| Author |
doc. Ing. arch. Jiří Buček |
| Studio |
SIAL architekti a inženýři spol. s r.o. Liberec |
| Location |
Pelléova 15, Praha 6 |
| Investor |
Korejská republika |
| Supplier |
Gemikaya |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
April 2022 |
| Fotograf |
Filip Šlapal |
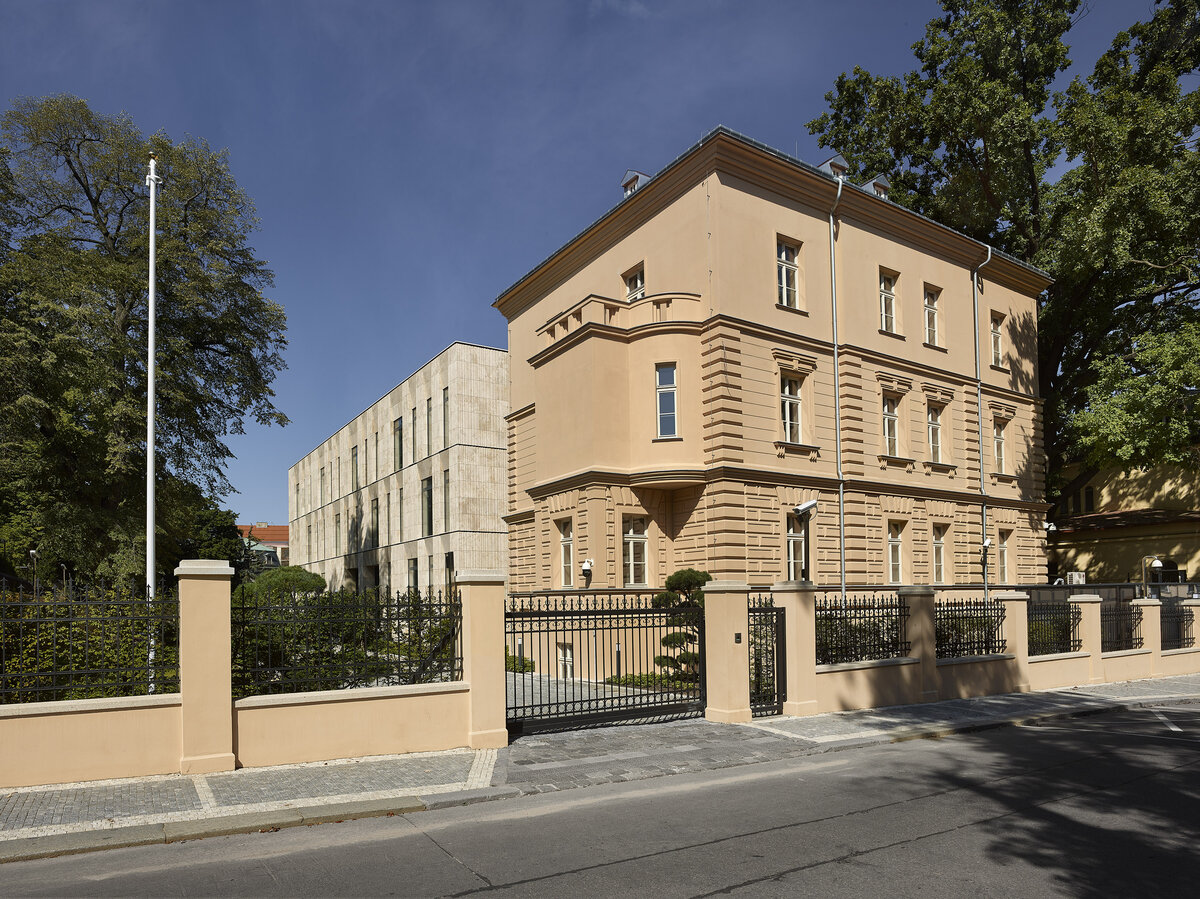
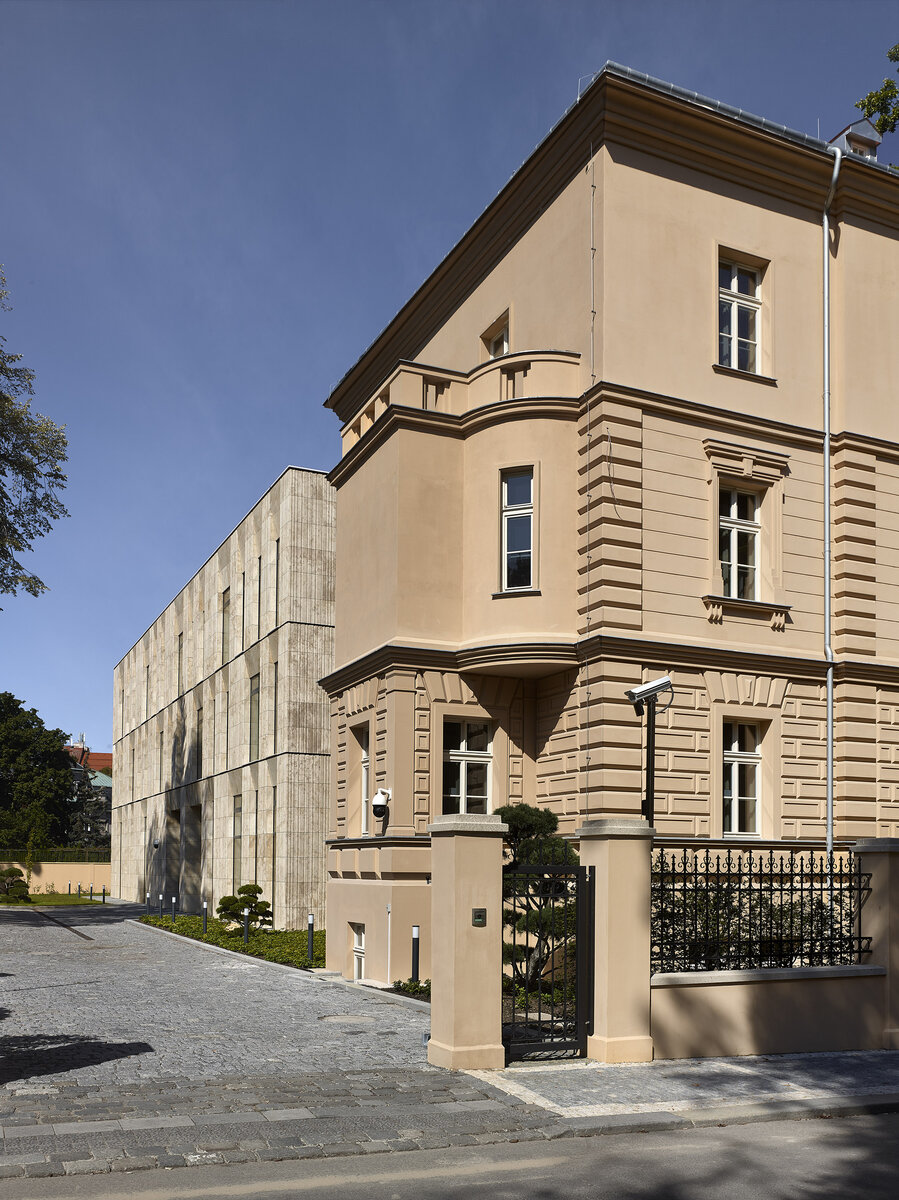
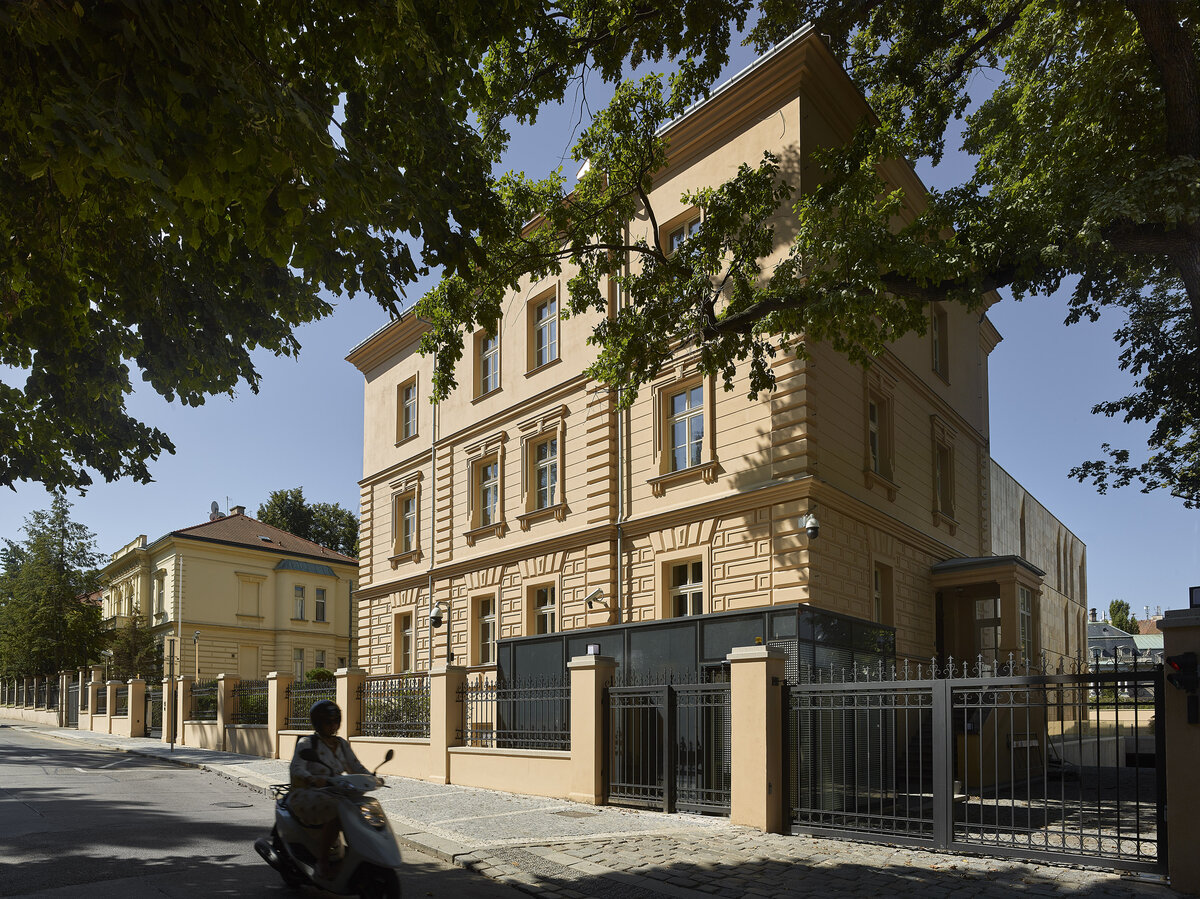
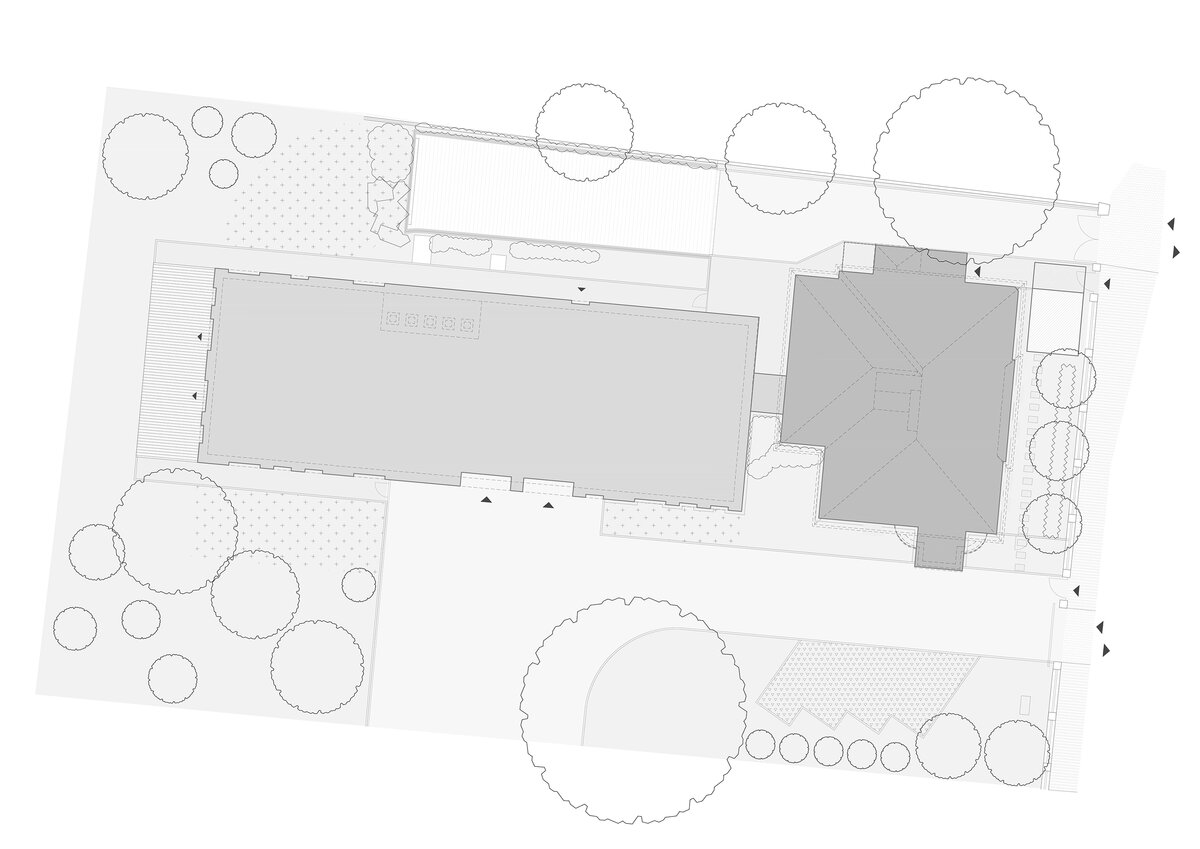
The project of the Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Pelléova Street in Prague 6 uses the concept of the reconstruction of the original villa in the street front and the construction of a new wing in the garden part of the property.
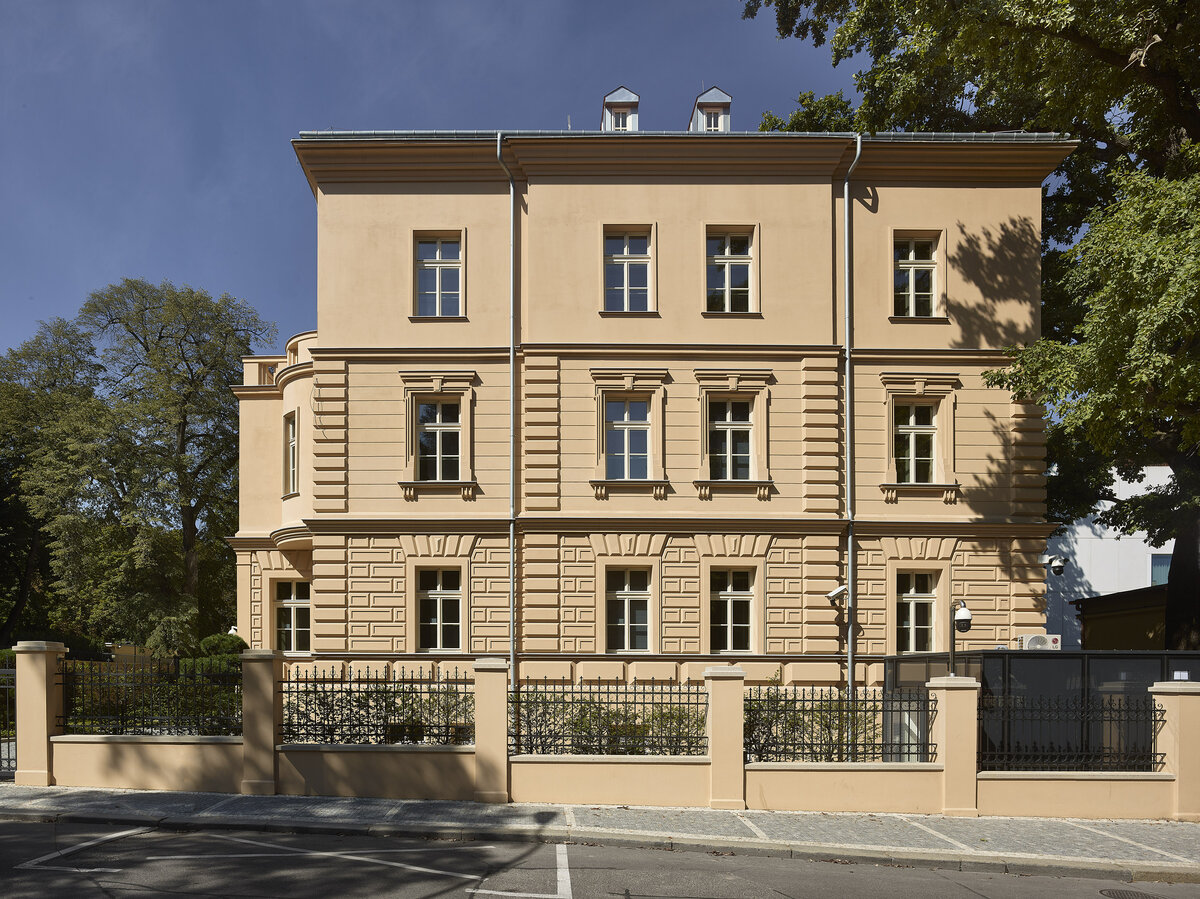
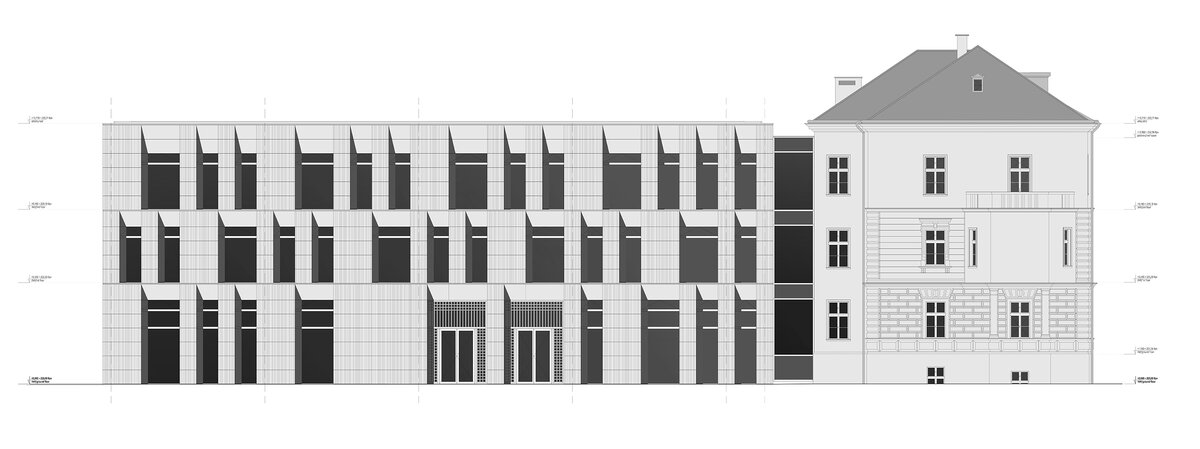
The restoration of the neo-Renaissance look of the villa corresponds to the state before 1909. The basis for the design was the original plans of the building in individual phases of construction. The public interior of the villa is reconstructed using original elements or their copies.
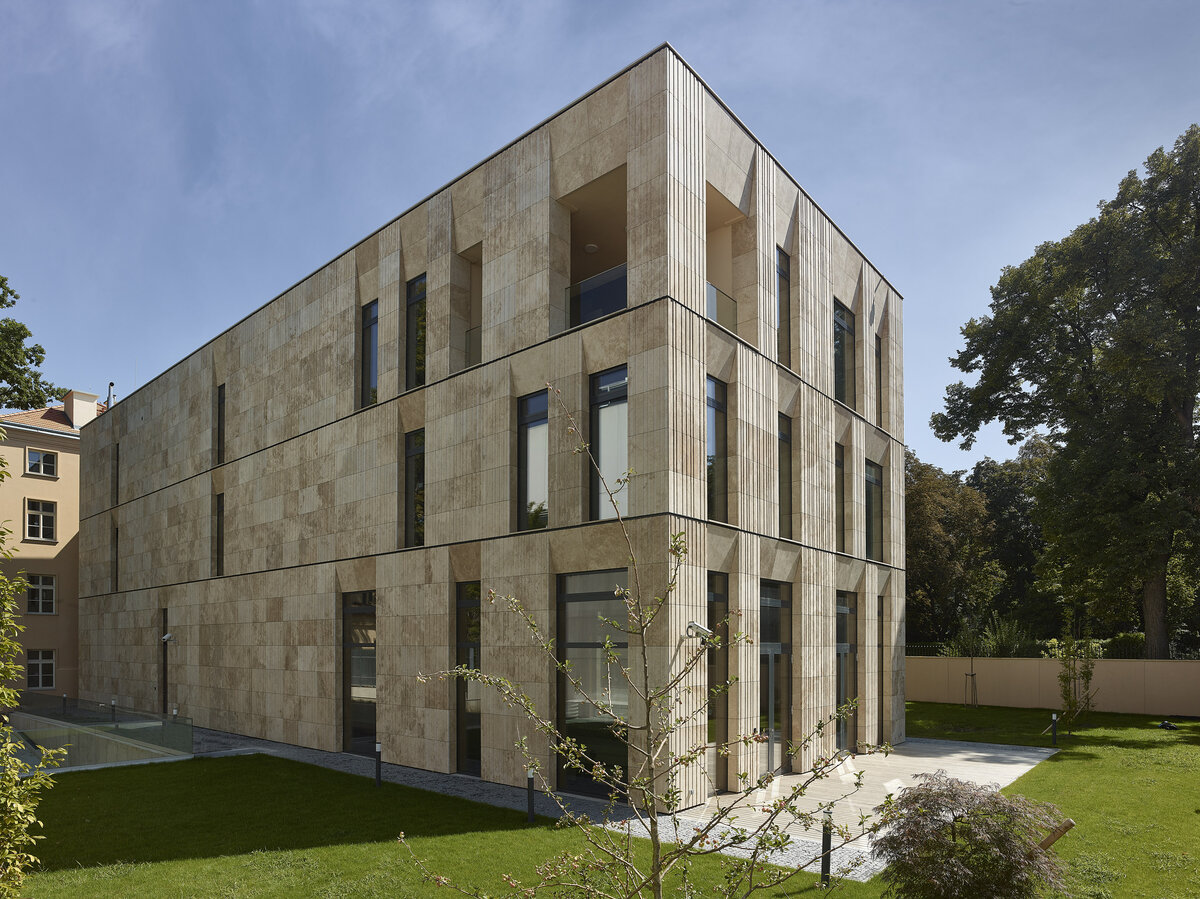
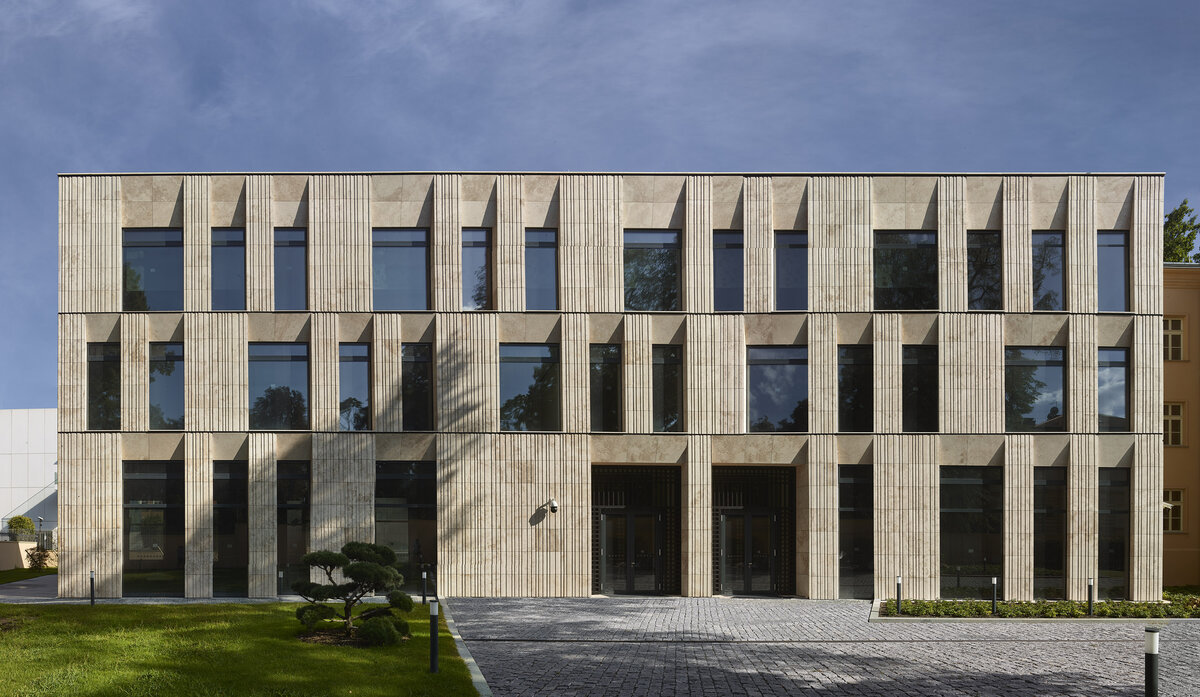
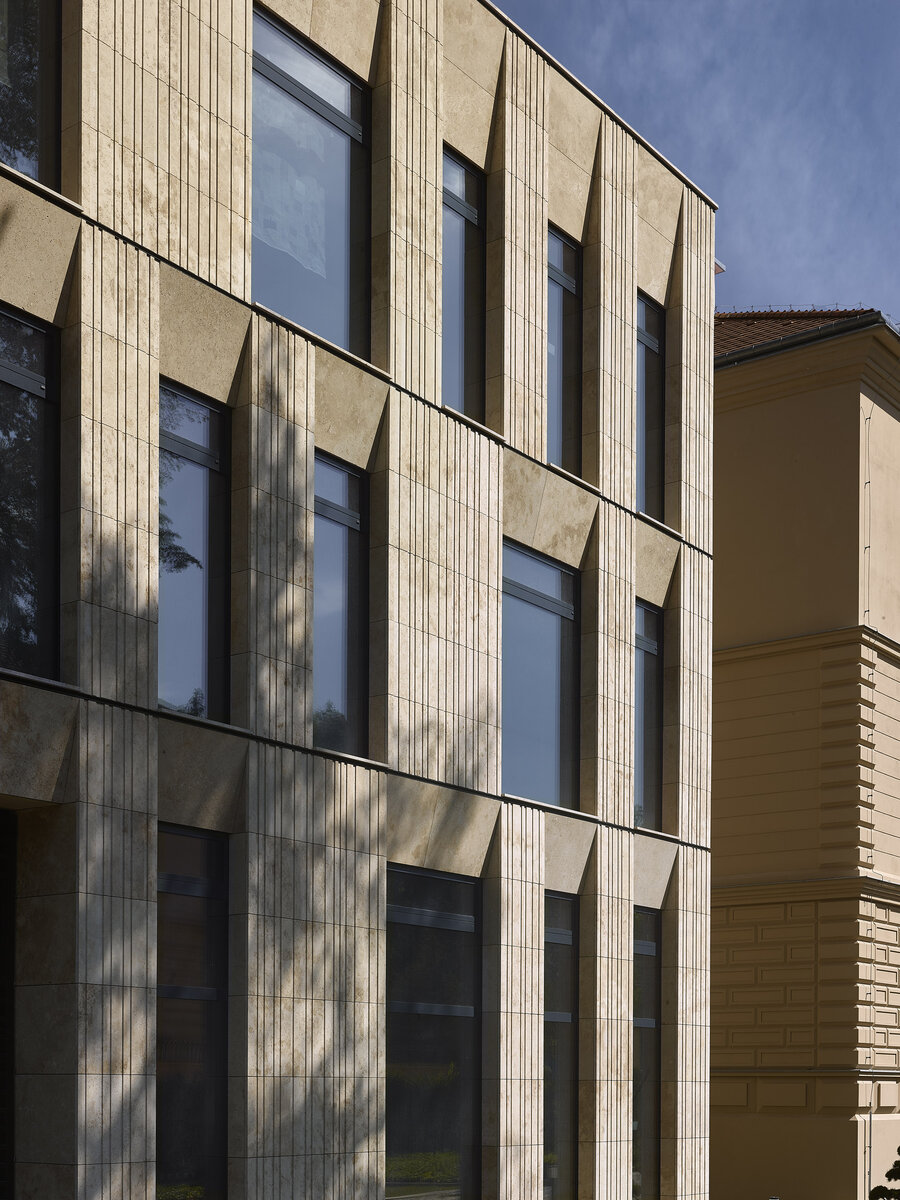
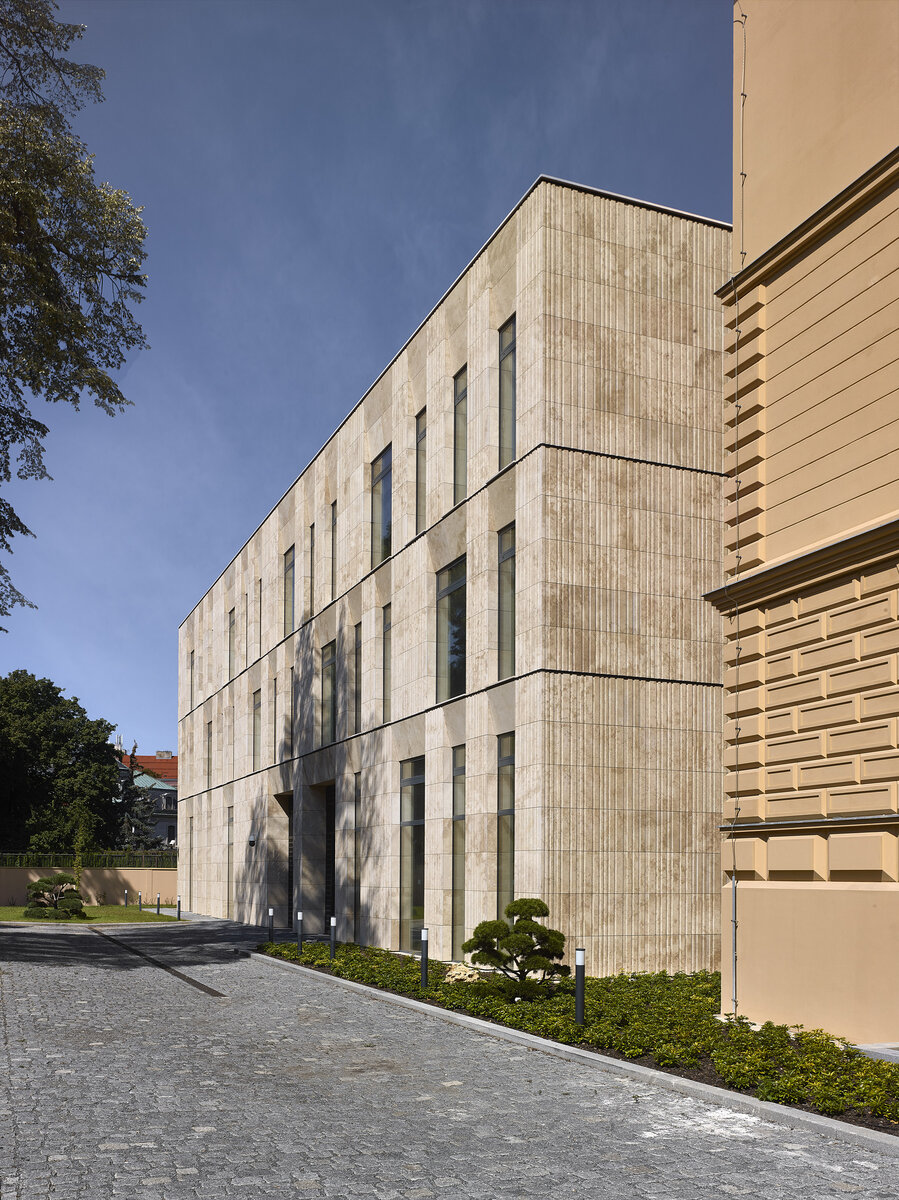
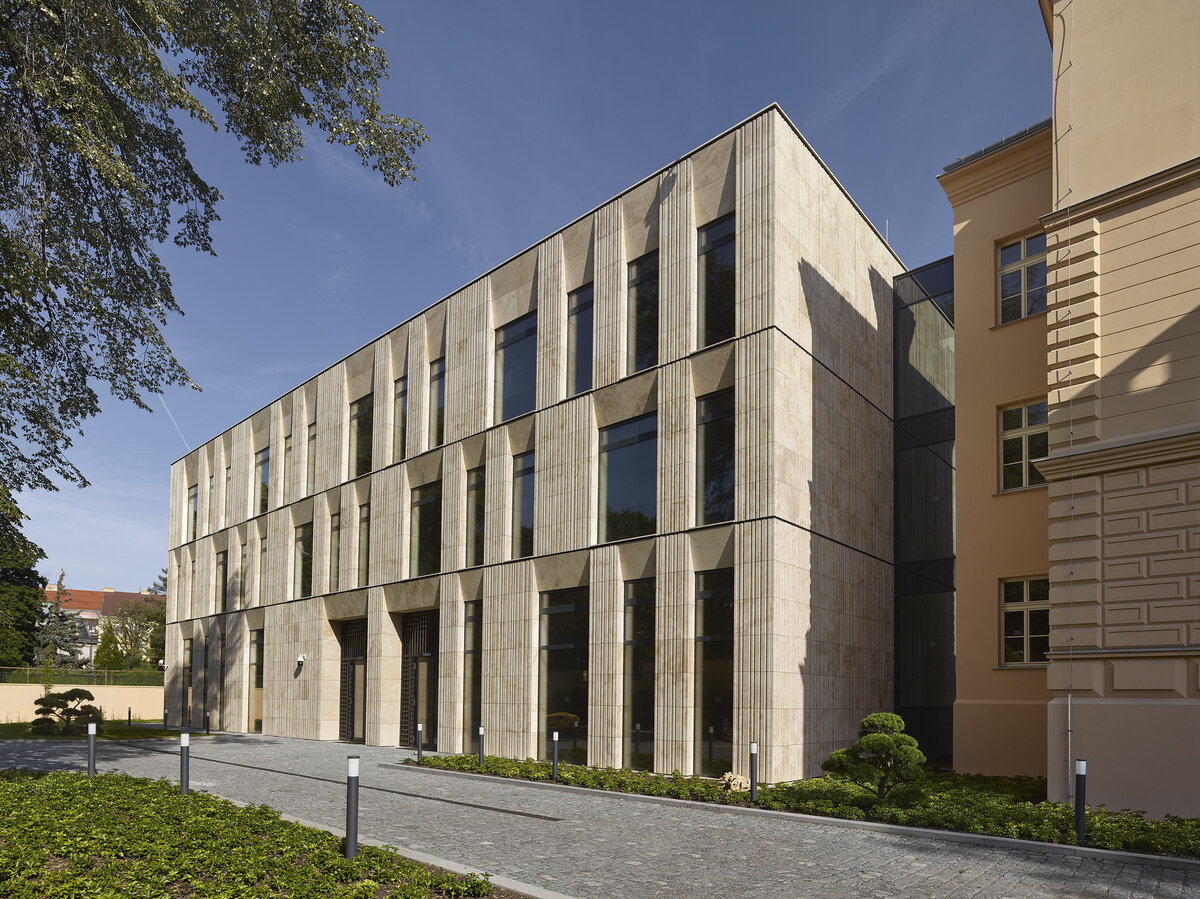
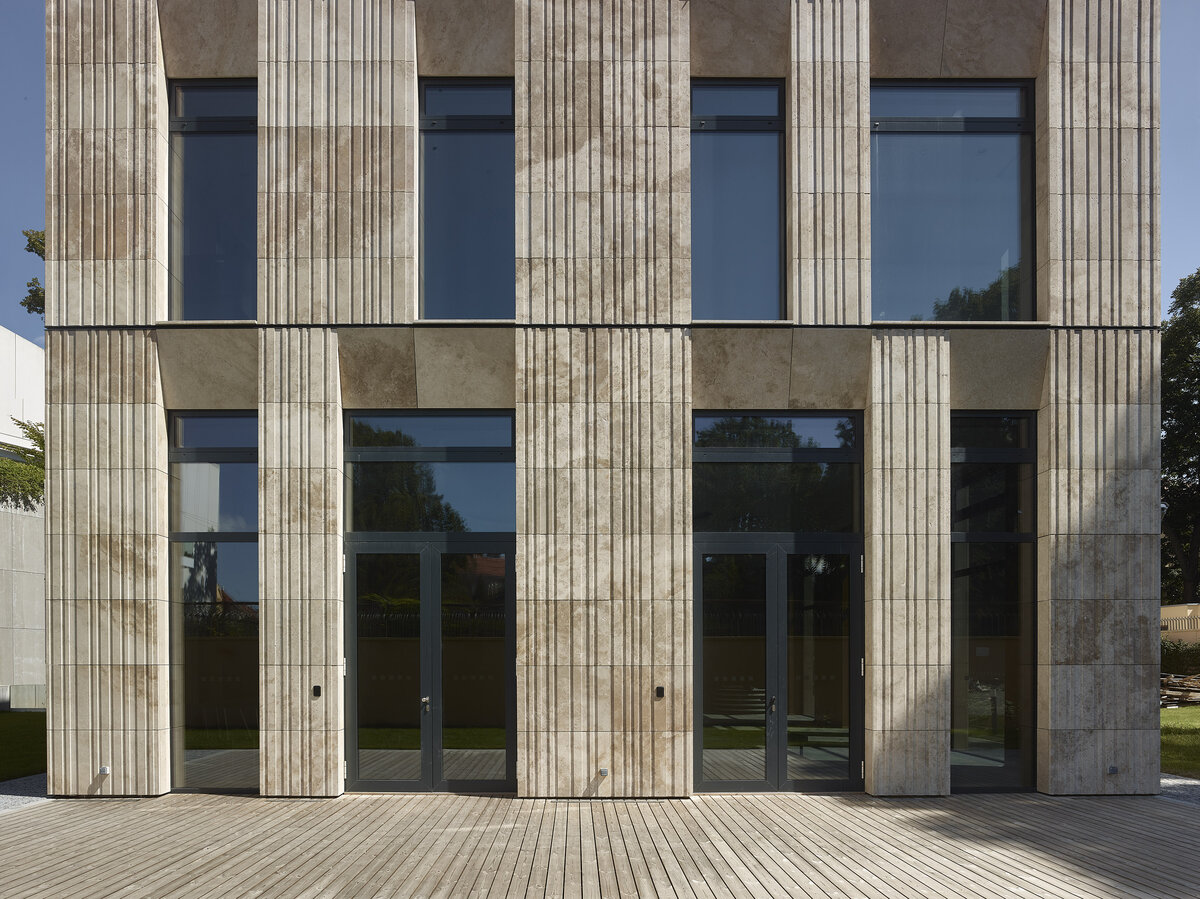
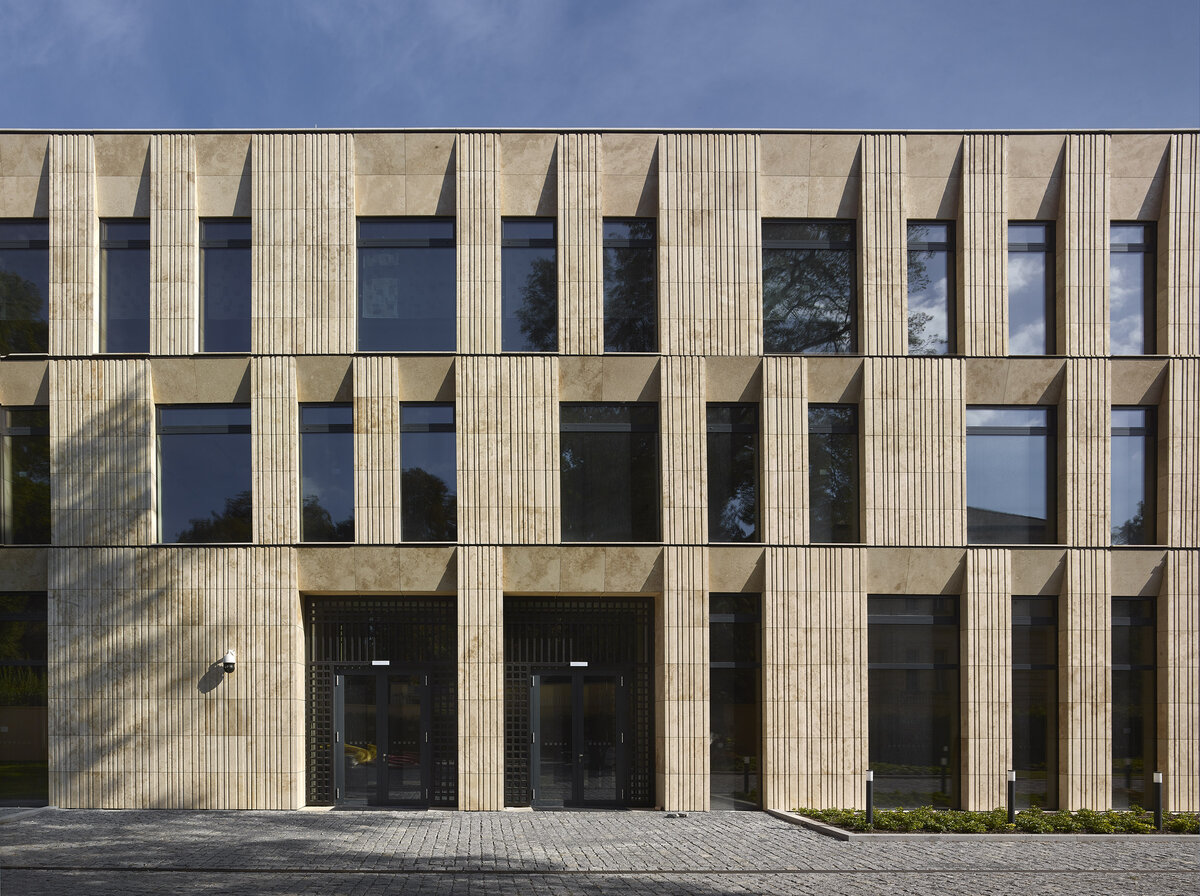
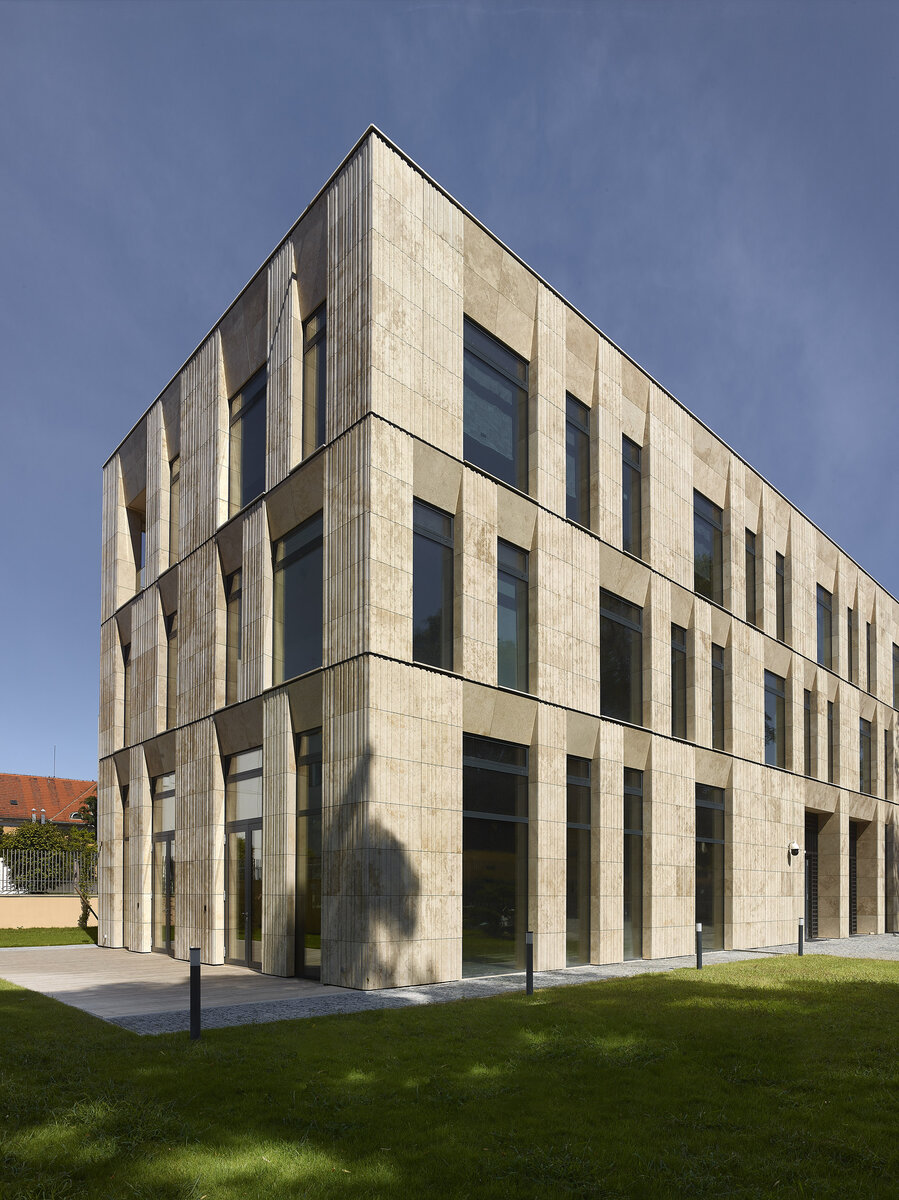
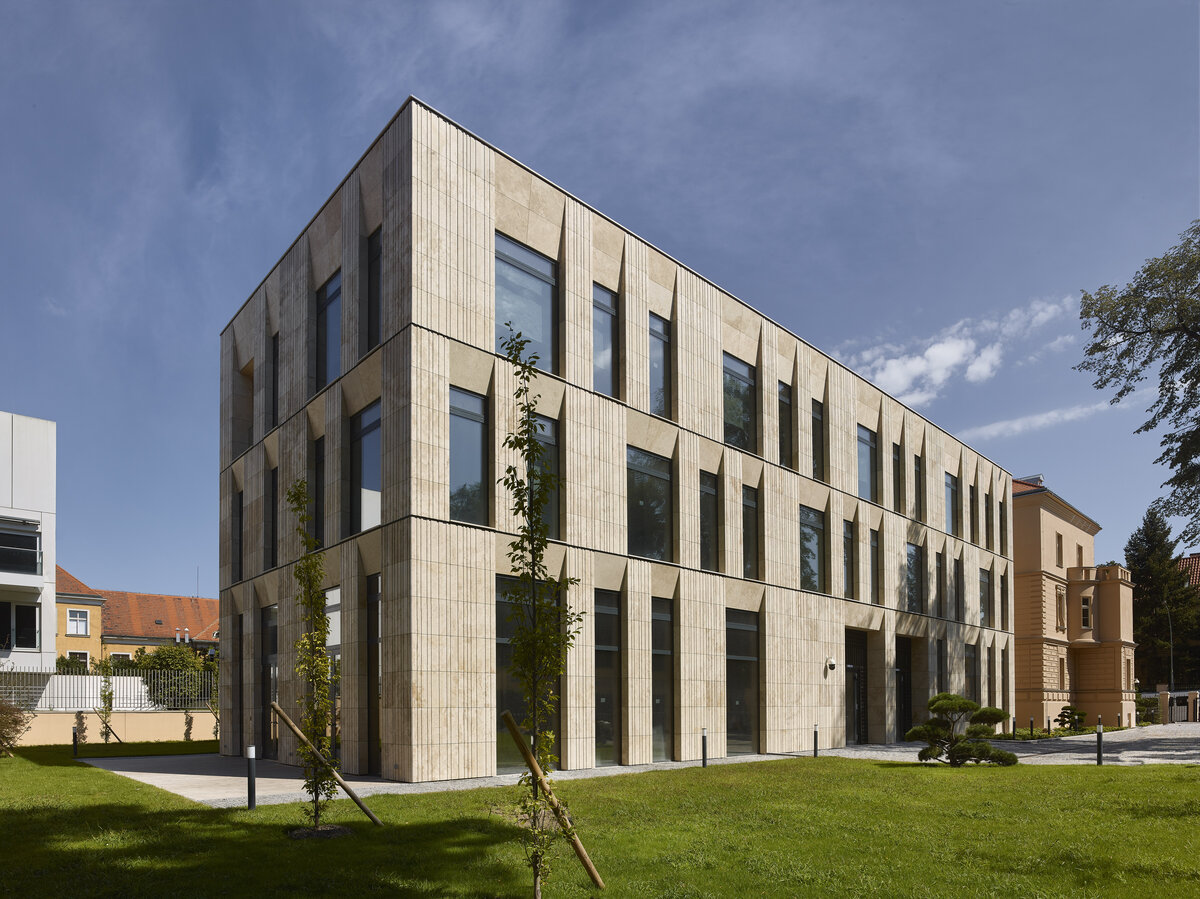
The mass of the west wing is designed as an architecturally contemporary building with a flat roof. The structural heights of the floors of the west wing are adapted to the existing villa and the height of the attic to the height of the original cornice. The window openings are distributed with a hidden regularity, so the division has a softer and less formal effect on the historical building.
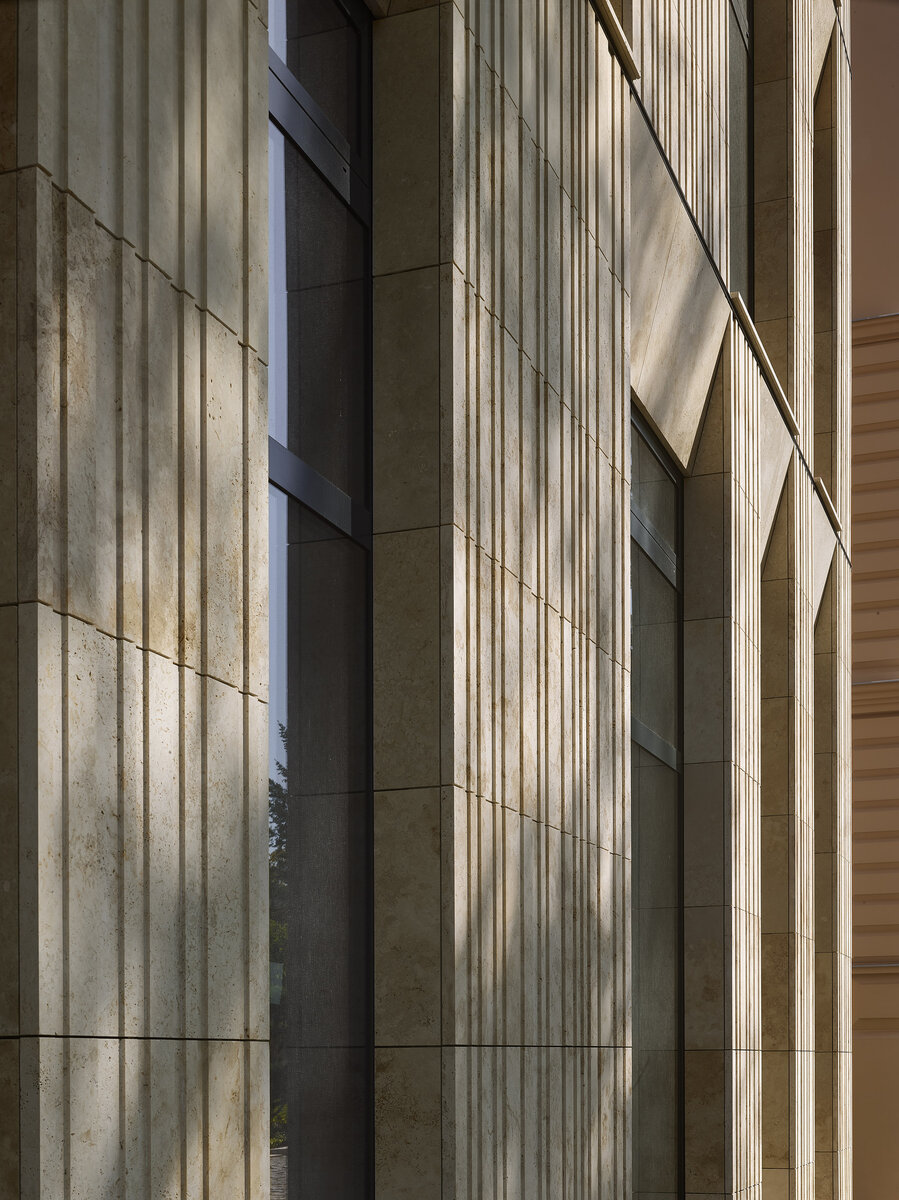
The travertine cladding of the facade is provided with vertical channeling, the transparent parts are made up of low-reflective glazing.
The garden part of the embassy is adapted for organizing social events, the grassy areas with existing mature trees are supplemented with residential decks.
a) construction solution,
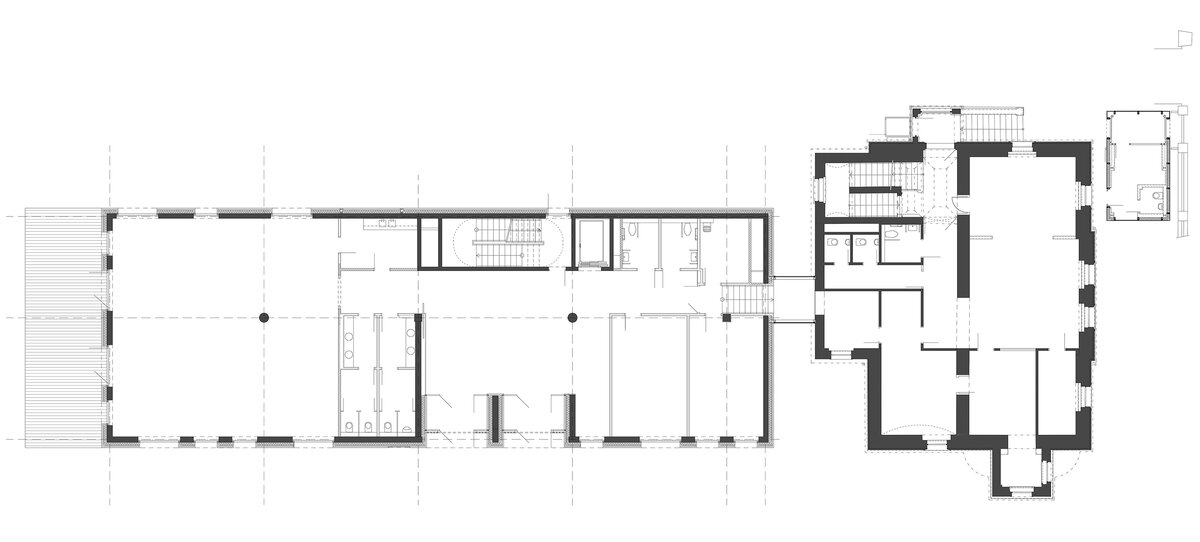
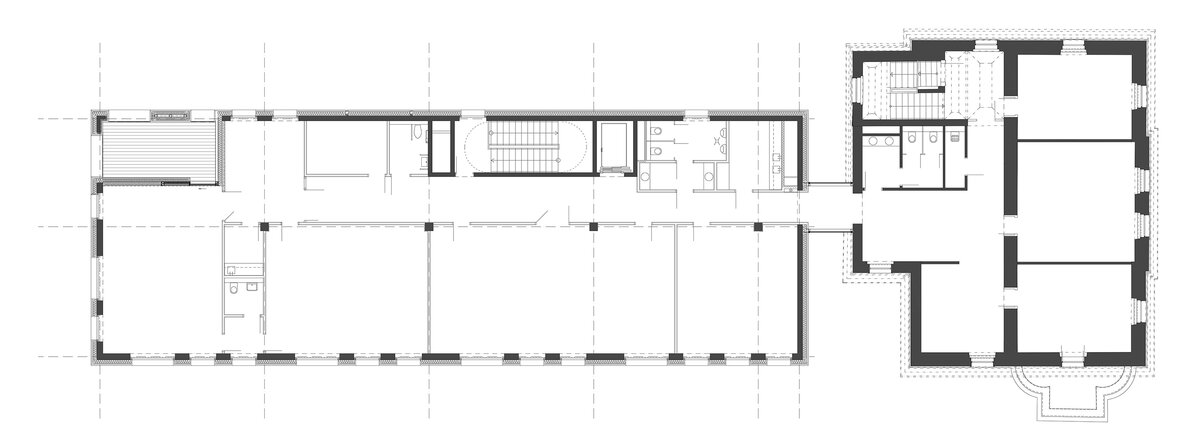
The project consists in the reconstruction of the existing street villa and the addition of a new garden wing for the purposes of the Embassy of the Republic of Korea. The historic street villa is reconstructed and preserved as an independent separate object, which is materially separated from the new construction of the west wing by a subtle glass neck. The restoration of the neo-Renaissance appearance of the villa corresponds to the condition after the building was increased to the current mass.
The mass of the west wing is designed as an architecturally contemporary building with a flat roof. The structural heights of the floors of the west wing are adapted to the existing villa and the height of the attic to the height of the original cornice. The design of the facades reflects the villa and residential character of the surrounding buildings. Facade travertine cladding is designed.
b) structural and material solutions,
Vertical support structures
The vertical load-bearing structures of the street villa are made up of solid brick walls with a total thickness of 600 - 700 mm, additional masonry for this part is also done in this way.
Horizontal supporting structures
Villa
As part of the ceilings above the 2.PP and 1.PP, the existing ceilings are preserved: typical brick vaults.
On the above-ground floors, new ceilings are made of steel-concrete construction supported by I300 steel profiles.
New construction of the west wing
The basic horizontal load-bearing element for all ceilings and the roof structure is a 220 mm thick ceiling board supplemented at the point of support by columns with headers or by strengthening the ceiling board around the perimeter and in the place of the openings, the board is reinforced with a bordering rib.
Circumferential shell
Villa
The facade of the street villa is reconstructed according to the model of the original historical design: its missing plastic division – bossage – is supplemented using facade elements (e.g. Verofill).
New construction of the west wing
The facade of the west wing consists of a ventilated facade with cladding of stone slabs on a system metal grid (e.g. Halfen). It will also include insulation using 200 mm mineral wool.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
B
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|