| Author |
Ondřej Píhrt a Pavel Směták / SOA architekti |
| Studio |
|
| Location |
Šmolíkova 26, Dědina, Praha 6 Česká republika |
| Investor |
Jan Dražan |
| Supplier |
Klimava s.r.o. |
| Date of completion / approval of the project |
January 2021 |
| Fotograf |
|
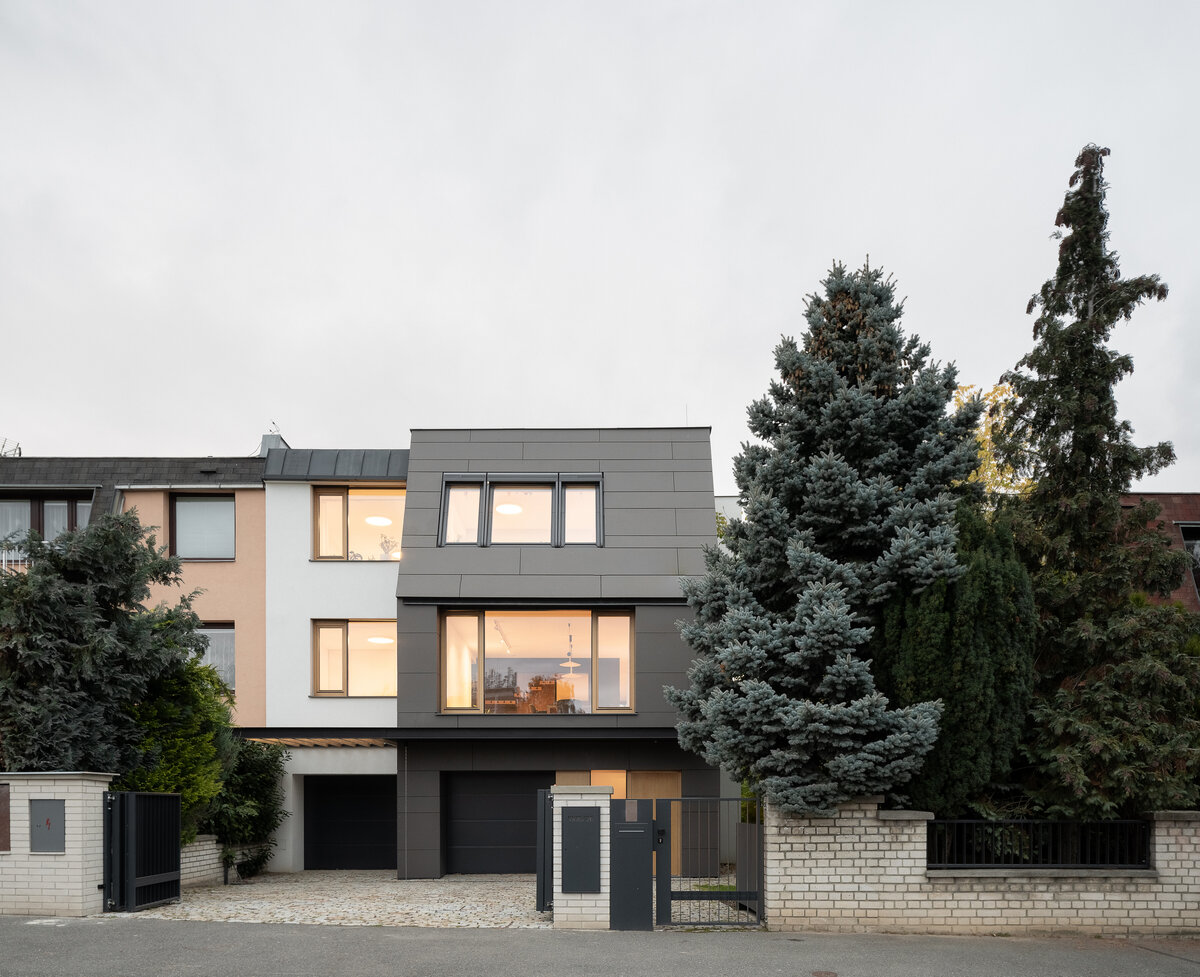
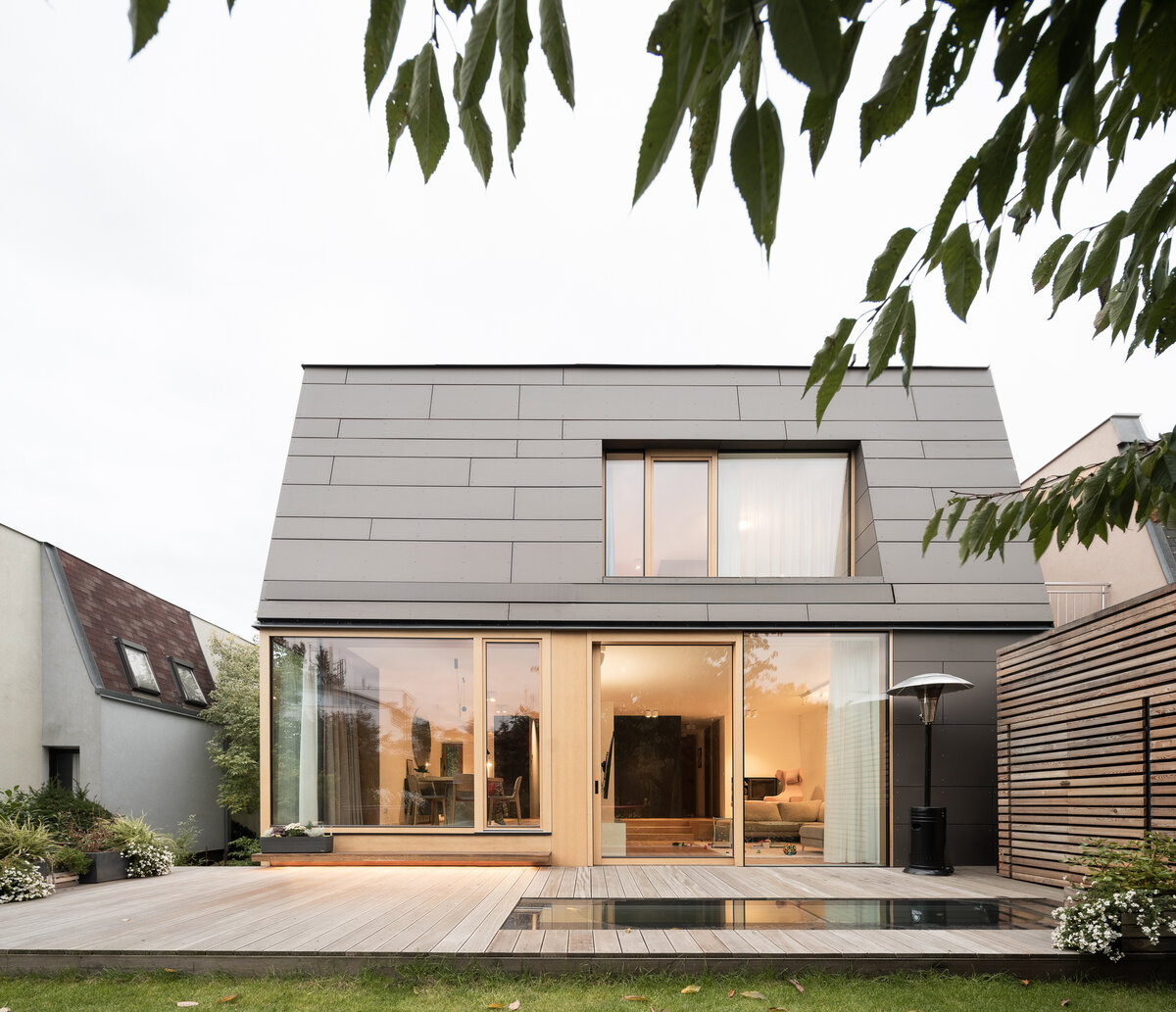
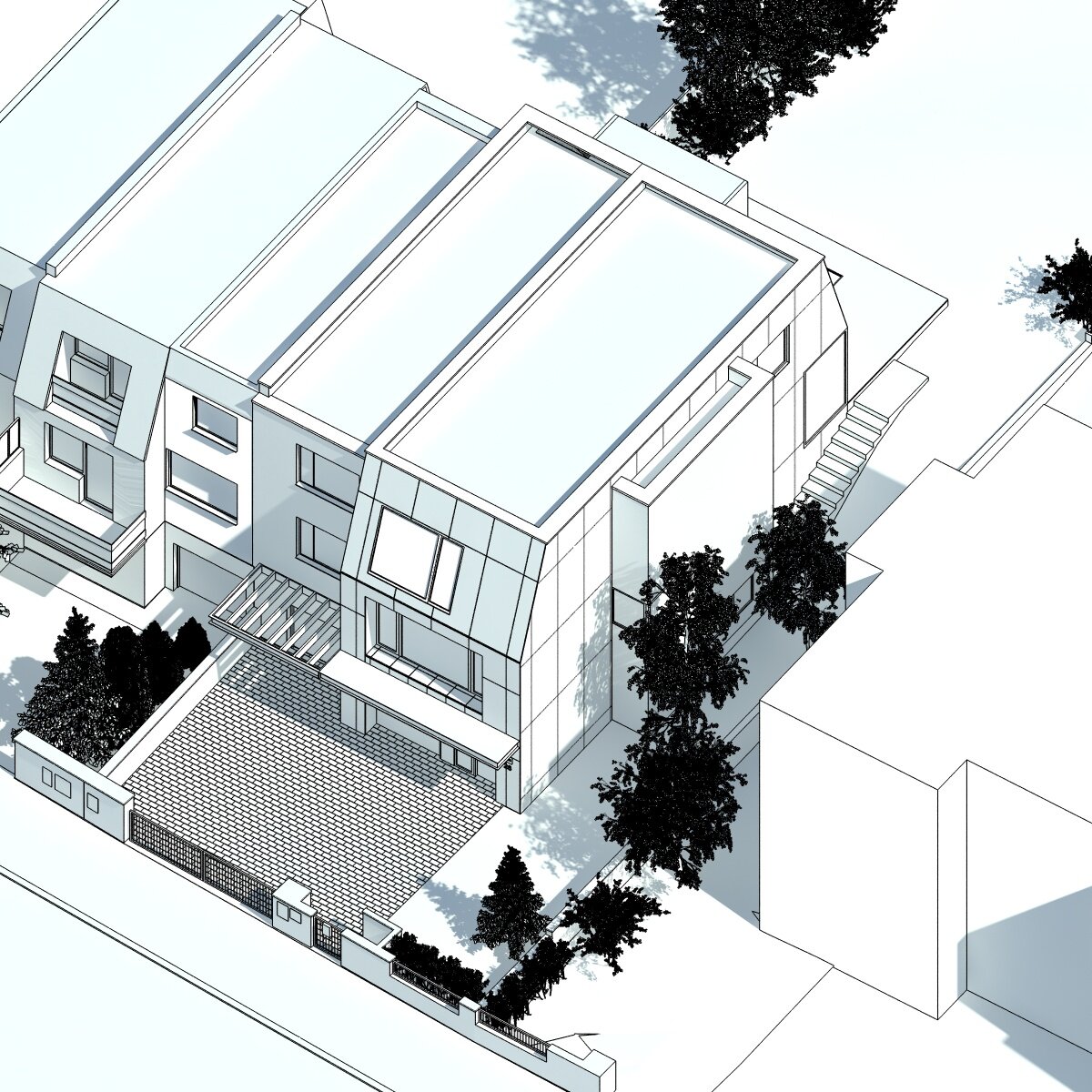
The reconstruction of a terrace house for the needs and comfortable urban living with the current standards for a family. The same terrace house design repeats in a few streets, using pseudo-mansard roofs, partial prefabrication, and materials from the early 1990s.
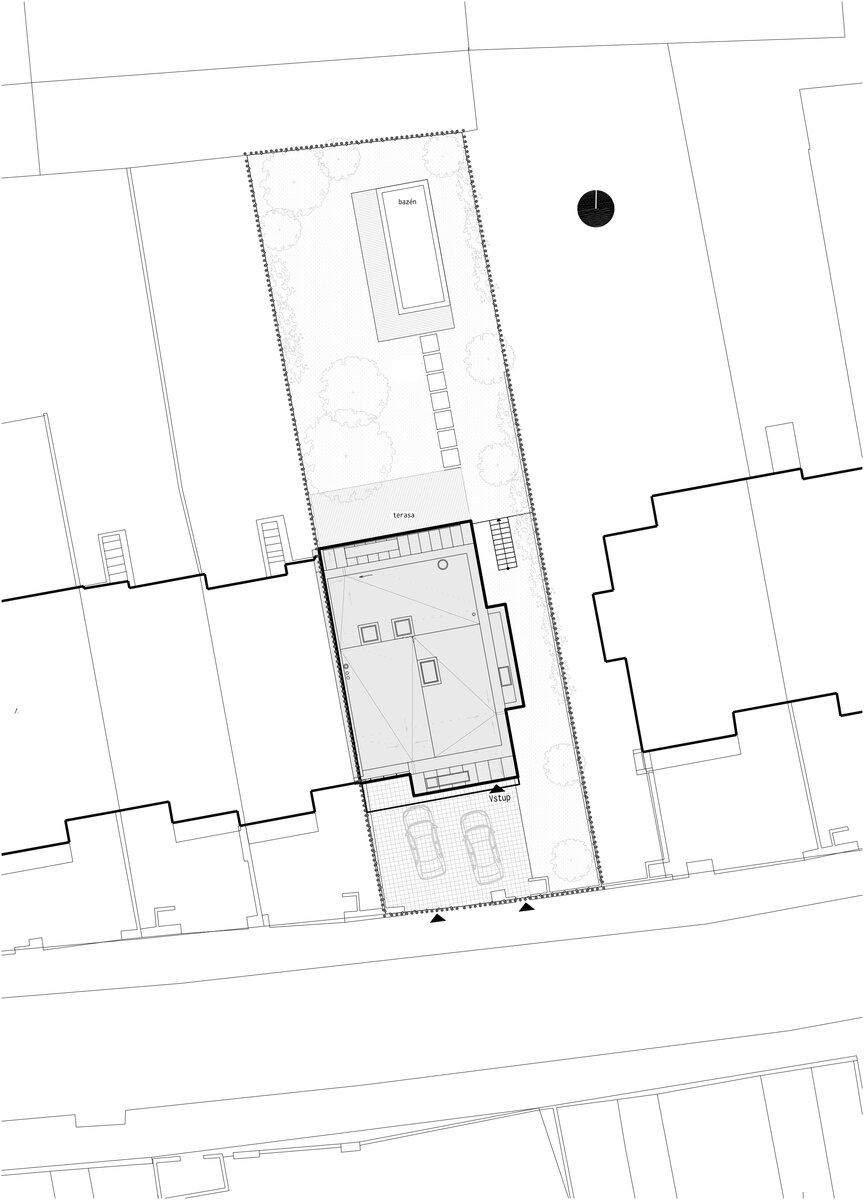
The terrain difference was used to the advantage in the original design. The street-level floor with small windows disappeared into the terrain. The entrance part of the house reminded a poorly lit basement. Fortunately, the end position of the terraced housing has a small garden with mature trees. The garden was difficult to access from the house due to the height difference. In addition, the main rooms were oriented in the direction of the sun but facing the street. The internal layout corresponded to the division of the house into separate apartments on each floor with a common entrance. Low clear height in the interior (2500 mm) defined its atmosphere.
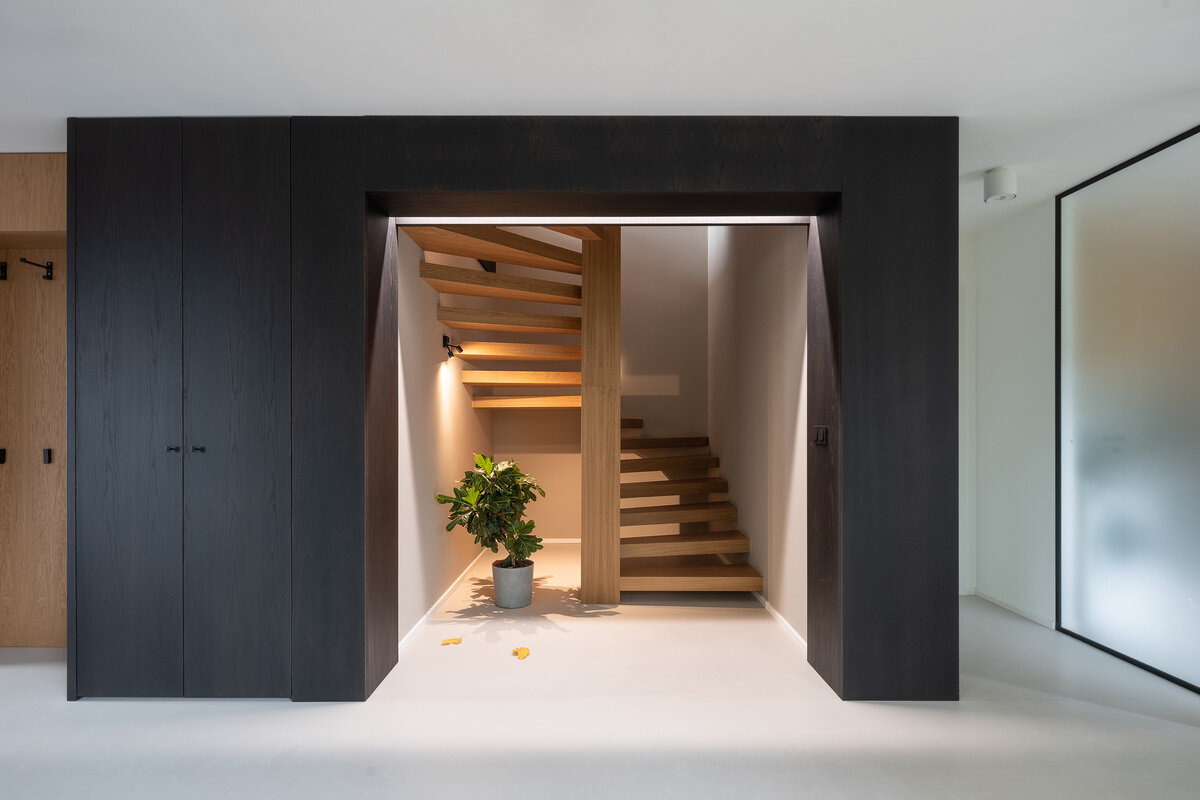
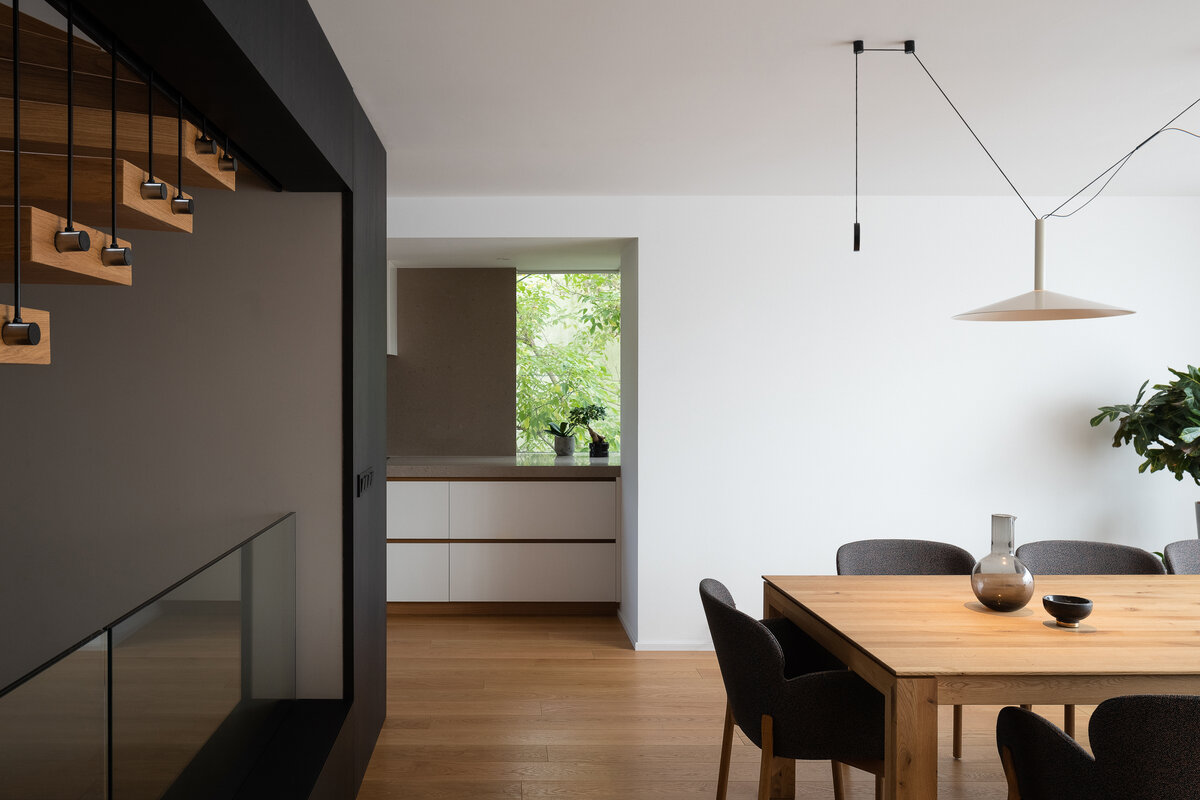
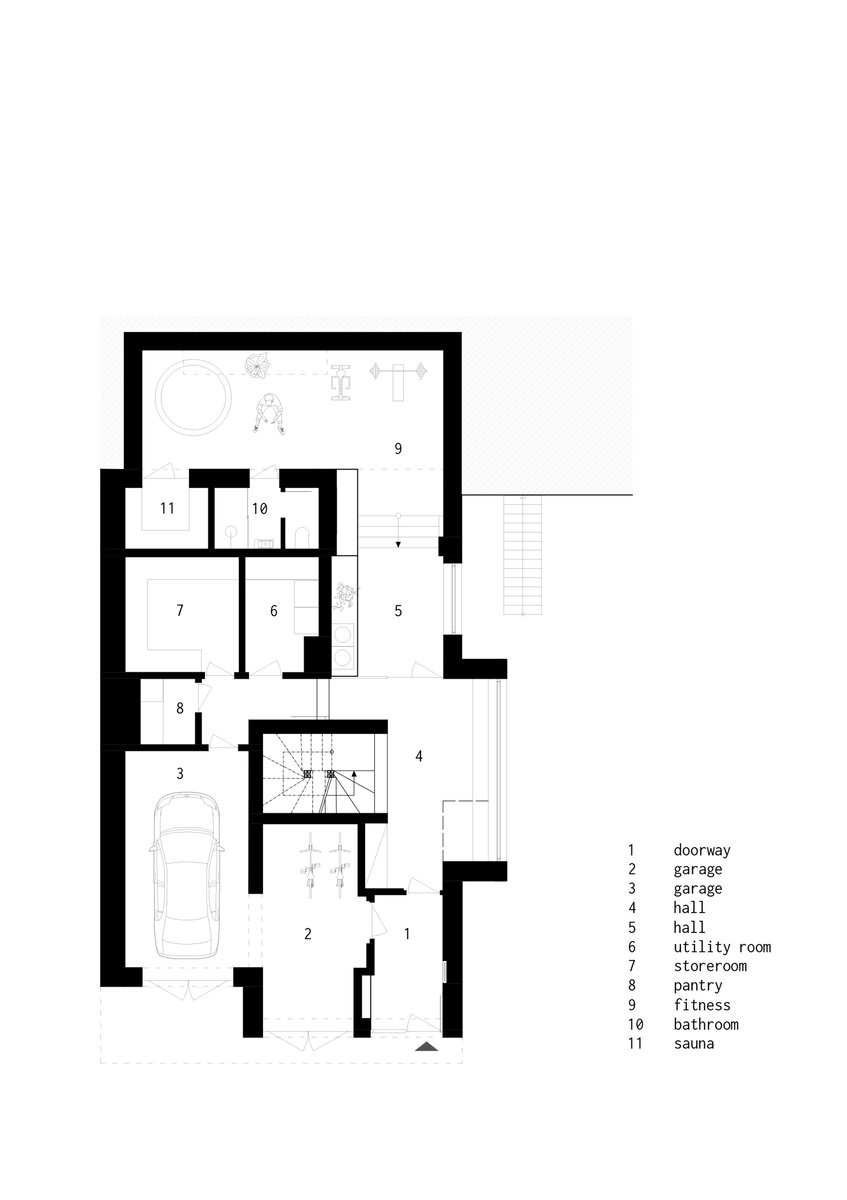
The adaptation, therefore, required the unification of the house into a whole for the needs of one family. The staircase became the center of the layout.
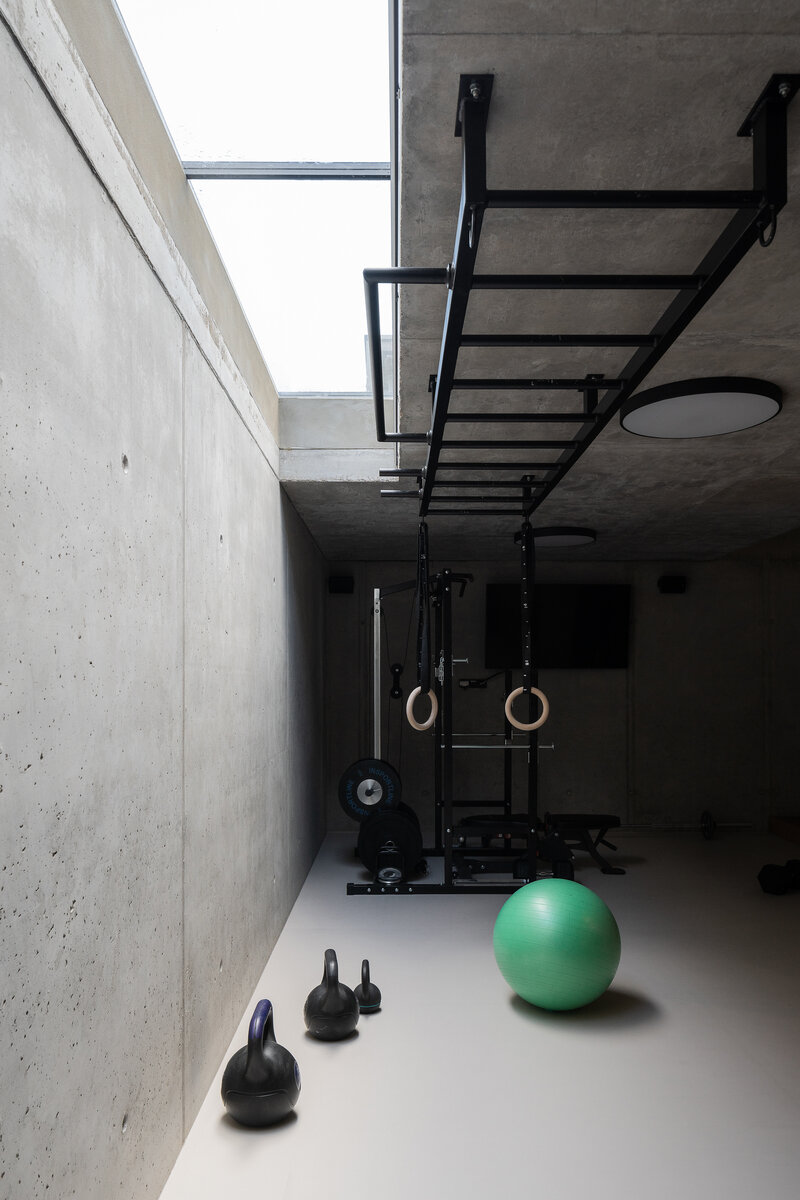
The service function of the ground floor remained unchanged. It transforms into a proper ground floor with maximum daylight. The newly added window into the entrance hall allows a view even from the staircase. The extension of the house runs deeper under the terrain and at the level of the garden, it is covered by a terrace. It hosts a home fitness. The use of different construction is showcased in exposed concrete.
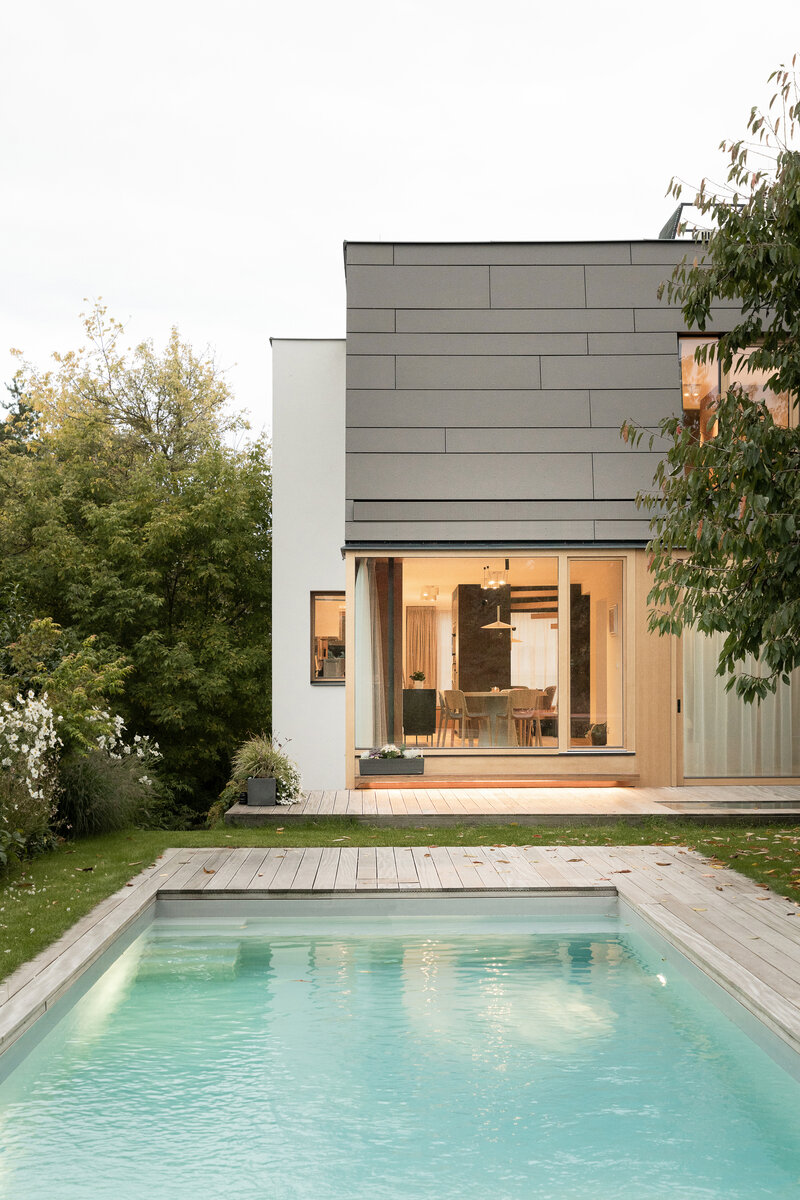
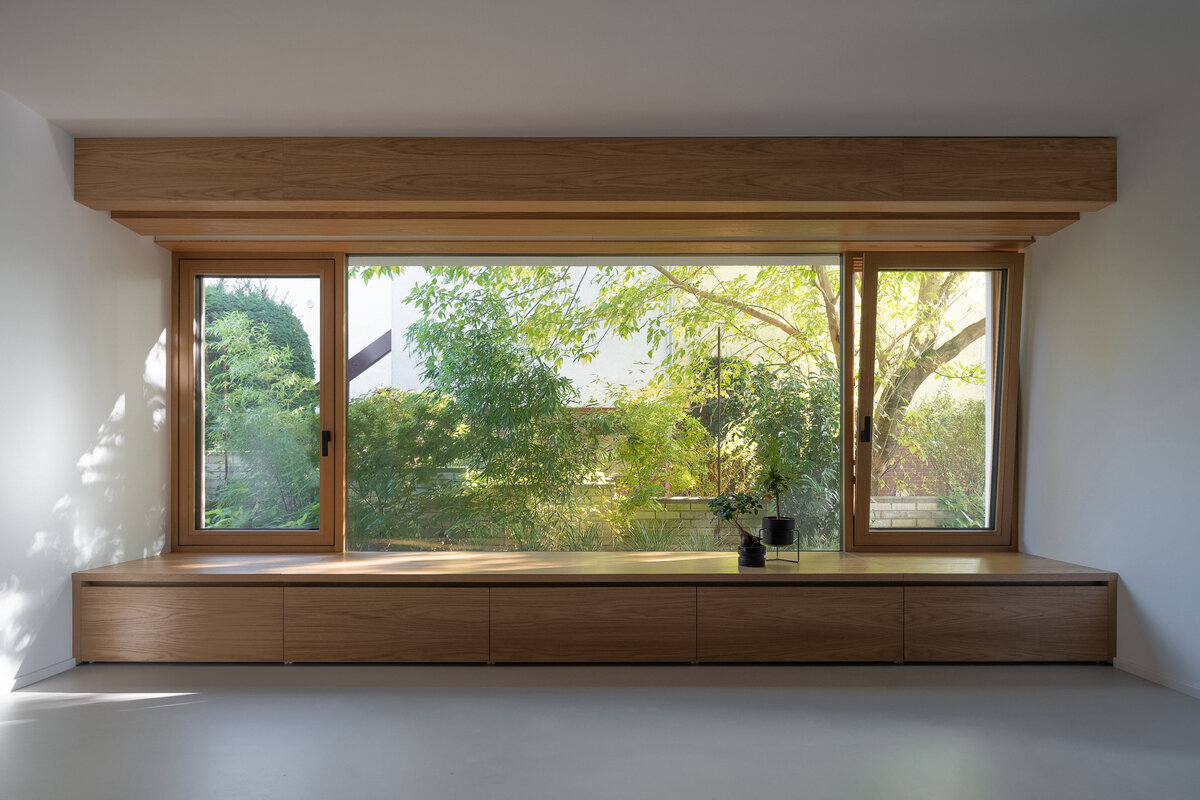
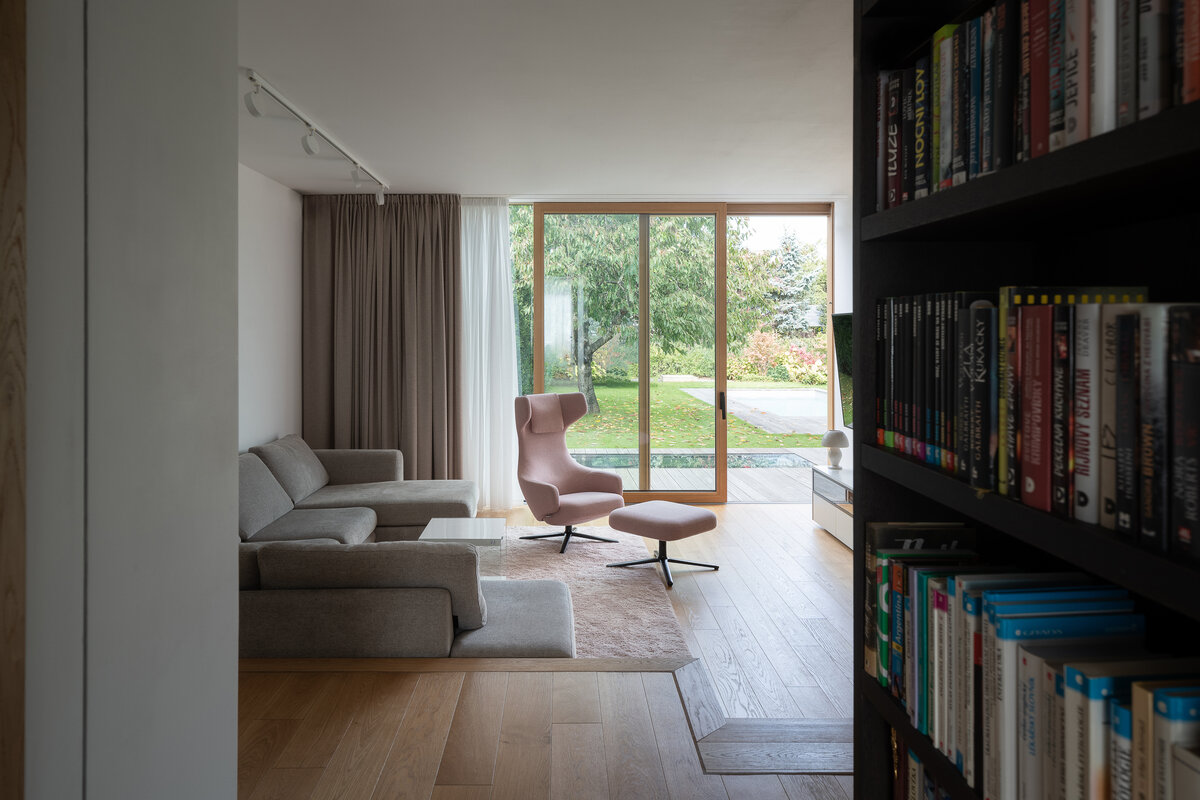
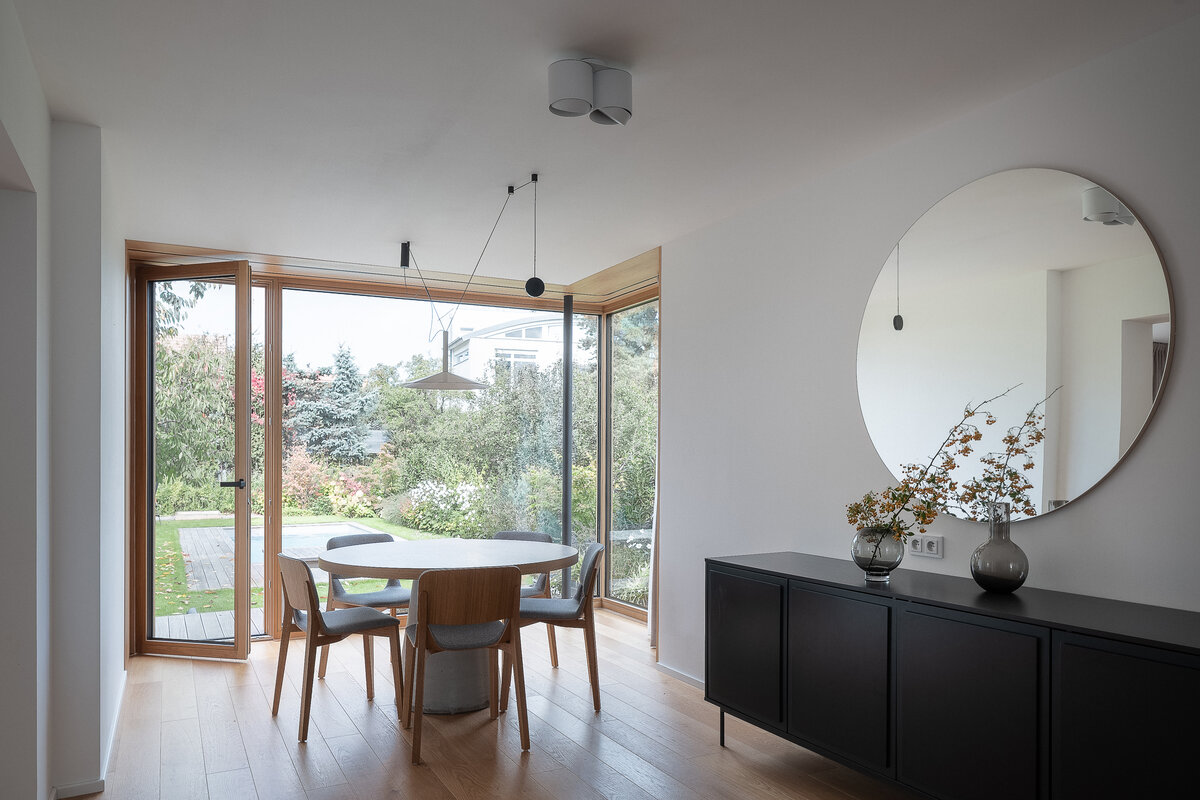
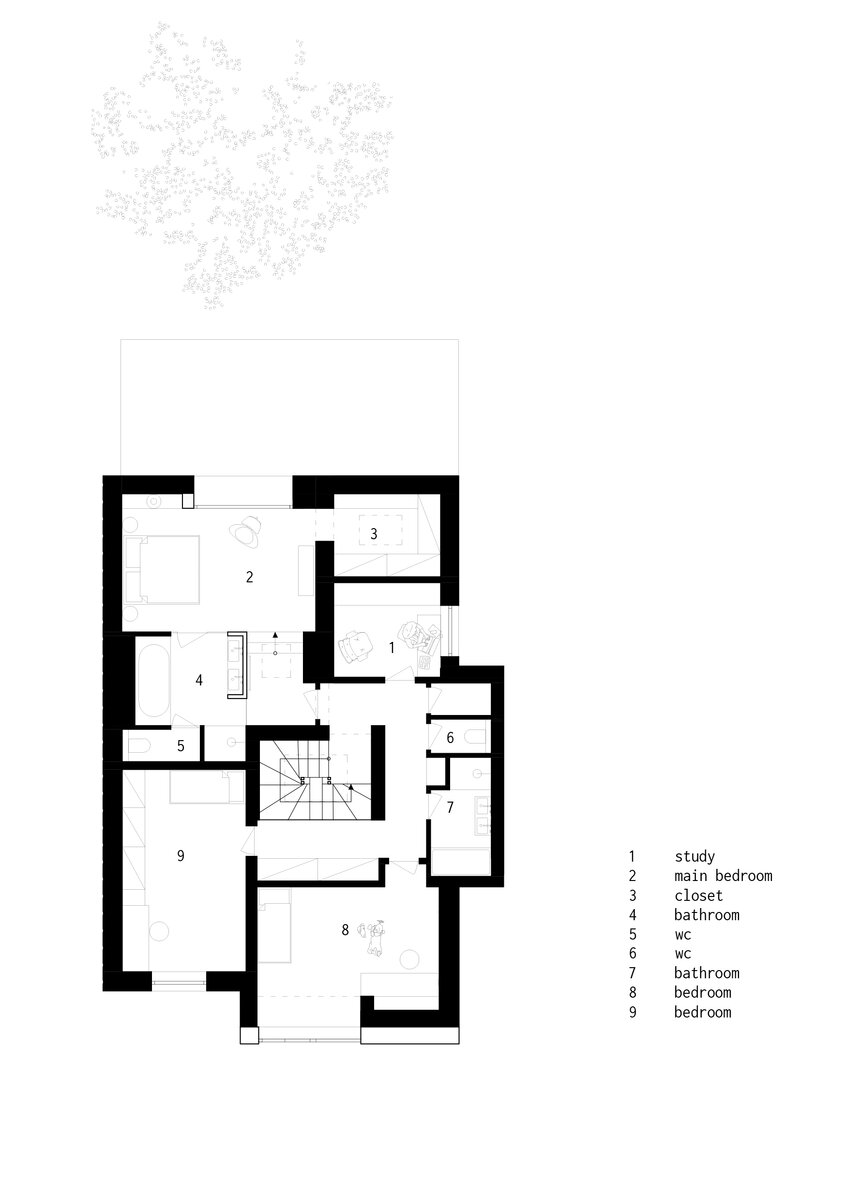
On the first floor, the individual rooms surround the central staircase creating an interconnected space. The visual connections and the views to the garden became an important element of the design. A large sliding door connects the living room with the garden. Clearance and height change of the floor helped the direct connection to the terrain level of the garden. Due to the increased height of the room, the entire floor became more dynamic.
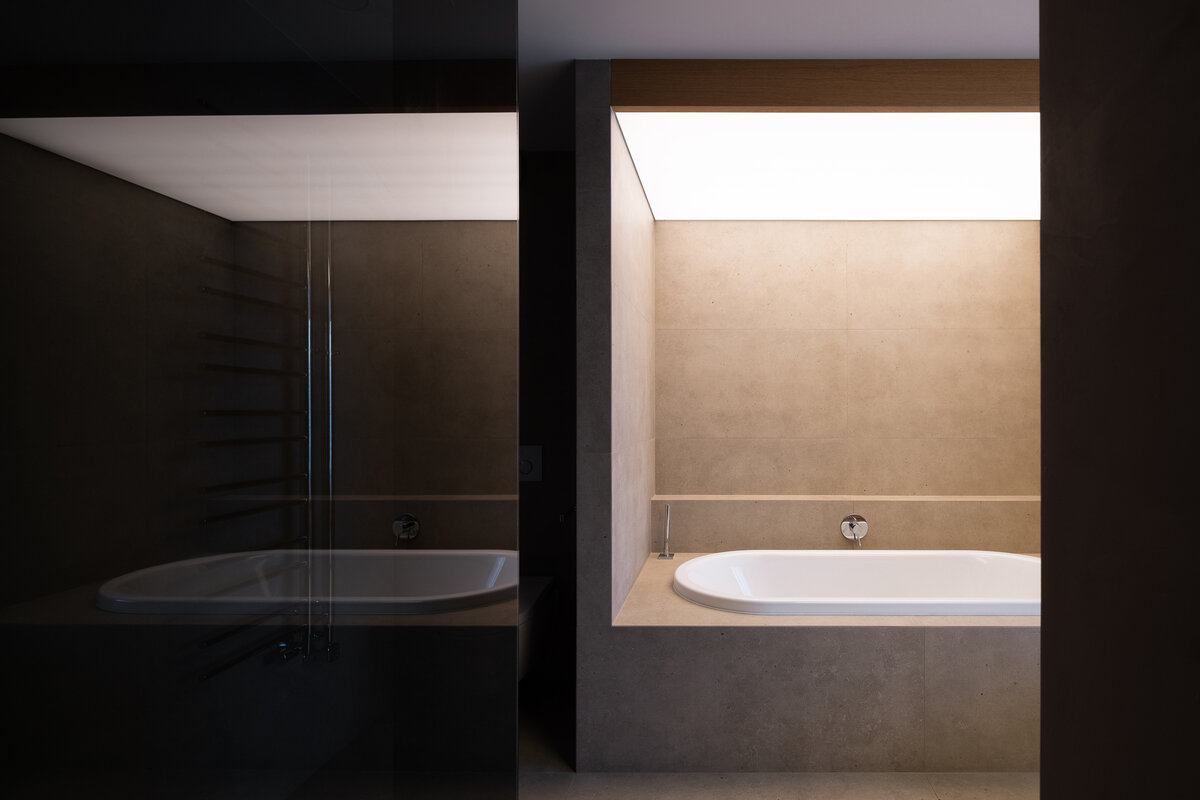
The top floor accommodates bedrooms accessible from a small walkway around the staircase. The master bedroom has a private dressing room and bathroom. The previously planned study room changed during the construction into an additional bedroom.
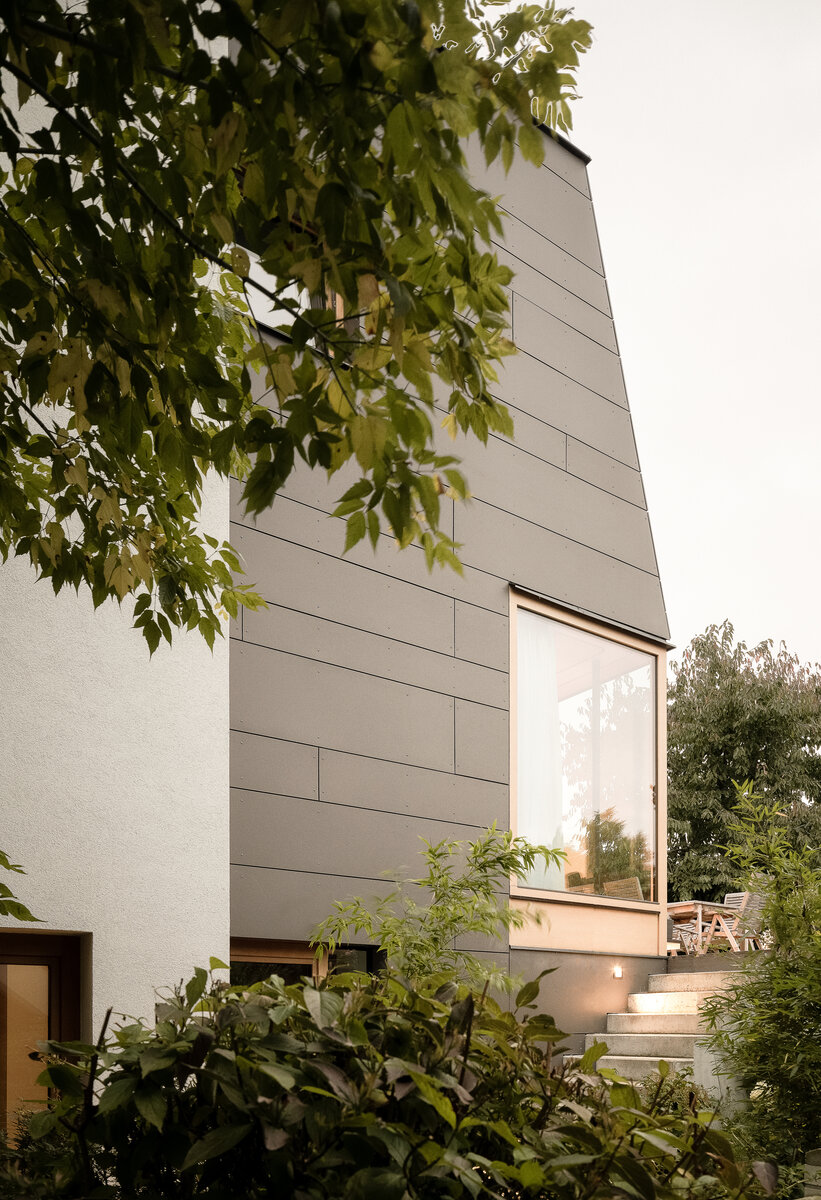
The exterior division of the house is based on the uniform shape of the original mansard. The facade cladding made of fiber-cement boards transitions to the roof. Oak windows with frameless glazing are optically connected with the edge of the roof. The roof cladding integrates a retractable sunblind that covers the entire terrace area in the garden.
The small garden was enough to satisfy all the requirements for the current use. The interior views define its composition. Despite demanding changes in the garden, the old cherry tree remained its dominant feature. A few weeks after moving in, the whole family harvested cherries.
Green building
Environmental certification
| Type and level of certificate |
-
|
Water management
| Is rainwater used for irrigation? |
|
| Is rainwater used for other purposes, e.g. toilet flushing ? |
|
| Does the building have a green roof / facade ? |
|
| Is reclaimed waste water used, e.g. from showers and sinks ? |
|
The quality of the indoor environment
| Is clean air supply automated ? |
|
| Is comfortable temperature during summer and winter automated? |
|
| Is natural lighting guaranteed in all living areas? |
|
| Is artificial lighting automated? |
|
| Is acoustic comfort, specifically reverberation time, guaranteed? |
|
| Does the layout solution include zoning and ergonomics elements? |
|
Principles of circular economics
| Does the project use recycled materials? |
|
| Does the project use recyclable materials? |
|
| Are materials with a documented Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) promoted in the project? |
|
| Are other sustainability certifications used for materials and elements? |
|
Energy efficiency
| Energy performance class of the building according to the Energy Performance Certificate of the building |
B
|
| Is efficient energy management (measurement and regular analysis of consumption data) considered? |
|
| Are renewable sources of energy used, e.g. solar system, photovoltaics? |
|
Interconnection with surroundings
| Does the project enable the easy use of public transport? |
|
| Does the project support the use of alternative modes of transport, e.g cycling, walking etc. ? |
|
| Is there access to recreational natural areas, e.g. parks, in the immediate vicinity of the building? |
|