| Author |
Ing. arch. Ondřej Chybík, Ing. arch. Michal Krištof / CHYBIK + KRISTOF , autor venkovních úprav: Ing. Zdeněk Sendler |
| Studio |
|
| Location |
Vizovice |
| Investor |
KOMA Modular s.r.o. |
| Supplier |
KOMA Modular s.r.o. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
November 2021 |
| Fotograf |
|
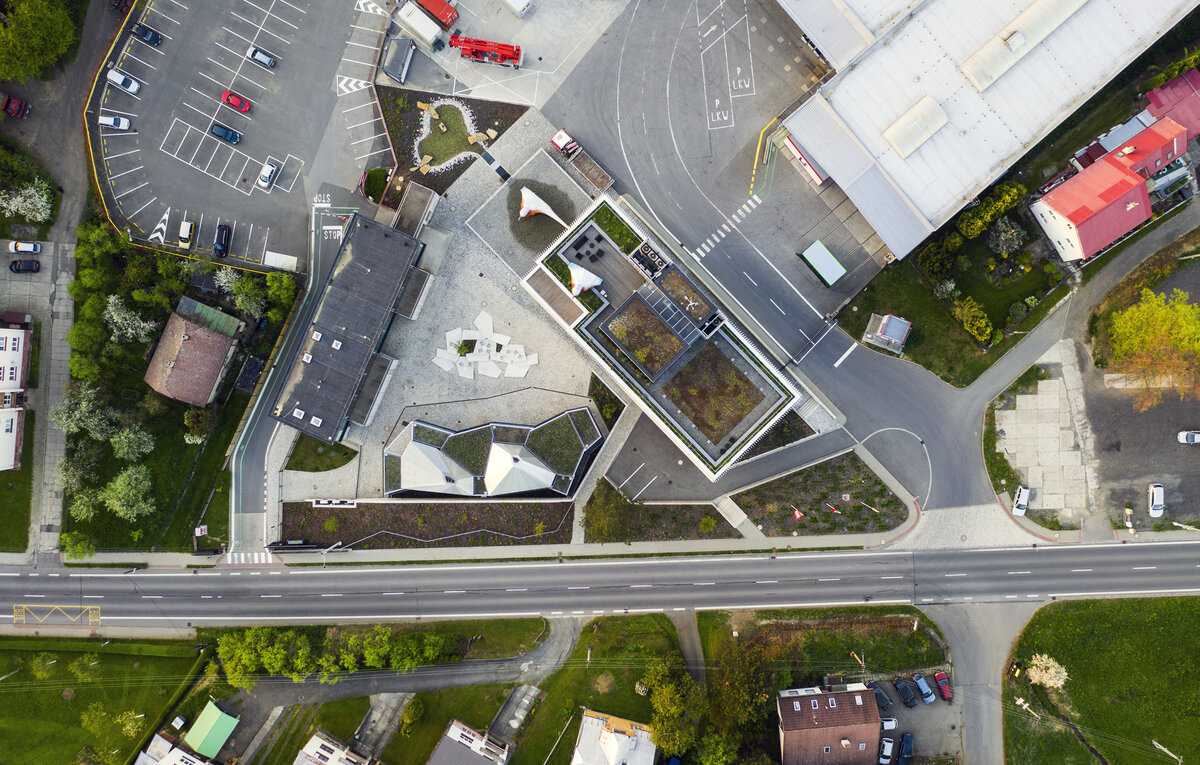
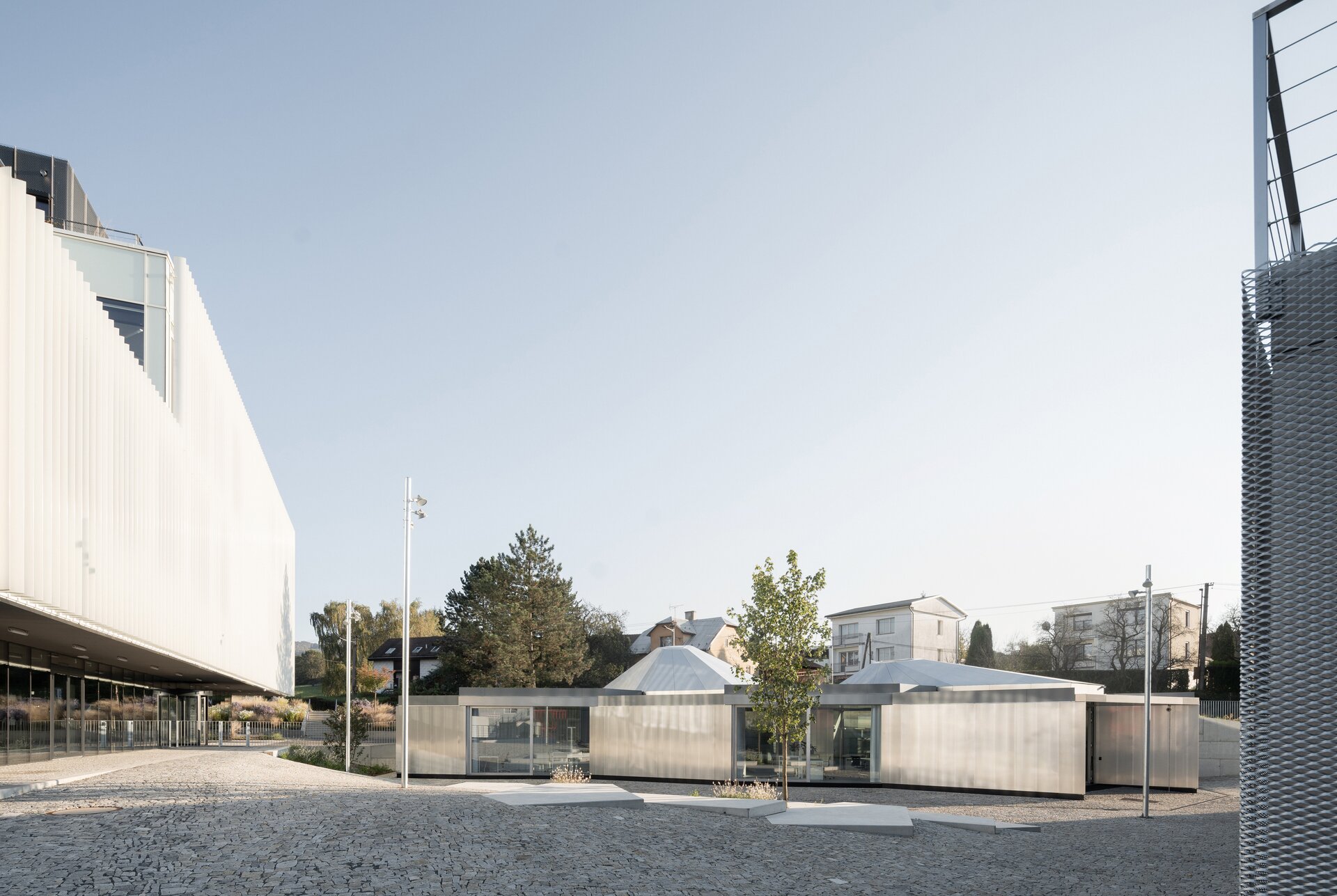
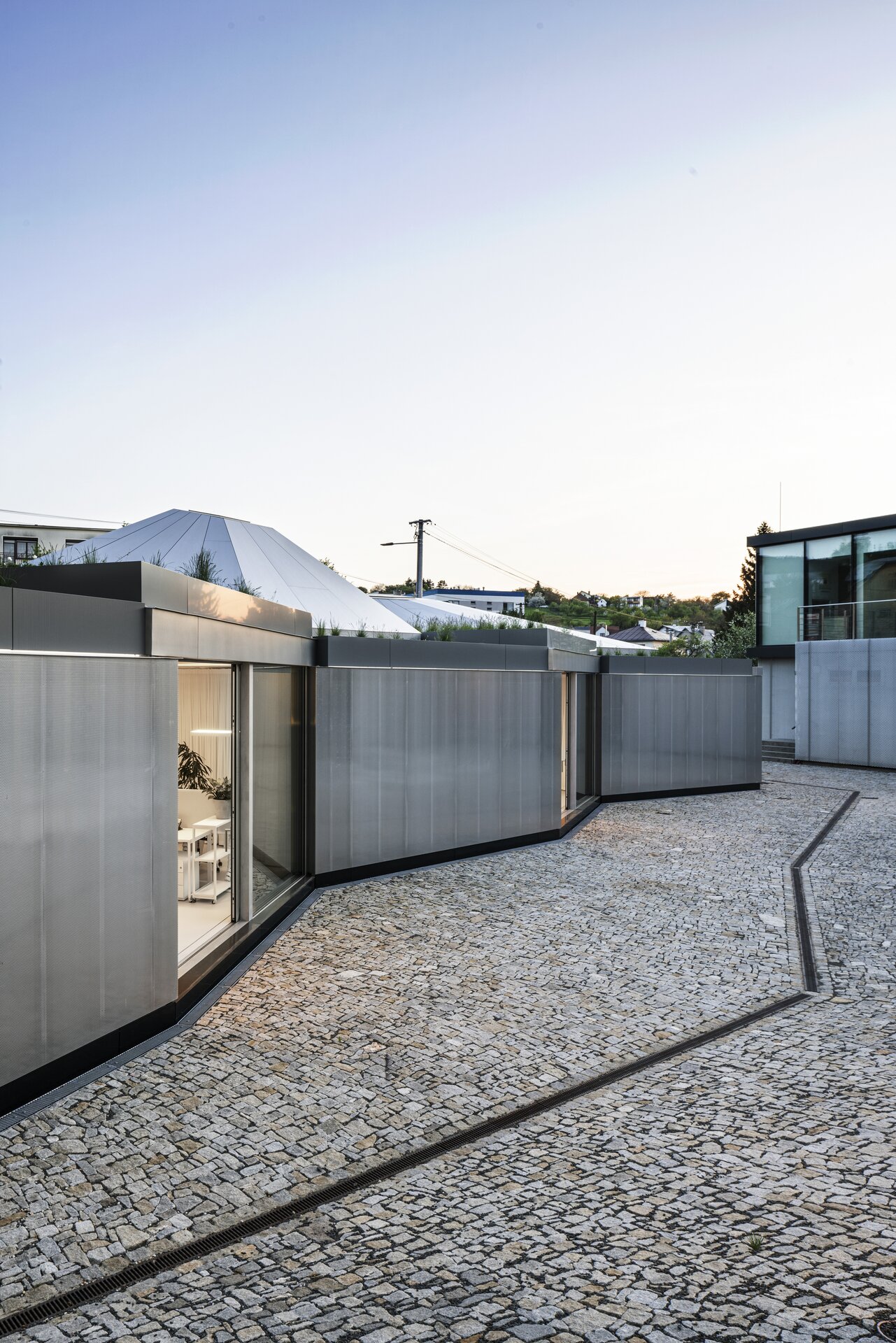
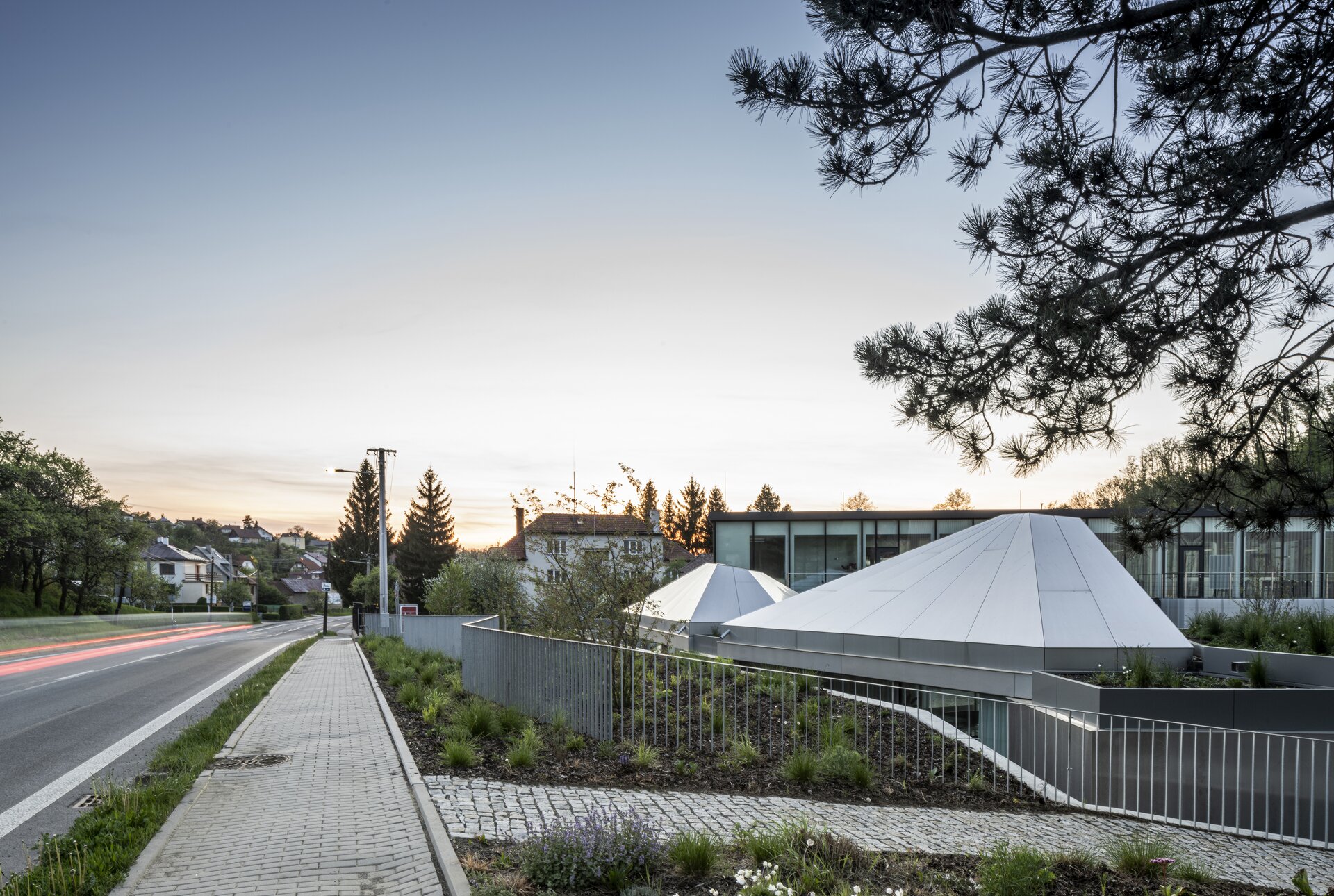
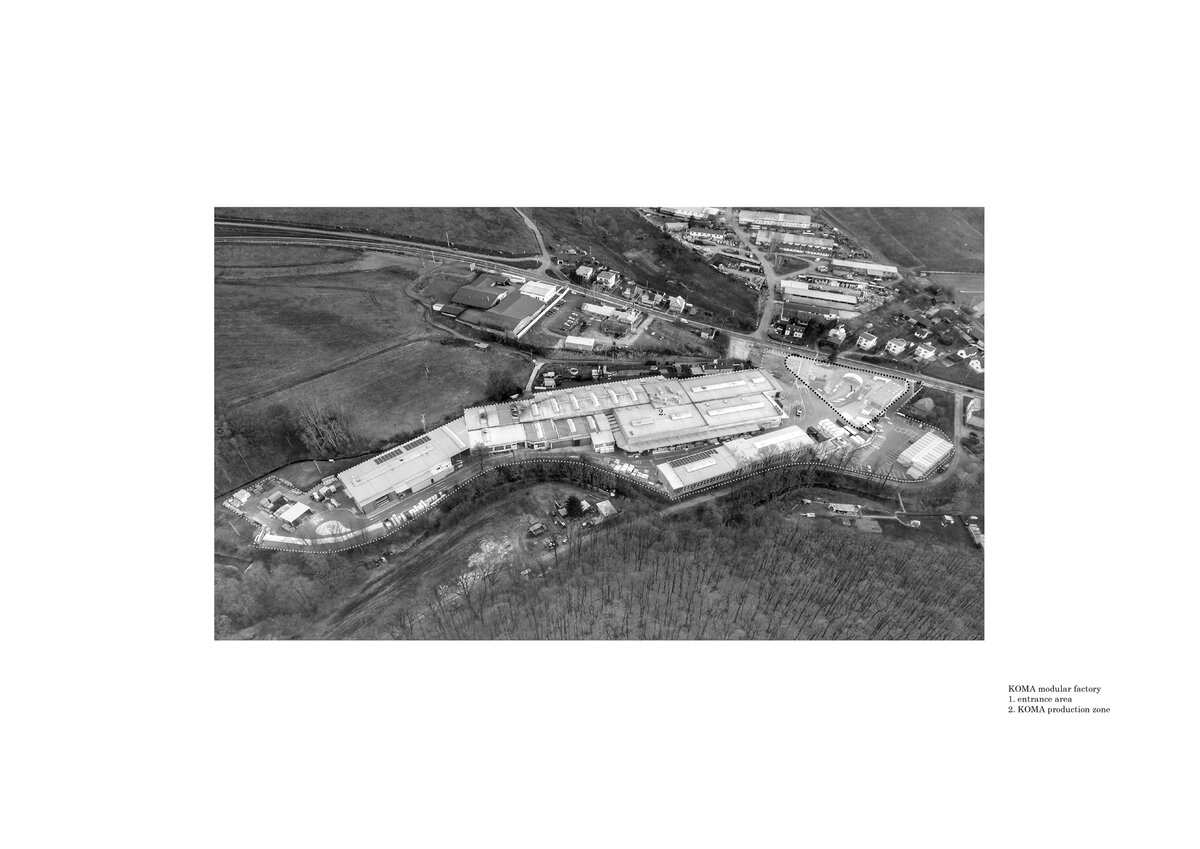
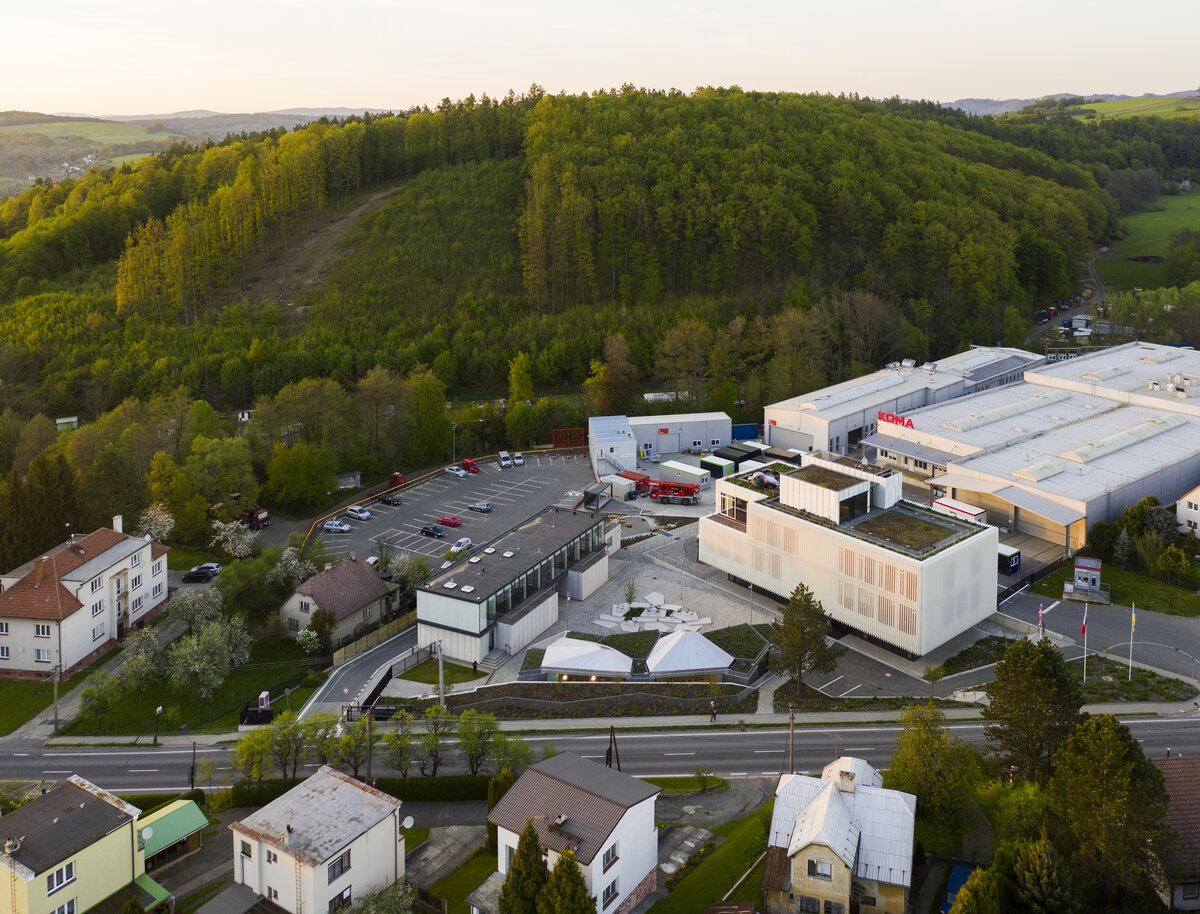
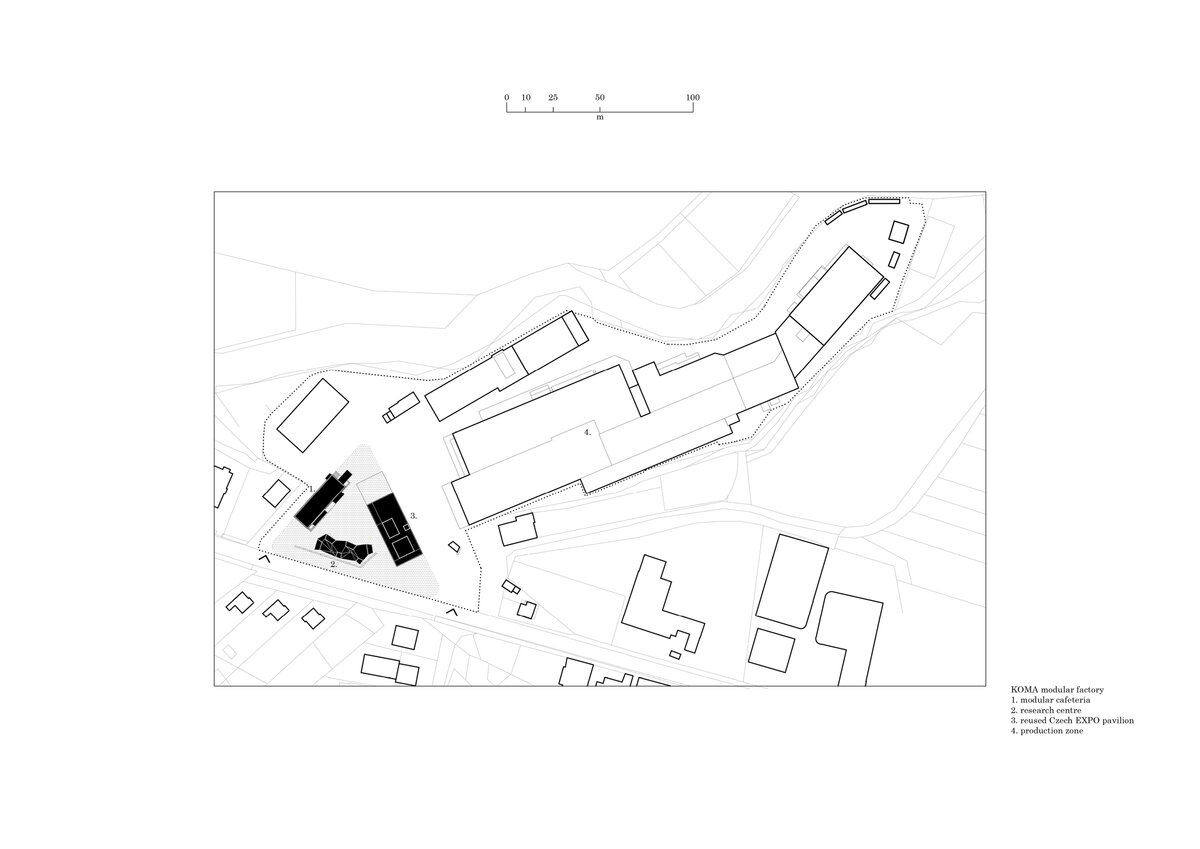
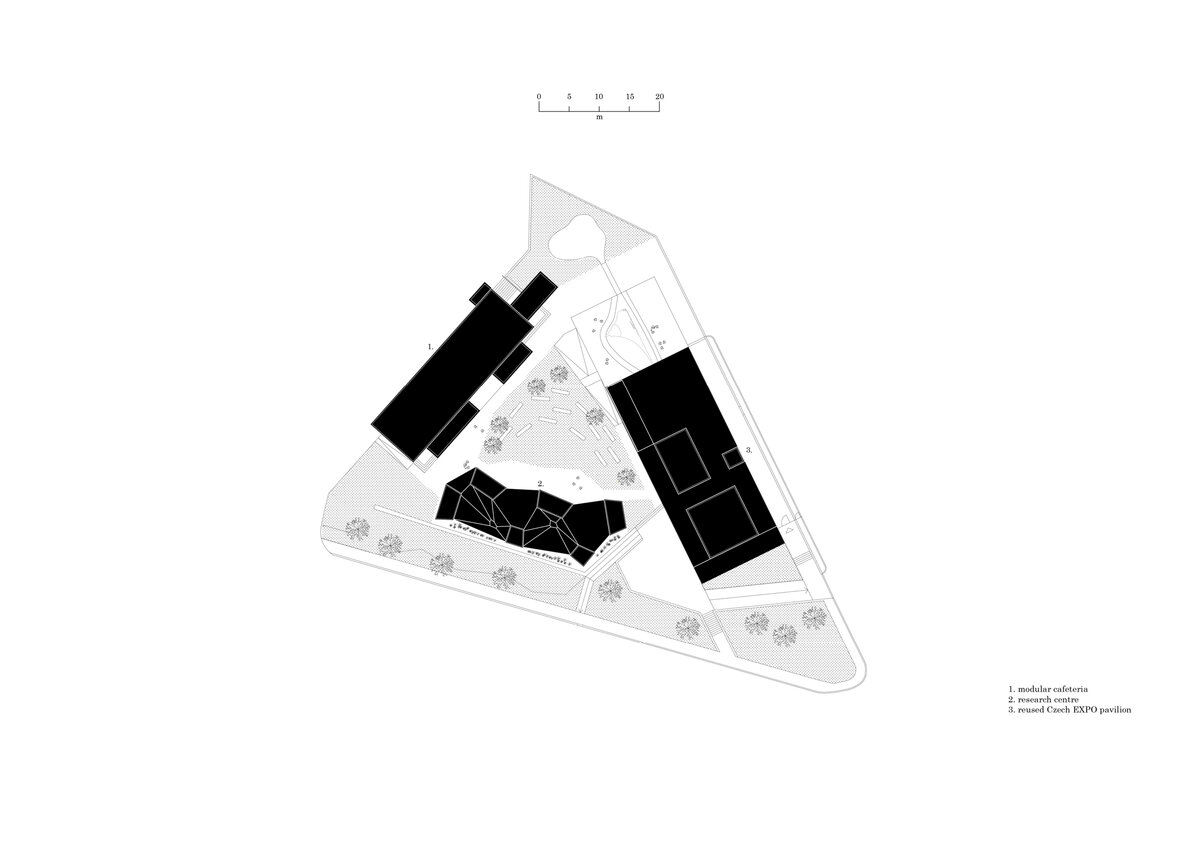
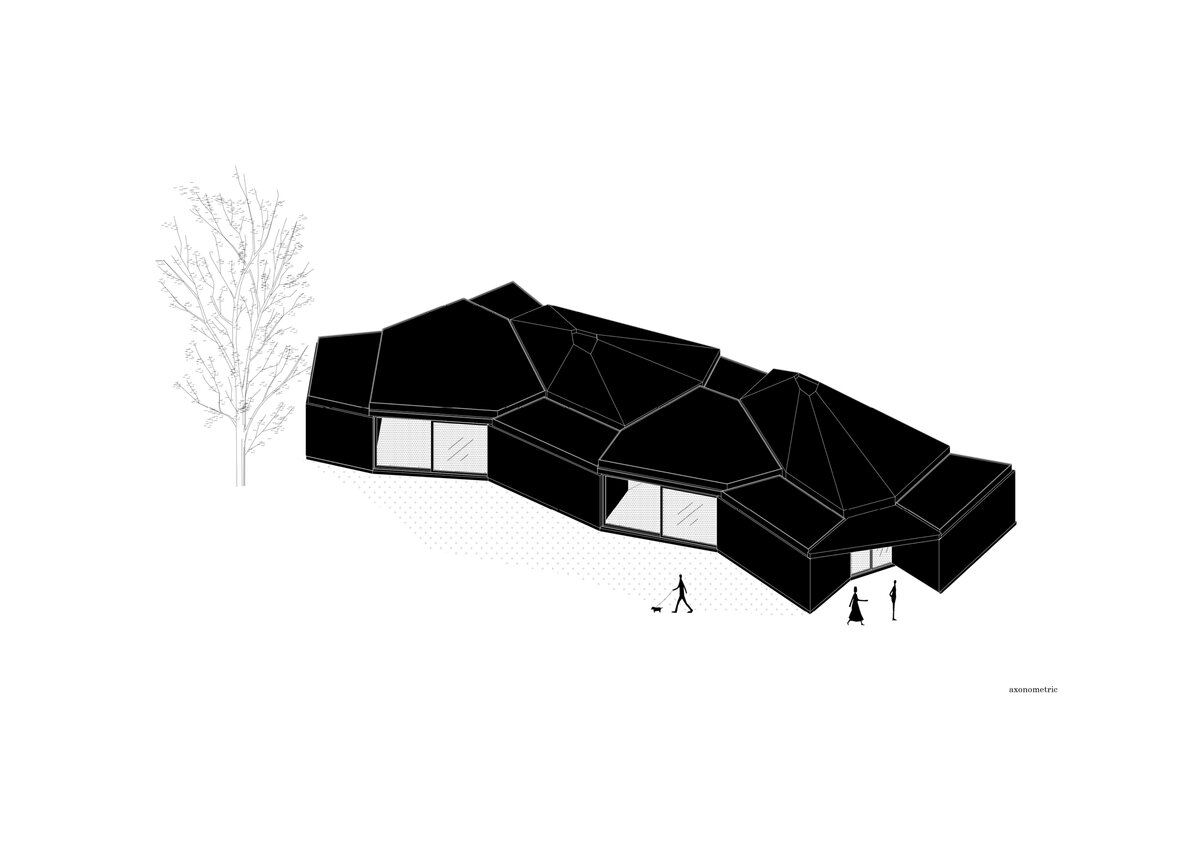
The work on the research center itself was preceded by designing a masterplan for an entrance and a public area for the factory. It aimed to create a space open to the public which will integrate the originally closed factory into its surrounding urban environment. The Modular research center is therefore the third, last phase of this project, which, with its location at the edge of the plot, and horizontal mass closes the entrance area and at the same time allows the public to see the KOMA manufacturing area.
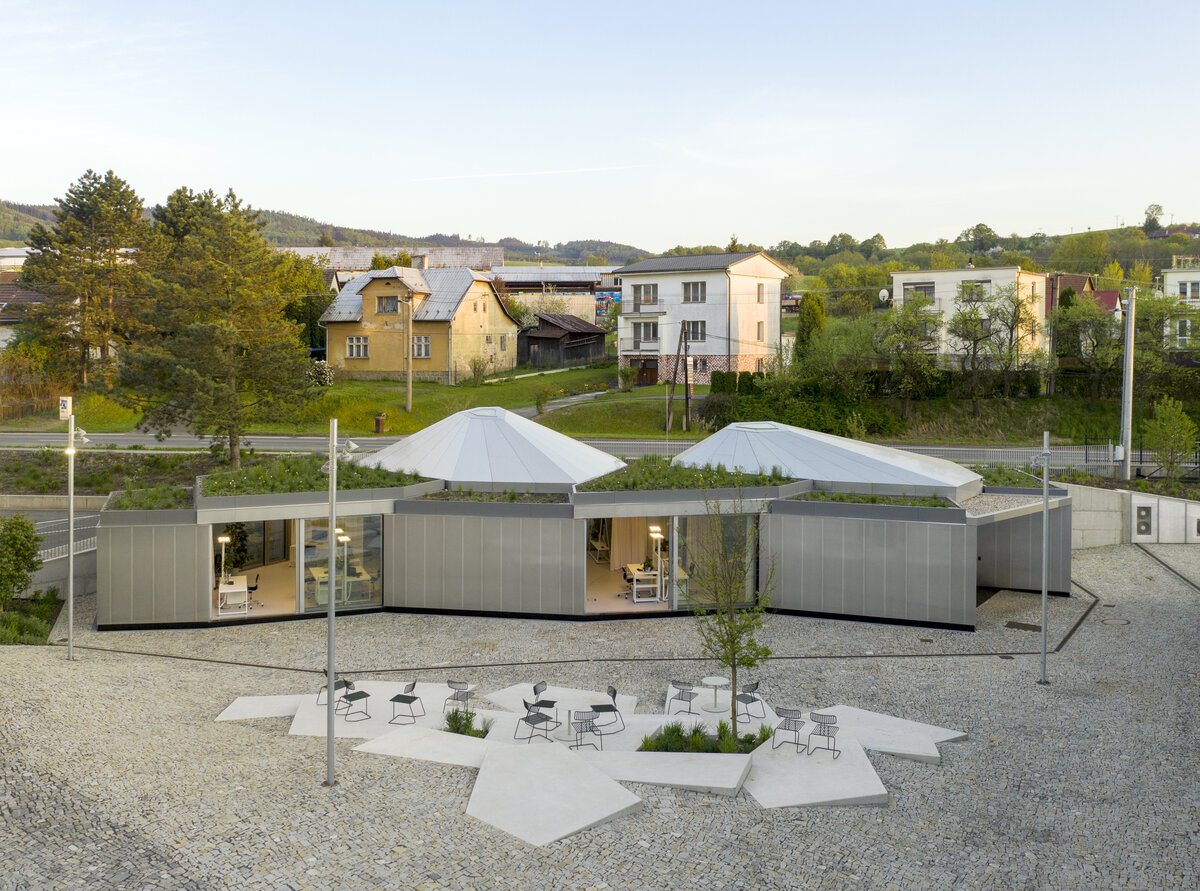
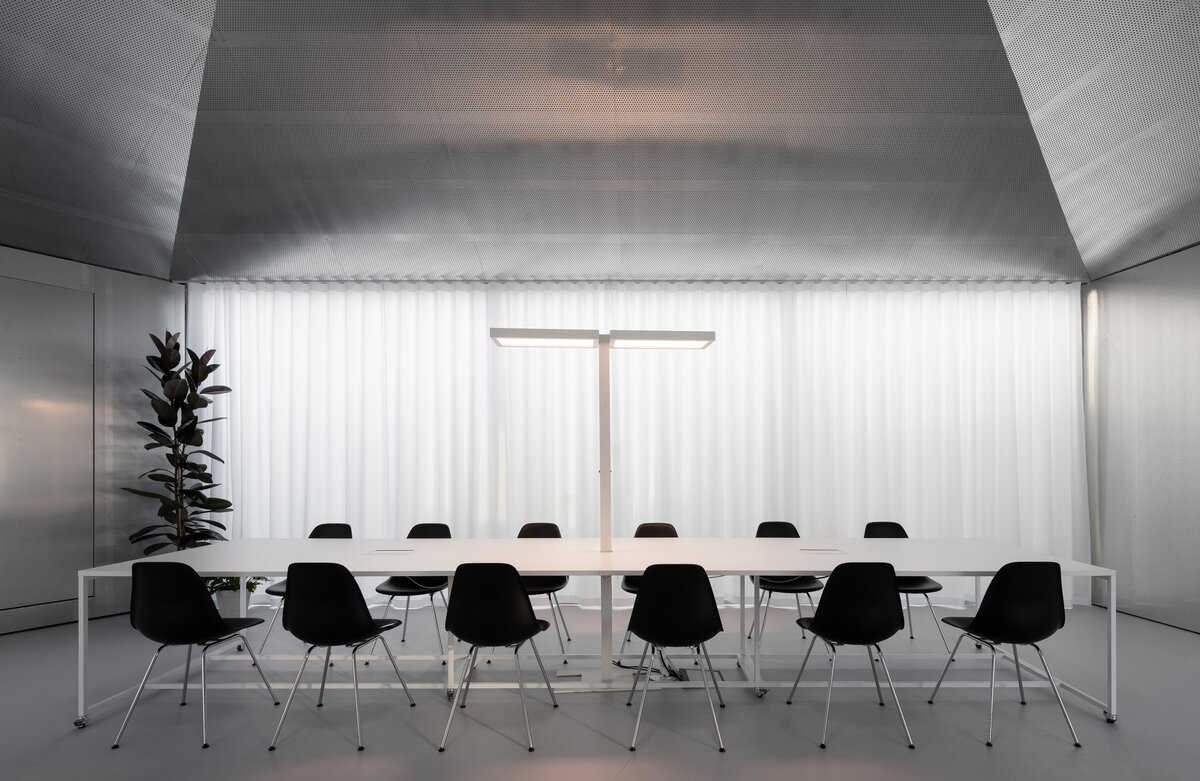
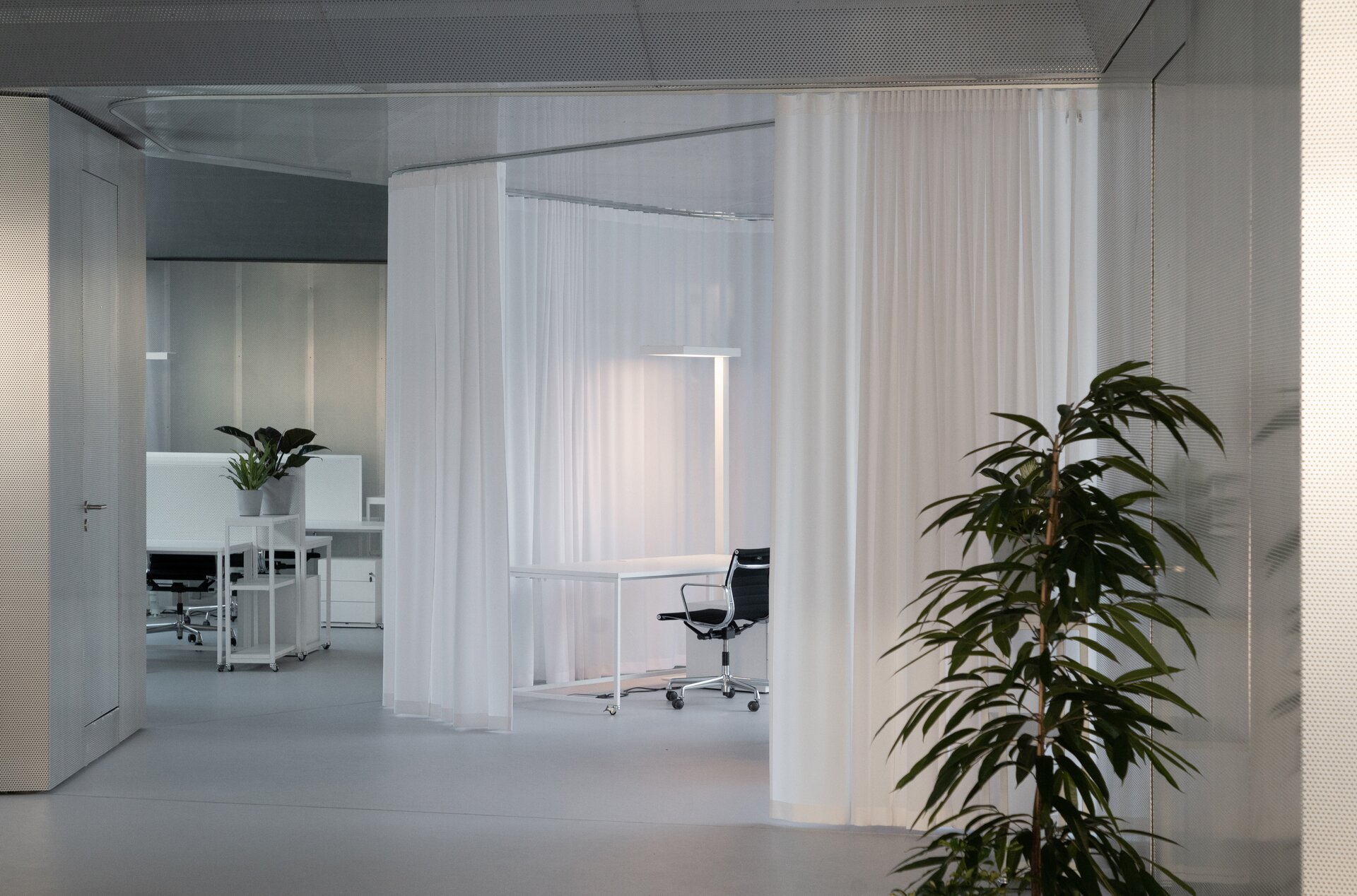
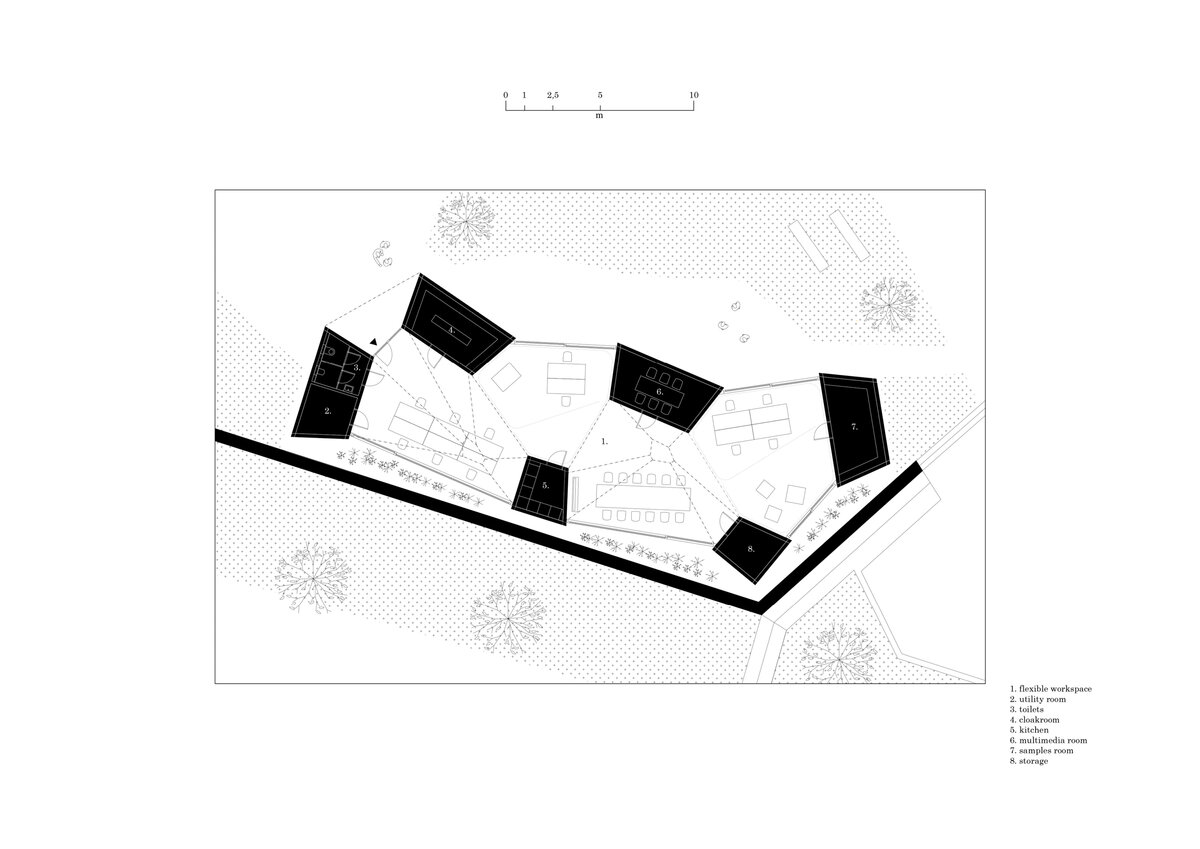
The building serves as a think-tank and a flexible space for developing new ideas in modular constructions. The open, sharedcentral space is spatially organized and segmented to avoid negative aspects of large open space offices. Drapes and othermobile elements allow the space to be to further sectioned.
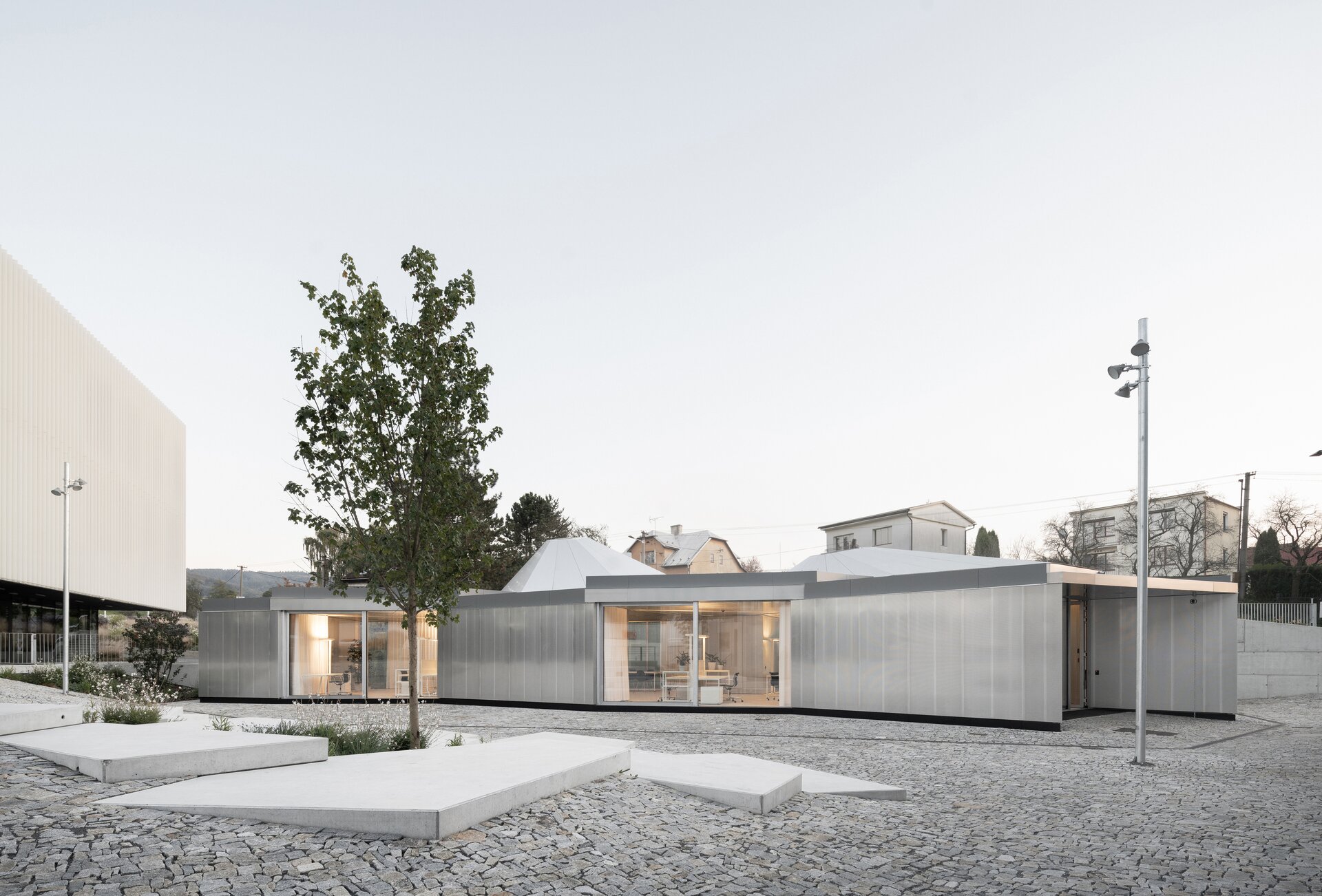
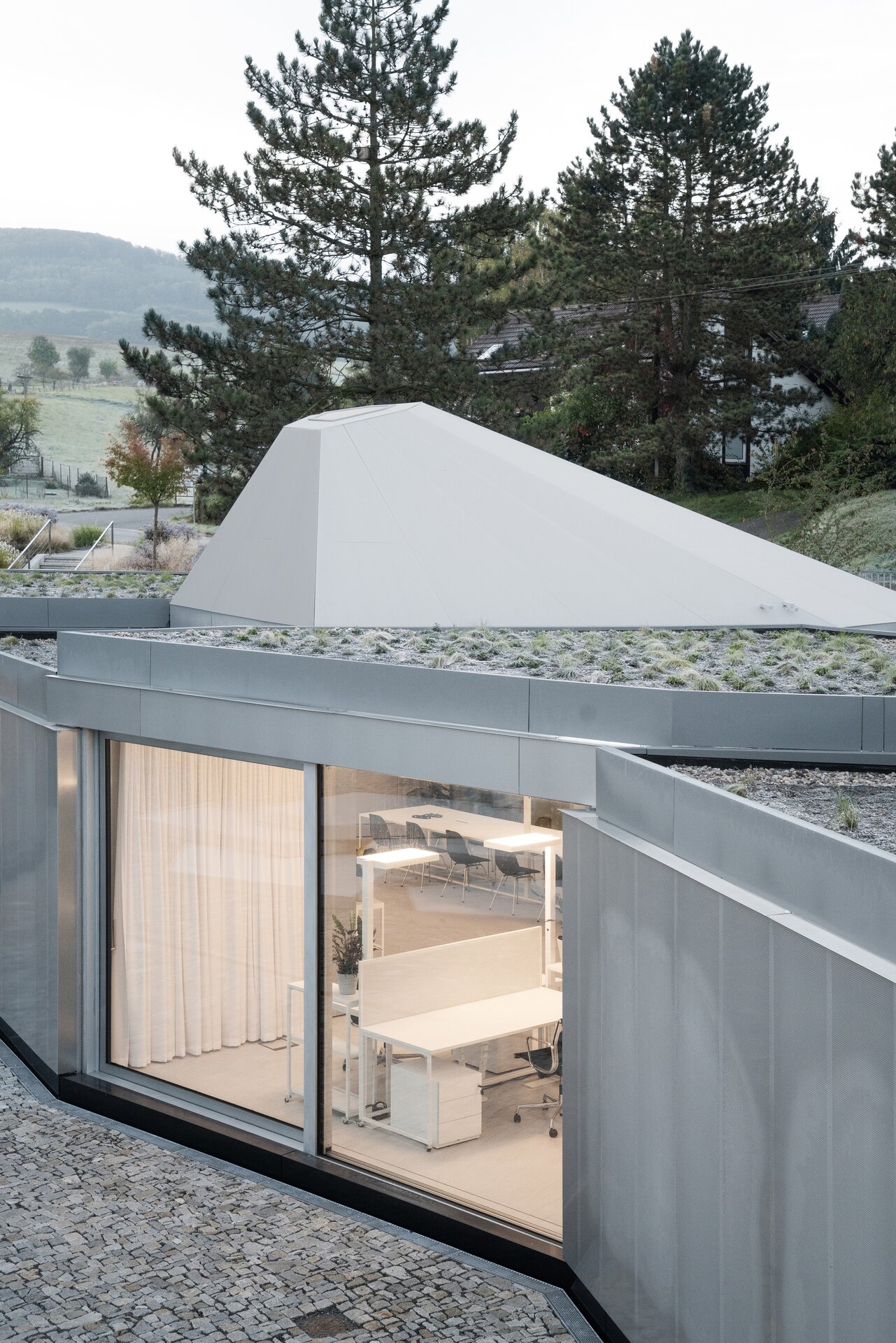
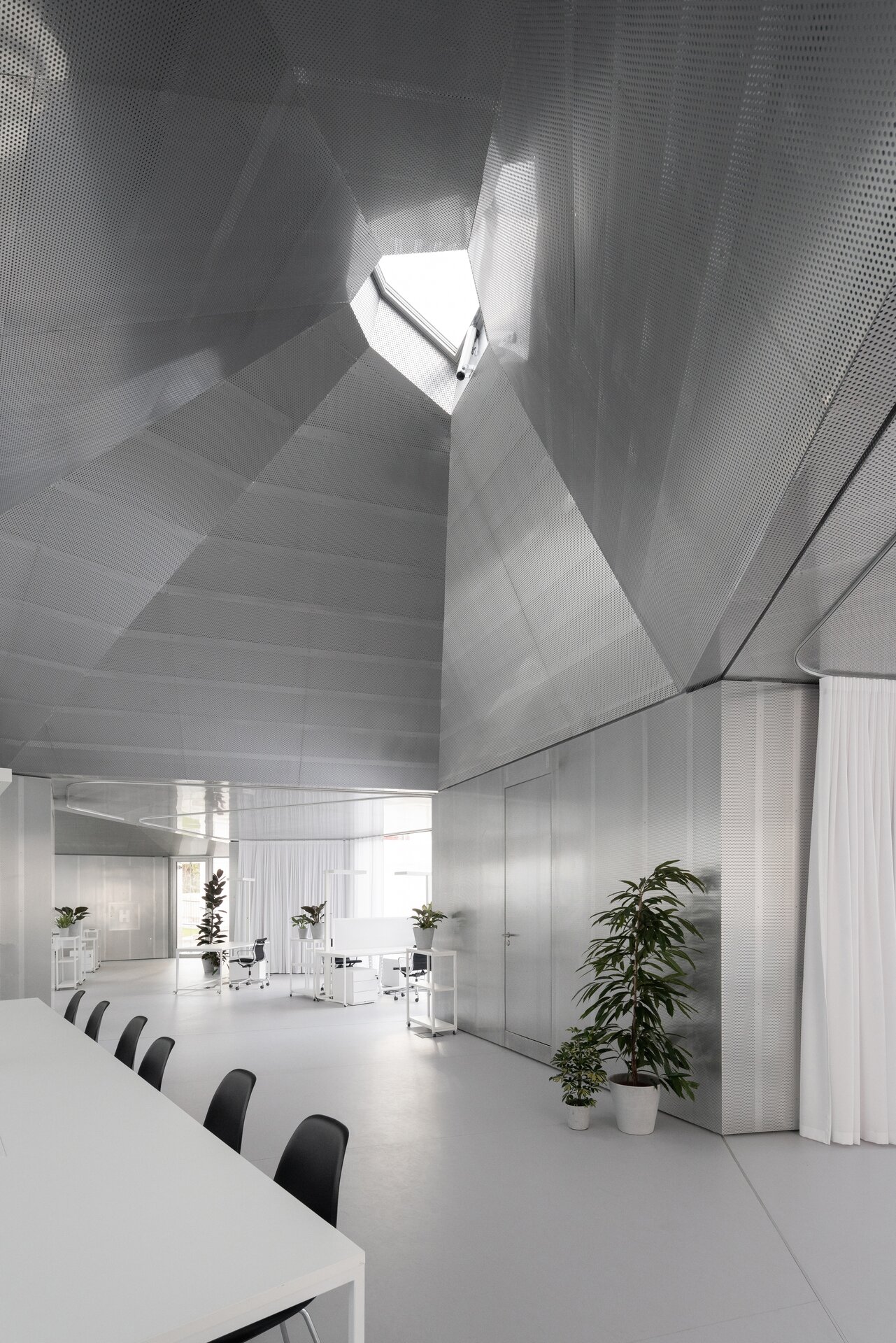
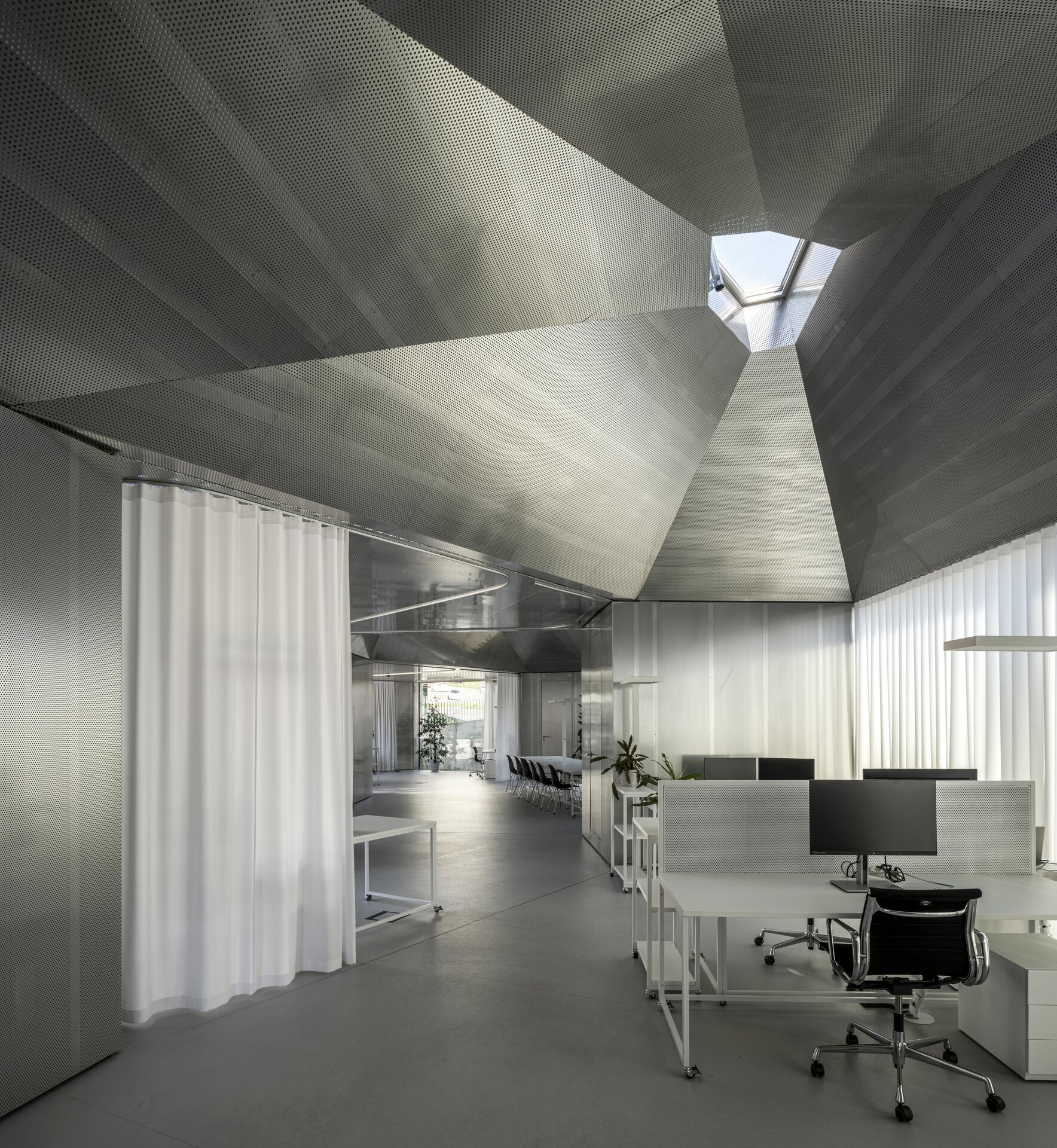
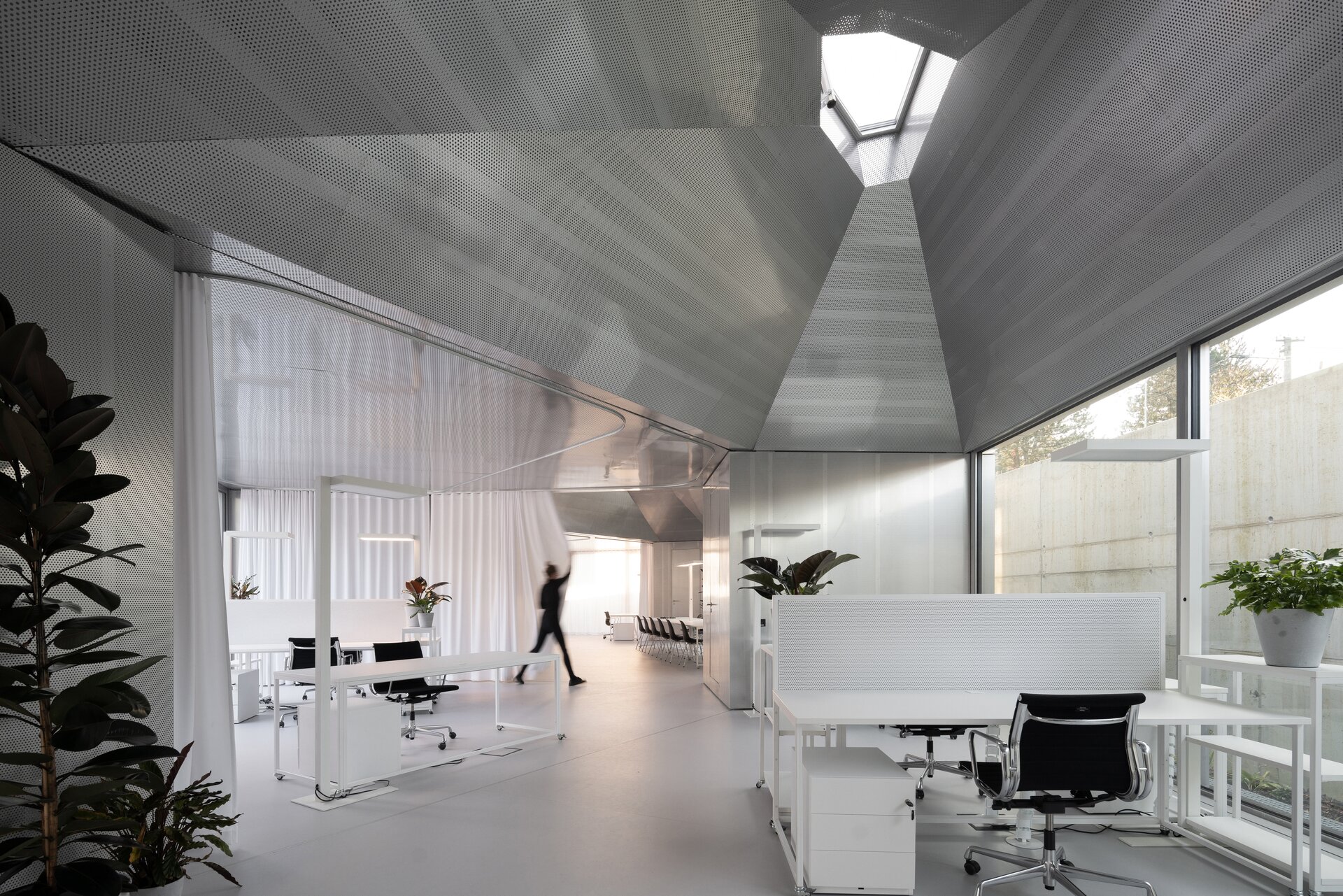
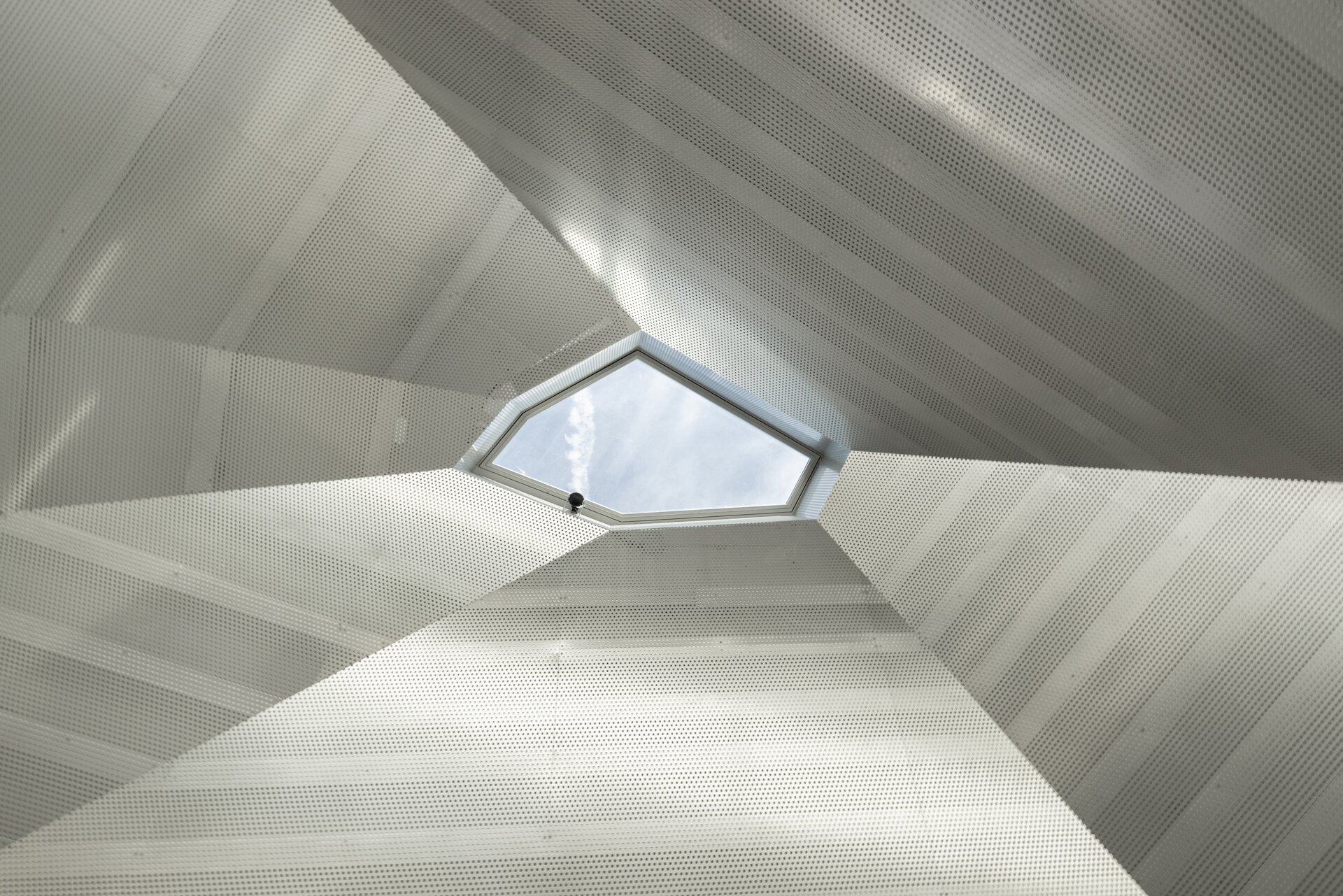
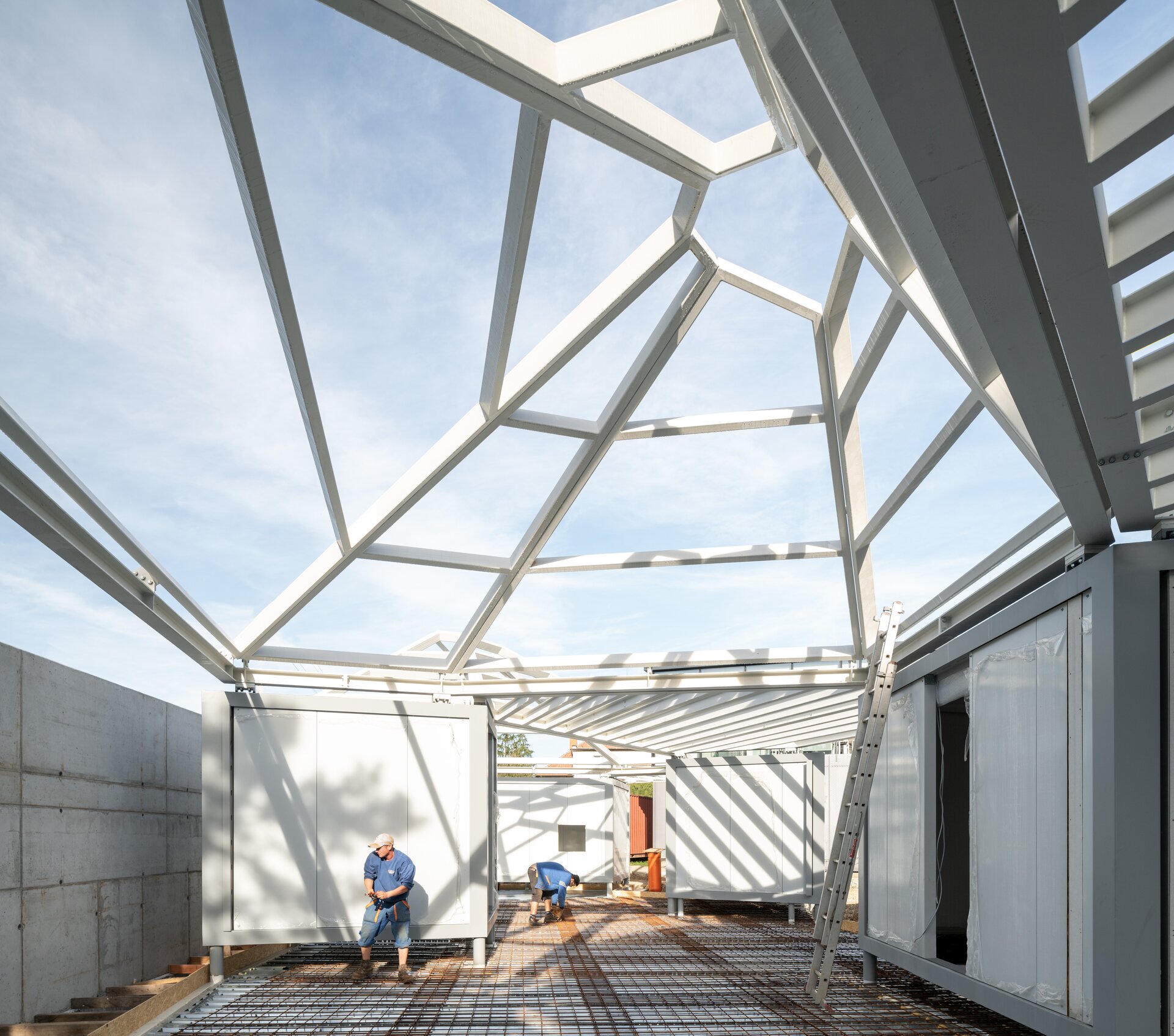
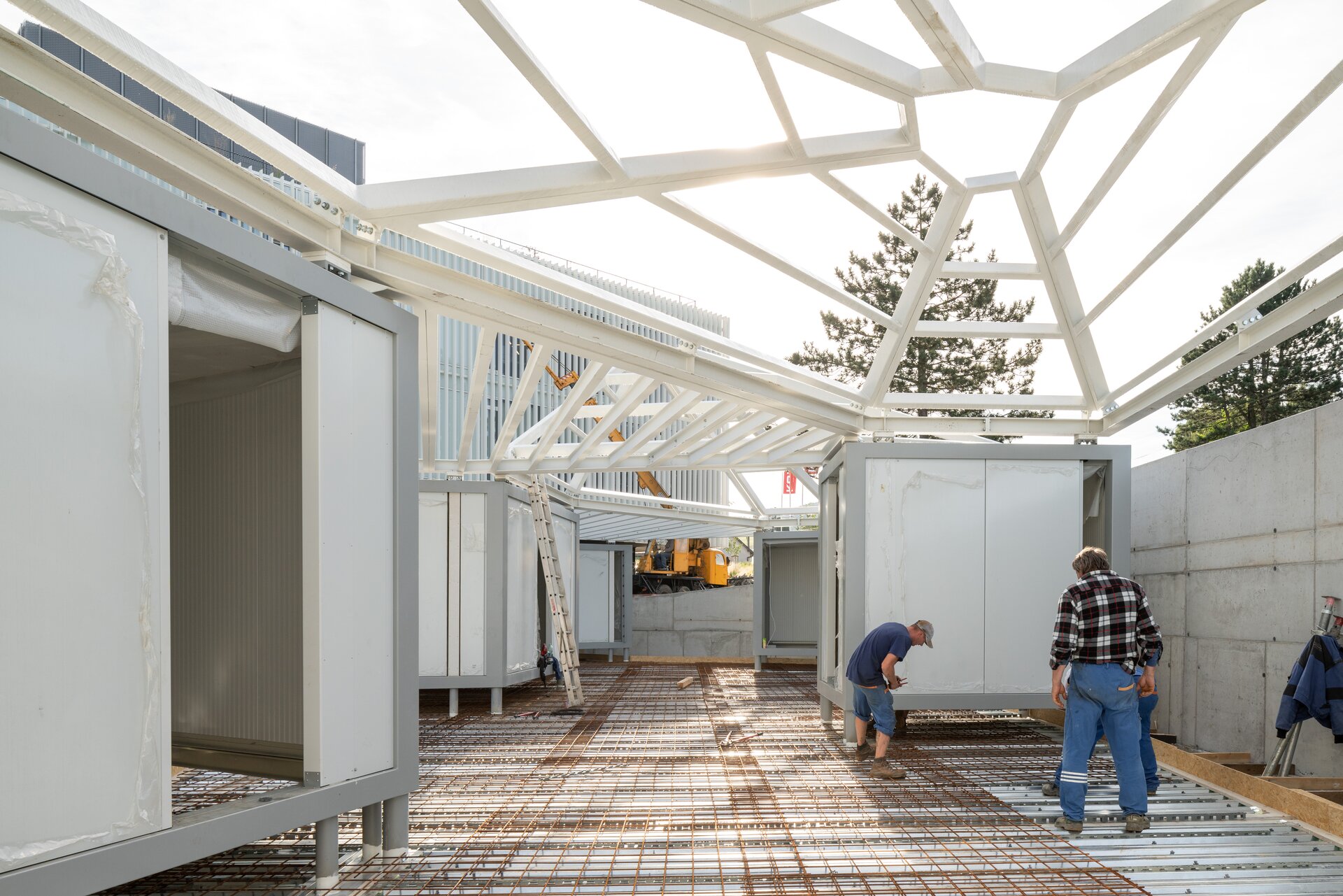
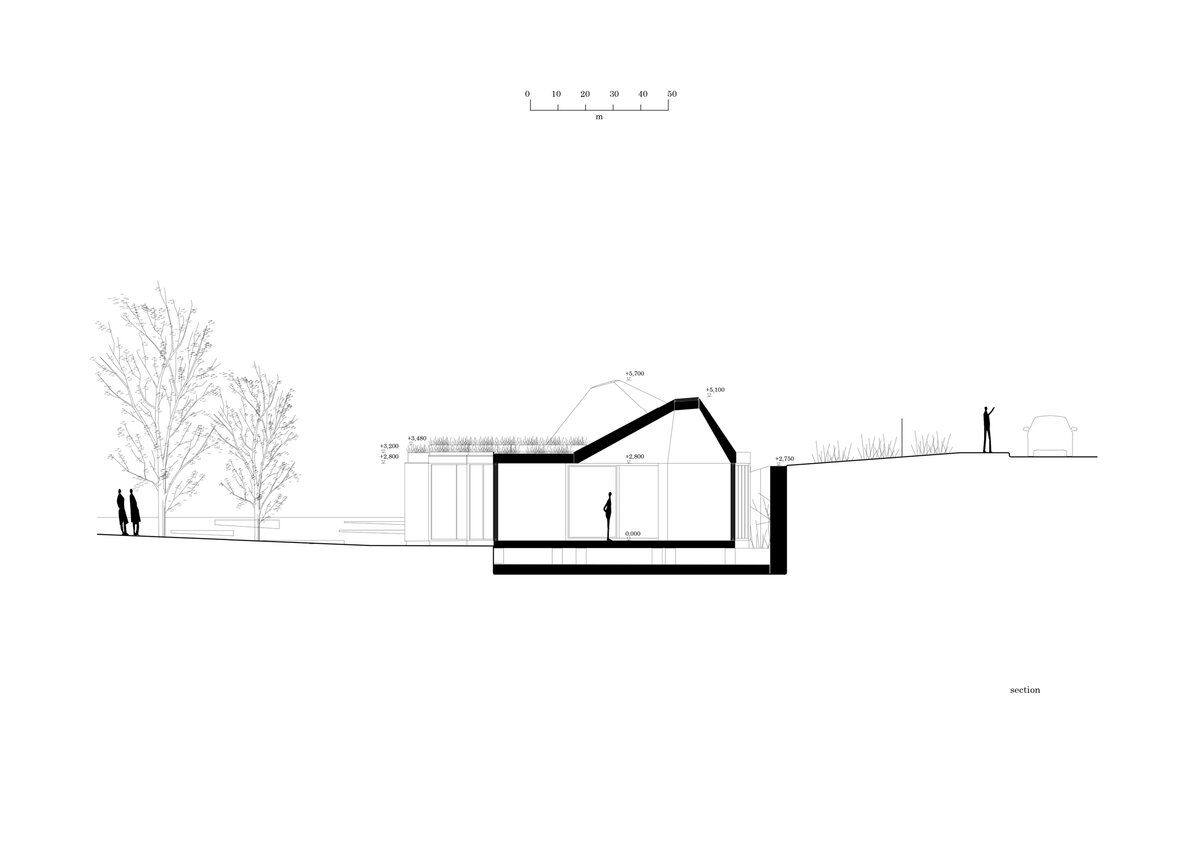
While modular structures are usually created by placing right-angled modules side by side, we realize new spatial possibilities through the creation of a new modular system. Spatial modules containing facilities are leveled onto the planar flooring modules, which are anchored to the foundation. Both modules then function as columns, allowing them to hold the roof modules and form a continuous main space. Making sure to keep the workplace breathable, all-glass surfaces between the modules draw in an abundance of light from all sides of the structure.
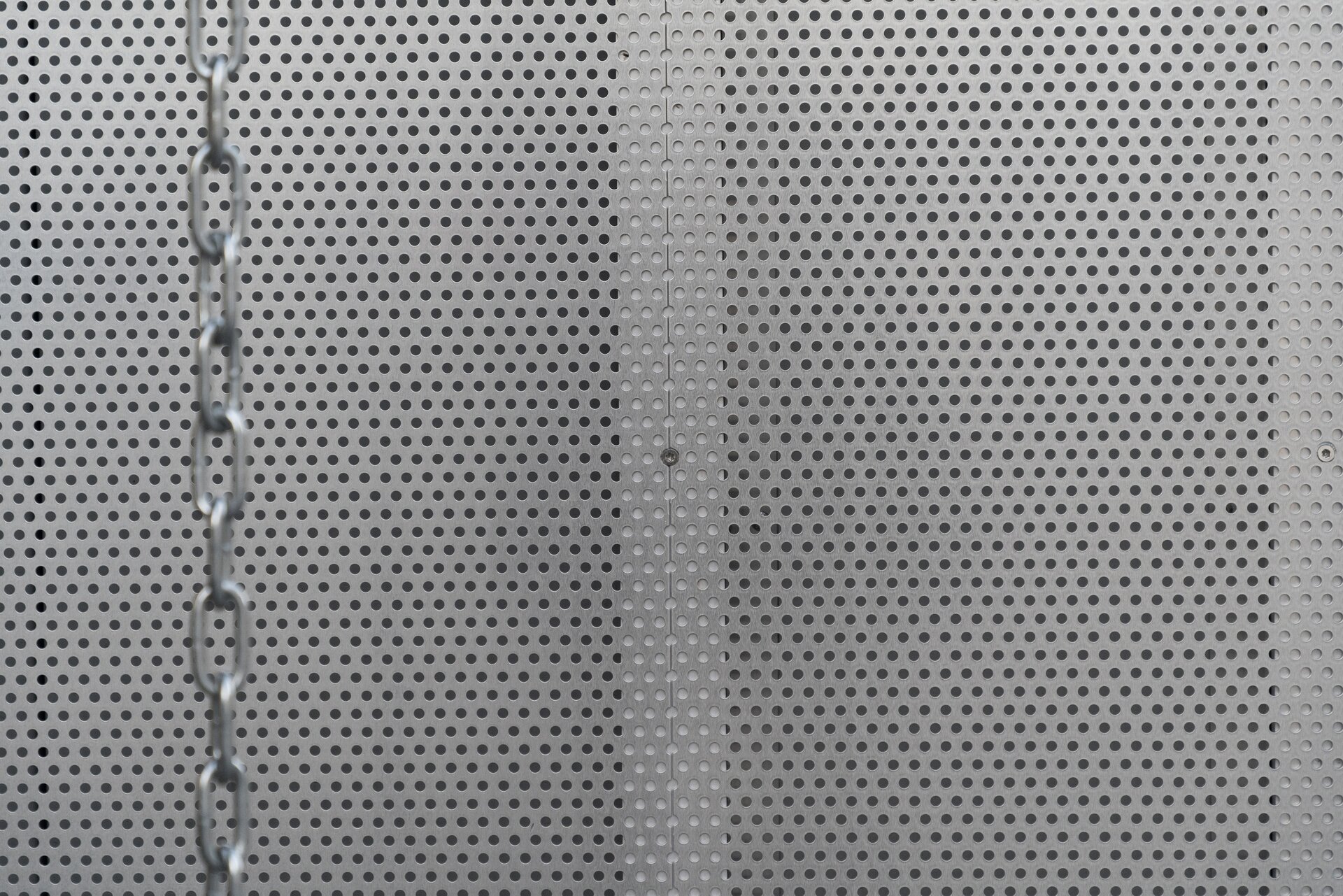
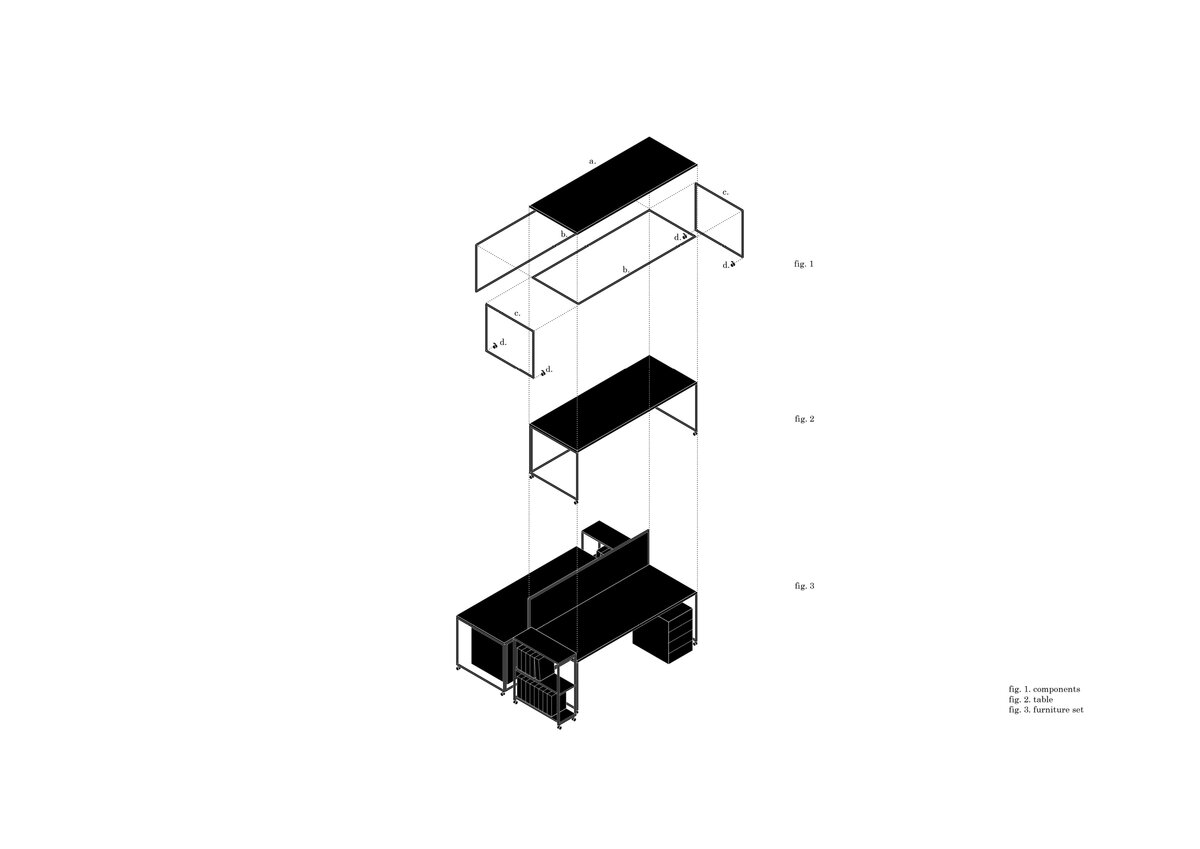
The furniture design concept follows the modular system by connecting elementary squares, rectangles and desks into a bespoke equipement. Thanks to this concept, the furniture can be supplemented, changed and adapted to new needs over time. The materials of the building are used to the maximum extent in their natural, true form and, thanks to the perforated surface and the visible details, they make it possible to see and understand the principles of modular buildings.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
B
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|