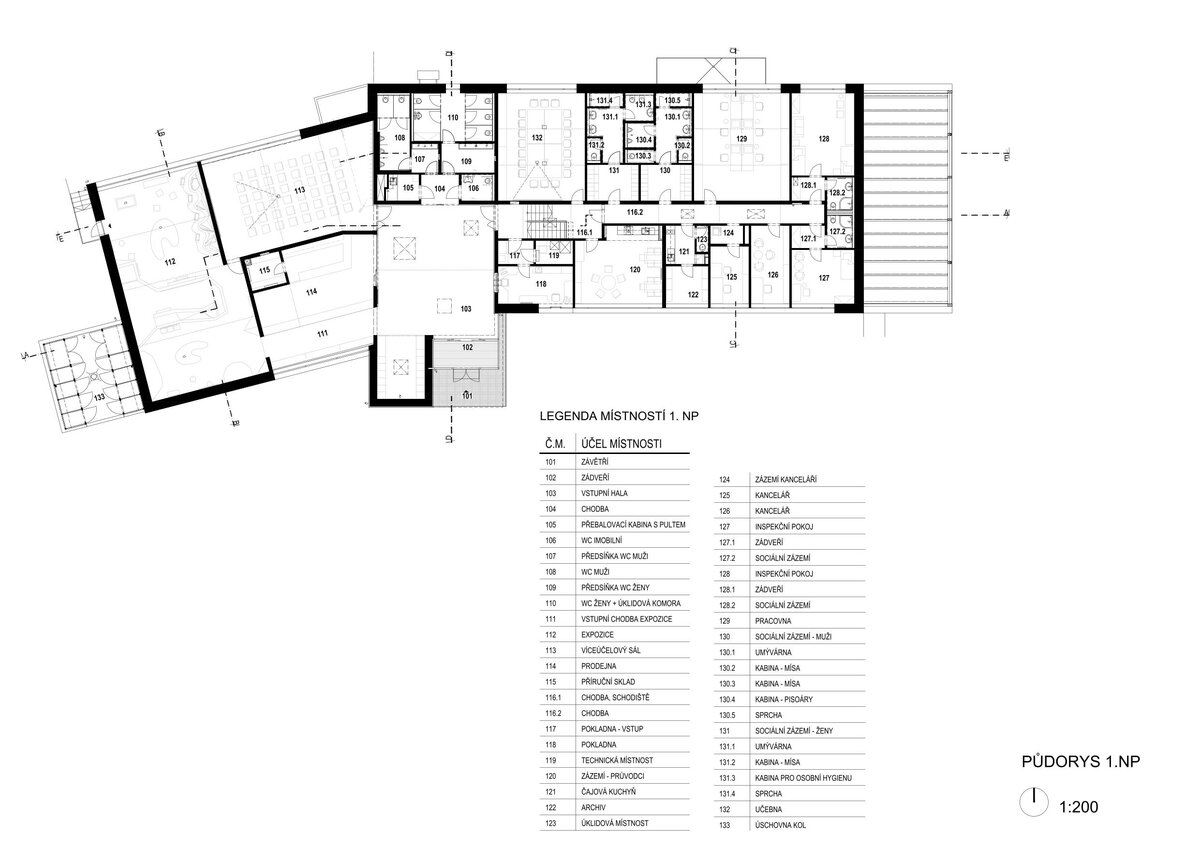
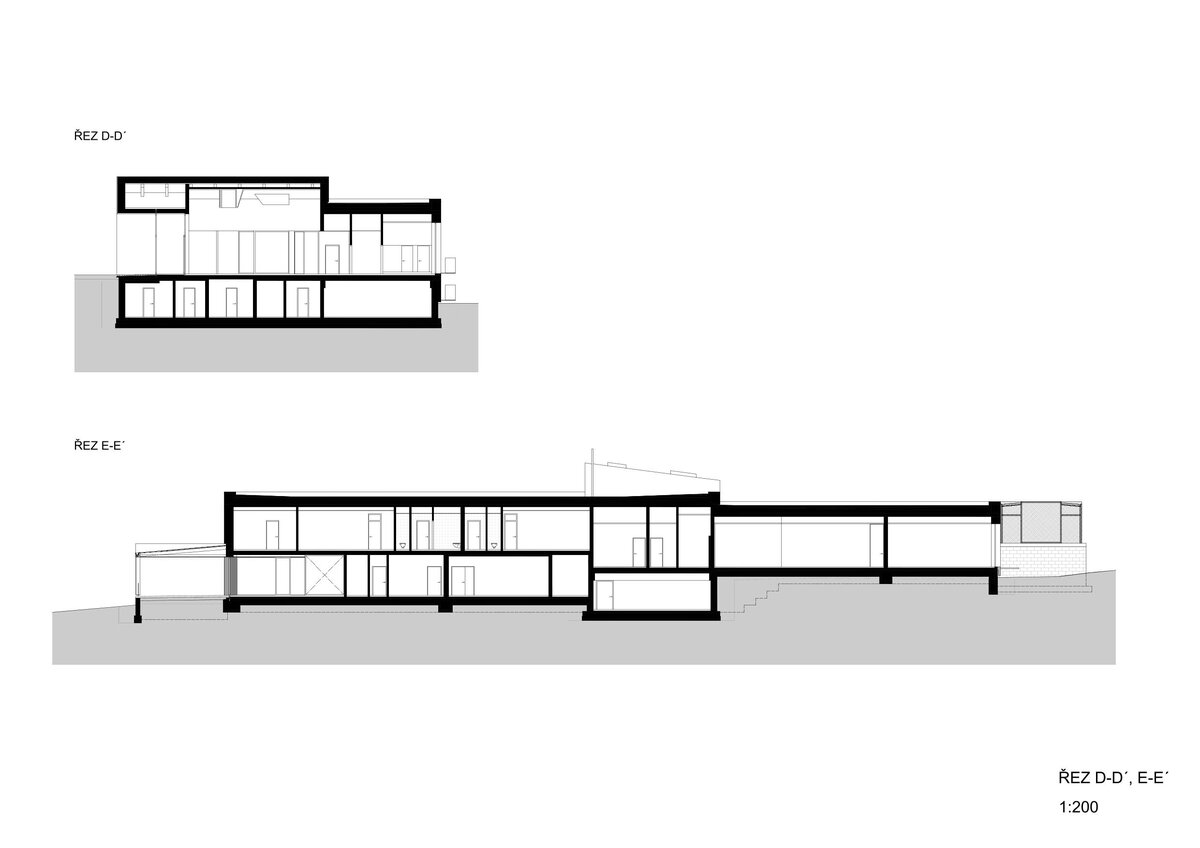
Operationally, the building is divided into three parts. The centrally located entrance hall can accommodate the largest accumulation of visitors before entering the exhibition. The lobby is connected to the exhibition hall with a shop and hall, luggage and stroller storage, public toilets, an info kiosk and ticket sales, which can also take place from the outdoor area in good weather without disturbing the entrance to the building itself. The west wing is dedicated to a two-storey exhibition, a shop selling regional products and promotional items and a multi-purpose hall. The eastern wing is mainly dedicated to the administration building and technical and operational facilities. It also includes exhibition space for short-term exhibitions and travelling exhibitions.
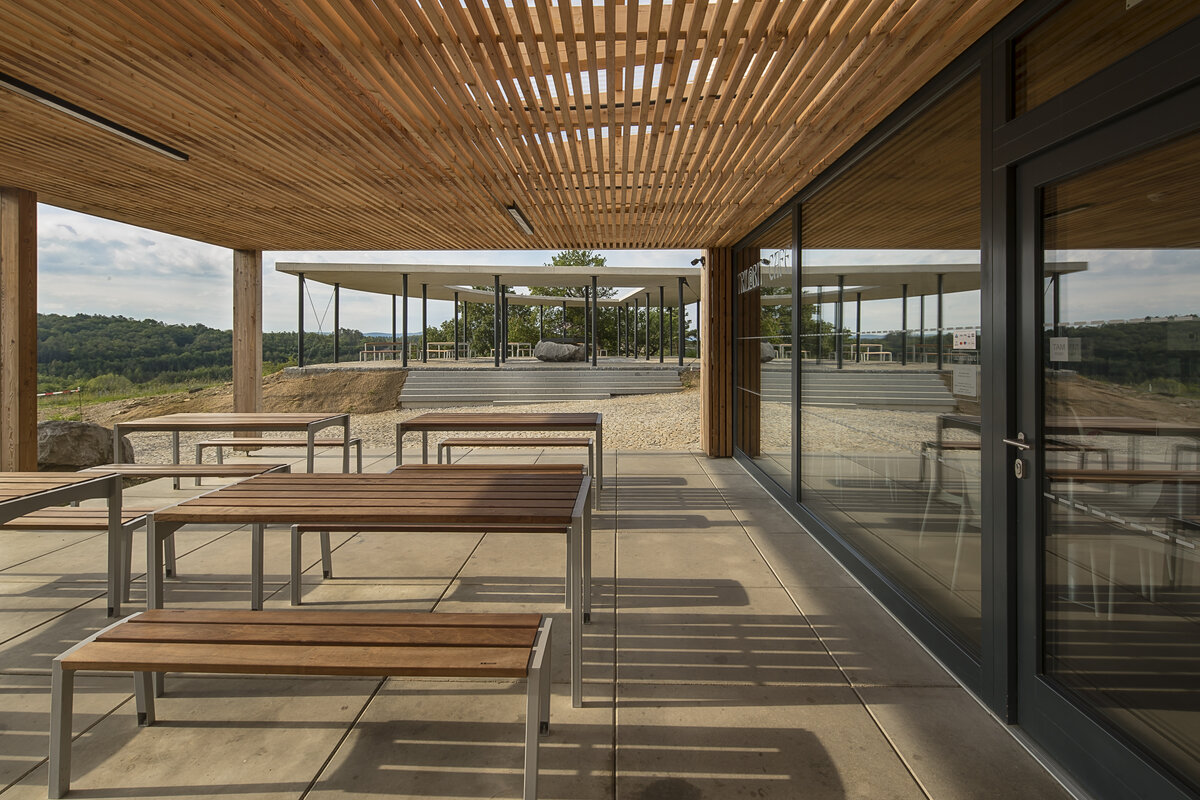
A geo-trail is built alongside the existing tarmac road leading from the car parks below to the open space in front of the Nature House as part of the outdoor exhibition. The entire area around the building, including the newly built service roads, is made of mineral concrete.
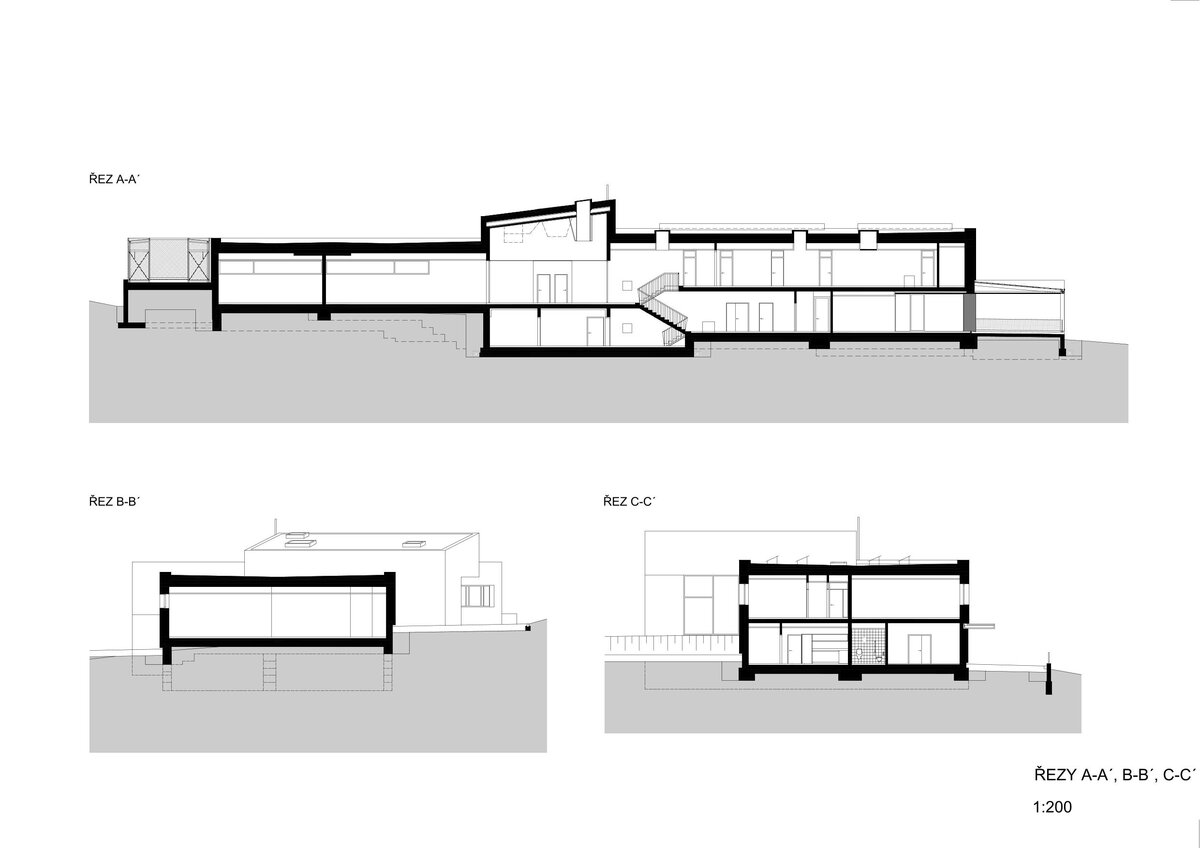
Structurally, it is a load-bearing wall system of reinforced concrete construction supplemented by internal partitions made of ceramic and concrete blocks. The building is based on monolithic foundation strips or footings and partly on a foundation slab.
The external façade is made as a ventilated façade of wooden larch slats and titanium zinc sheet in anthracite colour. The simple massing of the building is complemented by the additions of a bicycle storage room, a terrace and a diesel generator. In the case of the bicycle storage room, it is a simple steel structure sheathed with tension metal, the terrace is made of glued wooden profiles. In both cases, the roofing is made of translucent polycarbonate. In the interior of the building, the vertical reinforced concrete structures and concrete block walls are made in a visual manner, while the brickwork is plastered. In the entrance hall, the appearance monolithic reinforced concrete structure is complemented by the cladding of laminated foil panels in oak decor, which is also partially present in the multipurpose hall and in the public toilets in dark grey. In the basement, a contact insulation system made of EPS boards finished with a base layer of trowelled mass is designed in the unheated areas.
The ceilings are designed as a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, the pitched roof is made of steel beams with a trapezoidal sheet metal roof. The roof over the west wing of the exhibition and the entrance hall is designed as a vegetated roof, while the roof over the operating facilities is finished with a layer of washed duck. The ceilings are plasterboard or mineral ceilings, in the west wing of the exposition and entrance hall they are made of fiberboard. In the refreshment and toddler exhibit rooms, the ceiling is made of larch wood slats that flow seamlessly out onto the terrace. The floors are designed with a poured cement screed, finished with a self-levelling trowel in areas with increased aesthetic requirements.
The windows and assemblies on the façade of the building are wooden, glazed with triple glazing, with aluminum at the main entrance. All windows on the south façade are fitted with external aluminum louvres. The skylights are plastic, fixed glazed with insulating glass. The garage doors are designed automatic aluminum industrial doors with PU sandwich infill and system doors.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
A
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|