| Author |
Jiří Tencar, Pavel Šulc, Jiří Škopek, Michaela Václavská, Norbert Glejdura, Marek Machač, Monika Hrubešová, Lucie Roubalová, David Nývlt, Patricia Sičáková, Karolína Vojáčková, Ondřej Kramer, Michal Mazanec, Lukáš Skládal, Vojtěch Pražák, Ondřej Fábry, Vá |
| Studio |
ECOTEN a Pavel Šulc |
| Location |
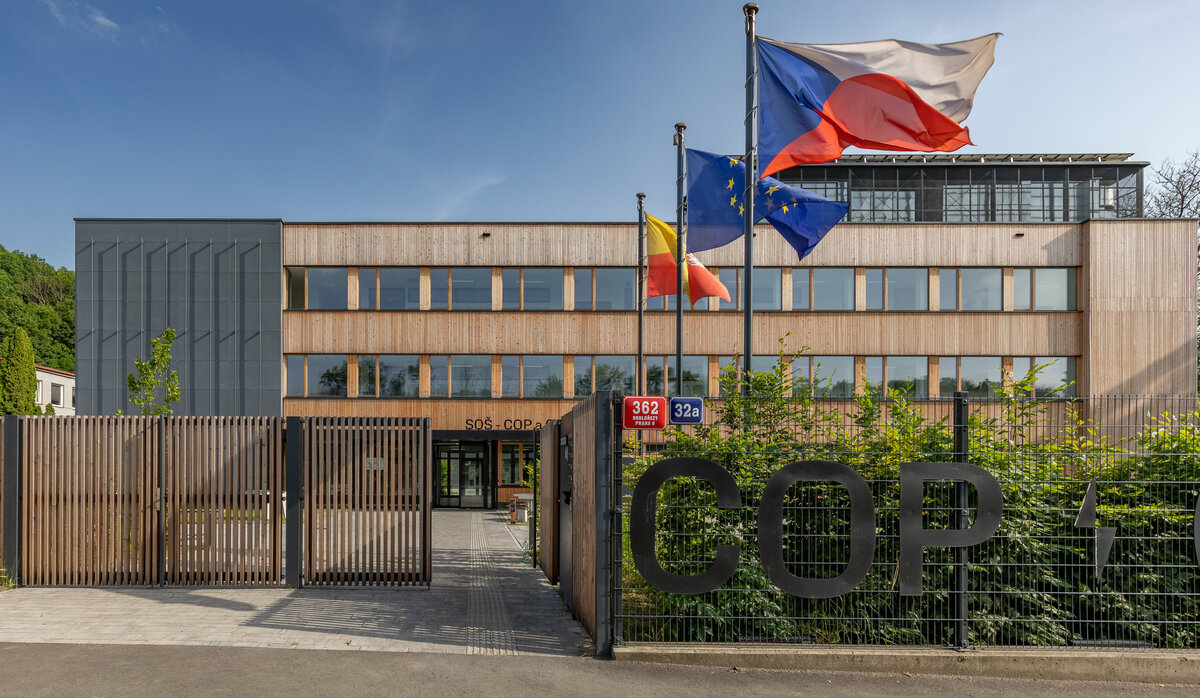
Českobrodská 362/32a, 190 00 Praha 9 |
| Investor |
Hl. město Praha skrze Střední odborná škola – Centrum odborné přípravy a Gymnázium
Poděbradská 179/1, 190 00 Praha 9 |
| Supplier |
Subterra, a. s.
Koželužská 2246/5, 180 00 Praha 8 |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
June 2022 |
| Fotograf |
Martin Micka |
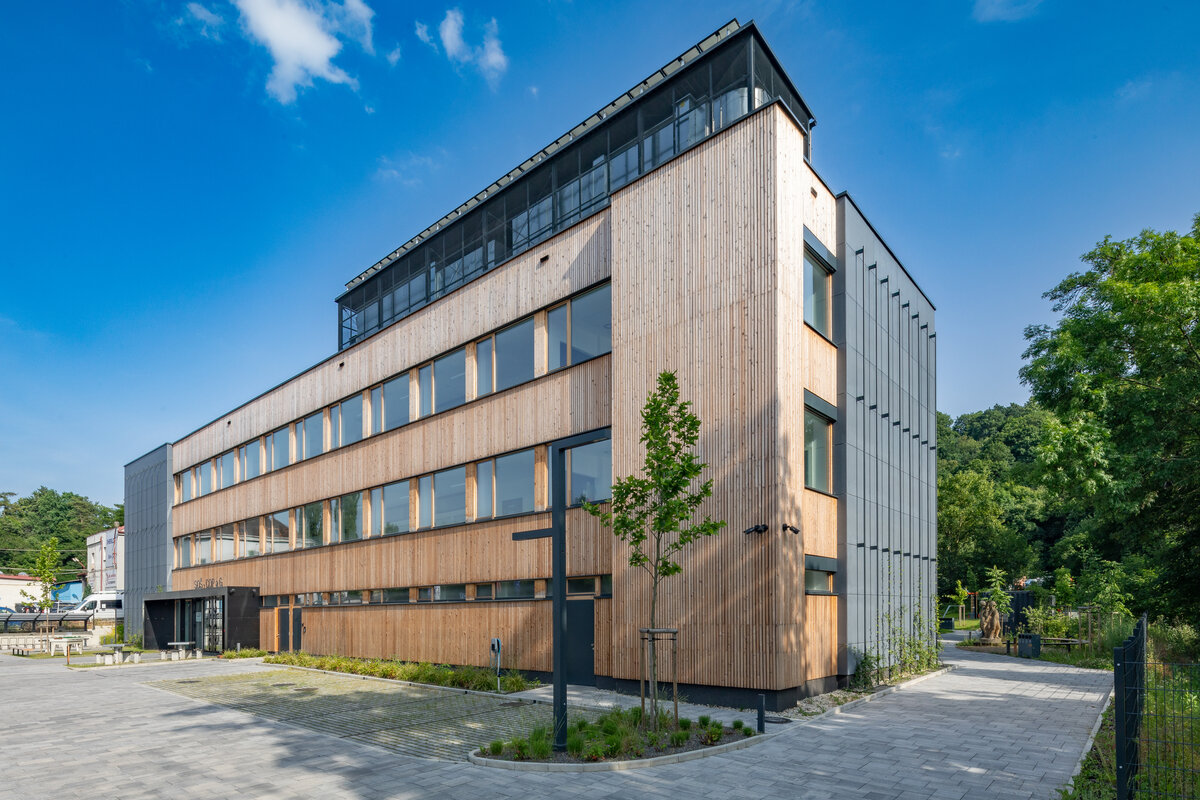
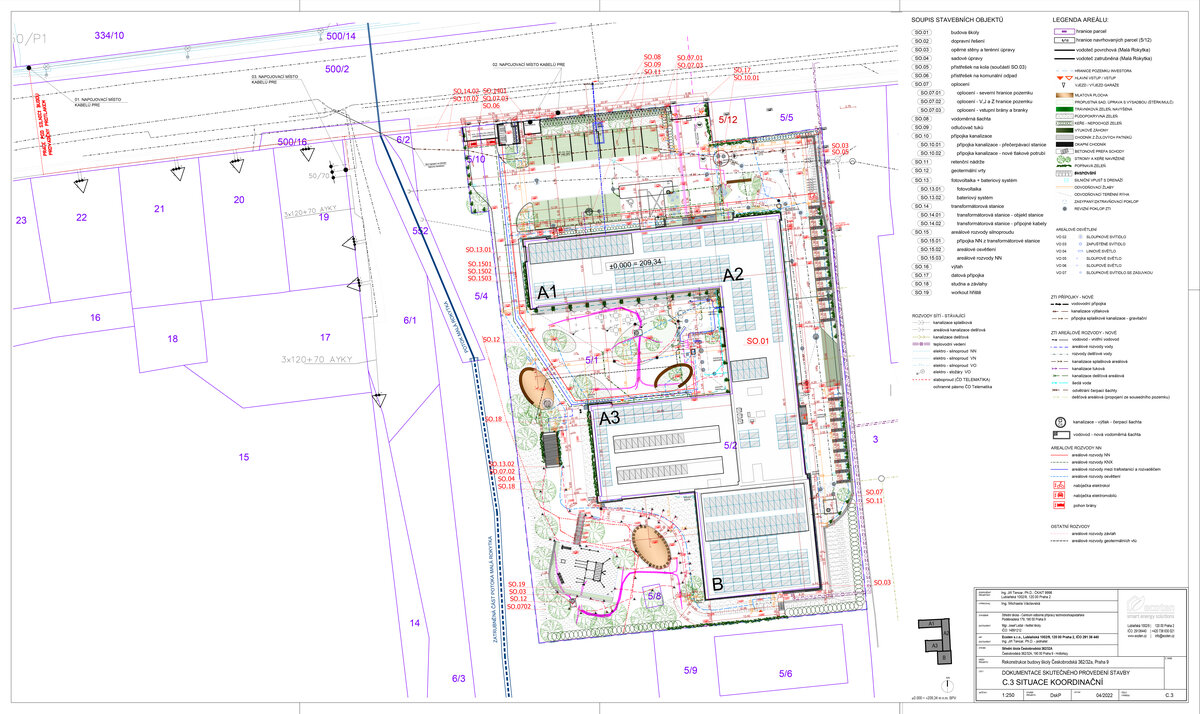
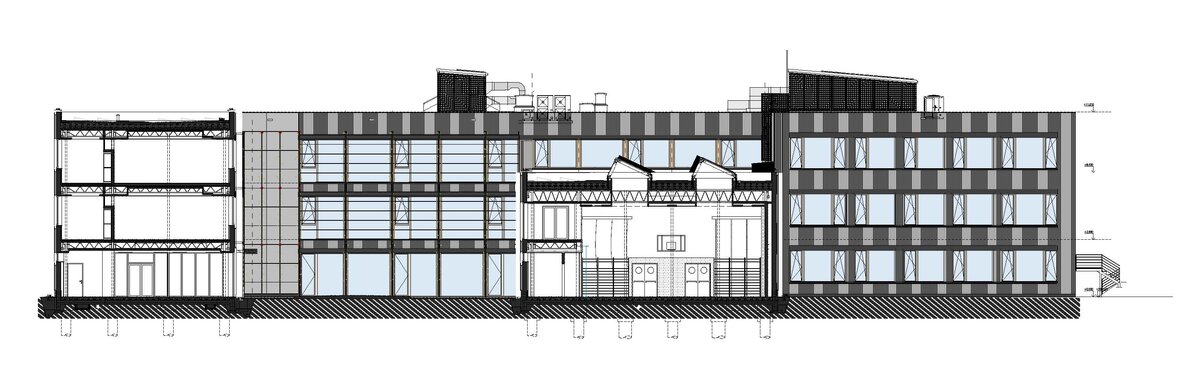
The reconstruction of the school in Českobrodská Street into a smart, sustainable, safe, operationally energy and carbon positive building represents a unique transformation of a 1970s building into a modern 21st century educational institution - it is well-organised, user-friendly and naturally ageing.
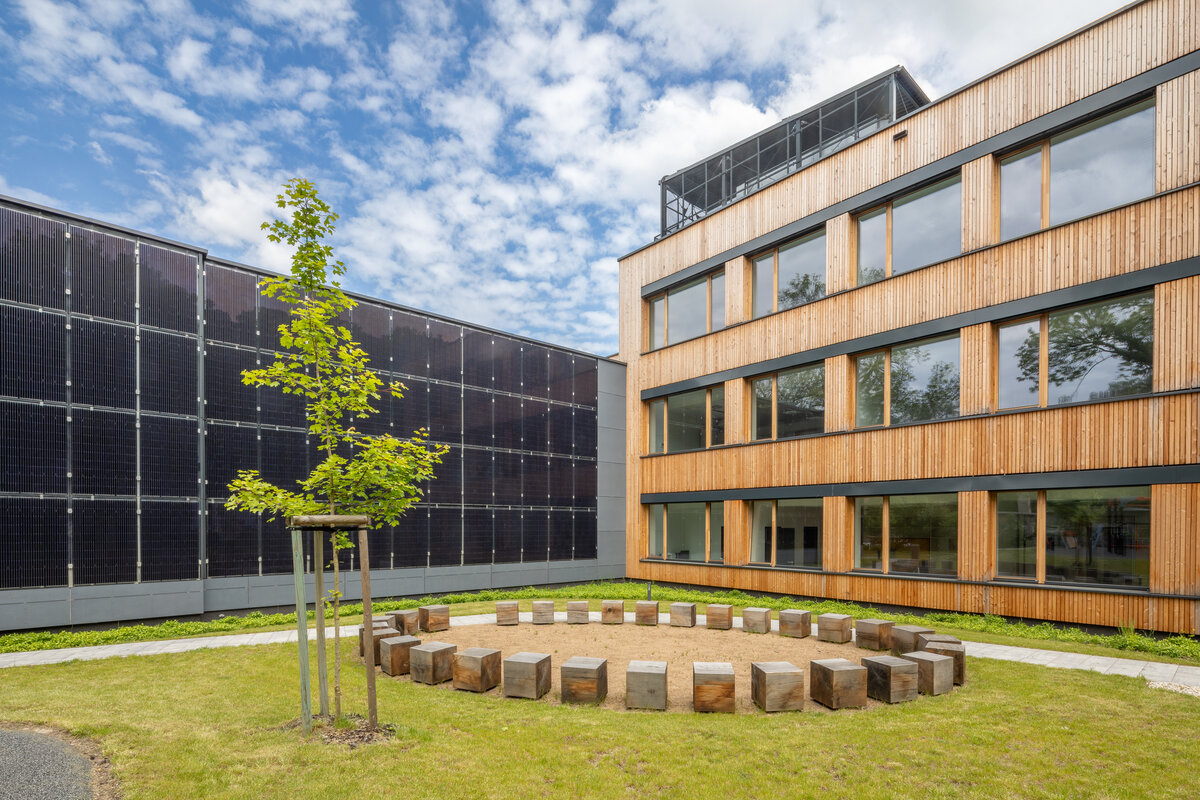
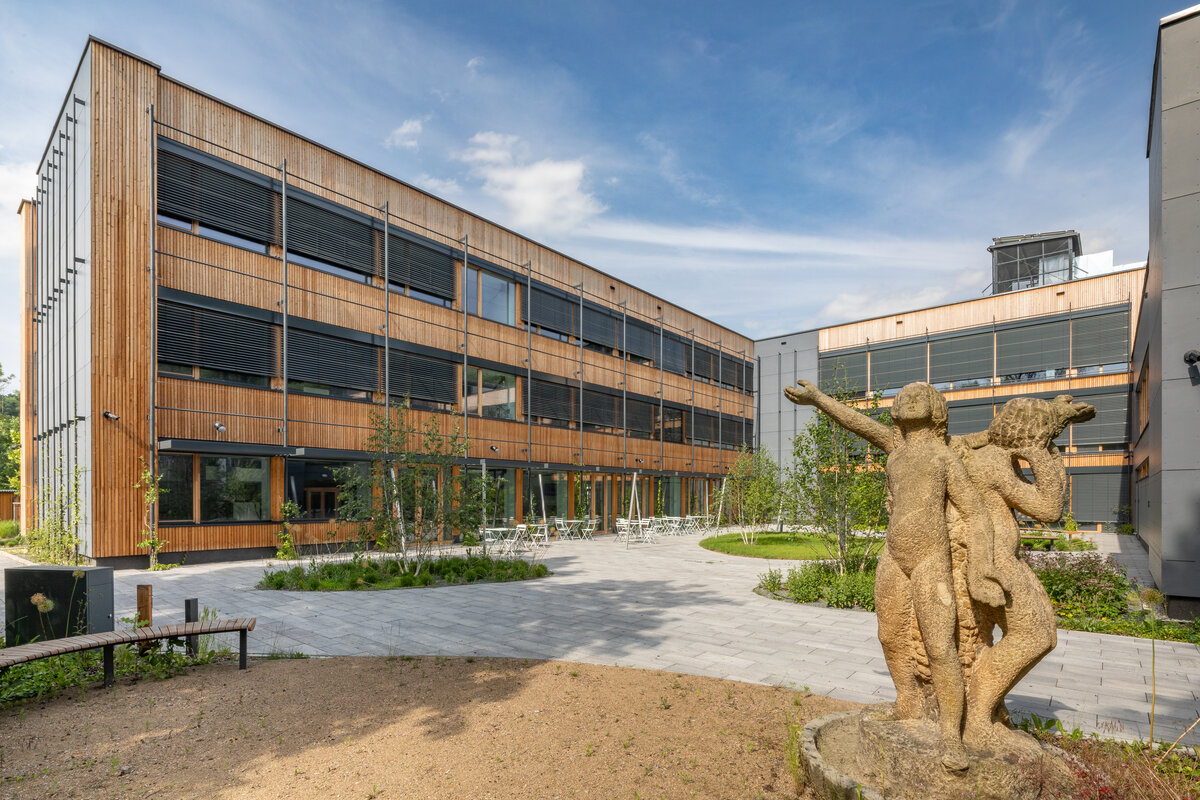
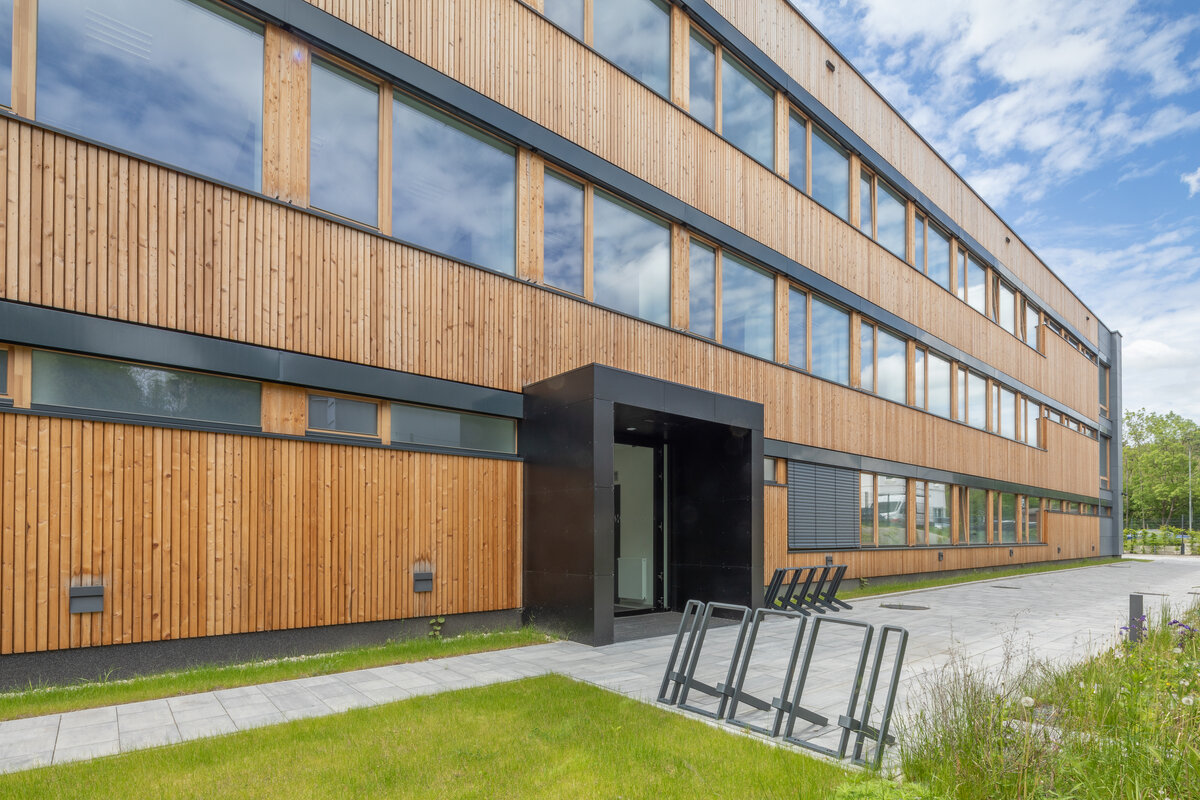
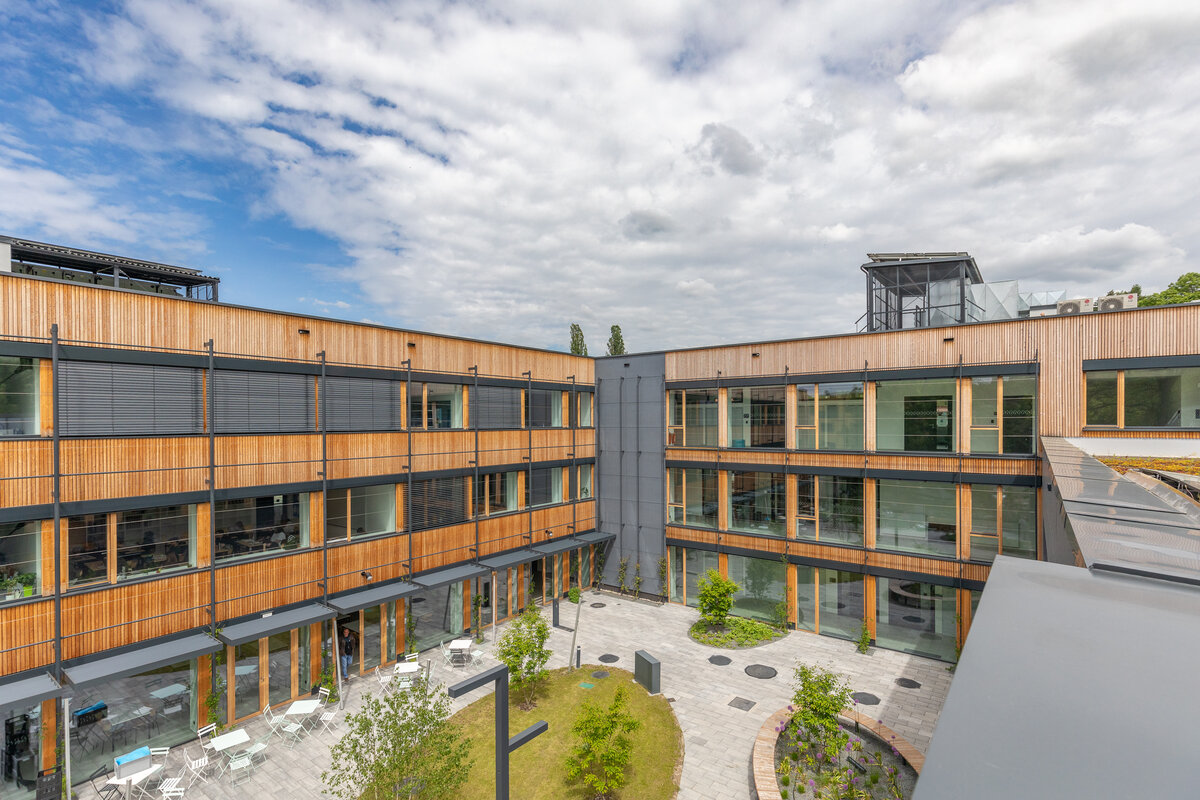
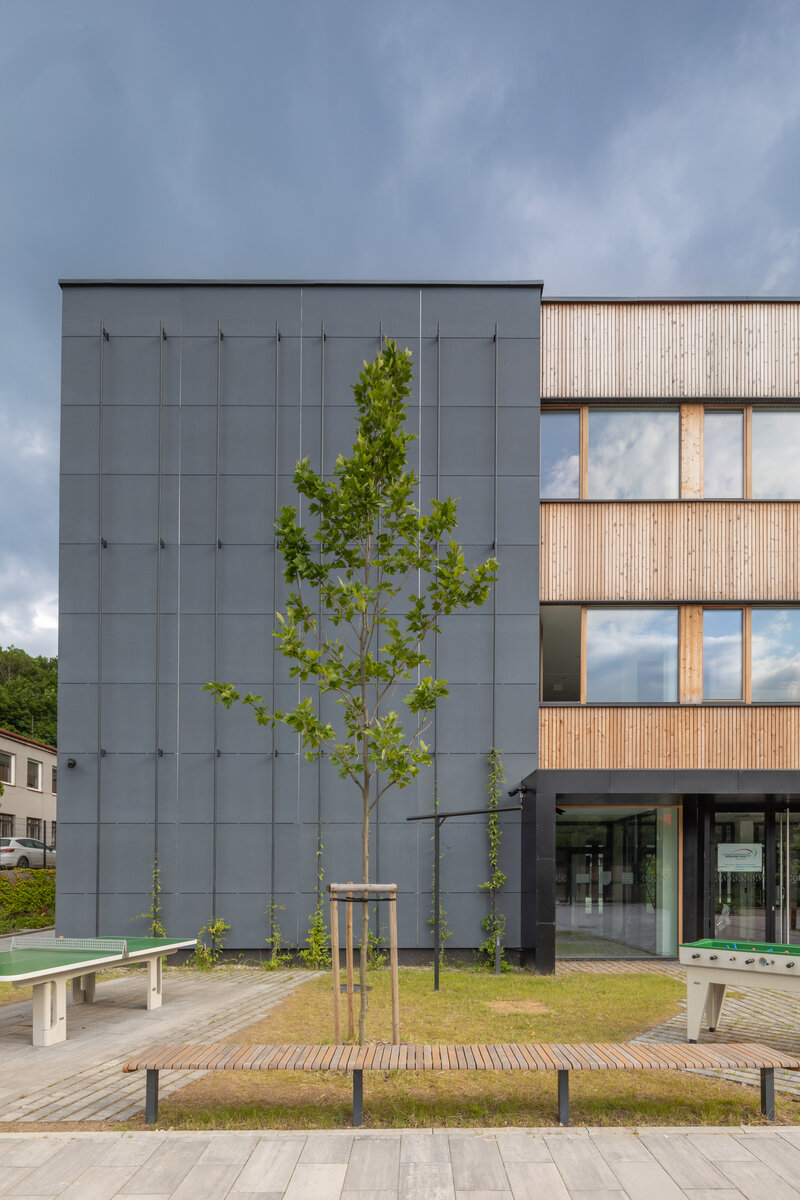
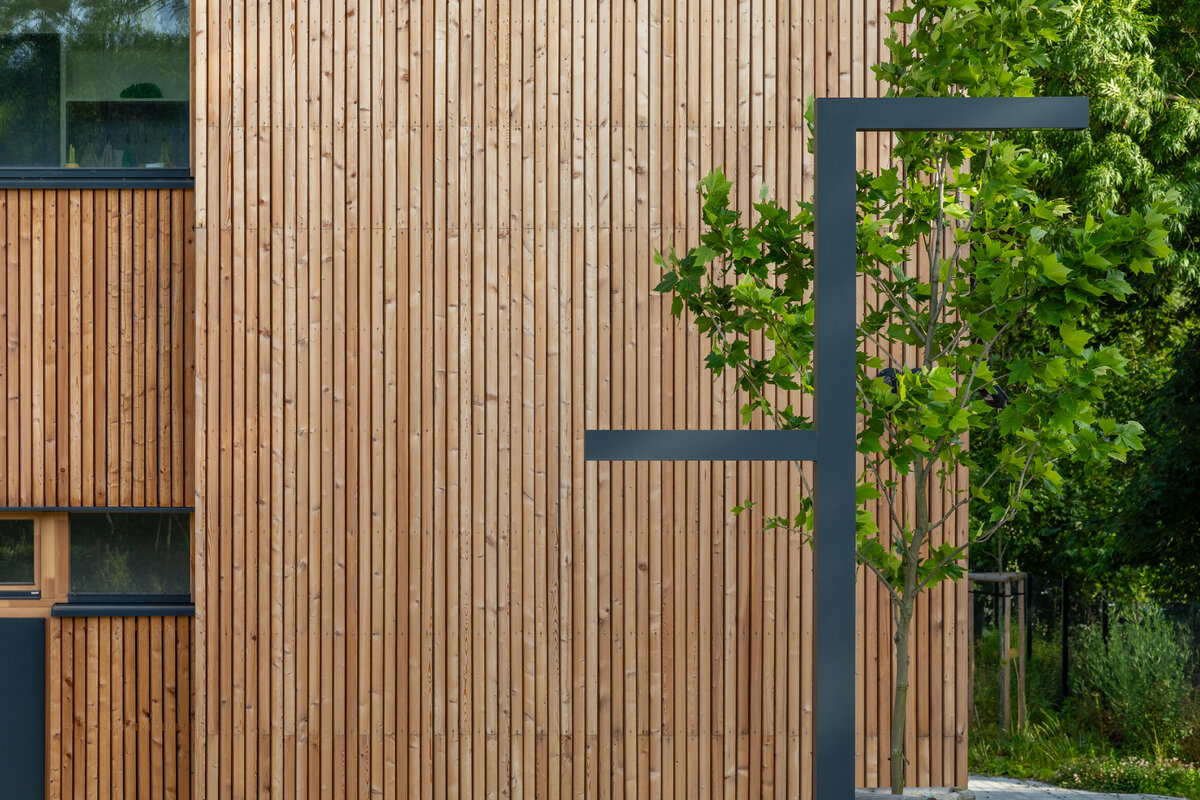
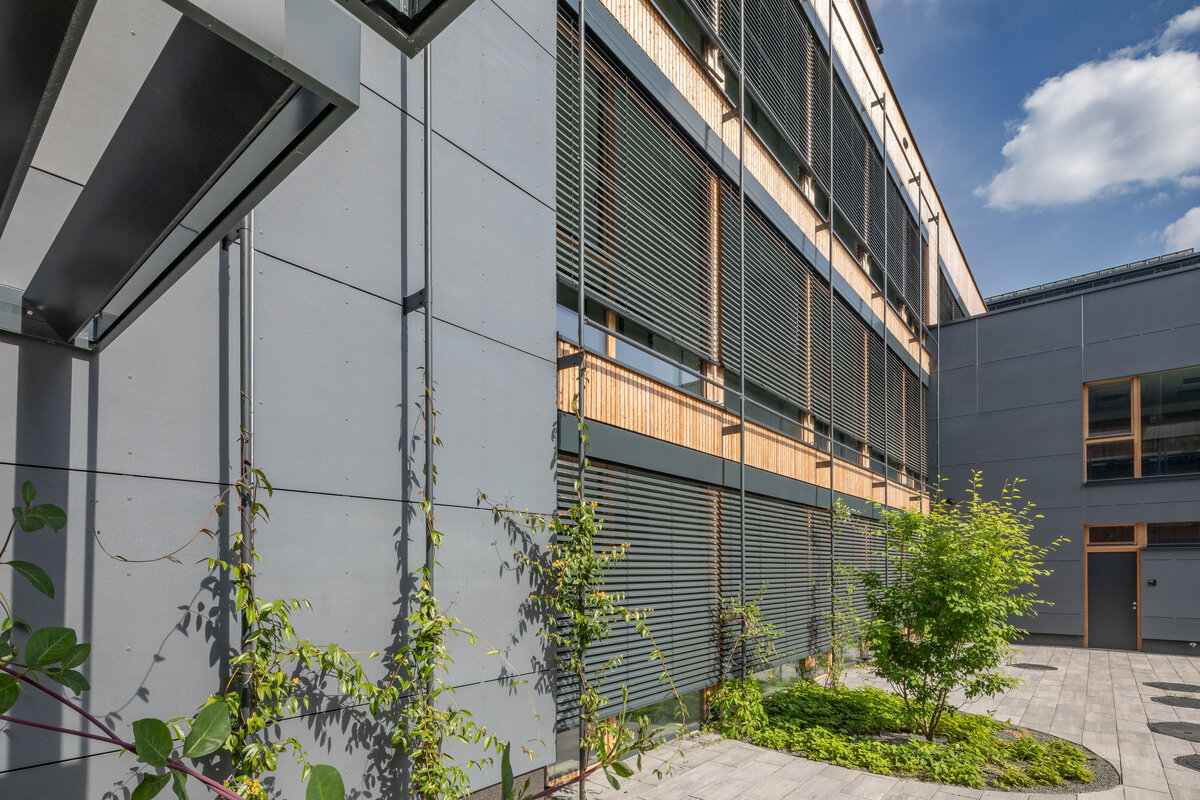
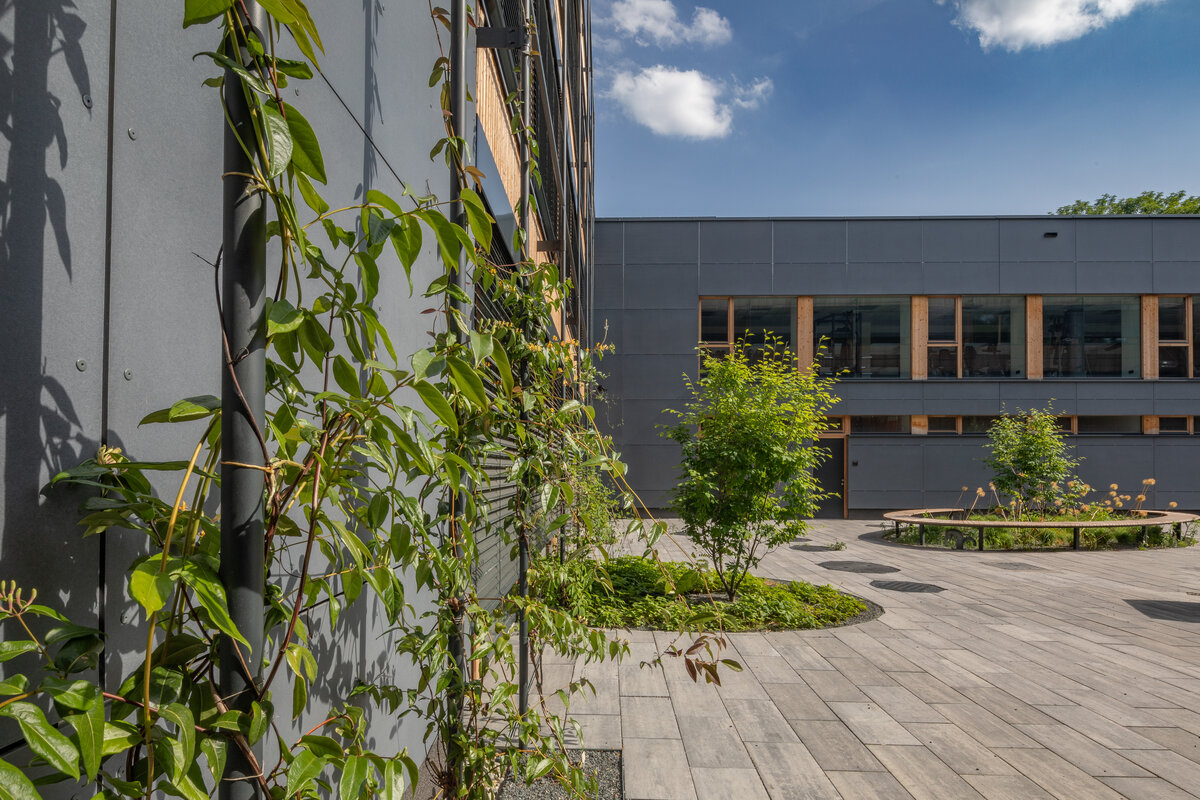
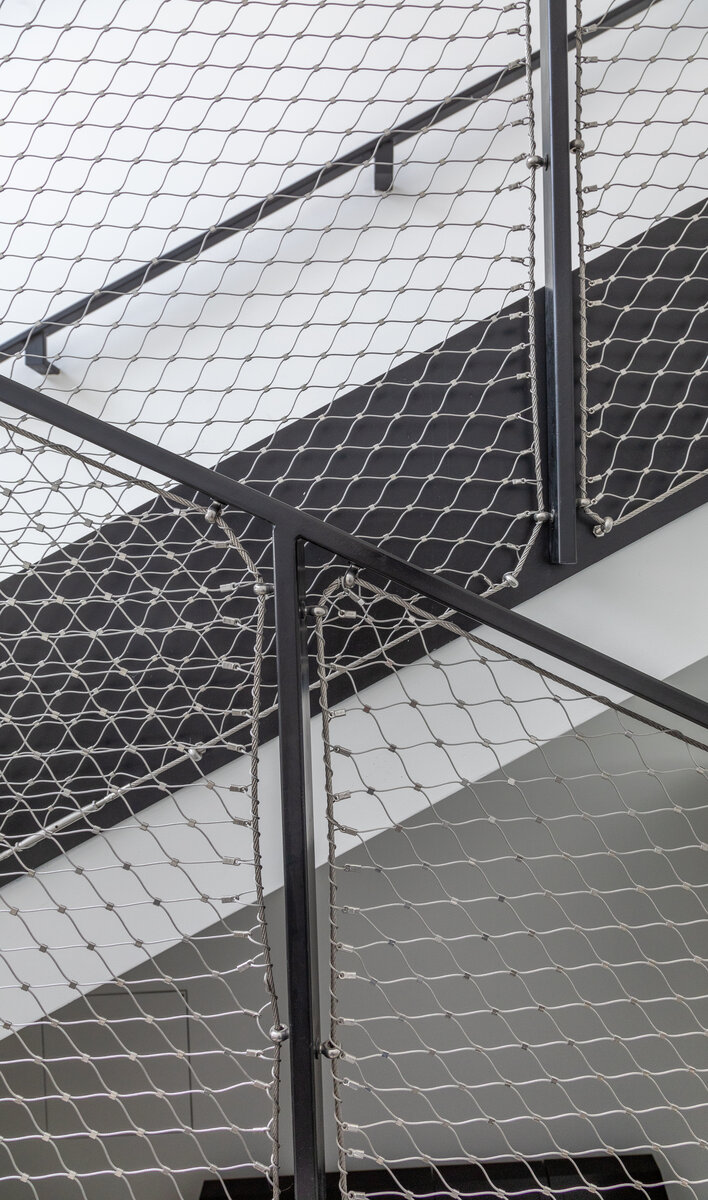
Vertical Siberian larch cladding is the dominant material on the facades, complemented by dark grey cembonite panels. Climbing greenery is gradually growing on the building, which will connect the building with the surrounding greenery and provide shading to the sun-exposed windows. The main entrance has distinctive anthracite frames.
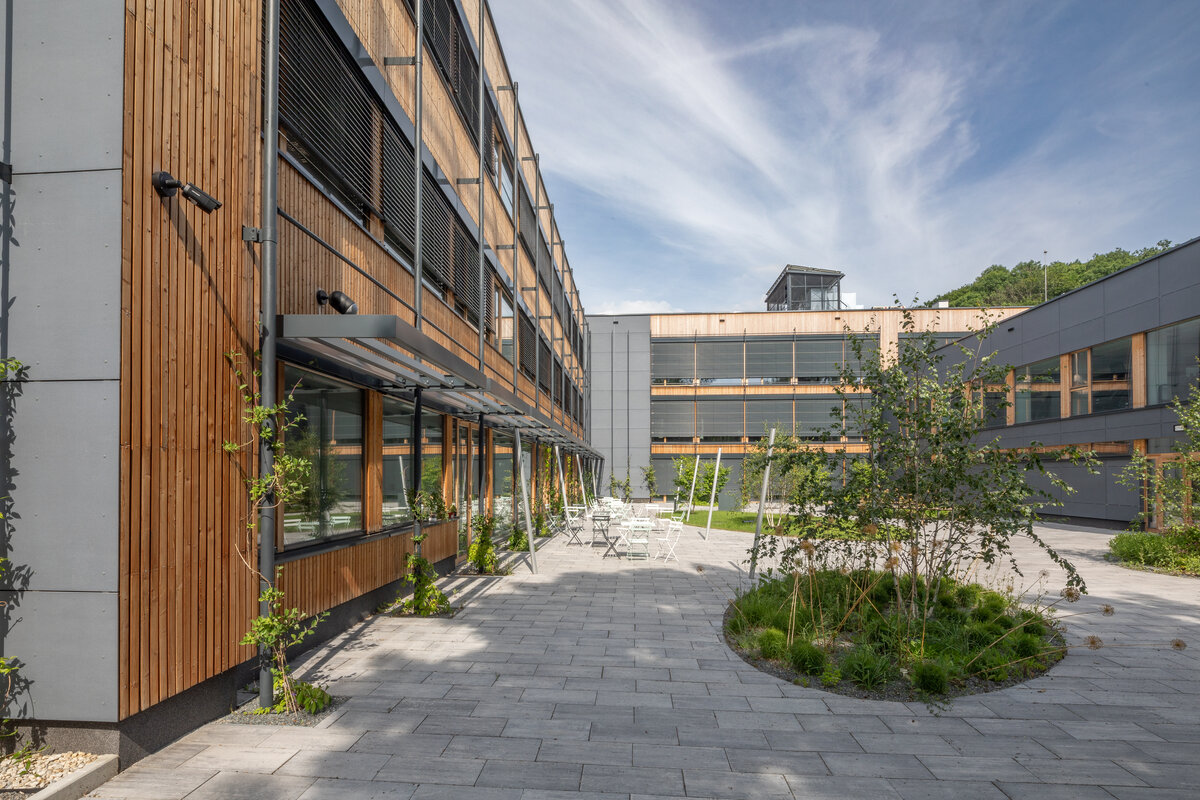
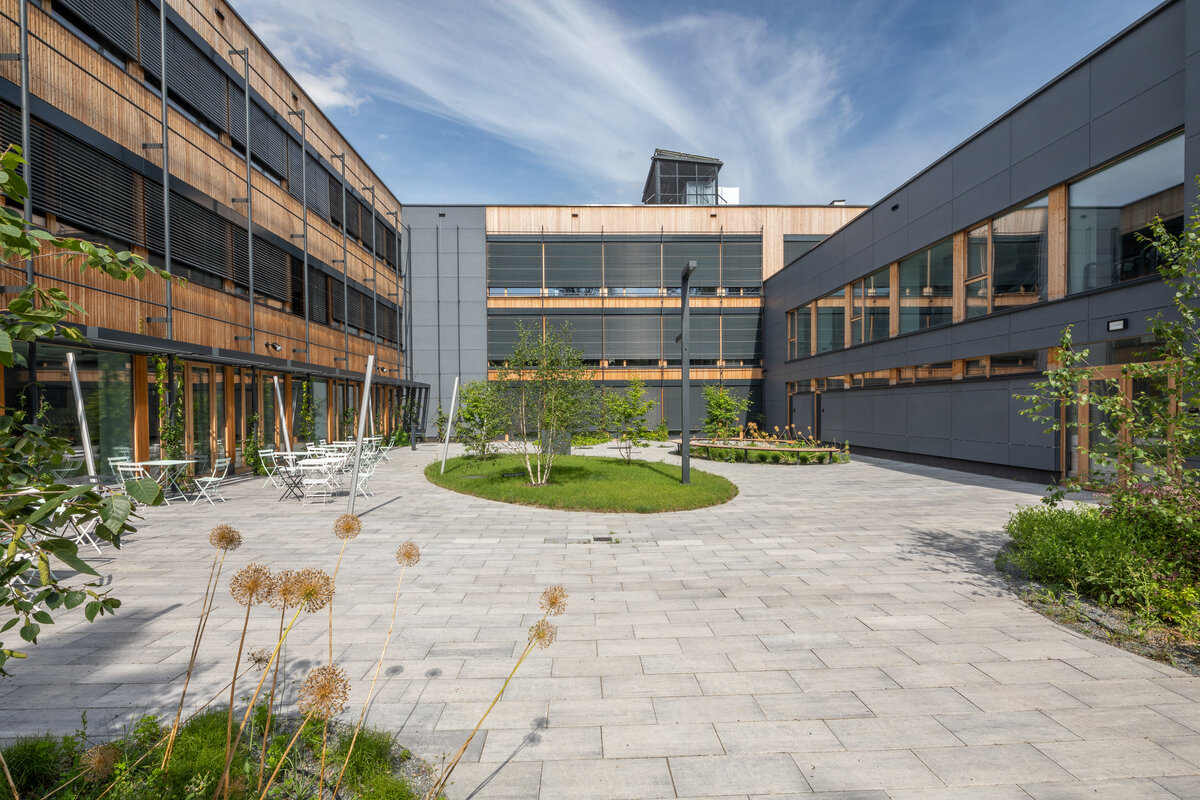
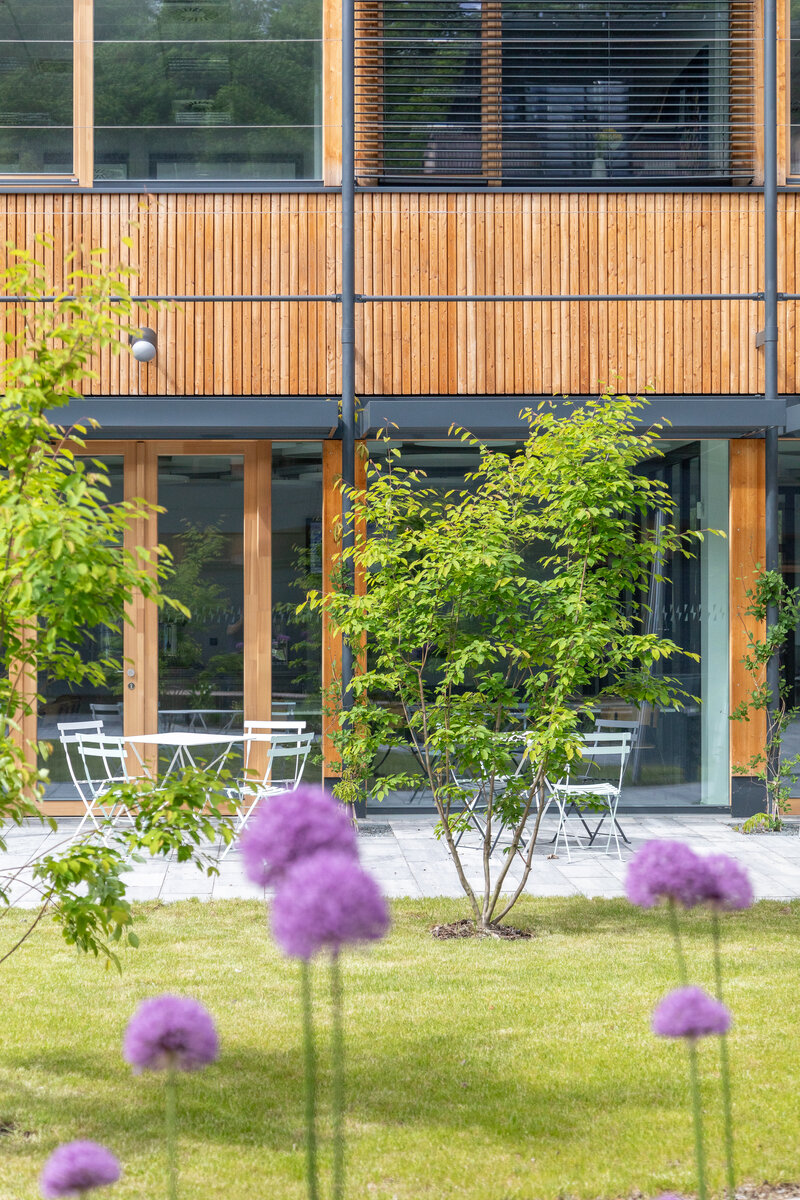
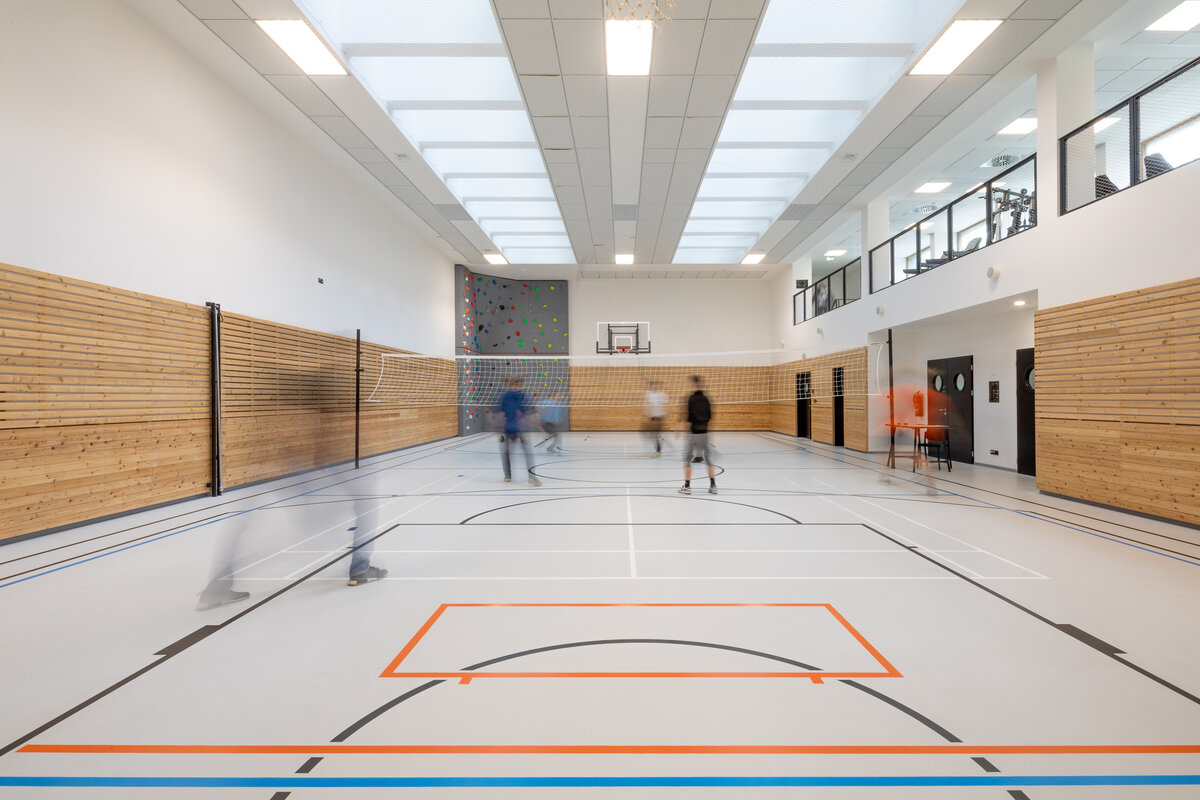
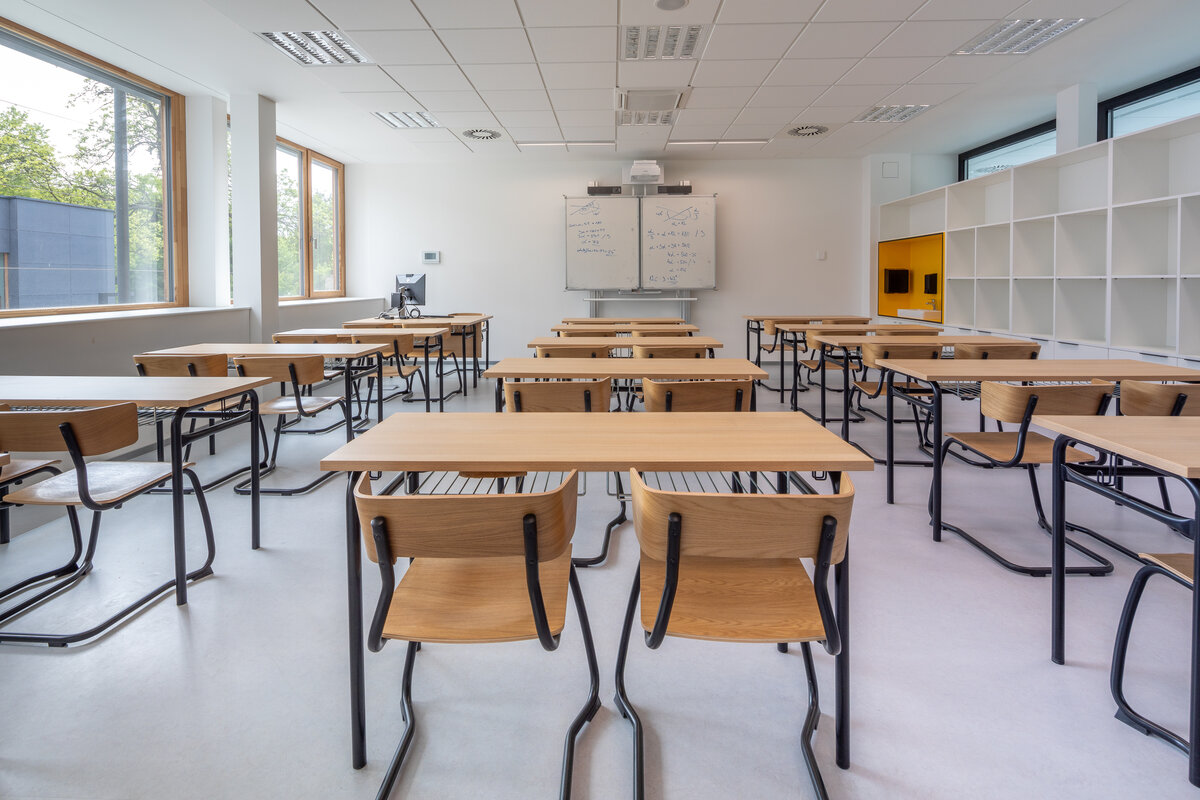
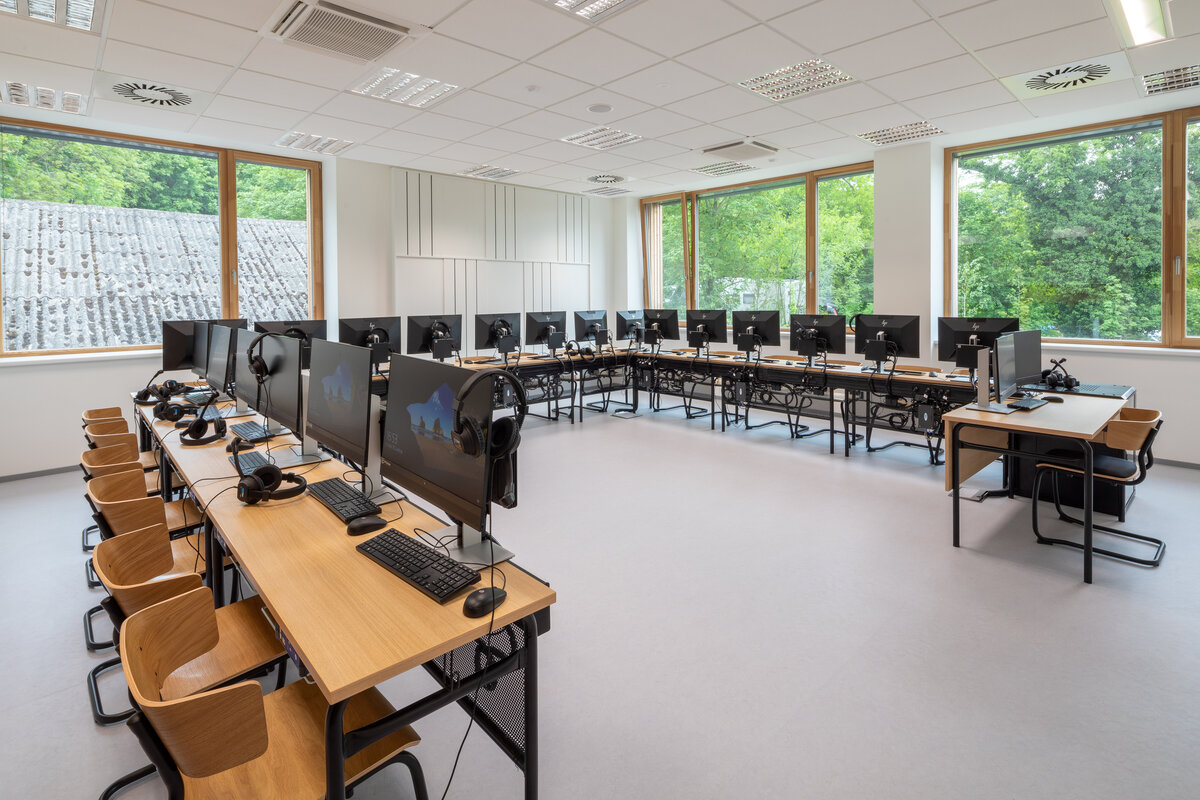
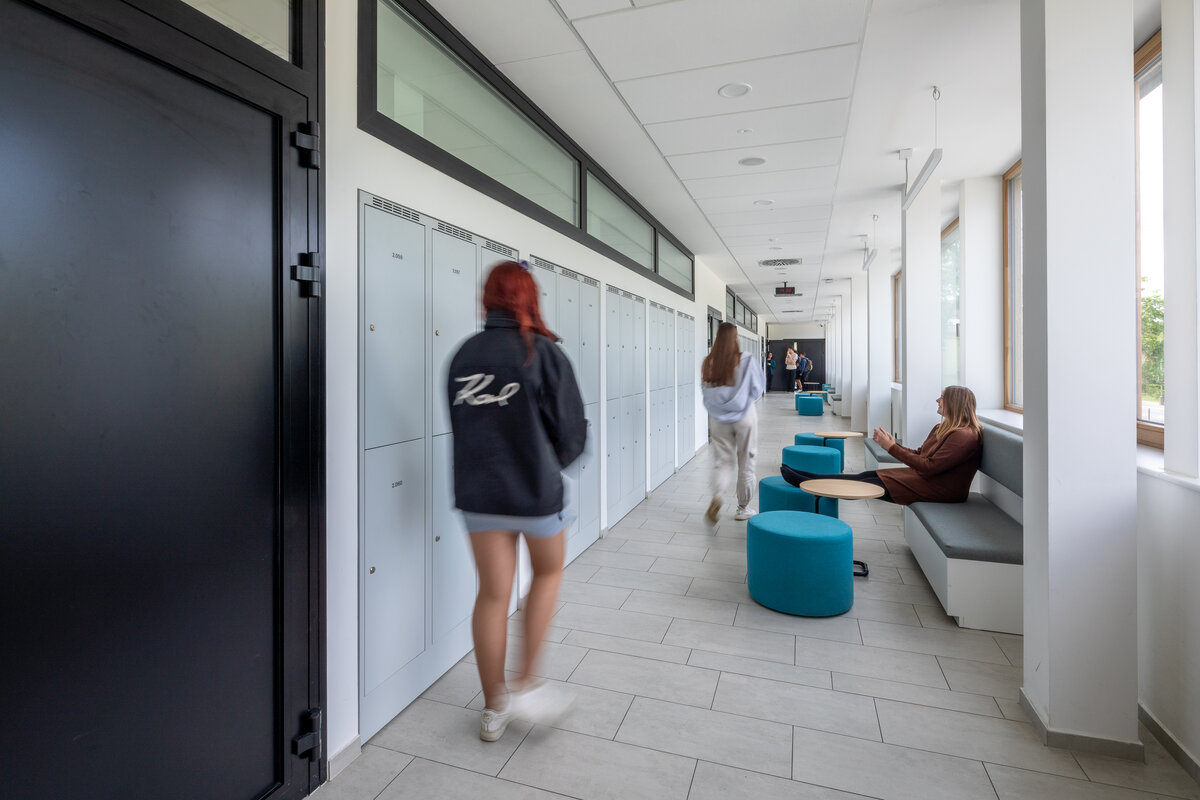
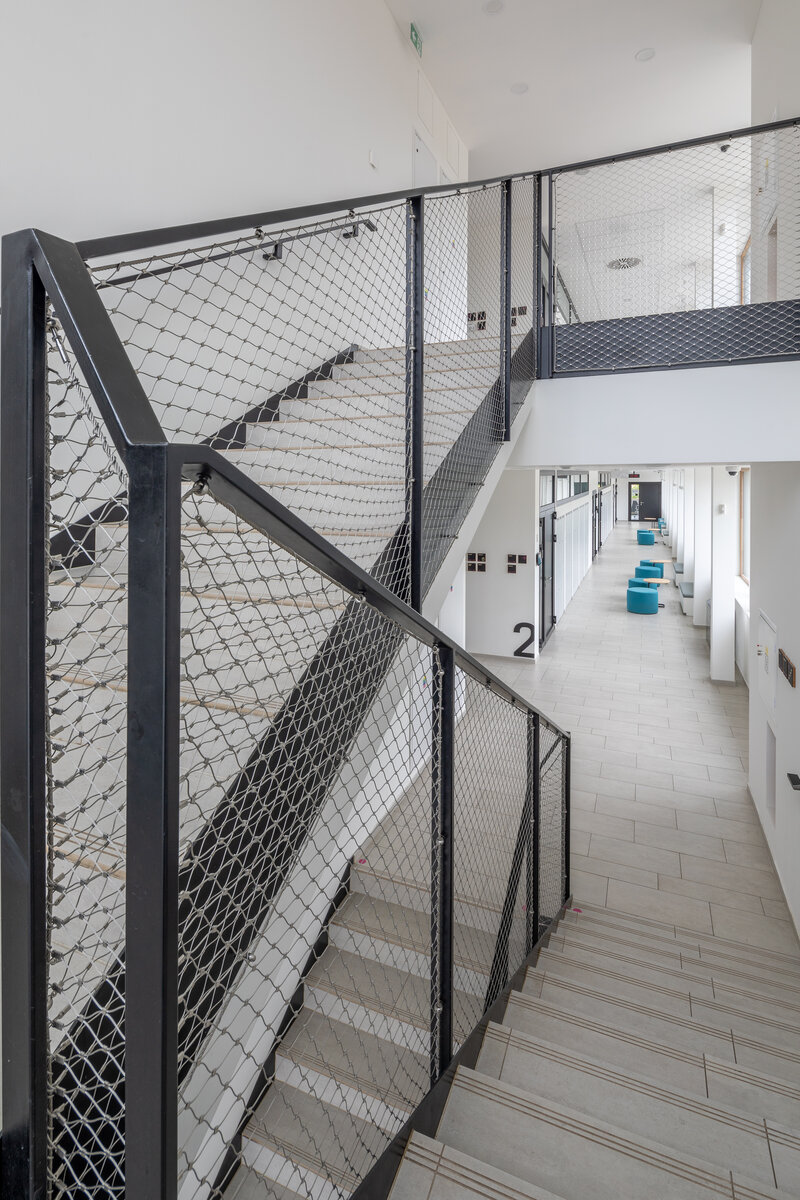
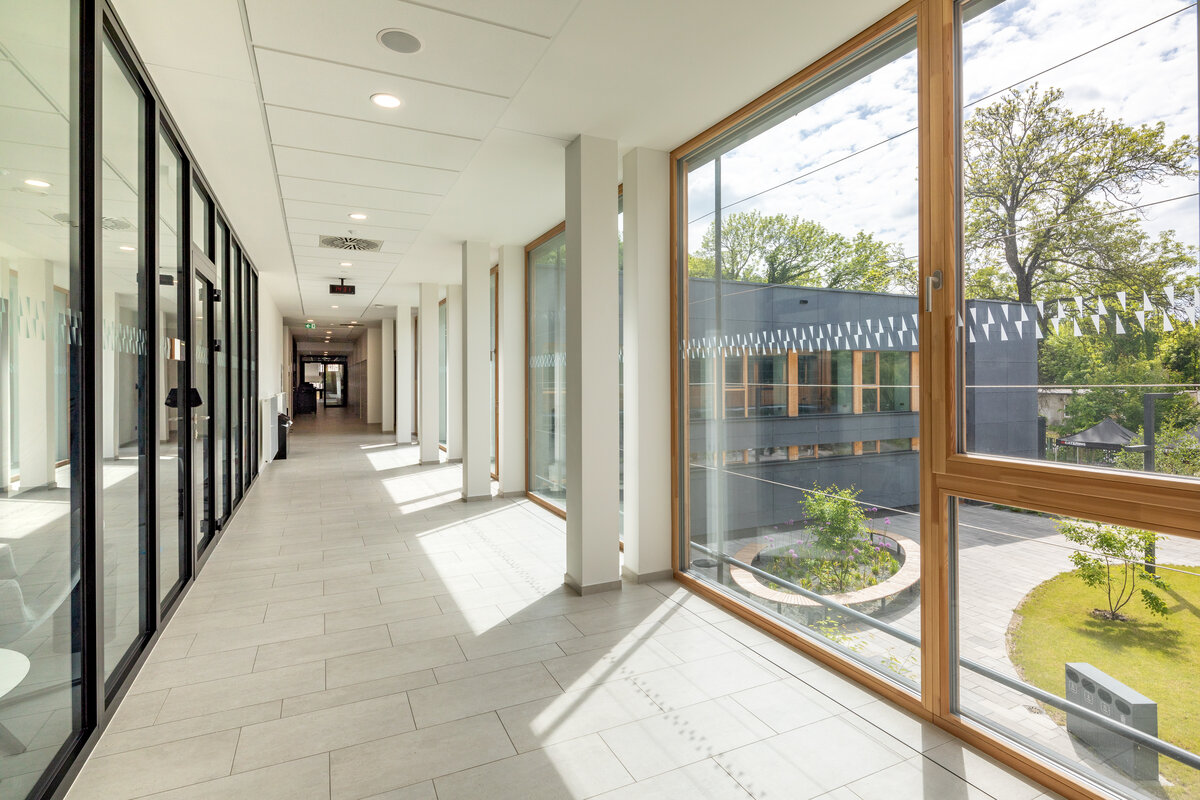
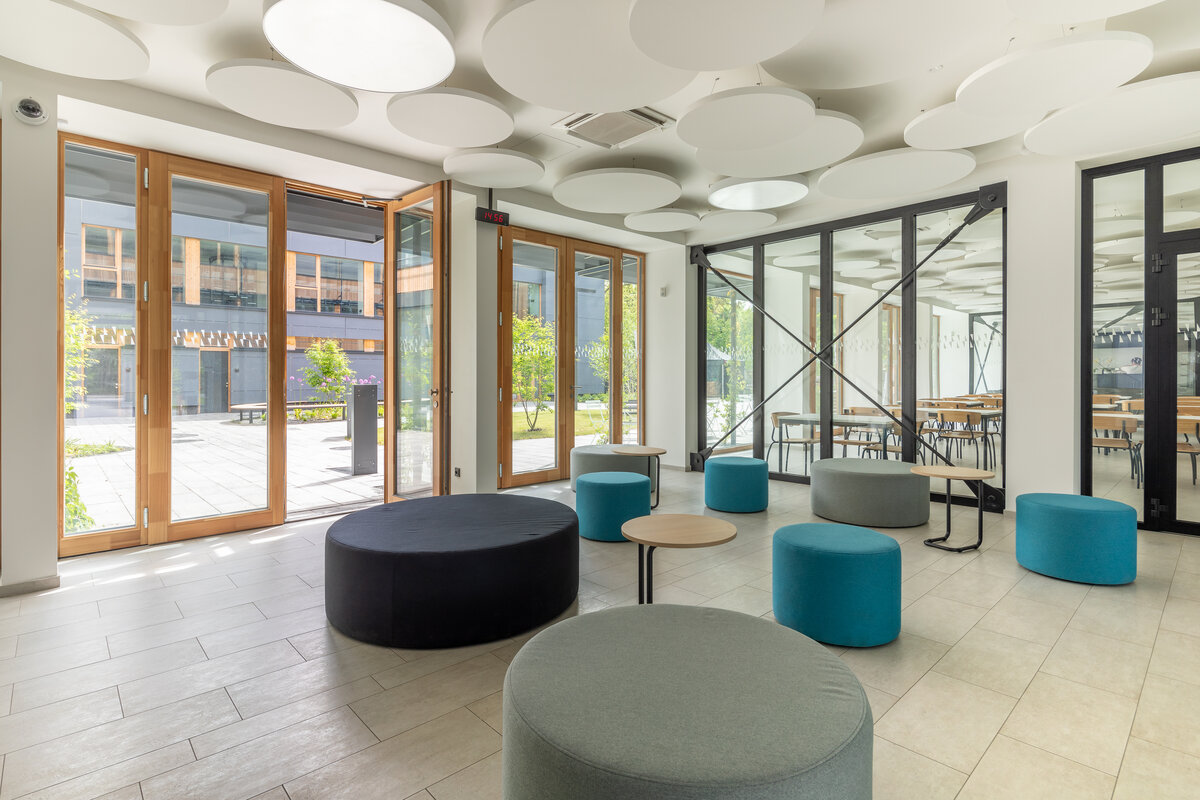
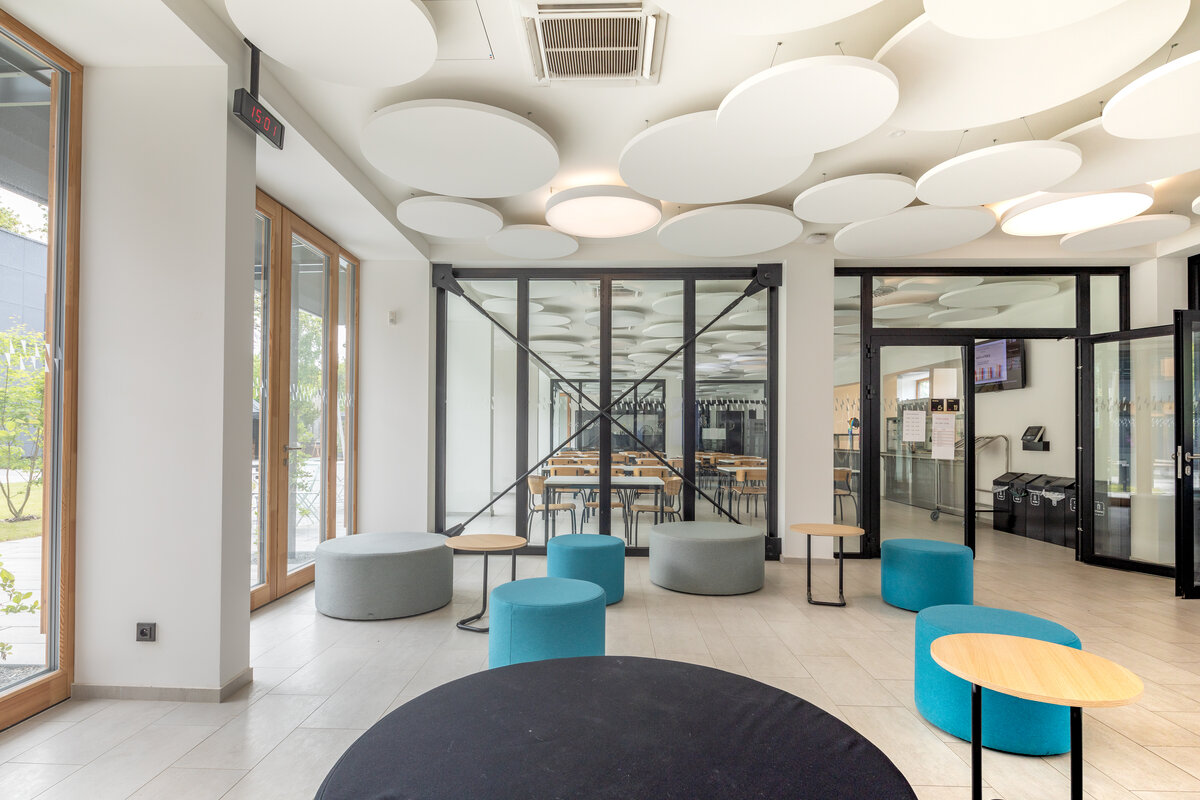
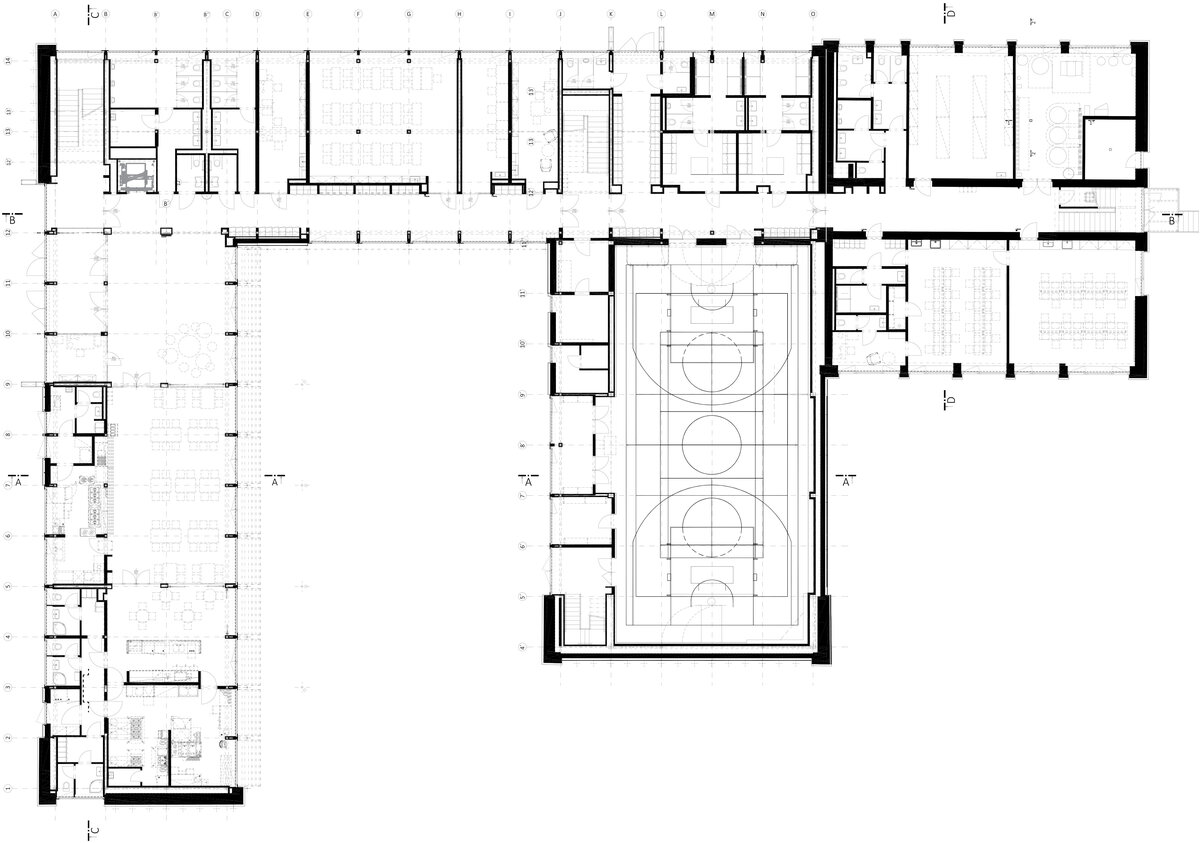
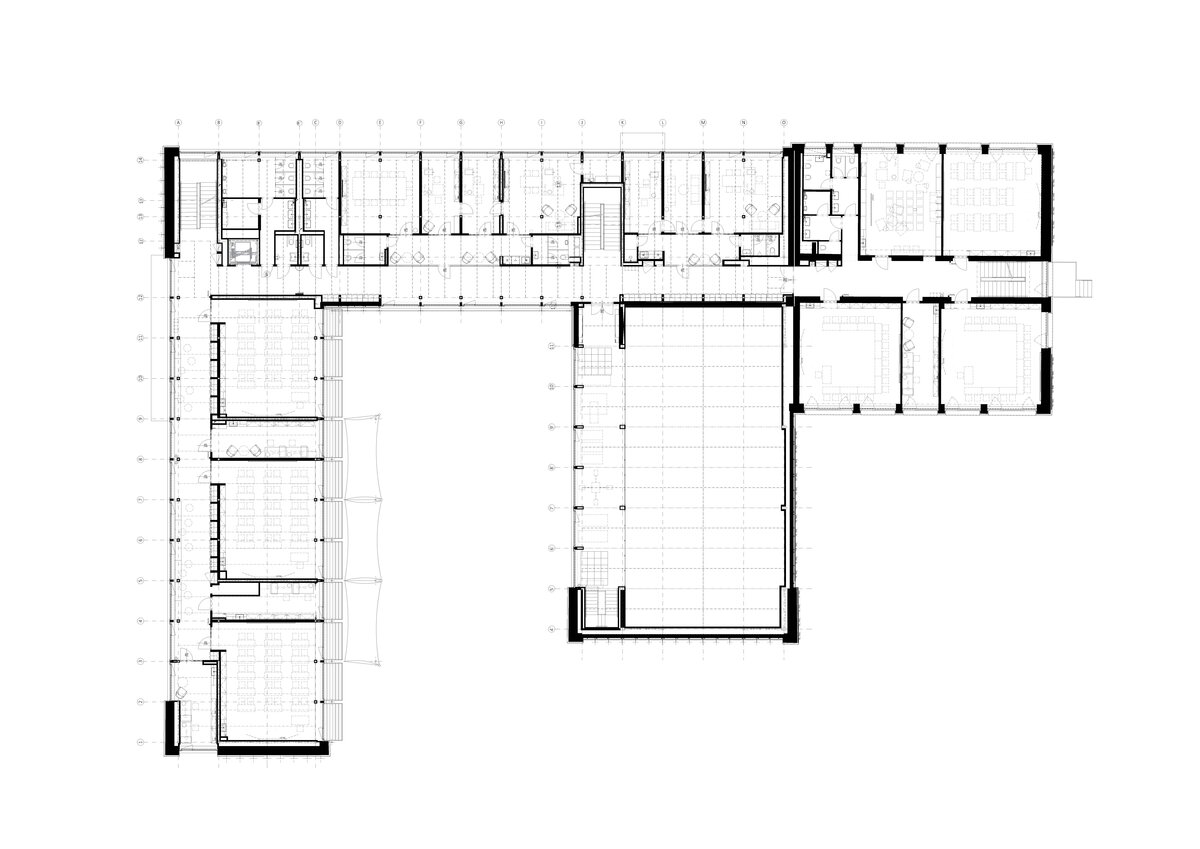
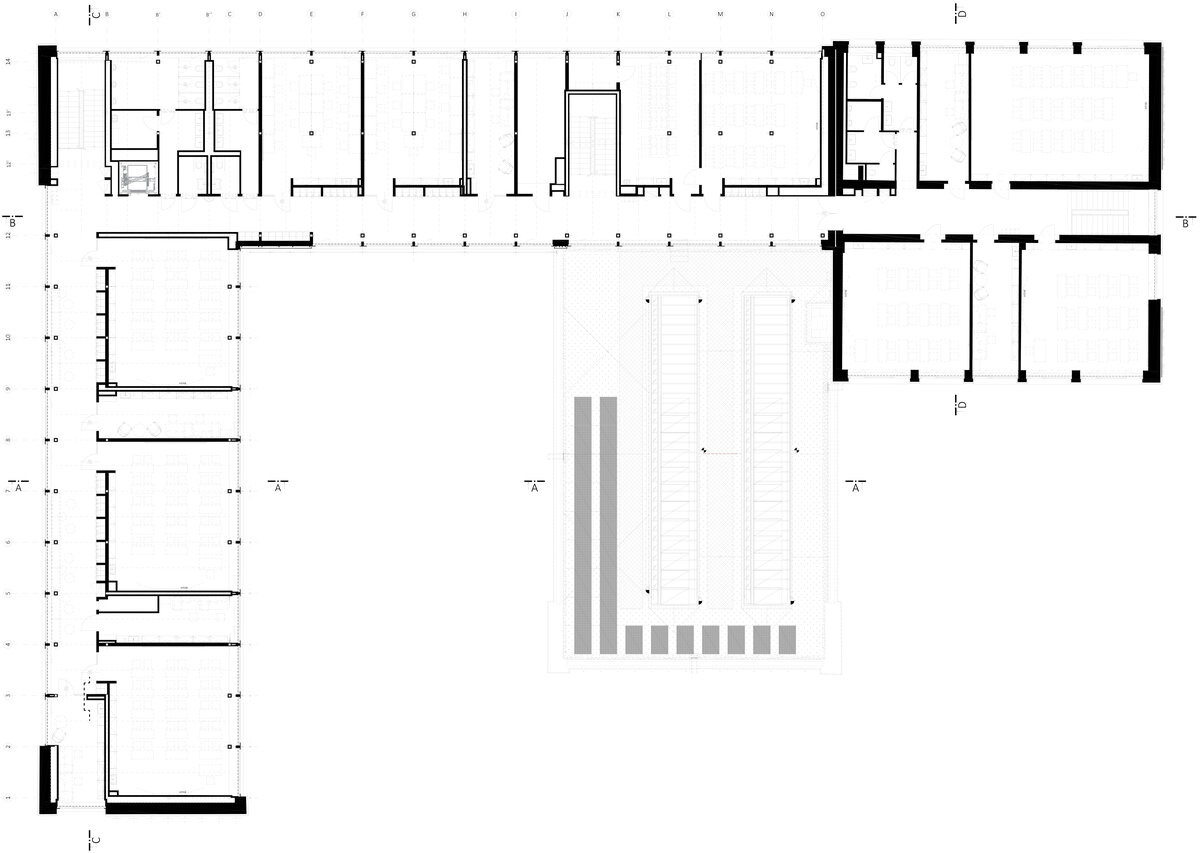
The school contains a diverse mix of courses from vocational to grammar school. The original layout maze has been replaced by a clear layout that respects the educational needs. The new school spaces are versatile and allow the institution to adapt to the future requirements of modern education. The generous circulation spaces are the backbone and also a meeting place in the building providing through large windows views of the surrounding greenery and the new outdoor atrium, which lies at the heart of the layout and to which both the main circulation spaces and the core classrooms turn. In addition, the entrance floor offers direct connections to the atrium from the lobby, the dinning hall and the cafeteria. Fabric awnings provide shade in the summer months, and mature trees will provide shade in the future. The atrium further flows into various outdoor spaces full of greenery, serving both for alternative outdoor learning and for active student recreation. The whole spatial concept is based on transparency, which should be a priority for public institutions.
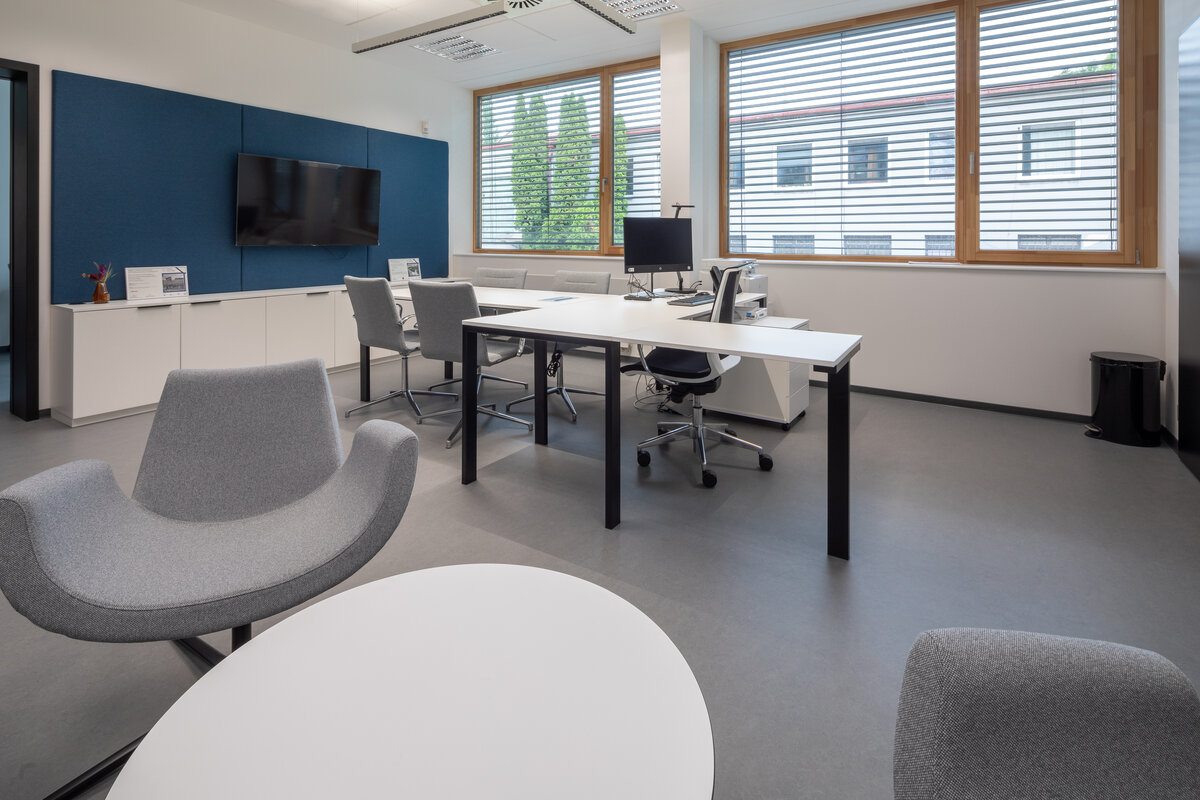
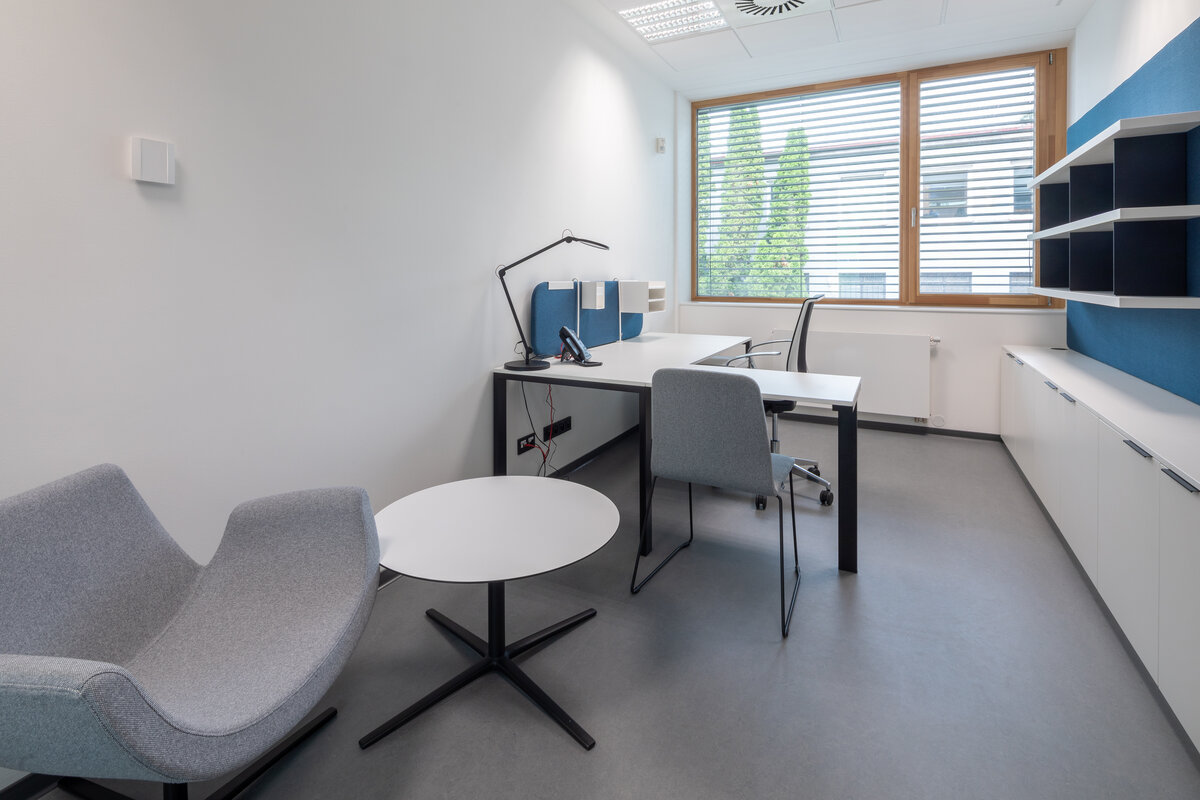
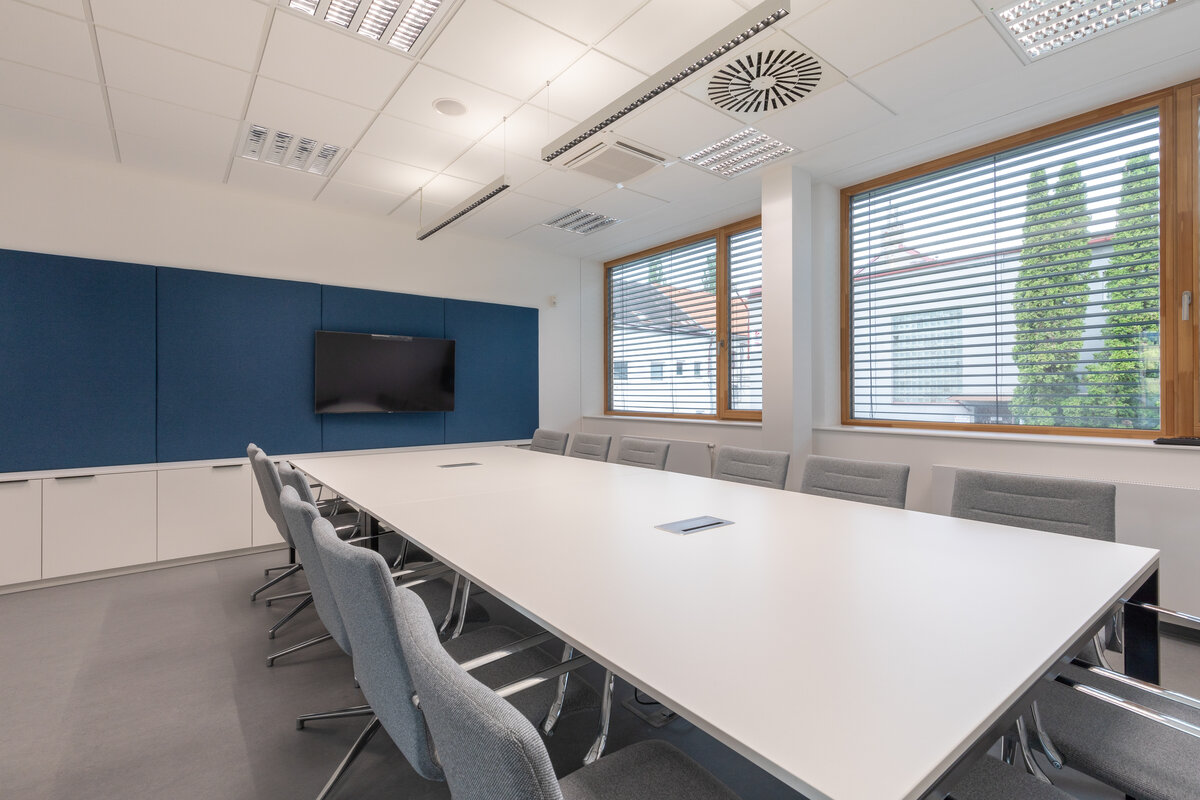
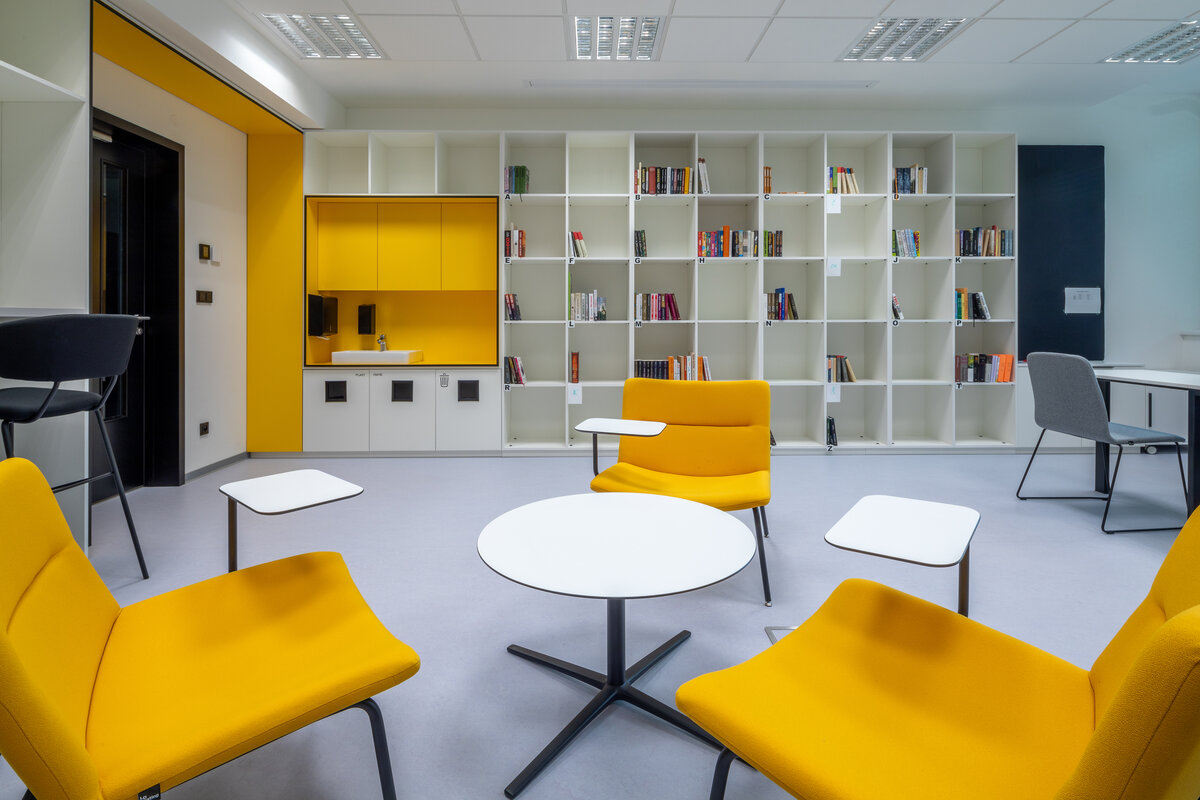
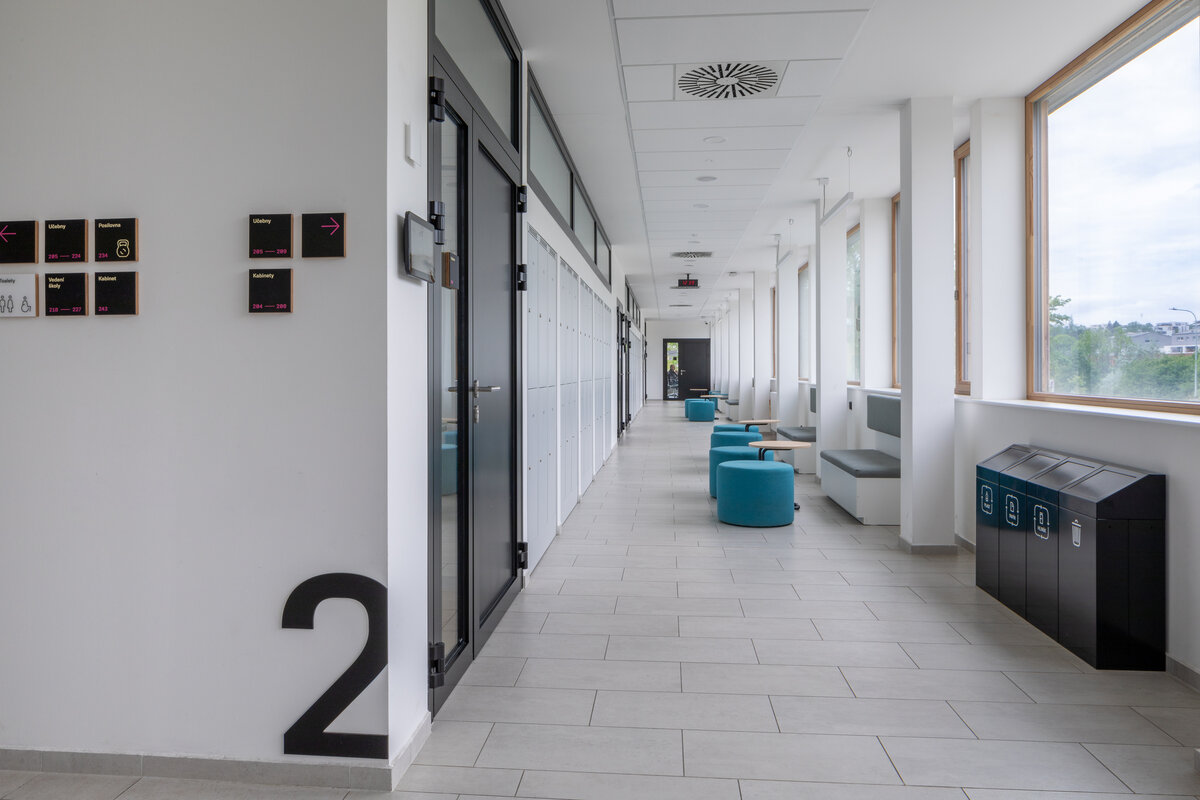
The interior concept supports the orientation in the building. There is a high use of glazed partitions, doorlights and overlights. The different typologically significant parts are distinguished by colour. Warm yellow classrooms, dark blue cabinets, administration and management offices are easily identifiable from the neutrally designed entrance areas and circulation. The color typology of the units is addressed not by the dominant use of color, but by color accents. As on the façade, metalwork and small structural details are chosen in contrasting black. An important element supporting orientation in the building is the information and orientation system developed by the graphic designer. The house and its immediate surroundings thus work in a pleasant symbiosis.
The innovative, smart, sustainable, inclusive and financially competitive refurbishment of school building tackling global challenges with local solutions is transferable to any typology reaching 21.Century standards. The building serves as a Living Lab working with very extensive volume of operational data which are used for further research and evaluation of building operation. The design is based on three pillars of sustainability and received the highest SBToolCZ certificate:
Environment
- Operationally Energy and Carbon Positive Building
- Innovative wooden curtain facade ENVILOP - an outcome of Czech applied research at CTU in Prague was used for the first time
- The building envelope complies with passive house standards
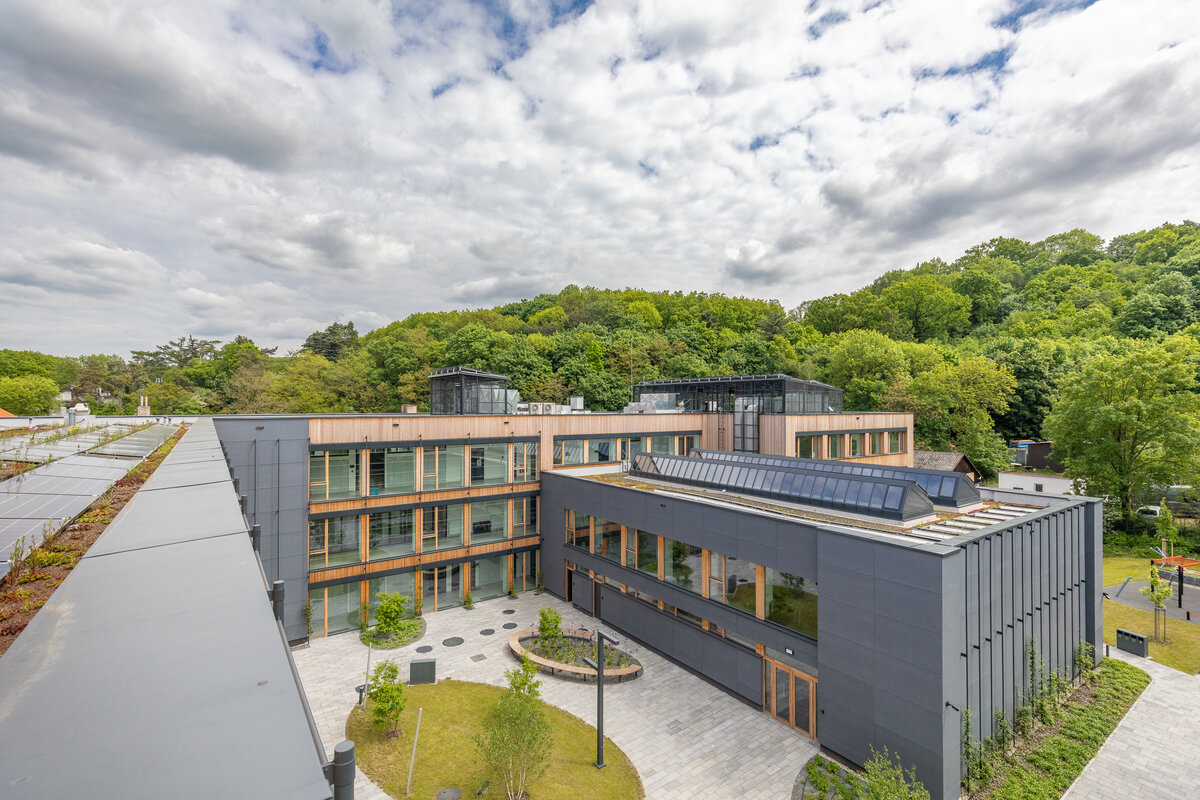
- Geothermal heat pumps (heating, cooling and hot water), 147 kWp PVs; 300 kWh battery
- Innovative Predictive Control System: One day ahead prediction of the building's energy consumption, PVs production and spot electricity prices. The main priority is energy self-sufficiency, then spot electricity prices and then price of battery discharge
- Grey water from showers and washbasins is cleaned and used for flushing toilets
- Rain water is accumulated and used for irrigation
- The building has an extensive green roof, vertical greenery
User comfort
- Forced ventilation with heat recovery and regenerative heat exchangers controlled by CO2&VOC sensors
- Microclimate manged by automatic control system based on the classrooms‘ schedule, the presence of people and could be partially controlled manually
- Ventilation, heating and cooling stops when windows are opened
- The lights are controlled by the level of daylight contribution in order to maintain 500 lux at the desk. Automatically controlled blinds. Lights and blinds could be also controlled manualy
Economy and management
- The Life Cycle Cost calculations as decision tool
- The full set of as-built documentation including all professions and operational manuals
- All significant energy consumption appliances and nods are measured and managed
- The waste chains were built from classrooms upto central collection place
All required stakeholders were involved in project (client, architect, general designer, oponent, representative of the school – staff, teachers and students, representative of facility manager, certified SBToolCZ expert)
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
SBToolCZ, zlatý certifikát
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
A
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|